Algorithmic Complexity
Review
fork and clone:
https://github.com/bethjohnson/algo-time-complexity-review
also:
https://pollev.com/bigcavern281
(this url is randomly generated...no meaning here :) )
Plan
- Overview of types of complexity
- Strategy for determining complexity
- Examples
Types of Complexity
Imagine you have an electronic copy of a directory of all past and present Hack Reactor students (in alphabetical order, one student per page, with name, picture, current job, and cohort) and you want to mail a directory to each student.
Problem size: # of students
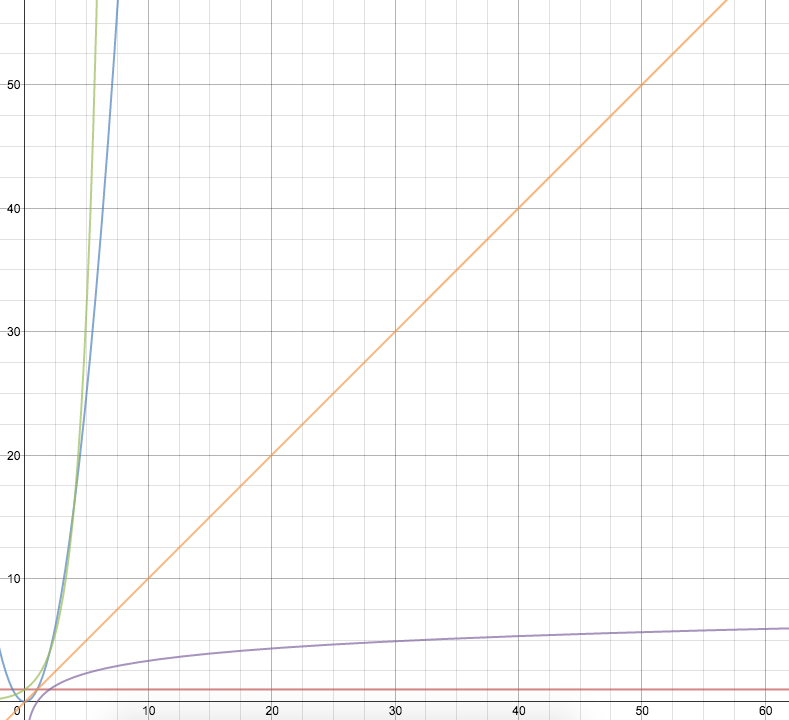
Major Types of Complexity
Constant: Increasing the problem size does not change the number of operations
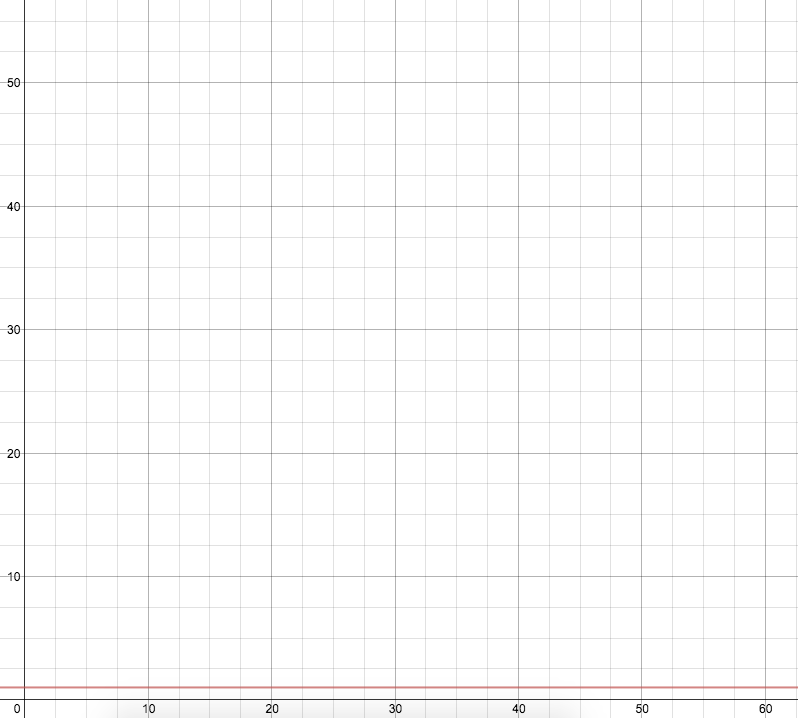
