Linux Workflow Familiarization
Linux User Group, Thapar University
29 February 2016


LINUX
Work Free. Play Free. Live Free.
Linux Basics
A few things you should know about it
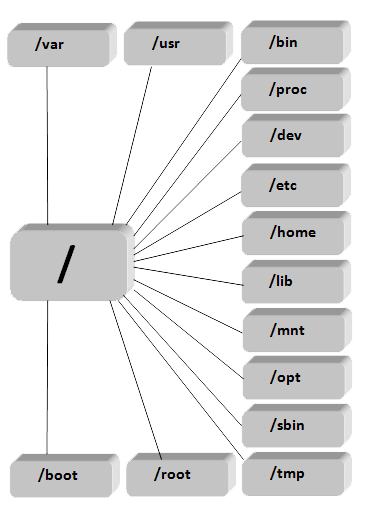
File System
- Linux has a single root filesystem
- It follows the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard
What is the terminal?
A terminal or a command prompt is a character based interface to the OS.
All it does, literally, is execute the program you tell it to.
Access Control
Some commands require superuser (admin) priviledges.
For that we use sudo.

xkcd.com
Working with Terminals
A few things about Linux terminals
Many types
Different Linux distros have different desktop environments and different terminal shells
E.G. - bash, ksh, zsh, tcsh
Autocompletion
Most terminal shells support automatic completion of commands, options and filenames.
This is activated by single or double press of <Tab> key.
Redirection
The pipe operator '|' is used to redirect the output of one command to the next (left-to-right).
Redirection operators < and > can be used to read from or write to a file.
Operators << and >> are used to read from or append to a file.
Navigation
Commands to help you find your way
Where am I?
$ pwd
/home/seekerThe 'pwd' command tells your location in the filesystem
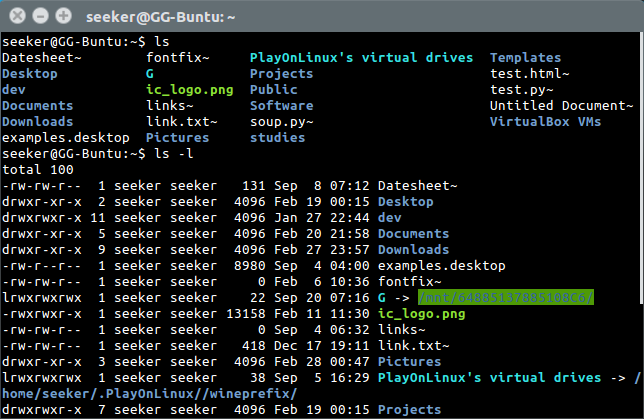
What is in this folder?
The 'ls' command lists the files and folders in the present working directory
How do I change folder?
The 'cd' command lets you change your location
$ pwd
/home/seeker
$ cd Documents/
$ pwd
/home/seeker/Documents
$ cd ..
$ pwd
/home/seekerWorking with files
Commands to help you do basic operations with files
View Files
In order to print file to terminal, we use 'cat'.
To scroll through big files, use 'less'.
To exit the program, press q.
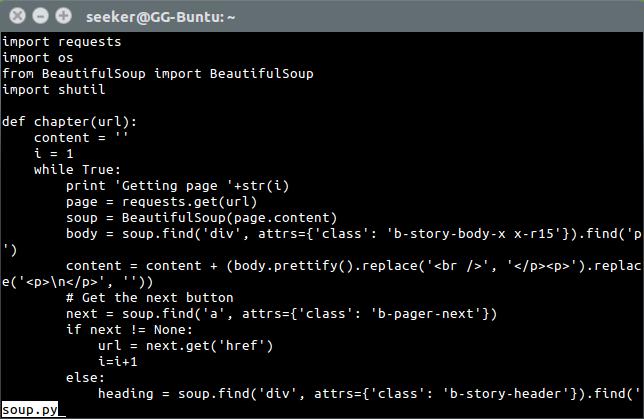
Move or Copy Files
In order to move a file we use 'mv'. It can also be used to rename the file.
'cp' is used to copy a file.
$ mv soup.py Documents/wolololo.py$ cp soup.py Documents/wolololo.pyCreate Directory
'mkdir' creates a folder.
$ mkdir Documents/testDelete Files
'rm' can delete a file.
'rmdir' can delete an empty directory.
$ rm soup.py$ rmdir test'rm -r' deletes the directory and everything in it.
$ rm -r testEdit Text- based files
In order to edit a file in terminal we can use 'vi' editor
A simpler and lightweight alternative is 'nano'
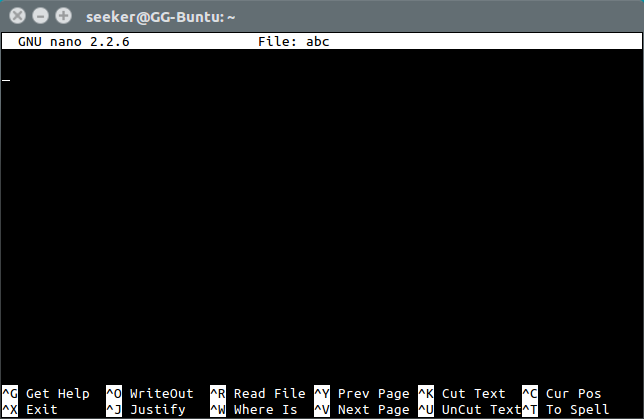
Advanced File description
'diff' is used to compare two files for differences.
