Algorithmic Complexity!
fork and clone:
https://github.com/beth/algo-time-complexity-review
Plan
- Overview of types of complexity
- Strategy for determining complexity
- Examples
Types of Complexity
Imagine you have an electronic copy of a directory of all past and present HR students (in alphabetical order, one student per page, with name, picture, current job, and cohort) and you want to print and mail a directory to each student.
Problem size: # of students
Major Types of Complexity
Constant: Increasing the problem size does not change the number of operations.
Example: Given a directory and the page a student is on, determine the cohort of the student.
# of Students
# of Ops
5
10
200
400
2
2
2
2
Major Types of Complexity
Linear: The number of operations is proportional to problem size.
Example: Given a copy of the directory, make a list of everyone from cohort 21.
# of Students
# of Ops
100
200
350
700
100
200
350
700
Major Types of Complexity
Quadratic: The number of operations is proportional to the square of the problem size.
Example: You printed all of the copies, but forgot to add page # and capitalize the first letter of everyone's first and last name. Correct each copy with a sharpie.
# of Students
# of Ops
5
10
12
24
5*15 = 75
10*30 = 300
12*36 = 432
24*72 = 1,728
Major Types of Complexity
Logarithmic: Multiplying the problem size by constant adds a the same number of operations.
Example: Given a name of a student, determine what cohort they are in (by dividing section of book in half repeatedly).
# of Students
# of Ops
8
16
128
256
3
4
7
8
How many times do I have to divide n by c to reach 1?
Major Types of Complexity
Exponential: The number of operations is proportional to some constant raised to the power of problem size.
Example: You are sending a gift card to either blue bottle or chai bar to each student with the directory. You want to make a list of all the possible ways in which you can give out the gift cards.
Major Types of Complexity
Example: You are sending a gift card to either blue bottle or chai bar to each student with the directory. You want to make a list of all the possible ways in which you can give out the gift cards.
S1 B B B B C C C C S2 B B C C B B C C S3 B C B C B C B C
S1 B B C C S2 B C B C
} 4 Ways
S1 B B B B B B B B C C C C C C C C S2 B B B B C C C C B B B B C C C C S3 B B C C B B C C B B C C B B C C S4 B C B C B C B C B C B C B C B C
} 8 Ways
} 16 Ways
} 32 Ways
} 64 Ways
5 students
6 students
Major Types of Complexity
Exponential: The number of operations is proportional to some constant raised to the power of problem size.
Example: You are sending a gift card to either blue bottle or chai bar to each student with the directory. You want to make a list of all the possible ways in which you can give out the gift cards.
# of Students
# of Ops
2
4
3
6
4
16
8
64
Major Types of Complexity
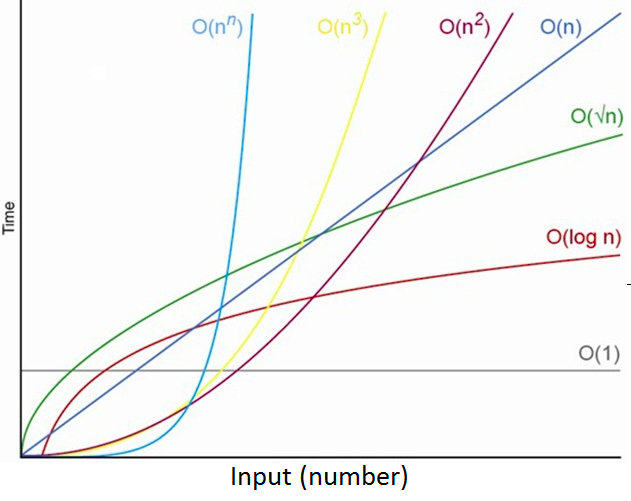
Determining Complexity
1. Determine what variable(s) represent problem size (this is n)
2. Write number of operations in terms of n
- Lines in series are ADDED
- Lines nested in other function calls or loops are MULTIPLIED
3. Find leading term and drop coefficients
What about?
