Bayesian Methods
A brief introduction to
T. Paternina
Machine Learning Journal Club
05/04/2017
Overview
- Quick reminder on probability
- Bayes' rule and HIV diagnosis
- Inference & comparing models
- Why Bayes'?
Quick reminder


***

Quick reminder

***
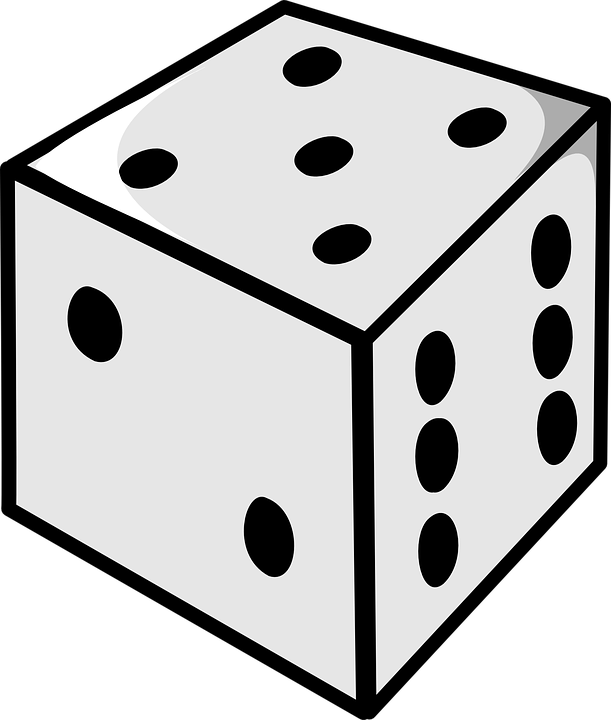
or
Quick reminder

***
Bayes' rule
Bayes' rule
| Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 43 | 9 | 52 | |
| 44 | 4 | 48 | |
| Total | 87 | 13 | 100 |



The probability of an event A conditioned by an event B is equal to the joint probability of A & B over the probability of B.





example from wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contingency_table)
HIV diagnosis
HIV diagnosis
(U.S. military style)
(x2)

(x2)

(x2)
HIV+
HIV diagnosis
(U.S. military style)
ELISA sensitivity (TP) = 93%
ELISA specificity (TN) = 99%
HIV+ prevalence = 1.48/1000
Posterior probability
Prior probability
Prior probability
0.00148
0.99852
0.93
0.07
0.99
0.01
Posterior probability
Updating probabilities
1st ELISA
Prior probability
Updating probabilities
1st ELISA
Prior probability
2n ELISA
Prior probability
Updating probabilities
1st ELISA
2n ELISA
3rd ELISA
Prior probability
Prior probability
Prior probability
Bayesian Inference & comparing models
Effectiveness of contraception

40
20 standard
20 pill
9 months


16
4
p:
probability of a pregnancy coming from the treatment group.
| p | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prior | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
Testing several models
k:
number of pregnancies in the treatment group.
What's the value of p?
Computing likelihoods
Likelihood:
probability of the observed data given a particular model.

| p | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prior | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| L | 0.0898 | 0.2182 | 0.1304 | 0.035 | 0.0046 | 0.0003 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| p | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prior | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| L | 0.0898 | 0.2182 | 0.1304 | 0.035 | 0.0046 | 0.0003 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| post. | 0.1748 | 0.4248 | 0.2539 | 0.0681 | 0.0780 | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Once you go Bayesian...
- Updating degree of belief as we gain information.
- Perform model parameter estimation from data.
- Quantify the level of uncertainty in a model.
References and resources
- Coursera course on Bayesian Statistics
- 2016 lecture by an expert on the field
- Website linking many resources
Bayesian Methods
By tpaternina
Bayesian Methods
- 585