Example: Given a directory and the page a student is on, determine the cohort of the student
Major Types of Complexity
Linear: Increasing the problem size by one adds the same number of operations each time
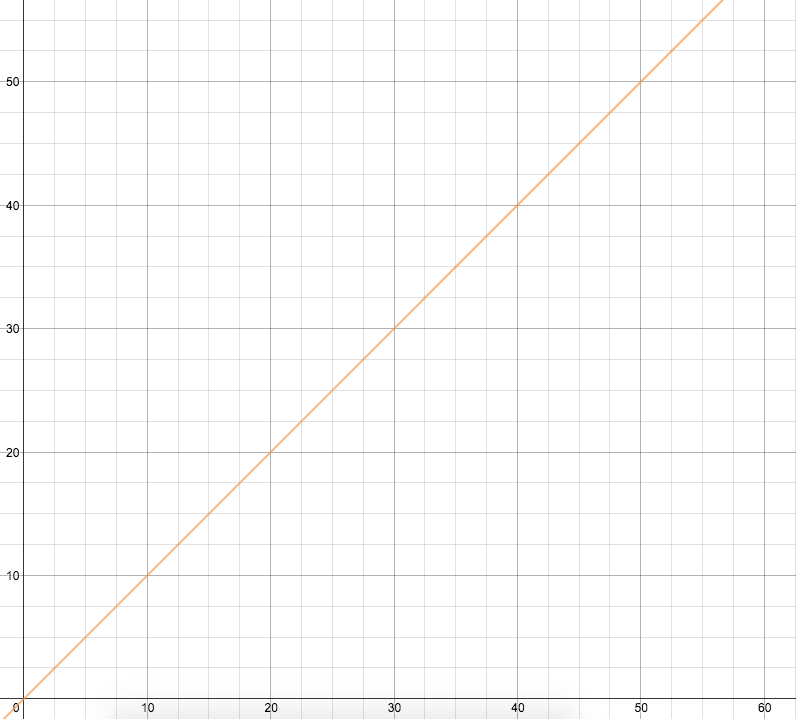
Example: Given a directory, make a list of all of the alumni from
HR 25
(If I go from 100 to 101 students, I'm going to add ~2 operations and
if I go from 1000 to 1001 students,
I still only add ~2 operations)
Major Types of Complexity
Quadratic: Increasing the problem size by one adds a number of operations proportional to the problem size
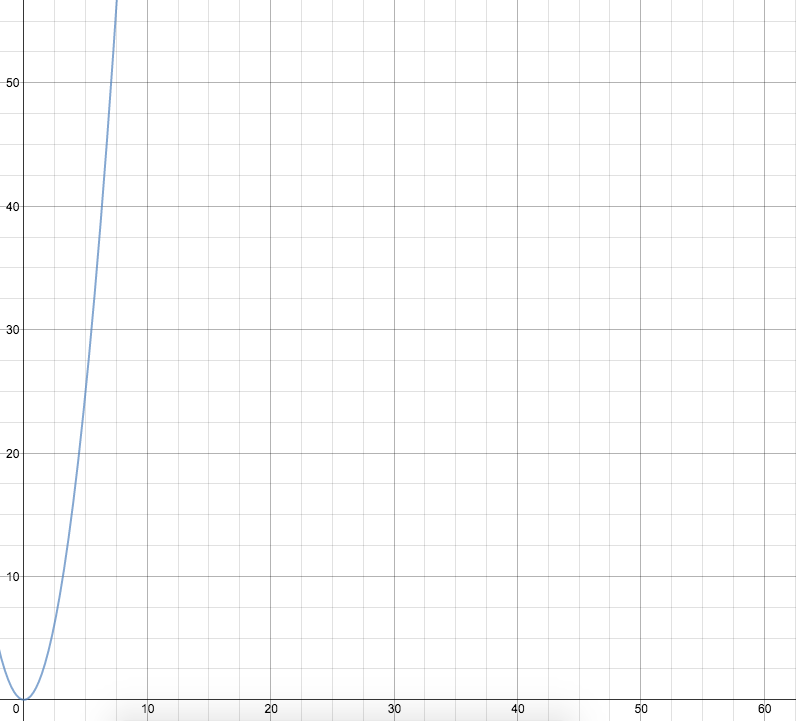
Example: You printed all the copies, but accidentally forgot the first letter of everyone's name. Go through and correct each student in each copy of the directory with a sharpie.
