Intro to APIs:
What are they? Why and how use them?
slides at https://slides.com/briannorberg/deck/
Brian Norberg
IT Analyst, Trinity Technology Services
brian.norberg@duke.edu
In this workshop, you will learn:
- What is a web API and what is REST
- What is required to make a REST call
- How and why we use APIs
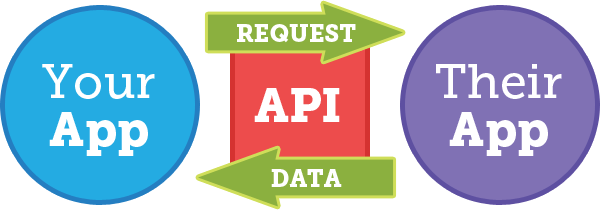
What is an API
API = Application Programming Interface = fancy way of saying the "thing" that enables one piece of software to talk to another piece of software
The War of the Web API:

VS
Soap API
REST
API


Why REST APIs
1) SOAP was developed by Microsoft and nothing good ever comes from there. Just kidding.
2) SOAP requires a knowledge of another protocol (a very verbose one too), whereas REST follows HTTP. REST makes API calling act like the rest of the web.
3) SOAP is reliant on XML and slower than REST requests.
4) All the cool kids use REST--
Google, Facebook, and Twitter
APIs are REST-based.
API in action
Go to my hometown, Chicago, in Google Maps, https://www.google.com/maps/place/Chicago
Open a new browser tab and go to the Google Maps api to request information about Chicago, http://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/geocode/json?address=chicago
Now let's look at the API docs to see what is happening above:
https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/geocoding/intro
What makes up a REST API Call?
1) root url - typically a subdomain or subfolder of domain, and includes "api" in it (googlemaps.com/api
or api.googlemaps.com)
2) endpoints - a unique url to a given resource or collection of resources (googlemaps.com/api/cities)
3) request methods - get, post, delete, etc.
4) parameters - directives you can add to the url to filter the returned results (parameters typically follow a "?" in the url string)


WTF... Access Key
REST API in Action
Go to the Colab api, https://streamer.oit.duke.edu/dev_console, and login with your netid and password
Click the "New API Key" button and fill out the form. Then enable all services.
Copy the API Key and click on the "Documentation" button to the left. Paste the key into the text entry box and click the "Explore" button.
Facebook Graph API
Go to the Facebook Graph API, https://developers.facebook.com/tools/explorer, and login with your Facebook credentials (if you are not already logged into Facebook).
Change "me" to "DukeUniv" and start messing around with adding parameters to see how the GET URL changes. Use the API documentation to help you, https://developers.facebook.com/docs/graph-api/using-graph-api.

WTF...Access Key, Take Two
API keys not only control whether we can access a server, they control how we can interact with that server.
Using APIs to make POST requests typically requires special permission and more than one access key.
Enter Twitter...
Most APIs require that you register your app and tell what access you wish it to have (check out the colab api registration page, http://apidocs.colab.duke.edu/)
Let's register an app with Twitter so we can test out posting a message to the platform from its API, https://apps.twitter.com.
