InfoSec
;
or,
All Your Base
Are Belong to
h4xx0rz
>>
();
●●●●●●●p@$$w0rDs
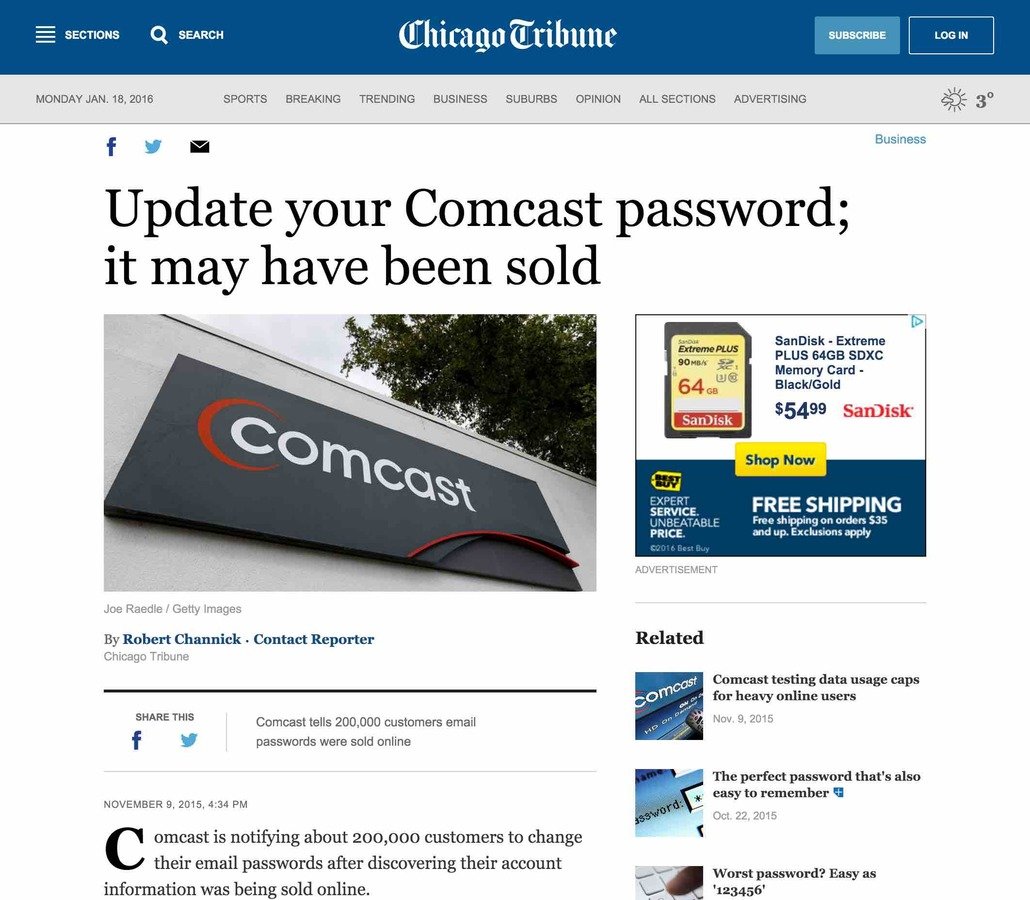
Your Passwords
are being sold
