Advanced
programming
Lecture 3


Måns Magnusson
Statistics and Machine learning
Department of computer and information science

Since last time?

Best practices
for scientific computing
based on the article

1. Write code for people

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
1.1 A program should not require its readers to hold more than a handful of facts in memory at once
1.2 Make names consistent, distinctive, and meaningful
1.3 Make code style and formatting consistent
2. Let the computer do the work

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
2.1 Make the computer repeat tasks
2.2 Save recent commands in a file for re-use
2.3 Use a build tool to automate workflows
3. Make incremental changes

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
3.1 Work in small steps with frequent feedback and course correction
3.2 Use a version control system
3.3 Put everything that has been created manually in version control
4. Don’t repeat yourself (or others).

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
4.1 Every piece of data must have a single authoritative representation in the system
4.2 Modularize code rather than copying and pasting
4.3 Re-use code instead of rewriting it
5. Plan for mistakes

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
5.1 Add assertions to programs to check their operation
5.2 Use an off-the-shelf unit testing library
5.3 Turn bugs into test cases
5.4 Use a symbolic debugger
6.Optimize software only after it works correctly

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
6.1 Use a profiler to identify bottlenecks
6.2 Write code in the highest-level language possible
7. Document design and purpose, not mechanics

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
7.1 Document interfaces and reasons, not implementations
7.2 Refactor code in preference to explaining how it works
7.3 Embed the documentation for a piece of software in that software
8. Collaborate

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
8.1 Use pre-merge code reviews
8.2 Use pair programming when bringing someone new up to speed and when tackling particularly tricky problems
8.3 Use an issue tracking tool
R packages

R packages

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
An environment with functions and/or data
The way to share code and data
~4 000 developers
> 7000 packages
Package basics

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Installation
Usage
library() :: :::
install.packages() devtools::install_github()
devtools::install_local()
Semantic versioning

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
"Dependency hell"
[MAJOR].[MINOR].[PATCH]
Package namespace

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
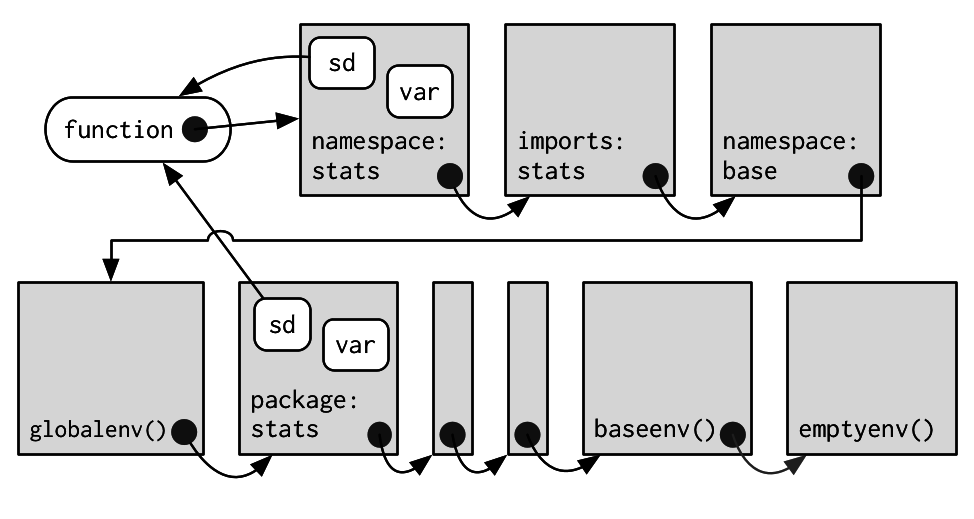
Examine packages

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
1. Who?
2. When updated?
3. In development?
Git and GitHub

Version control?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Why version control?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
- Collaboration
- Storing versions (properly)
- Restoring versions
- Understanding what happens
- Backup
Why git?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
- Simple to use
- Distributed
- Fast
- Common in practice
- R packages uses github
- Integrated with R-Studio
Basic git