1. Native JS methods (think about the time complexity of native method - how would you write it? check out the polyfill)
2. Recursive functions (draw a decision tree)
Determining Complexity
1. Determine what variable(s) represent problem size (this is n)
2. Write number of operations in terms of n
- Lines in series are ADDED
- Lines nested in other function calls or loops are multiplied
3. Find leading term and drop coefficients
Example: Given a copy of the directory, make a list of everyone from cohort 21.
Algorithm
for each page
if cohort is 21
add to list
n
1
0 or 1
Determining Complexity
Example: You printed all of the copies, but forgot to add page # and capitalize the first letter of everyone's first and last name. Correct each copy with a sharpie.
Algorithm
for each copy
for each page in copy
write page count
capitalize first name
capitalize last name
n
n
1
1
1
Determining Complexity
fork and clone:
https://github.com/beth/algo-time-complexity-review
example: contains
function contains(array, target){
return array.indexOf(target) > -1;
}function contains(array, target){
function indexOf(){
var index = -1;
for (var i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
if (array[i] === target){
return index;
}
}
return index;
}
return indexOf() > -1;
}
example: partialContains
function partialContains(array, target, start){
return array.slice(start).indexOf(target) > -1;
}function partialContains(array, target, start){
var newArray = array.slice();
var index = newArray.indexOf(target);
return index > -1;
}
Example - countChar
function countChar(string){
var counts = {};
var currChar, currCharCount;
for (var i = 0; i < string.length; i++){
currChar = string[i];
currCharCount = 1;
for (var j = i+1; j < string.length; j++){
if (currChar === string[j]){
currCharCount++;
}
}
if (!counts.hasOwnProperty(currChar)){
counts[currChar] = currCharCount;
}
}
return counts;
}// do what is inside of here n times {
// 1 operation
// 1 operation
// do what is inside of here (n-i) times {
// worst case: 1 operation
}
// worst case: 1 operation
}
}Example - countChar
// do what is inside of here n times {
// 1 operation
// 1 operation
// do what is inside of here (n-i) times {
// worst case: 1 operation
}
// worst case: 1 operation