'file' is used to ascertain type of file.
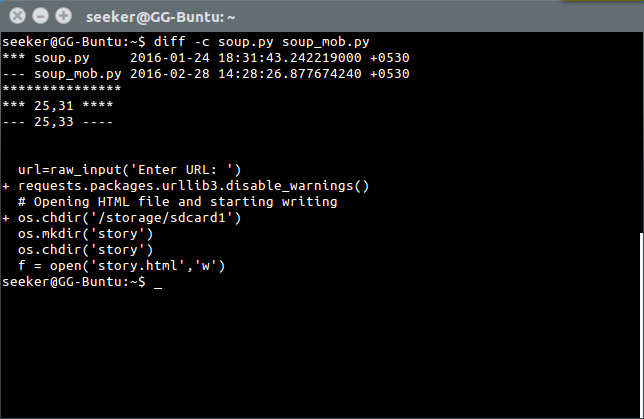
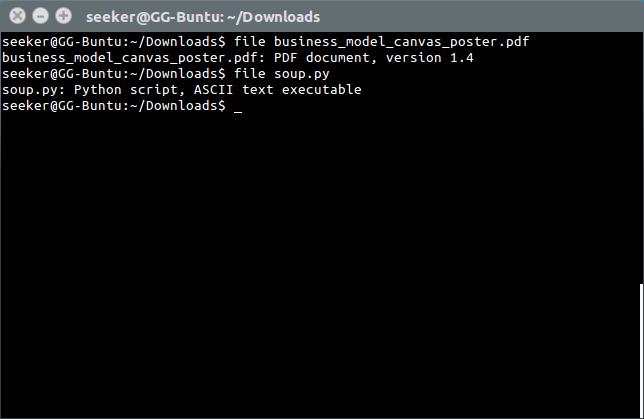
Generic Commands
Commands that can come very handy
Manual Pages
'man' opens documentation on usage of programs.
'man -k' searches for all available commands.
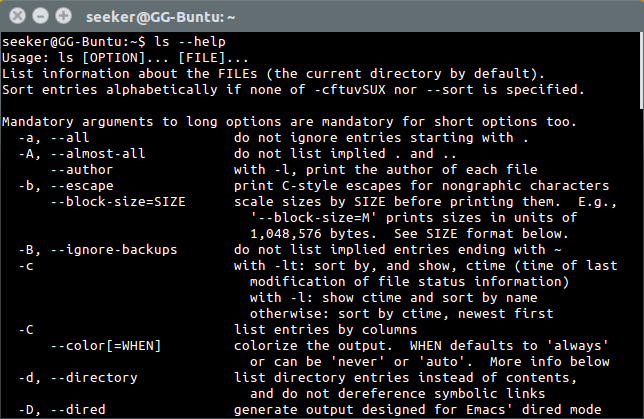
parameter '--help' shows basic usage information.
Strings
'grep' is a powerful string searching utility.
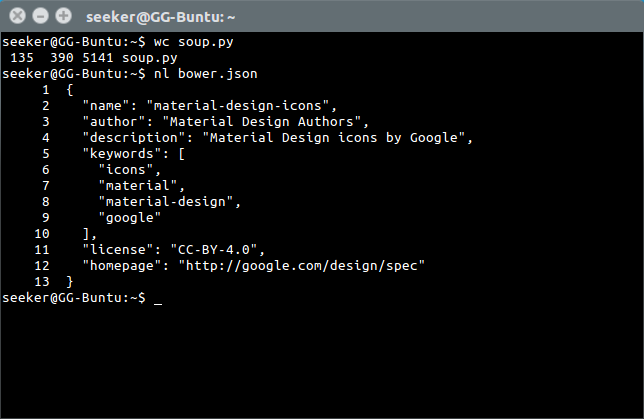
'wc' is used to generate statistics about strings.
'nl' is used to number lines.
File search
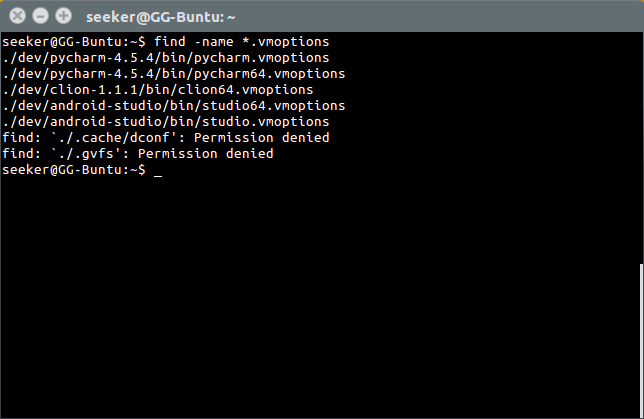
'find' is used to search for files in real time.