(If I go from 100 to 101 students, I'm going to have ~100 more operations, and
if I go from 1000 to 1001 students, I'm going to have ~1000 more operations)
Major Types of Complexity
Exponential: Increasing the problem size by one adds a number of operations proportional to some constant raised to the power of the problem size
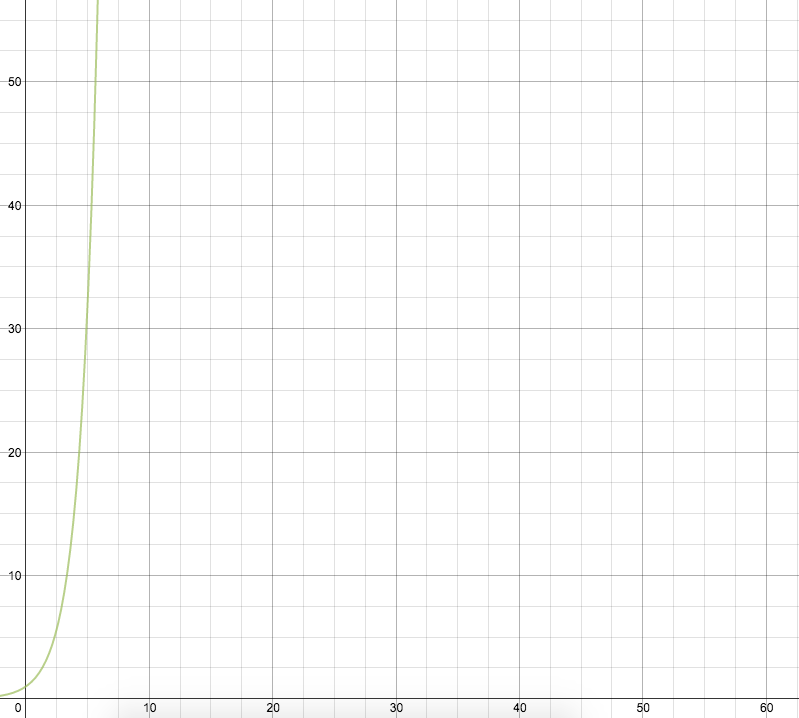
Example: You are sending a gift card to either blue bottle or chai bar to each student with the directory. You want to make a list of all the possible ways in which you can give out the gift cards.
Major Types of Complexity
Example: You are sending a gift card to either blue bottle or chai bar to each student with the directory. You want to make a list of all the possible ways in which you can give out the gift cards.