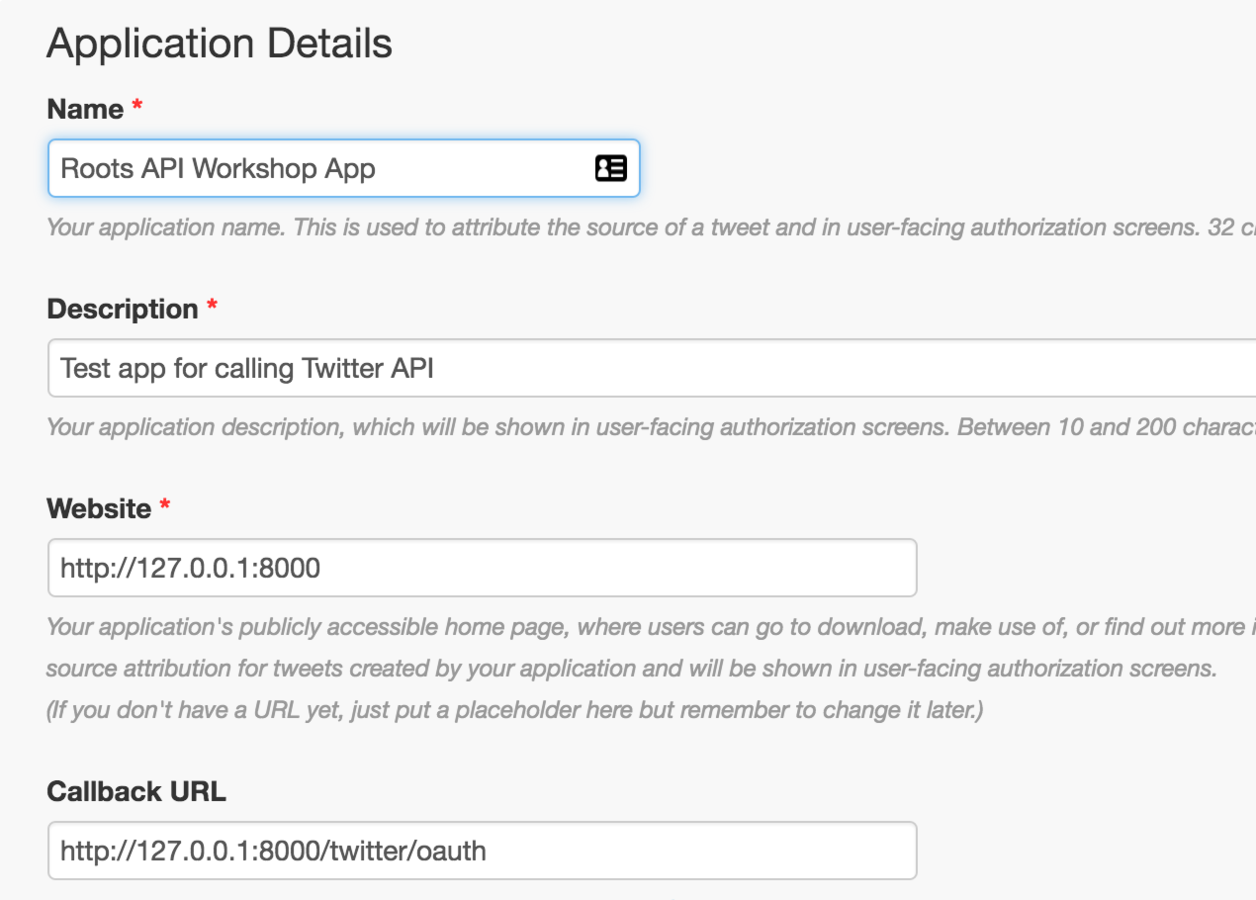
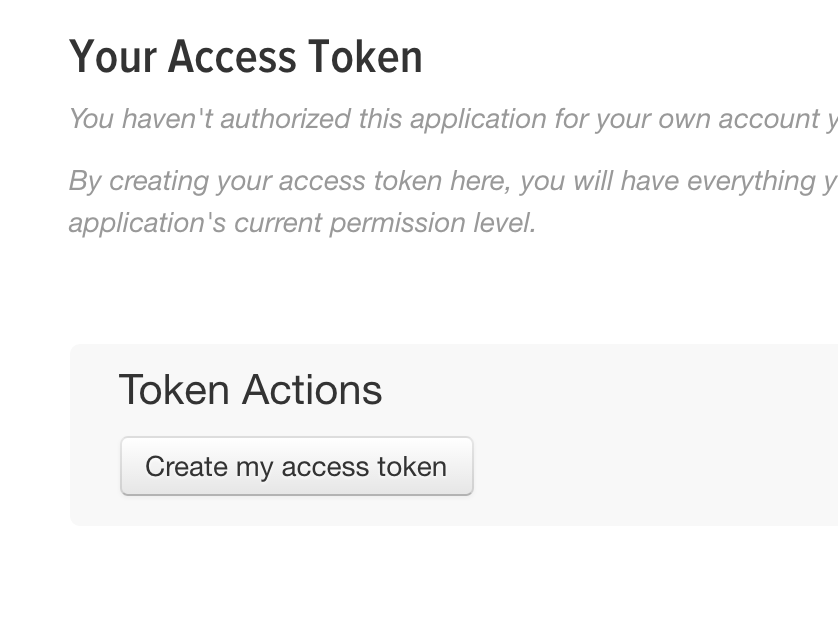
Configure your Twitter App
Download Postman app
Post a Message to Twitter with Postman, Part 1
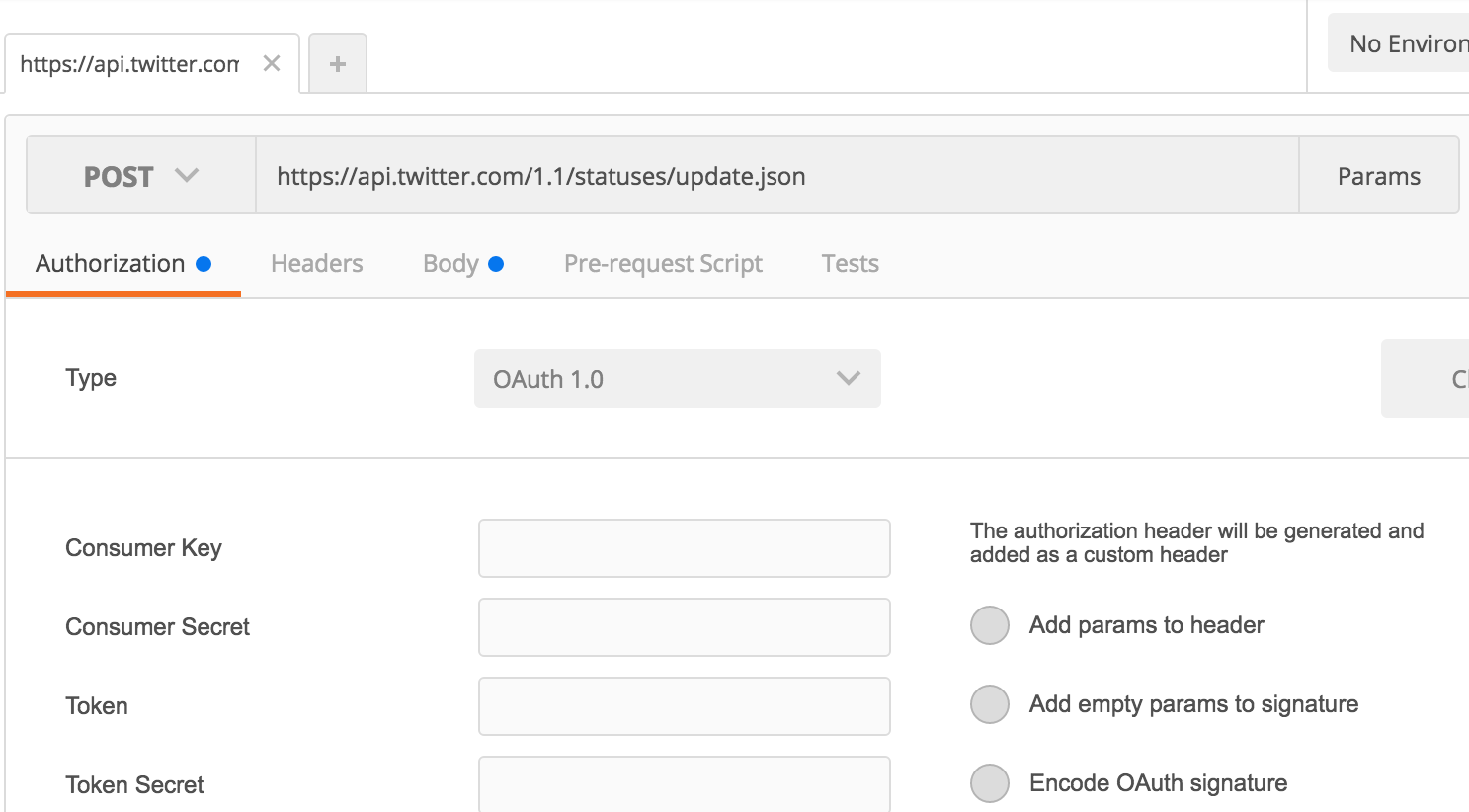
1) Select "POST" from dropdown list
2) Add "https://api.twitter.com/1.1/statuses/update.json" as POST URL
3) Select "OAuth 1.0" for Type, then add your Twitter credentials
4) Check "Encode OAuth signature" box
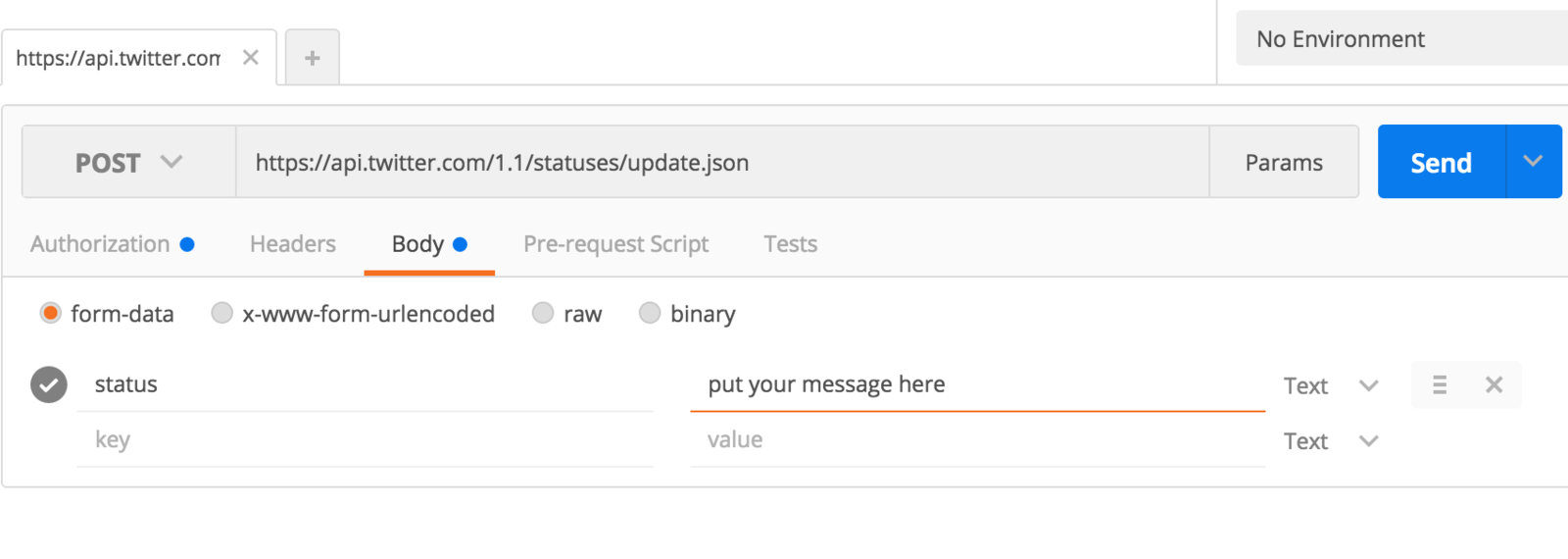
Post a Message to Twitter with Postman, Part 2
1) Click the 'Body' tab
2) Add "status" in the 'key' field
3) Add your message in the 'value' field and hit "Send"
