Doing DH in the Classroom
Slides at: https://goo.gl/U6phUx
Brian Norberg / brian.norberg@duke.edu / IT Analyst, Trinity Technology Services
with Amanda Starling Gould / amanda.gould@duke.edu / DH Specialist, Franklin Humanities Institute

So Targaryen, Thomas Malory, and Edward Said are in the Same Course Description

- Discovery
- Ask Humanities questions
- differently
- with contemporary media
- Experimentation
- Public Engagement or publicity
-
Attract students to class
- digital = sexy
Unfamiliar Ways of Reading
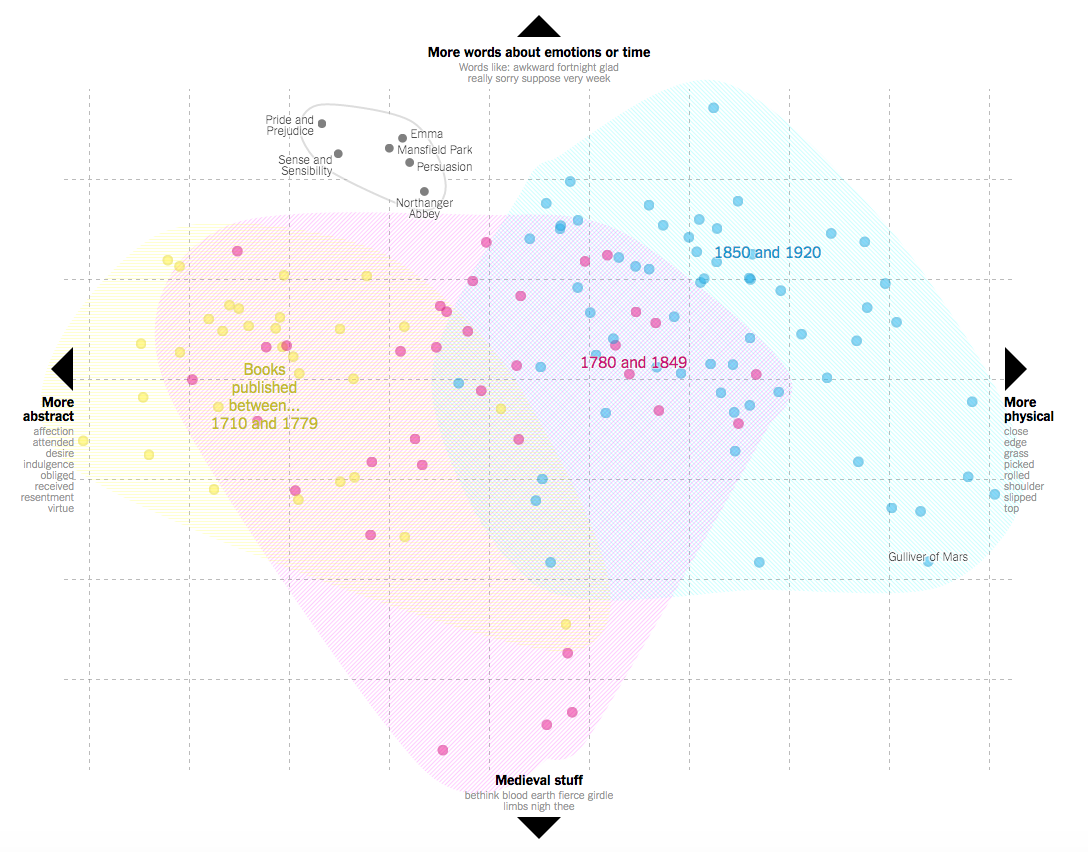
New Ways of Looking at Material
Find Contemporary Media to Work With
Give Students the Ability to Curate the Material

Engage the Public and Research Community
- Students work more public and goes beyond "writing just for the teacher"
- Develop resources for other researchers to use

Deconstructing DH

When doing digital projects it's best to ask what students can't do to determine what they can do. Students can't:
- Collect resources and decide best way to represent them
- Pick what tool to use without guidance
- Work alone and without clear assessment criteria

What Teachers can do to scaffold their students' digital work
-
Prepare for imperfect work (your expectations should be similar to those for traditional assignments)
Ask Not What Students Can Do for You...