S1 B B B B C C C C S2 B B C C B B C C S3 B C B C B C B C
S1 B B C C S2 B C B C
} 4 Ways
S1 B B B B B B B B C C C C C C C C S2 B B B B C C C C B B B B C C C C S3 B B C C B B C C B B C C B B C C S4 B C B C B C B C B C B C B C B C
} 8 Ways
} 16 Ways
If I go from 2 to 3 students, I'm going to have ~2^2 more operations
If I go from 3 to 4 students, I'm going to have ~2^3 more operations
Major Types of Complexity
Logarithmic: Increasing the problem size by a factor of c adds a constant number of operations (ex: doubling problem size adds the same number of operations each time)
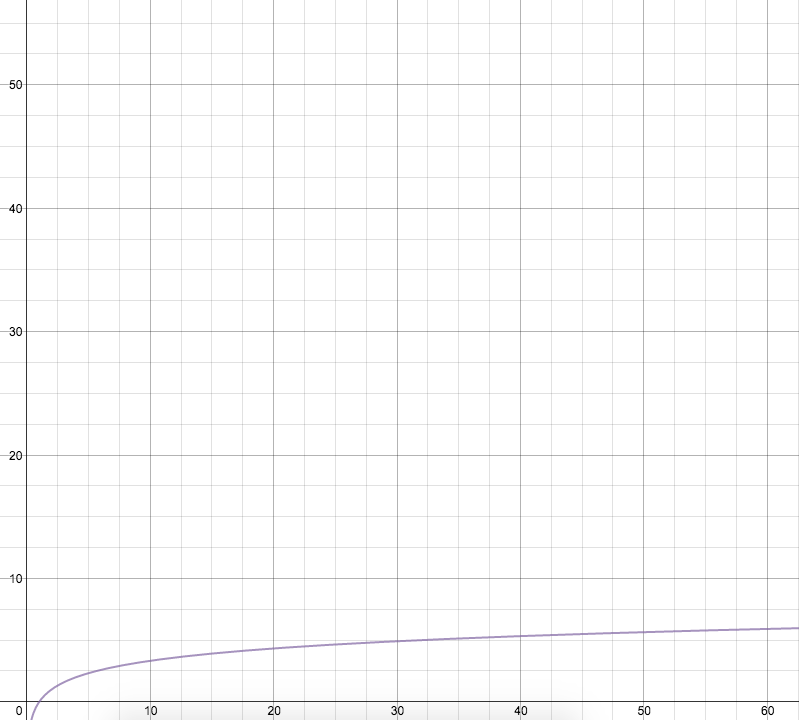
Example: You are looking for a specific student and you know their name - you find them by starting in the middle and seeing if it is to the left or the right, then repeating process with that section of pages.
(If I go from 64 to 128 students, I only have to do 1 more operation, and if I go from 1024 to 2048 students, I only have to do 1 more op)
Determining Complexity
1. Determine what variable(s) represent problem size (this is n)
2. Write number of operations in terms of n
3. Find leading term and drop coefficients
What about?
1. Function calls inside of functions that add complexity
2. Recursive functions
Determining Complexity
fork and clone:
https://github.com/bethjohnson/algo-time-complexity-review
also:
https://pollev.com/bigcavern281
(this url is randomly generated...no meaning here :) )
Example - countChar
function countChar(string){
var counts = {};
var currChar, currCharCount;
for (var i = 0; i < string.length; i++){
currChar = string[i];
currCharCount = 1;
for (var j = i+1; j < string.length; j++){
if (currChar === string[j]){
currCharCount++;
}
}
if (!counts.hasOwnProperty(currChar)){
counts[currChar] = currCharCount;
}
}
return counts;
}// do what is inside of here n times {
// 1 operation
// 1 operation
// do what is inside of here (n-j) times {
// worst case: 1 operation
}
// worst case: 1 operation
}
}Example - countChar
// do what is inside of here n times {
// 1 operation
// 1 operation
// do what is inside of here (n-j) times {
// worst case: 1 operation
}
// worst case: 1 operation
}
}}
(n - j) * 1
3 + (n - j)
1
1
1
}
3 + (n - 1)
+ 3 + (n - 2)
+ 3 + (n - 3)
+ ... + 3 + (n - n)
3 + (n - 1) + 3 + (n - 2) + 3 + (n - 3) + ... + 3 + (n - n)
3n + (n-1 + n-2 + n-3 + ... + n-n)
3n + (sum of all numbers from 0 to n-1)
3n +
Example - factorial
factorial(5)
5*factorial(4)
4*factorial(3)
3*factorial(2)
2*factorial(1)
1
Example - tournament
function tournament(players){
var results;
if (players.length < 3){
return players[0];
} else {
results = hotPotato(players);
return tournament(results);
}
}players.length = 81
results.length =
27
function tournament(players){
var results;
if (players.length < 3){
return players[0];
} else {
results = hotPotato(players);
return tournament(results);
}
}players.length = 27
results.length =
9
function tournament(players){
var results;
if (players.length < 3){
return players[0];
} else {
results = hotPotato(players);
return tournament(results);
}
}players.length = 9
results.length =
3
Example - quadTree
/ / \ \
| \ \ \
| \ \ \
Example - (balanced) quadTree
July 2015 - Time Complexity Review
By Beth Johnson
July 2015 - Time Complexity Review
- 733



