Material Design
Introduction to
By Shehan Tissera

Outline
- What is Material Design?
- Goals
-
Principles & Properties
- Material Properties
- Environment
- Light & Shadow
- Objects in 3D space
- Authentic Motion
- Animation
- Color
- Imagery & Text
- Sample Applications
- Resources
What is Material Design?
Material Design in a Nutshell
Material Design's Goals
Google's high level concept was to create :
A Visual language that synthesizes
- Classic principles of good design (UI/UX)
- Possibility of technology and science
Material Design's Goals
Google's high level concept was to create :
A single underlying system that allows a unified experience across platforms and devices.
First Class input methods
- Touch
- Voice
- Mouse
- Keyboard
Material Design's Principles
Motion provides meaning


Bold, Graphic, intentional
Material is the metaphor

Material is a metaphor
- Rational space & motion
- Grounded in tactile reality
- Inspired by paper & ink
- Surfaces & edges provides visual cues
- Light surfaces & movement convey how objects move, intent & exist in space in relation to each other
- Should appear technologically advanced
- Open to imagination & magic
Bold, graphic, intentional
- Foundation in print
- typography, grids, space, scale, color & imagery
- Create hierarchy, meaning and focus
- edge to edge imagery
- large scale typography
- intentional white space
- Core functionality should be immedately apparent
- Emphasis on user actions
- Immerse the user in the experience

Motion provides meaning
- User actions initiate motion
- Reinforce the user as the prime mover
- User motion can transform the whole design
- All actions take place in a single environment
- Objects have continuity as they transform
- Motion
- focuses attention
- maintains continuity
- Feedback is subtle yet clear
- Transitions: efficient & coherent
Material can
- change shape / elevate
- cast shadows
- display content
- join together / split apart / heal
- be spontaneously generated & destroyed
- move along any axis
Material cannot
- pass through other materials
- cannot occupy same space as another material object
- bend
- change thickness
Material Properties
Environment
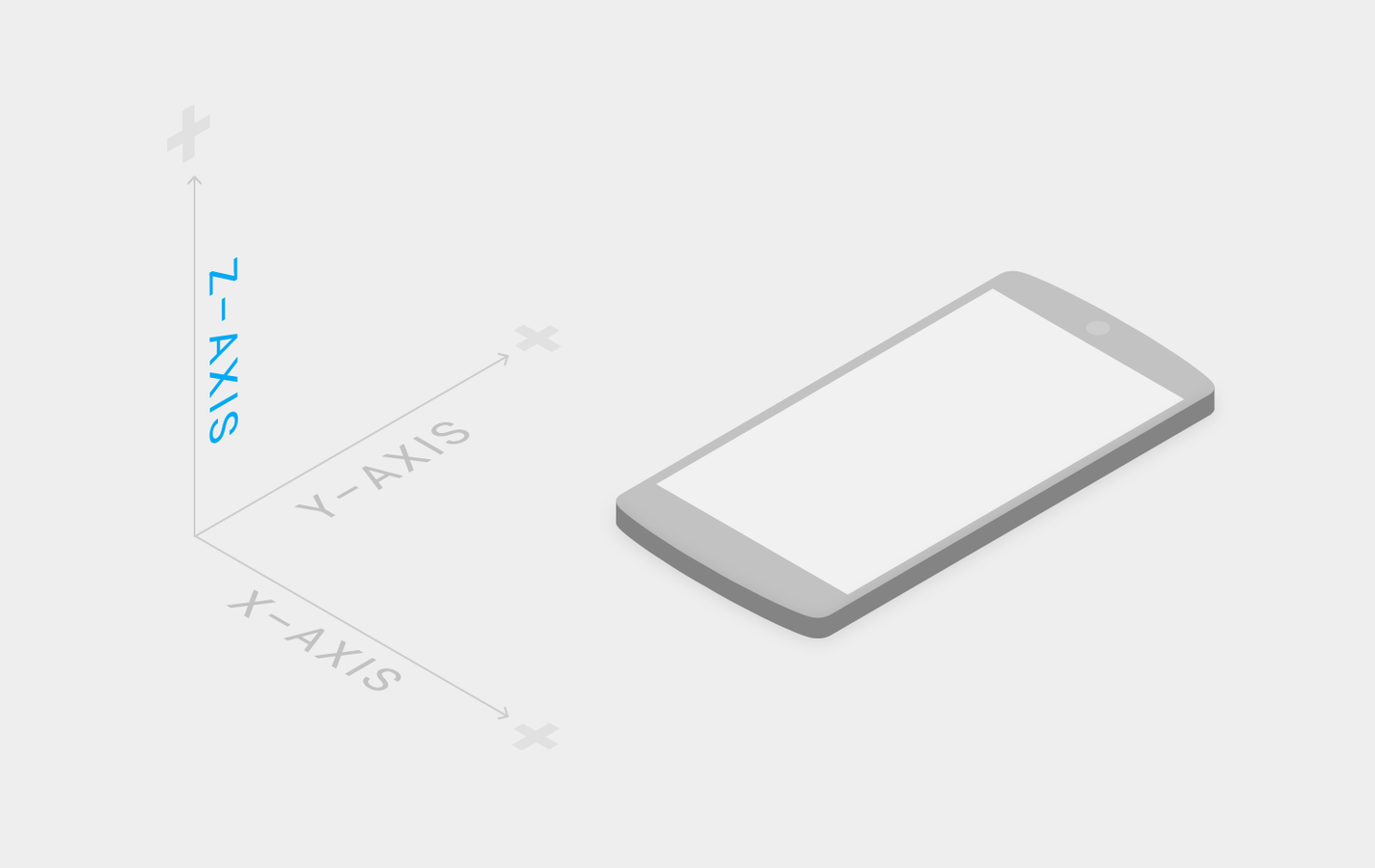
- Flat design in a 3D world
- All objects are rendered on sheets
- All sheets have a z-axis 1dp think (dp = device independent pixel)
- z-axis is always perpendicular to plane of display
Light & Shadow