why?
- Direct access to the affected account
- May compromise other accounts (email, bank, etc)
- Add password cracking corpus
how?
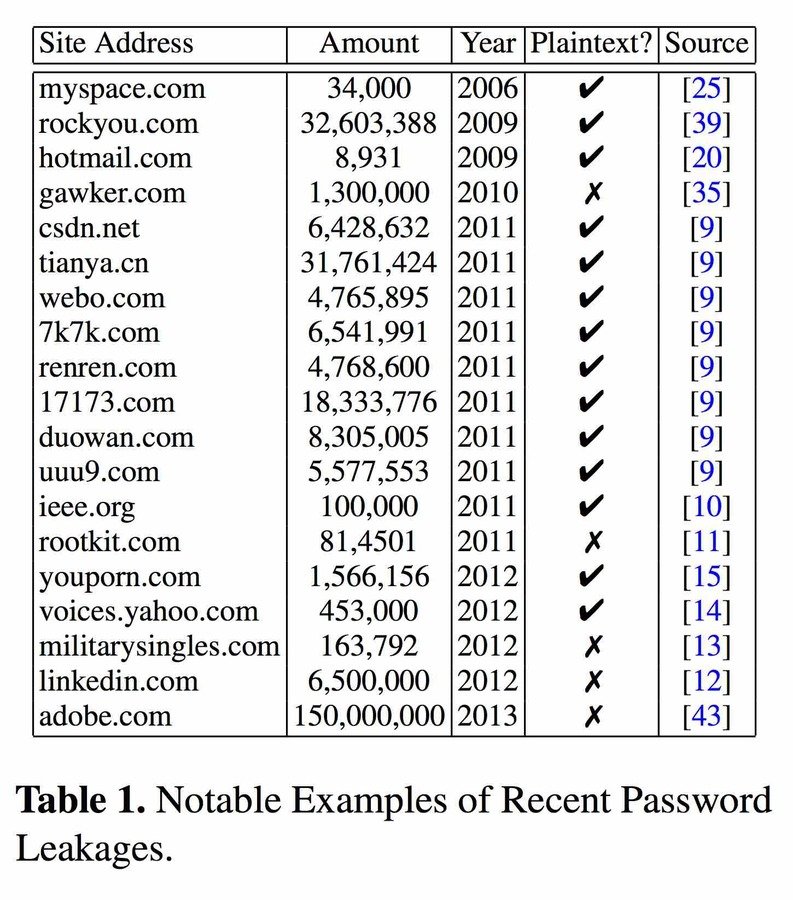
- Server Hacked (Gawker 2010)
- Vulnerability in Site (RockYou 2009)
- Database Backup Stolen (Bitly 2014)