- Decide how much of the class will be digital and when it will occur
-
Have defined learning outcomes for digital aspects
-
Create guidelines and, if possible, documentation
Setting Digital Ground Rules
Talk to an IT Person...


some who does a bit of both teaching and technology support. And don't forget librarians, learning innovation staff, and other colleagues can help too.

Type of Digital Projects
- Whole Semester (e.g. websites, digital exhibits, databases) - teacher needs to decide on course theme, tool to create project, and guide students on finding, describing, and entering resources with documentation
-
Replace a Paper (e.g. multimedia essays, timelines, maps) - instead of putting materials in an essay, student puts knowledge into another medium; teacher must decide on possible media and grading guidelines
-
Lesson Plan (e.g. podcasts, text analysis projects, geospatial projects) - teacher needs to know a little bit about the digital method explored, decide on tools to use, and develop structured activities to build up to final project
- Omeka, Drupal, and Wordpress are a web publishing platforms that can be used to share digital collections and exhibits
- These are semester-long and beyond projects
Examples: Race and Ethnicity in Advertising (Duke Library), Sonic Dictionary & Project Vox
The CMSs: Omeka, Drupal, Wordpress
- Sway is a cloud-based, interactive storytelling platform from Microsoft.
- This is a replace a paper type project
- Allows users to create narratives and presentations with content one uploads to the Sway application or finds on the Internet
- More flexibility than Powerpoint and less seasickness-inducing than Prezi
- 3 templates (slide and horizontal or vertical scroll)
- Very easy to use; accessible through Duke’s Office 365 Suite
Example: Adapt and Survive & The Haka
Sway
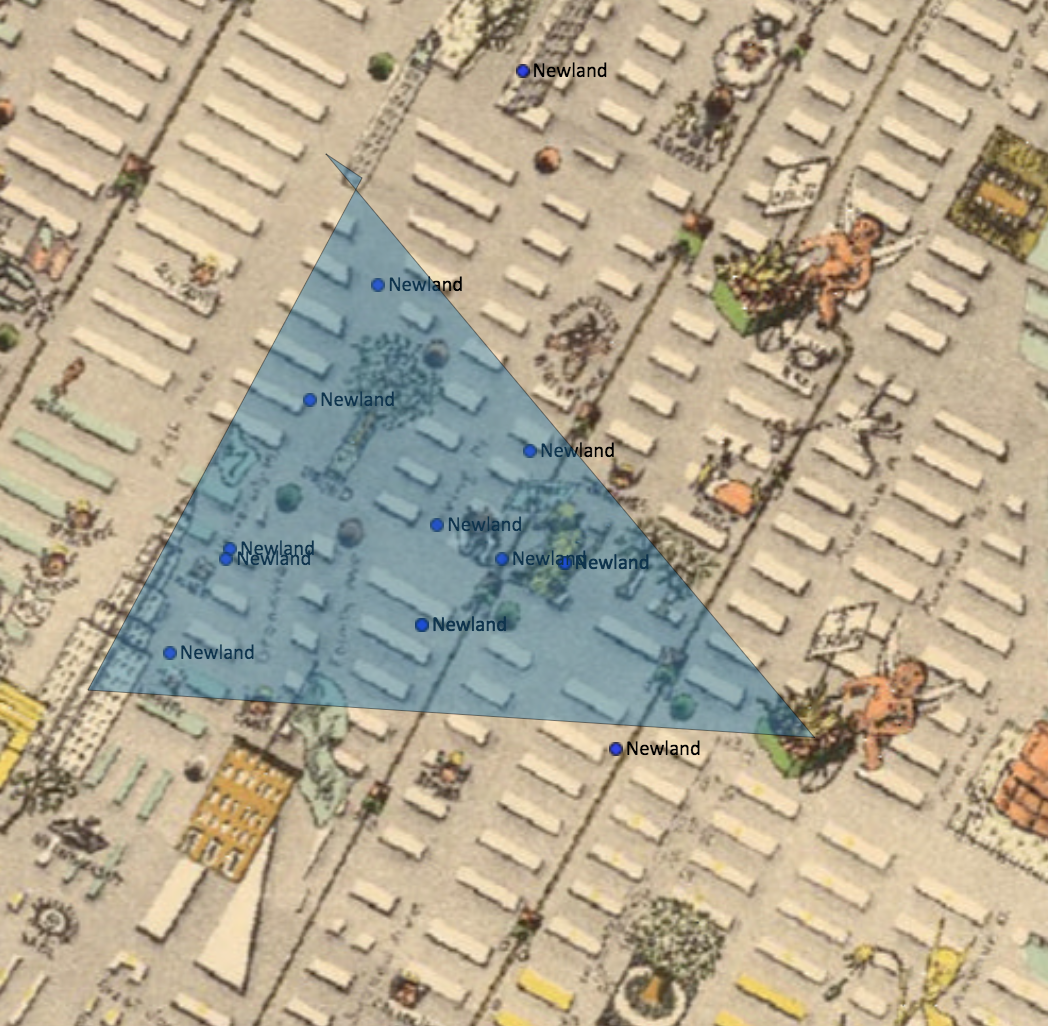
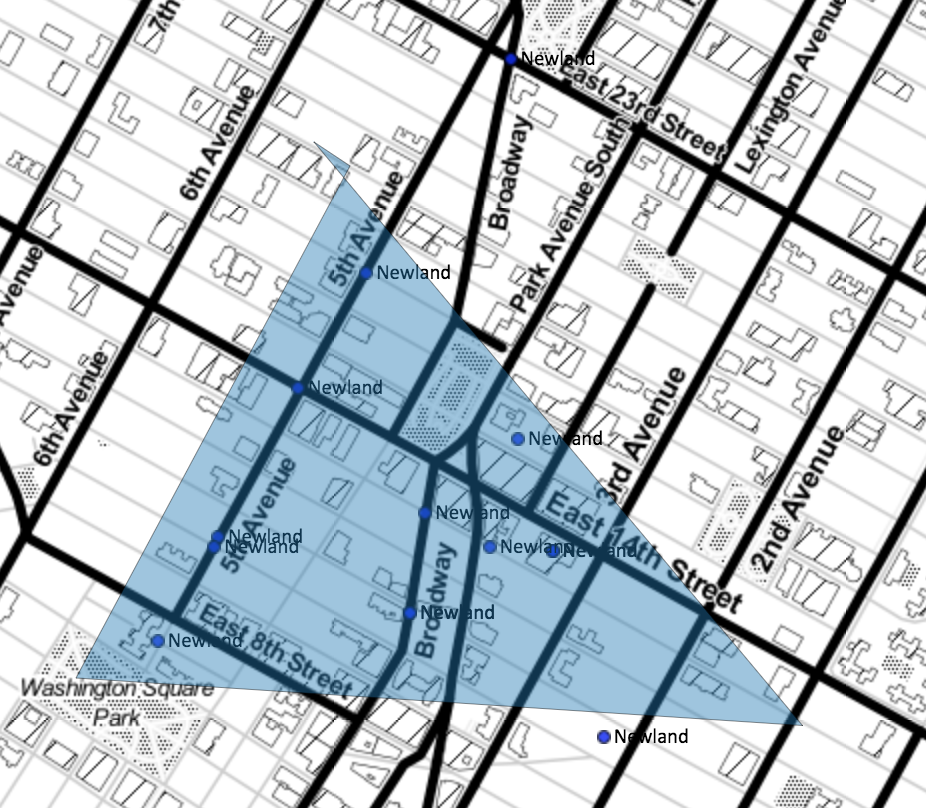
- StorymapJS allows users to create spatial narrative by adding images one uploads to the application or images, video, and audio from the Internet to slides that are associated with points on a map or background image
- This is a replace a paper type project
-
Cloud-based application that is extremely easy to use and free; iframeable
Examples: Games of Thrones & City Plaza Solidarity Space (go to digital stories tab)
StorymapJS
- TimelineJS allows users to create a temporal narrative by adding images one uploads to the application or images, video, and audio from the Internet to slides that are associated with points in time on a timeline
- This is a replace a paper type project
-
Customize display and behavior of timeline as needed