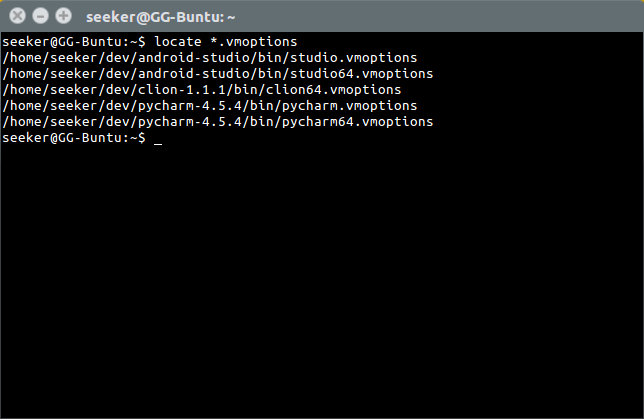
'locate' is used to search for indexed files.
Revision
Redirection: pipe operator '|', <, >, <<, >>
Current location: pwd
List files: ls , tree
Change directory: cd
Open text based file: cat, less
Revision
Edit text based file: nano, vi/vim
Usage help: man, --help, info
String searching: grep, strings
File searching: locate, find
Root privilege access: sudo
Process Management
Commands to handle processes
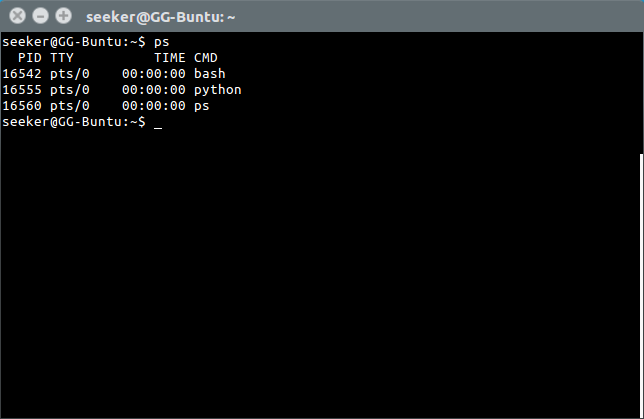
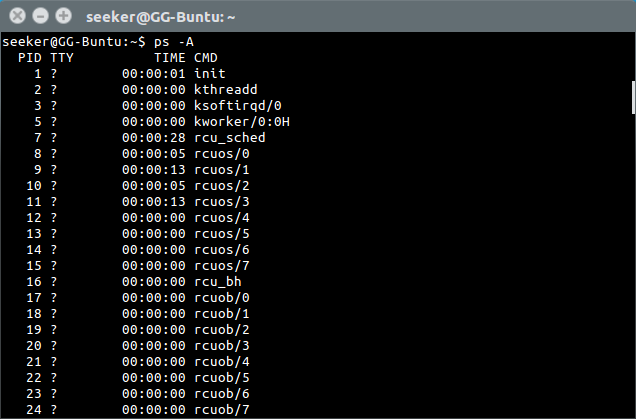
Check Active Processes
'ps' is used to list the processes attached to that shell.
'ps -A' is used to list all processes running on the machine.
Kill Processes
'kill' is used to terminate a background process.
ctrl+c is used to terminate the foreground process.
Background Processes
ctrl+z is used to suspend a process.
Appending & executes a command as a background process.
'jobs', 'bg' and 'fg' can help manage background processes.
OS based commands
Commands to interact with the linux environment
Users and User Groups
Linux's way of managing permissions etc.
File permissions
A file in linux has three kinds of permissions associated with it: read, write and execute.
$ chmod 764 scraper.shThe command 'chmod' allows us to edit the permissions of a file, also called modes.
| Owner | Group | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Read | Y | Y | Y |
| Write | Y | Y | N |
| Execute | Y | N | N |
| Numeric: | 7 | 6 | 4 |
$ chmod 764 scraper.sh
$ chmod +ux scraper.shInstalling Software
Linux distros come with package managers.
Software for linux often need to be processed using 'make' to install it.
E.G.- apt-get (dpkg), pacman, yum





Revision
List processes: ps
Terminate processes: kill, kill -2, kill -9
Manage background jobs: jobs, bg, fg
Run as background process: &
Edit file permissions: chmod +-augorwx
Revision
Keyboard Shortcuts:
| Ctrl-C | Terminate foreground process safely |
| Ctrl-Z | Suspend foreground process |
| Ctrl-D | Close current shell |
| Ctrl-L | Clear shell buffer |
How to learn about Linux?
The best way to learn about linux is to explore, use creativity to create hacks for whatever you wanna do (hacks are the norm in linux) and to google (or duckduckgo) for whatever you want to do.
Where to start?
This free Introductory course by Linux Foundation on edx.org can get you started. FYI, the course is much more detailed than these slides.
Thank You
Can you now tell me what does do?
$ ./a.outLinux Workflow Familiarization
By Shubham Agarwal
Linux Workflow Familiarization
Introduction to Linux and the terminal workflow
- 333