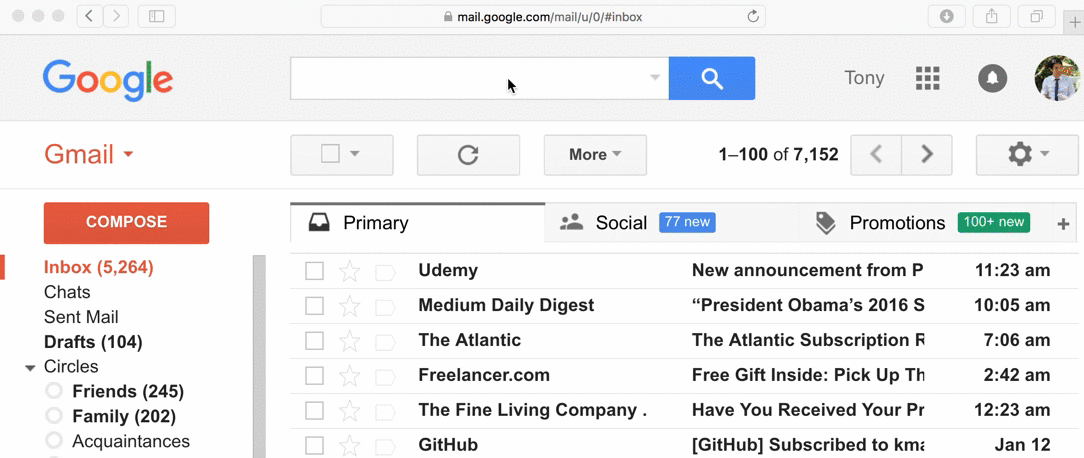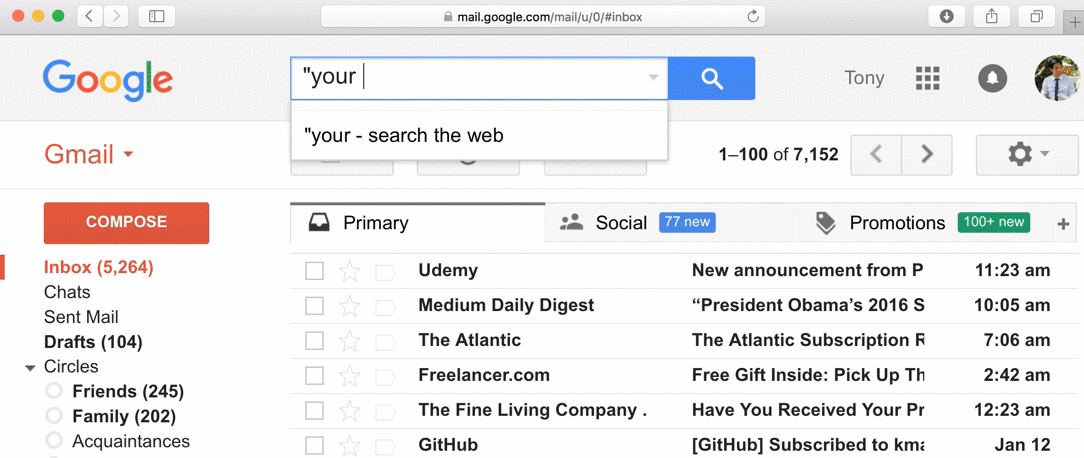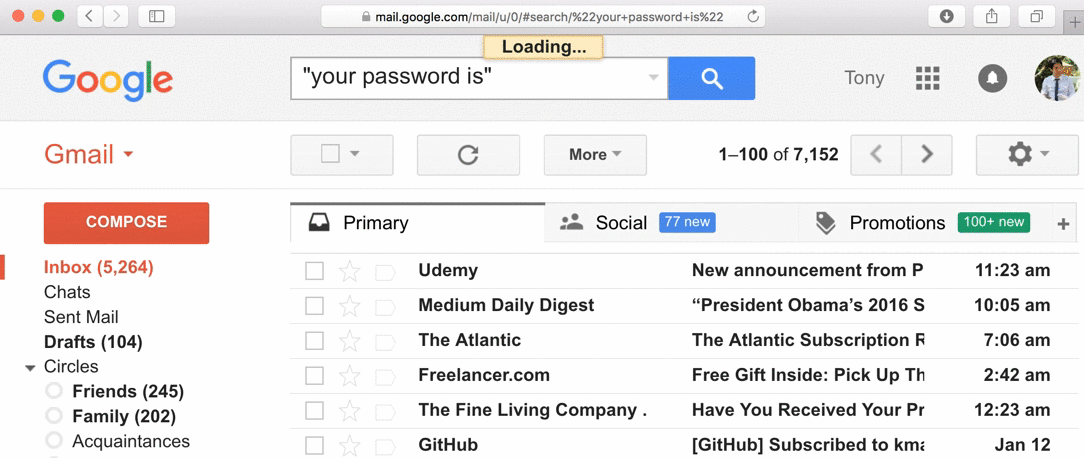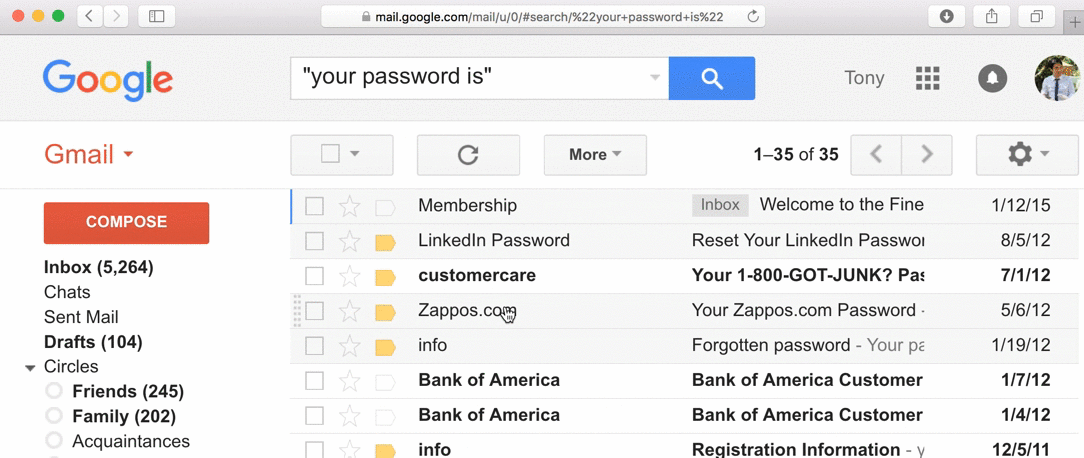