-
Cloud-based software that is straightforward to use: data is rendered from a Google Spreadsheet
Examples: Republican Run-Up & ADAPT (go to digital stories tab)
TimelineJS
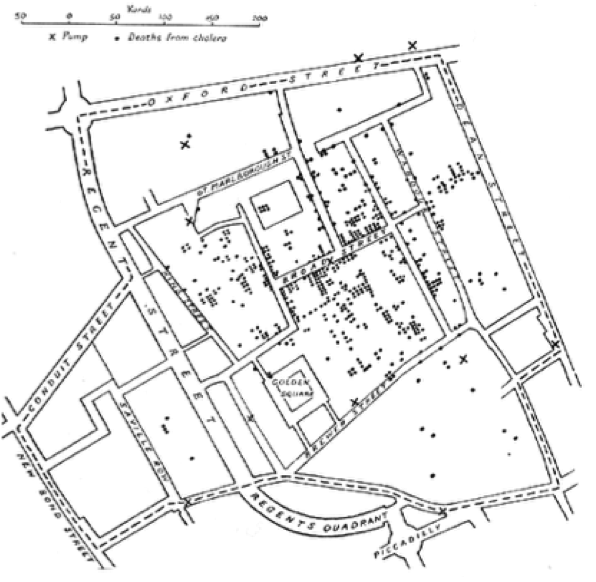
- When the location of objects matter to the information being shown/argument being made.
- These locations are symbolized and compared to find patterns that would be hard to recognize otherwise.
- Spatial analysis projects are lesson plan projects
What is Spatial Analysis
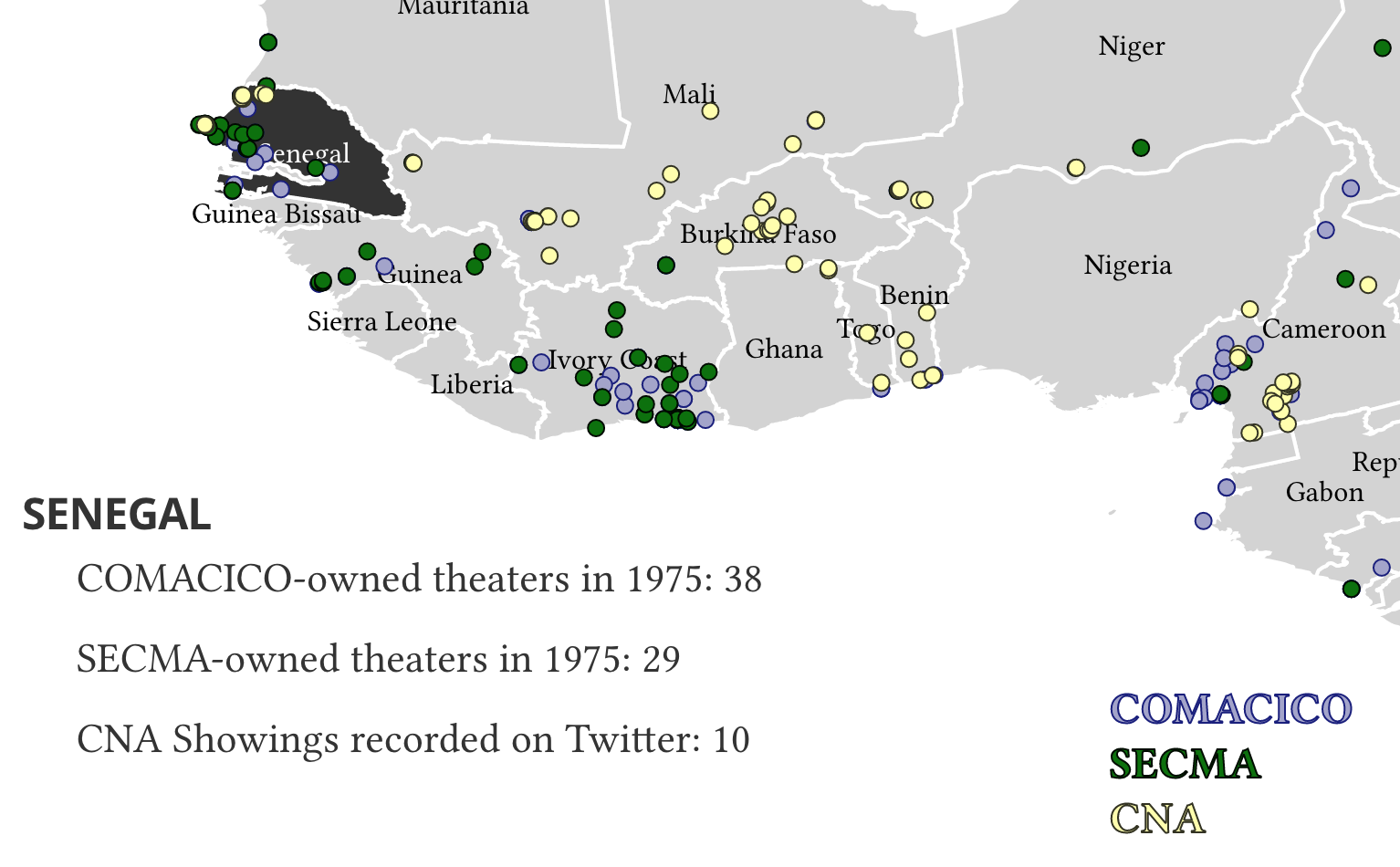
- Google My Maps allows users to create custom maps by dropping pins on a map and associating them with image, video, and other multimedia; add polygons, lines, and directions to highlight connections between points
- Easy to use, free cloud-based application; need Google account; iframeable
- Not narrative-driven; similar to Omeka’s Geolocation plugin
Examples: Global Ecological Solutions Map & Imaging Kanto
Google My Maps
-
Story Maps combines of the narrative strength of StorymapJS with the spatial analysis capability of more advanced GIS software
-
Add narrative text, videos, images, and maps
-
Cloud-based application available through Duke Libraries ArcOnline license; iframeable; Library Guide
Example: The Uprooted & Legacies of Labor
ESRI Story Maps

