Java Exceptions
by Valentine Paramonov
What's an Exception?
An exception is a runtime error, an abnormal condition that arises in a code sequence at runtime.
A Java exception is an object that describes an error that has occurred in a piece of code.
1
Run Time VS Compile Time Errors
Compile Time Errors
- Syntax errors
- Typechecking errors
- Absent classes (invalid imports)
int[] ints = "Typechecking Error";Error:(5, 22) java: incompatible types: java.lang.String cannot be converted to int[]2
Run Time VS Compile Time Errors (2)
Run Time Errors
- Referencing a non-existing (null) object
- Accessing an element of an array by an illegal index
- Dividing by 0
int n = 1 / 0;Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at it.ffinance.exceptions.Exceptions.main(Exceptions.java:5)3
Exception-Handling
Throwing
When an exceptional condition arises, an object representing that exception is created and thrown
Catching
When the time comes to react to that exception, it's being caught and processed
Exception-Handling in Java
Exceptions are managed by these five keywords: try, catch, throw, throws and finally
4
Try-Catch-Finally
5
try {
// something throws an exception inside here
} catch (ExceptionTypeA exceptionA) {
// process ExceptionTypeA exception
} catch (ExceptionTypeB exceptionB) {
// process ExceptionTypeB exception
} finally {
// this executes after the try block
// regardless of whether the exception(s)
// was/were processed or not
}try, catch and finally are always blocks.
Either catch, finally or both blocks must follow the try block.
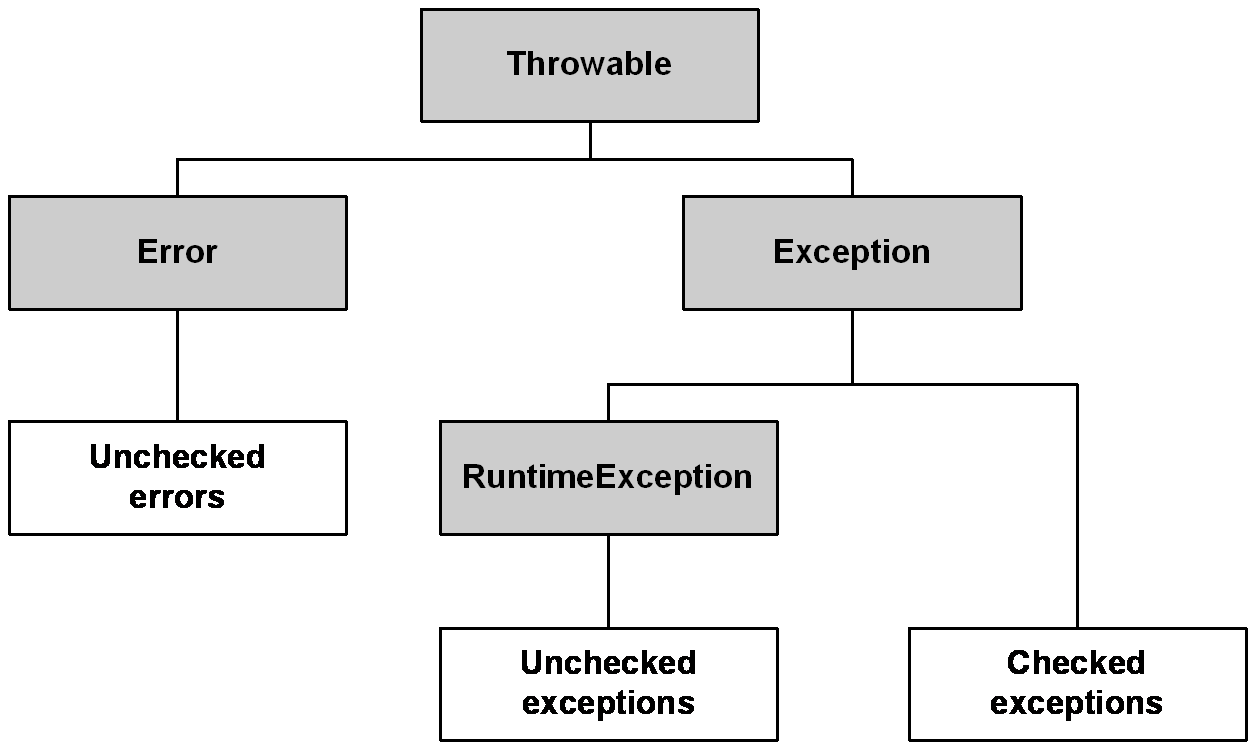
Exception Types
6
Uncaught Exceptions
7
java.io.IOException: Server returned HTTP response code: 500 for URL:
http://www.example.com/index.html
at sun.net.www.protocol.http.HttpURLConnection.getInputStream(Unknown Source)
at edu.citynavigator.map.editor.MapEditor.loadMap(MapEditor.java:685)
at edu.citynavigator.map.editor.MapEditor.init(MapEditor.java:130)
at sun.applet.AppletPanel.run(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source)Exception message
Stack Trace
The stack trace allows to pinpoint the place from which the exception was thrown
Checked VS Unchecked Exceptions
8
Checked
- Extend Exception class
- Must be declared in method's signature
- The method that throws such an exception must be surrounded by the try-catch block
Unchecked
- Extend RuntimeException class
- Not necessarily to include into method's signature
Declaring Thrown Exceptions
9
interface Doer {
public void doStuff() throws SomeCheckedException;
}
class Jack implements Doer {
@Override
public void doStuff() throws SomeCheckedException {
// throw SomeCheckedException exception
}
}Declaring Thrown Exceptions (2)
10
interface Donter {
public void dontDoStuff();
}
class Mike implements Donter {