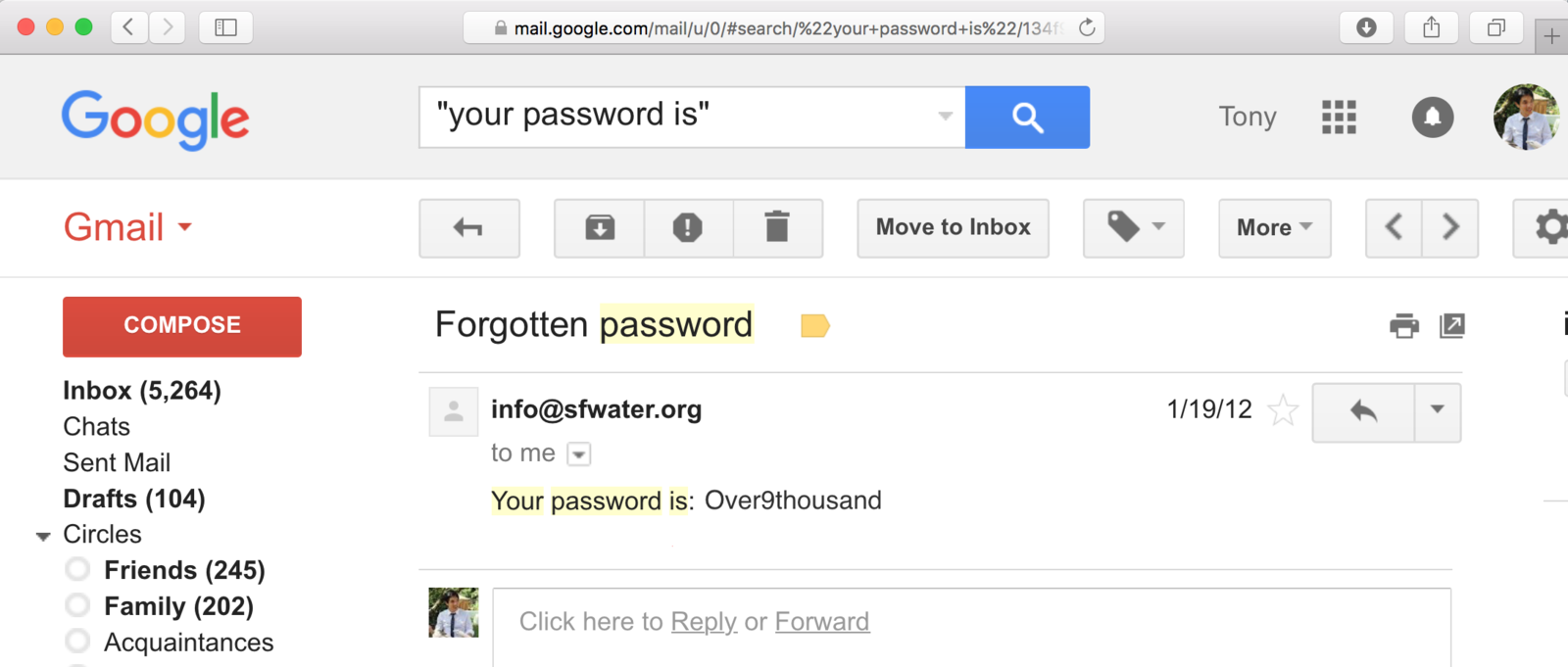
let's look at how
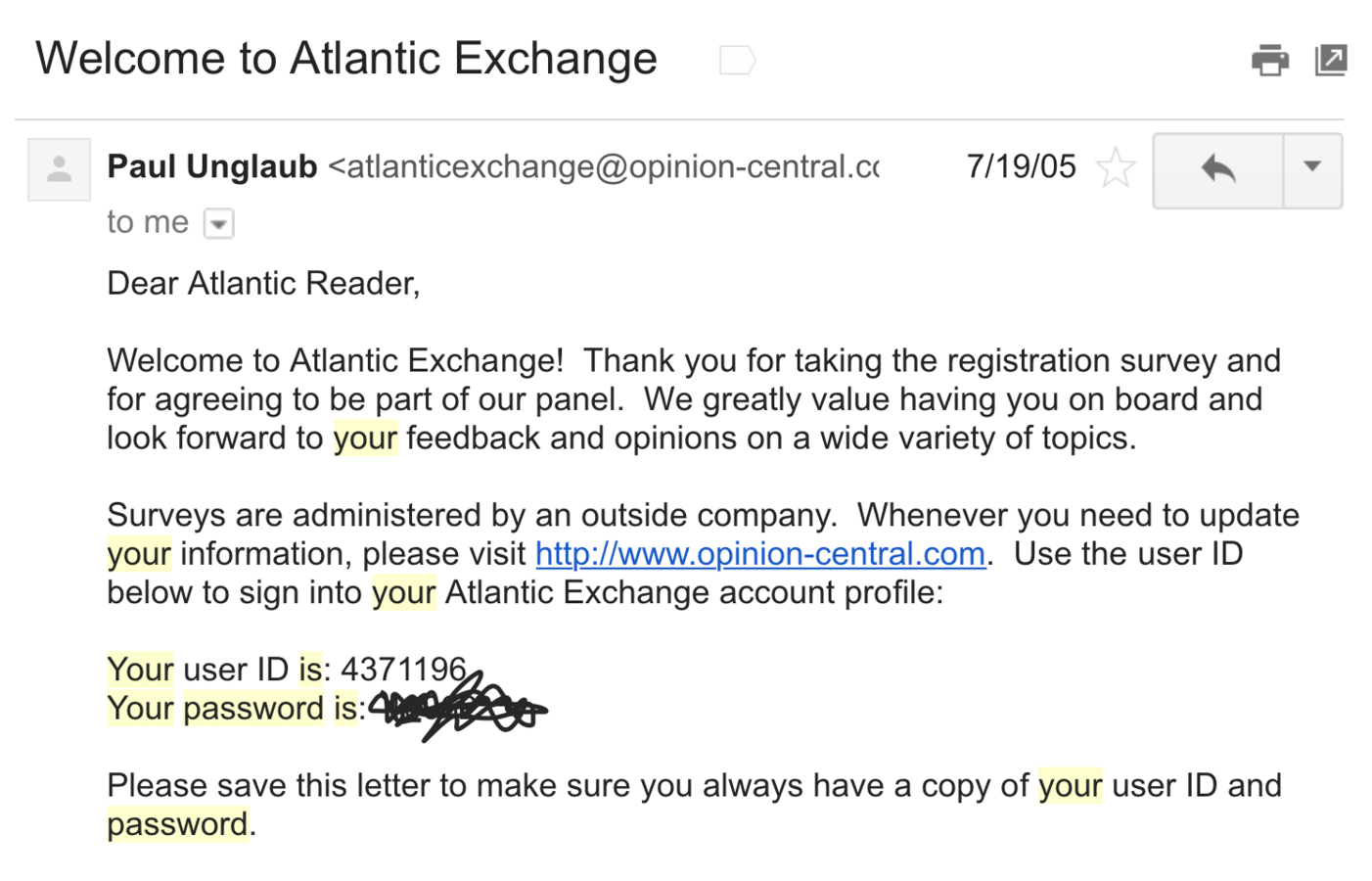
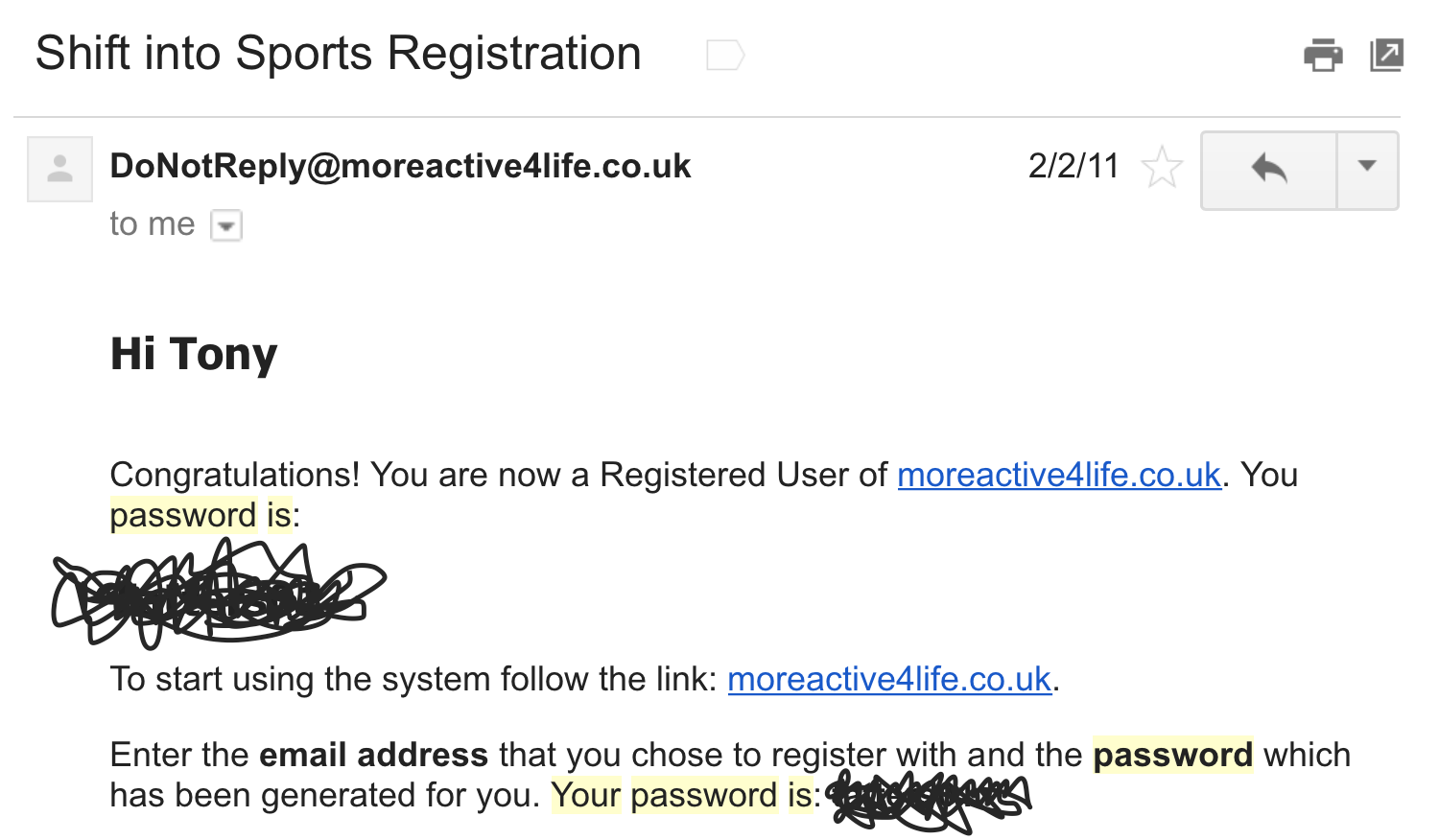