}
}}
(n - i) * 1
3 + (n - i)
1
1
1
}
3 + (n - 1)
+ 3 + (n - 2)
+ 3 + (n - 3)
+ ... + 3 + (n - n)
3 + (n - 1) + 3 + (n - 2) + 3 + (n - 3) + ... + 3 + (n - n)
3n + (n-1 + n-2 + n-3 + ... + n-n)
3n + (sum of all numbers from 0 to n-1)
3n +
Example - factorial
factorial(5)
5*factorial(4)
4*factorial(3)
3*factorial(2)
2*factorial(1)
1
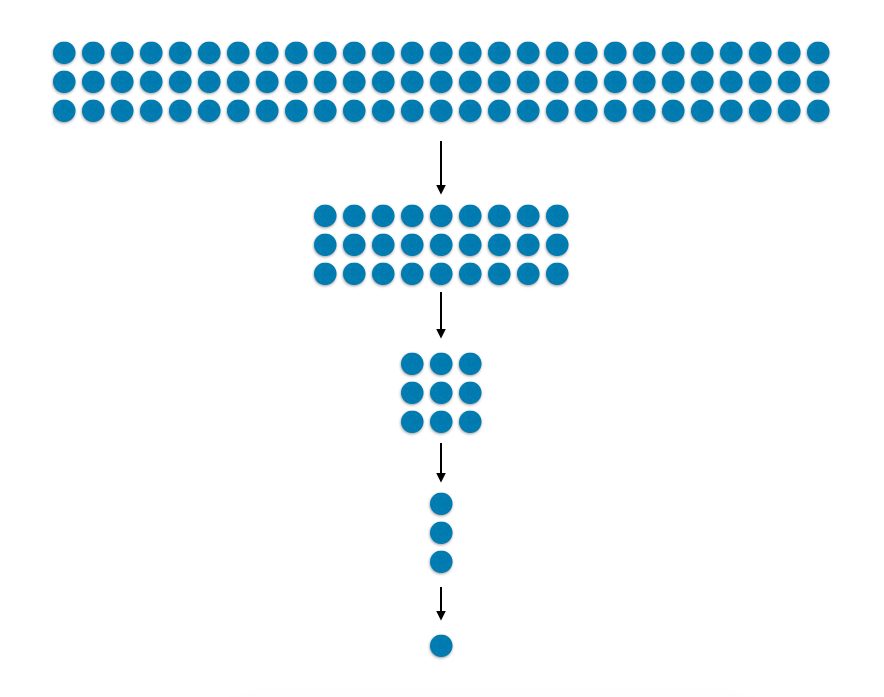
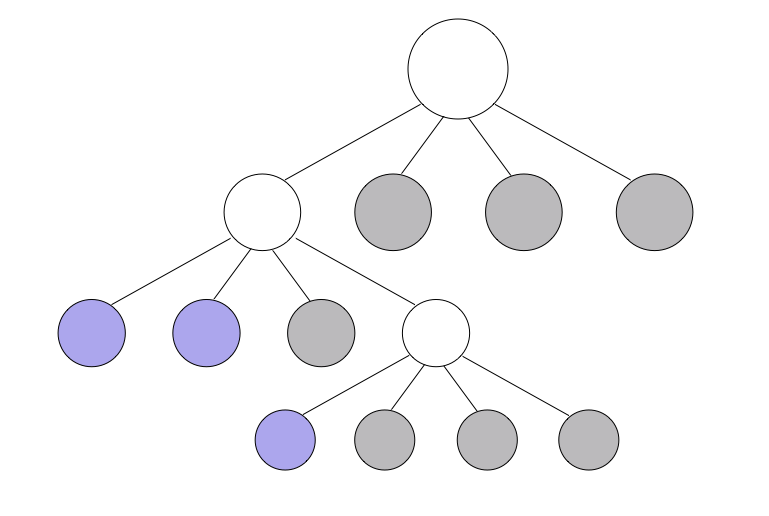
Example - tournament
function tournament(players){
var results;
if (players.length < 3){
return players[0];
} else {
results = hotPotato(players);
return tournament(results);
}
}
Example - allPasswords
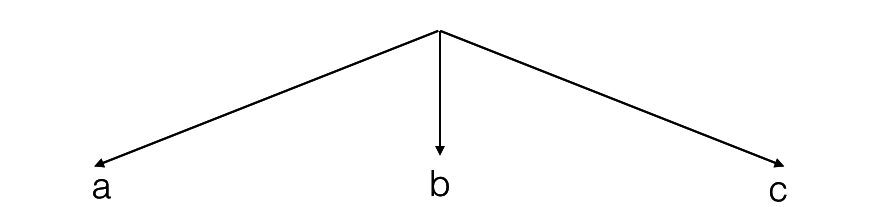
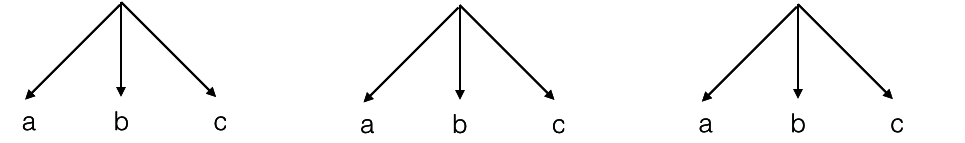
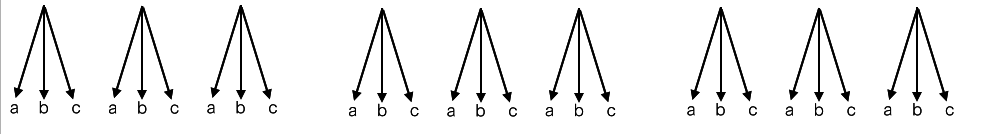
c = number of characters in alphabet
n = max number of characters in password
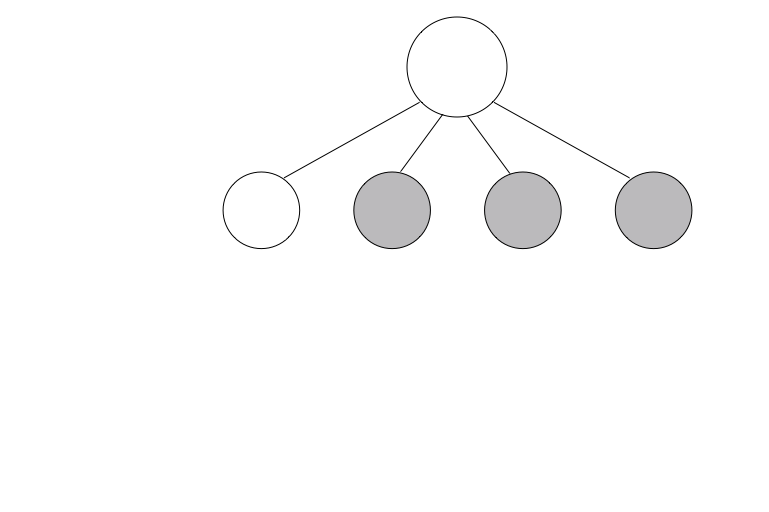
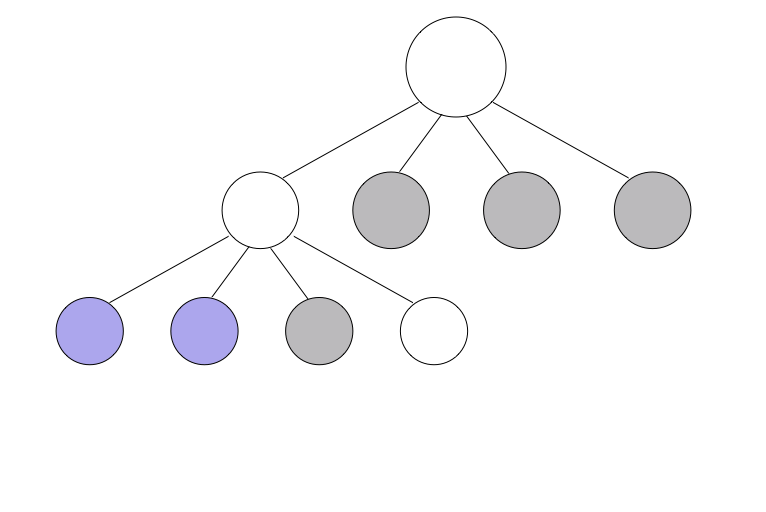
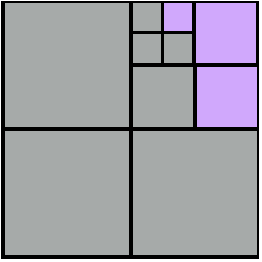
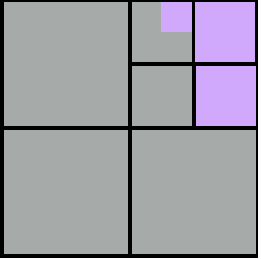
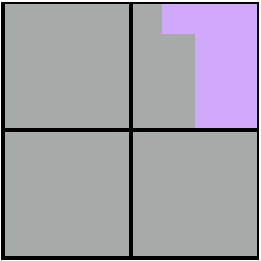
Example - quadTree
HR - Time Complexity Review
By Beth Johnson
HR - Time Complexity Review
- 3,095