- Key light creates directional shadows
- Ambient light creates soft shadows from all angles


Shadow cast by key light
Shadow cast by ambient light
Combined shadow from key and ambient lights
Objects in 3D space
- All material objects have a resting elevation
- Elevation usually changes from user interaction
- Objects should return to resting elevation
- Elevation is responsive
- Shadows provide visual cues about arrangement
- Every object has a single parent
- May also have children or siblings
- Children inherit properties from their parents
- Rotation
- scale
- elevation
Authentic Motion
Observing an object's motion tells us whether it is light or heavy, flexible or rigid, small or large.
- Accelerate objects swiftly and decelerate them slowly to avoid abrupt changers in velocity.
- When an enters the frame, ensure that it's moving at its peak velocity.
Animation
- Upon input, instantaneous visual feedback
- Touch ripple is core visual to express contact
- New material could originate from point of origin
- When element is activated it should lift on touch
- and should quickly return to its rest elevation
- Meaningful Transactions
- Should have a visual continuity
- Hierarchical timing
- Consistent choreography
Color: Palettes & Themes
- Color Palettes
- Limit selection to two palettes: primary & accent
- 3 color hues from primary palette
- 1 color from accent with possible fallback options
- Use alpha values of black for grey text, icons & dividers
- Tool-bars should use the primary 500 color
- Status bar should use the darker primary 700 color
- Use accent color for primary action & components
Imagery & Text
- Use bold images to communicate & differentiate
- Make typography legible on imagery with scrims.
Sample Applications
Resources
Material Design
http://www.google.com/design/spec/material-design/introduction.html
Angular Material
Material Color Palette
Material Design
By Shehan Tis
Material Design
This is a presentation which explains about the new Material Design
- 772