- Text analysis looks at elements such as word frequencies, co-occurrence, and statistically generated ‘topics’ to perform ‘distant reading’ of large collections
- Textual analysis projects are lesson plan projects
What is Textual Analysis?
-
Voyant Tools is a web-based text reading and analysis environment.
-
Work with your own corpus or practice on one of the included corpuses
-
Does work frequency, co-occurrence, word clouds, topic models, etc.; allows exporting of graphs and iframes
-
Cloud-based application that pairs well with a free text repository like Project Gutenberg
Example: A Republic of Emails
Voyant Tools

Don’t let the fancy technology lure you in.
Select the technology that best fits:
- What you want to communicate
- Your audience’s knowledge/expectations
- Your technical capability
Scope is the key
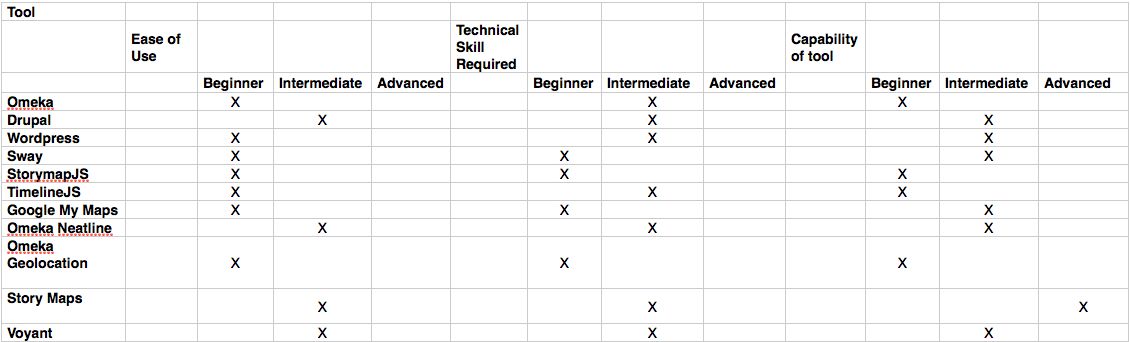
Tool Matrix
More Tools, Tutorials, and Projects

Brian Norberg / brian.norberg@duke.edu / IT Analyst, Trinity Technology Services
Amanda Starling Gould / amanda.gould@duke.edu / DH Specialist, Franklin Humanities Institute
Classroom DH
By Brian Norberg
Classroom DH
Slides for describing why try dh in the classroom
- 1,065