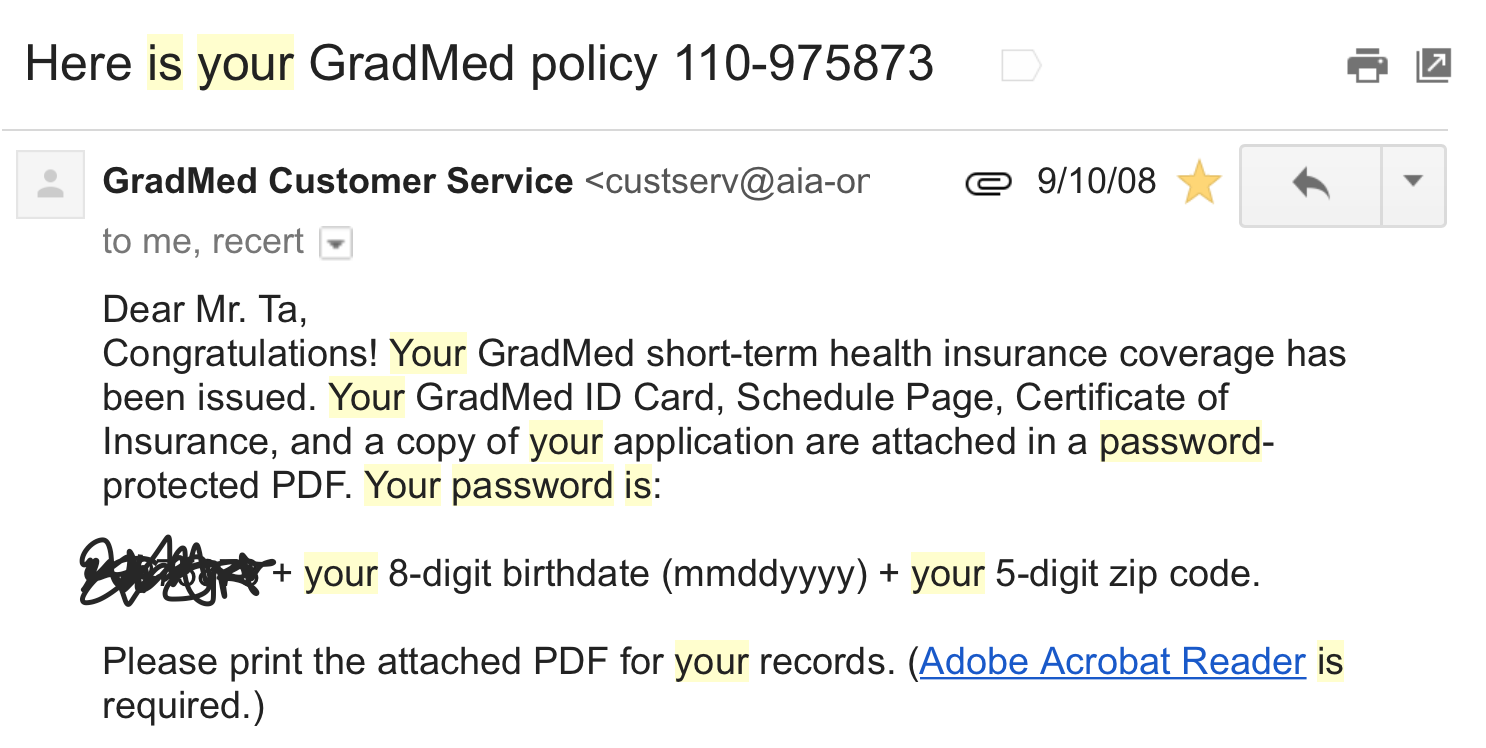
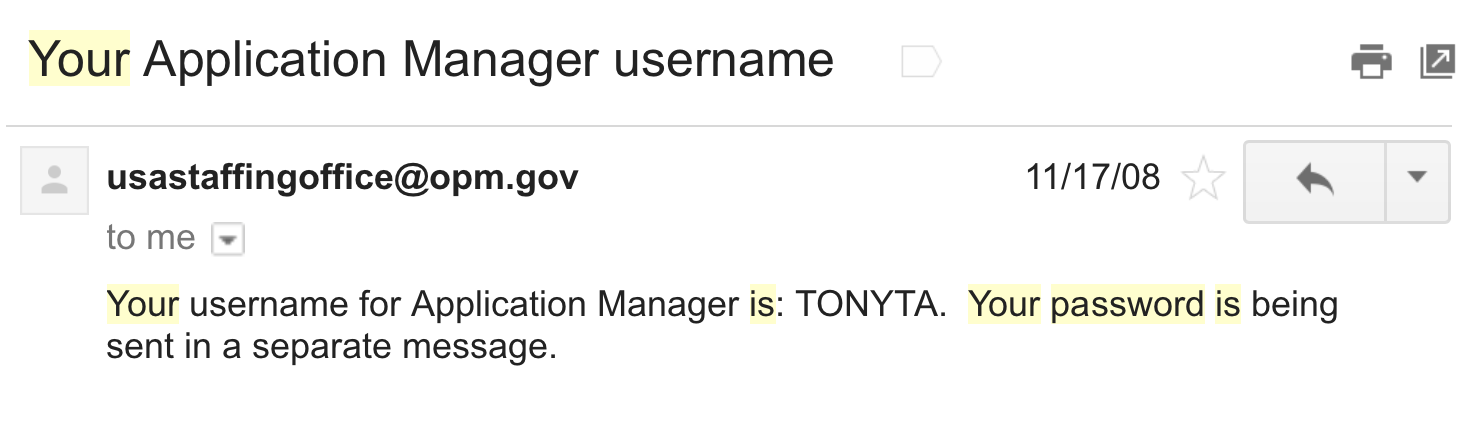
passwords are being stored...
Plaintext