@Override
public void dontDoStuff() throws SomeUncheckedException {
// throw SomeUncheckedException exception
}
}
class Jill implements Donter {
@Override
public void dontDoStuff() {
// throw SomeUncheckedException exception
}
}Throwing Exceptions
11
throw new Exception(); // checkedthrow new RuntimeException(); // uncheckedChecked
Unchecked
Thrown exceptions are objects, thus have to be instantiated [new keyword]!
throw Exception; // won't compileCatching Exceptions
12
try {
throw new SomeCheckedException();
} catch (SomeCheckedException sce) {
System.out.println(sce.getMessage());
}try {
throw new SomeCheckedException();
} catch (SomeCheckedException sce) {
System.out.println(sce.getMessage());
throw sce;
}Exceptions can be rethrown from the catch block
Finally Block
13
try {
// do something that throws exception
} finally {
// is executed after the try block
}try {
// do something that throws exception
} catch(SomeException exception) {
// process exception
} finally {
// is executed after the try block
}Catch statement can be omitted
Finally Block IRL
14
try {
File file = new File("a.txt");
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
try {
// throws FileNotFoundException
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// throws IOException
int read = inputStream.read();
// continue reading
} catch (FileNotFoundException fnfe) {
// process fnfe
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close(); // throws IOException
}
}
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// process ioe
}DIY Exceptions
15
class SomeCheckedException extends Exception {
}class SomeUncheckedException extends RuntimeException {
}To declare a checked exception
To declare an unchecked exception
throw new SomeCheckedException();
throw new SomeUnheckedException();To throw them
Try-With-Resouces
16
try (AutoCloseable closeable) {
// Perform operations on closeable
} catch (Exception exception) {
// process exception
}File file = new File("a.txt");
try (FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(file)) {
int data = input.read();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// process ioe
}Available since Java 7
The example from slide 14 can be rewritten as
Multi-Catch
17
try {
// Something that throws multiple exceptions
} catch (ExceptionTypeA | ExceptionTypeB exception) {
// process exception
}Available since Java 7
Q&A
18
Demonstration
19
Suddenly, you feel a dark presence...
20
Eiga's Challenge
21


Eiga's Challenge
What you'll need
- Java 8
- Git (optional)
- IntelliJ IDEA (optional)
How to start
https://github.com/Valentin-Paramonov/Eigas-Challenge
or
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0BwU6hY4pw6KycHhJanY3NWg2UE0/view
22
Java Exceptions
By Valentine Paramonov
Java Exceptions
- 423