Review Time: How and Why we use APIs
How
1) Get access key(s)
2) Choose request method (GET, POST)
3) Read API documentation to learn about endpoints, allowed parameters, and return formats of API
Why
1) To consume data (Get)
2) To create data (POST)
3) To embed code (Get revisited)
This is where we are now!
When in Doubt, Google It!
1) Copy into your favorite text editor:
https://gist.github.com/bnorberg/1459c88e0ae4a924bd986f63b0dd4114
2) Create a Google Maps API key
3) Find coordinates for the "Oit-Telecommunications Bldg" and "Duke University"

When in Doubt, Part 2:
Use Someone Else's Code
1) Get a OIT VM following these directions, https://duke.box.com/s/y7u16x289ujfrdsimk9mm8llokxyjt40
2) Install Twarc Twitter archiving tool following these directions, https://duke.box.com/s/14ekzpjb6st0pn7y5cvv8cf1gpank5v9

What's Next?
Explore all the APIs out there: http://www.programmableweb.com/apis/directory
Check out Code Academy's API tutorials: https://www.codecademy.com/apis
Learn to Google it: Once you know what API you want to interact with, choose your programming language and Google if there is already a client written in that language to interact with your API of choice. Chances are, there is.
Intro to APIs - old
By Brian Norberg
Intro to APIs - old
- 1,005