but why would you ever?
- Really easy to implement (lazy)
- Allows for easy password recovery
- Straightforward, simple comparison
NEVER use plaintext

but who is that stupid?
- 30% of websites store passwords in plaintext
- MySpace, RockYou, Hotmail
- If they know your password, they're storing plaintext
wtf?!
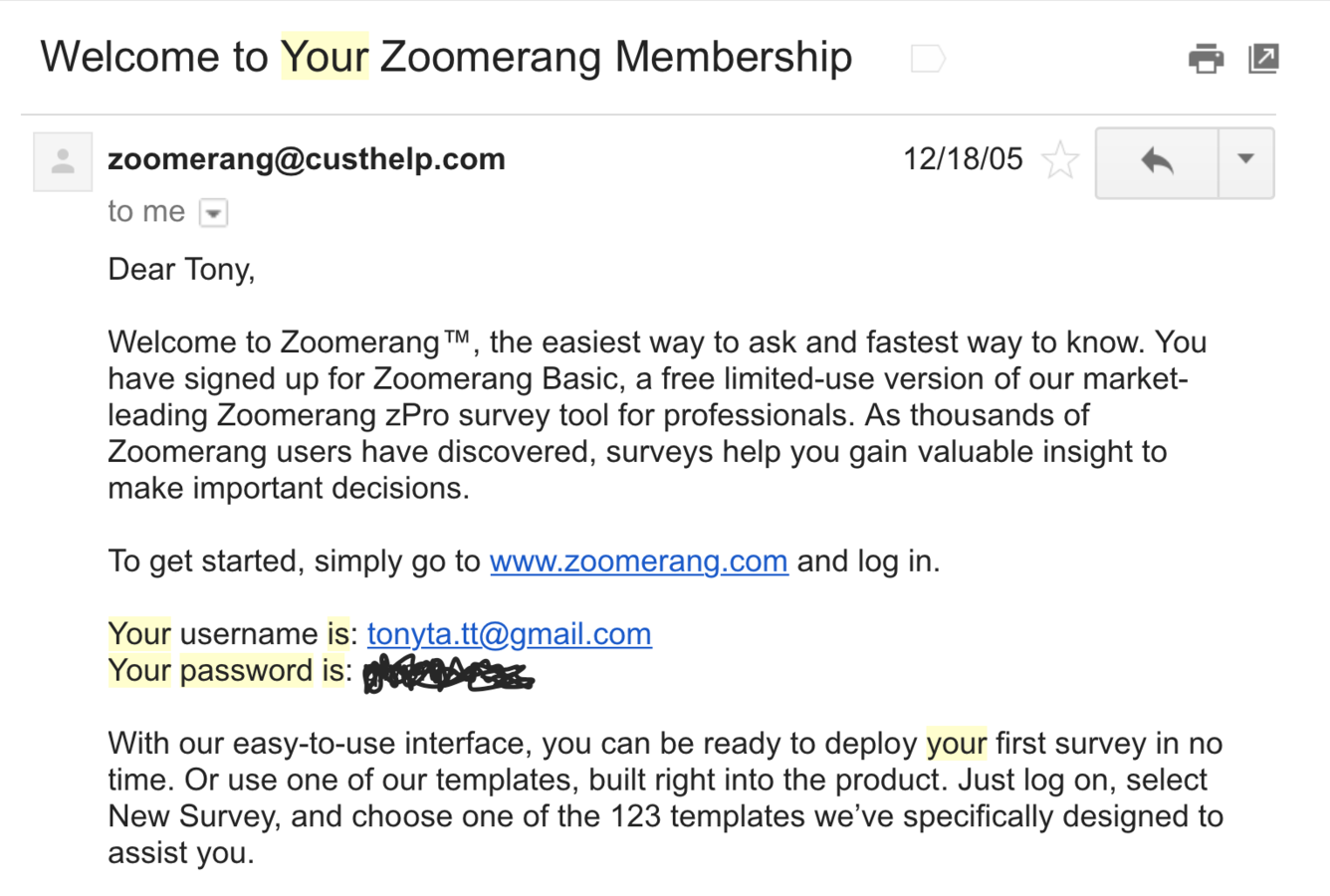
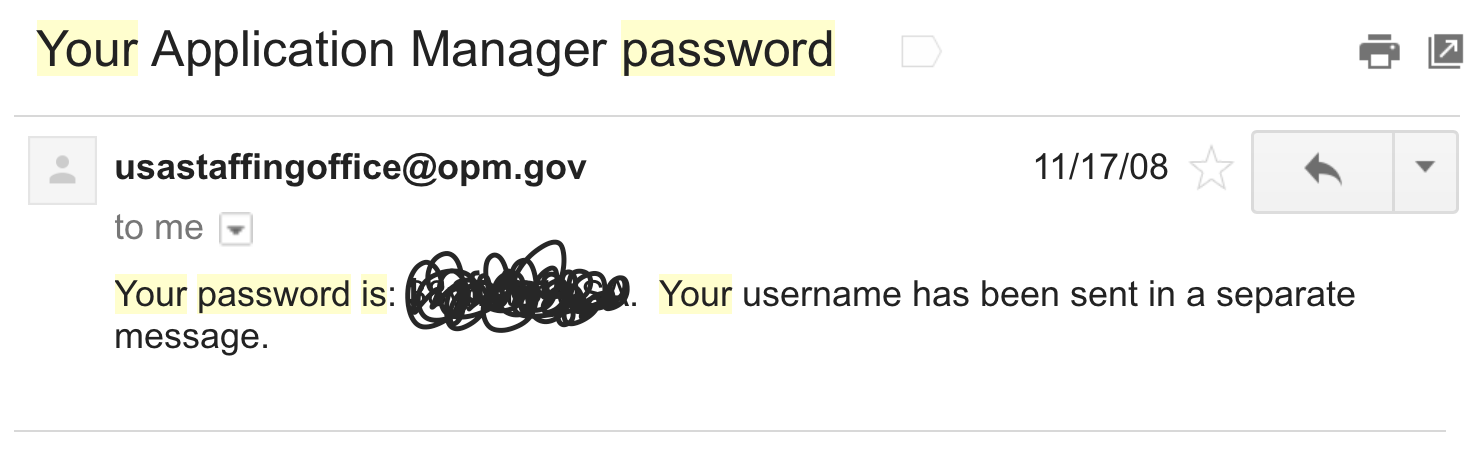

Reversible Encryption
just as bad
- Encrypt a password with a secret key
- Unencrypt it (with the key) to compare to the input
If someone has your database,
they probably already have your secret key
now what?
Hashing
Hashing
Specifically, a "one-way cryptographic hash"

password123
8640bd46
hash
(black box)
digest
input

password123
8640bd46

password100
c9a7ffb9

password123
8640bd46

yoMama$566
1eb323d6

password123
8640bd46
don't store the password
store the digest
but what about password?
how do it know?
8640bd46
digest in database:
password100
c9a7ffb9
≠
8640bd46
password123
8640bd46
=
8640bd46
We don't know the password, but we can still authenticate the user with her password
win?


Cracking Passwords

brute force
- Hash every password combination
- If any digest matches, you know the input password
0000000
0000001
0000002
0000003
0000004
0000005
0000006
00000A5
00000A6
00000A7
00000A8
00000A9
00000B0
00000Ba
0000ga0
0000gaa
0000gab
0000gac
0000gad
0000gae
0000gaf
0001dFk
0001dFl
0001dFm
0001dFn
0001dFo
0001dFp
0001dFq
000h4xu
000h4xv
000h4xw
000h4xx
000h4xy
000h4xz
000h4xA

- 180 billion MD5 hashes per sec
- Alphanumeric:
- 26 lowercase
- 26 uppercase
- 10 numbers
- 8 character password:
- (26 + 26 + 10) ^ 8 = 280 trillion
- 280 trillion / 180 billion = 1555 secs
- or just 25 minutes!!!
dictionary
- Have a corpus of common passwords
- If any digest matches, you know the input password
rainbow tables



Salting

password123
e73f51aa
digest
input

password123
8640bd46
digest
input
7fc7c392
salt
Salting
- Salts are public, stored as plaintext
- Every user has a different, random salt
Salting
e73f51aa
salt:
password100
300829ce
≠
e73f51aa
7fc7c392
digest:
7fc7c392
+
password123
e73f51aa
=
e73f51aa
7fc7c392
+
why is this better?
- You have to try every combination on each user
- a hit only applies to one user
password123
7fc7c392
e73f51aa
password123
a778eef2
53026489
password123
b8d12a9a
160bba71
user 1:
user 2:
user 3:



















Slow Hash Algorithms

MD5 vs bcrypt
- MD5
- Designed to be fast and efficient
- GPU accelerated
- bcrypt
- Designed to be slow and resource intensive
- CPU only (can't be accelerated)

password123
8640bd46
MD5 vs bcrypt
180 billion per sec
280 trillion iterations in 25 minutes

password123
d523c864
158 per sec
280 trillion iterations in 56,000 years
MD5
bcrypt
Plaintext
Recap
Hashed
Slow Hash + Salt
😡😡😡
🙂
💩
😹
Case Study

Ashley Madison used bcrypt


Lessons
- Many sites are dumb enough to store plaintext passwords
- Even if hashed, they are still vulnerable to being cracked
- Even if using the best tools, human error (stupidity) can leave you and your password vulnerable.

/giphy shrug
fin.
Password Hygiene
- long and strong
- completely random
- conpletely different
- hint: use a password manager
Questions?
slides.com/tonyta/passwords
Passwords
By Tony Ta
Passwords
- 776