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
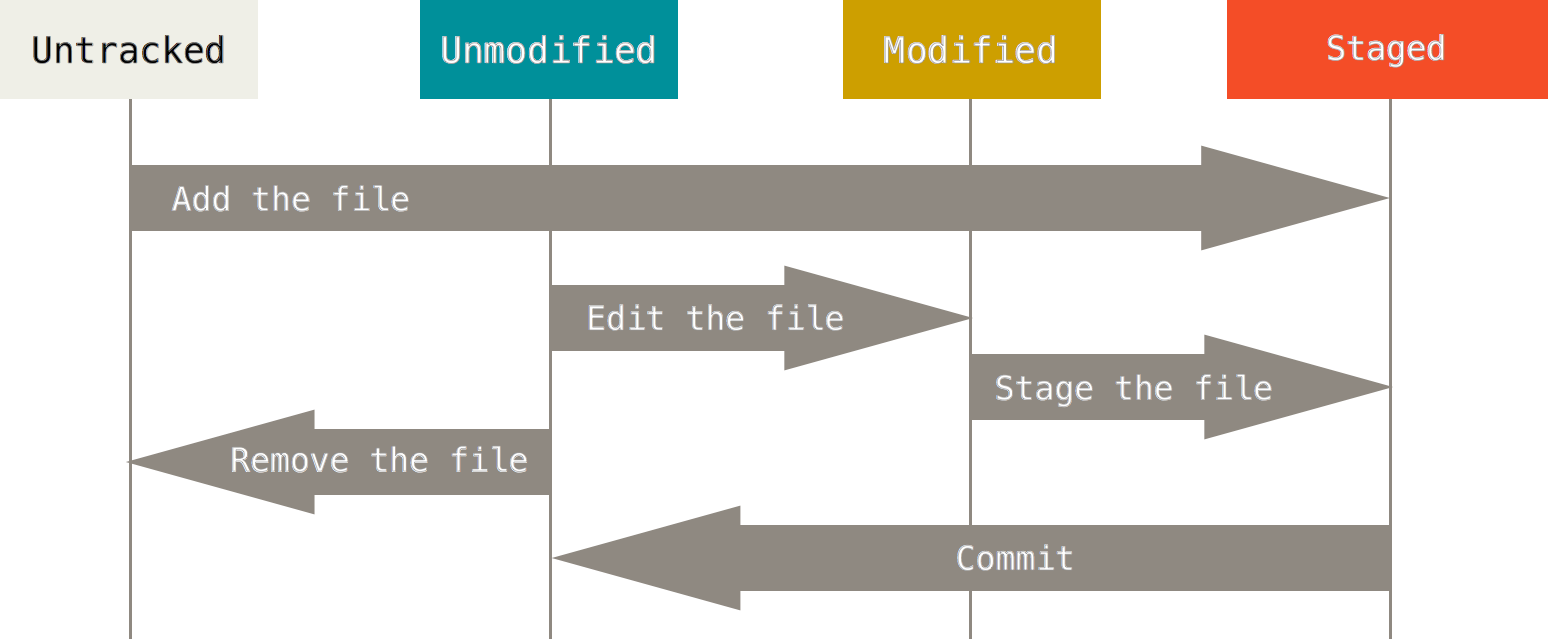
github

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
- Remote (push/pull)
- Barebone homepage (using md)
- Collaborations
- Issue tracker / Wiki / discussions
Free for public repos
Private repos cost
Student accounts
Creating R packages

Why part of the course?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Writing performant code (best practice)
The way to collaborate (R ecosystem)
Combine code, data and analysis
Easy to distribute and reuse (public api)
Learn how to reuse code from other packages
Package structure

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
R/
man/
vignette/
tests/
data/
scr/
inst/
DESCRIPTION
NAMESPACE
Documentation with ROxygen

Why roxygen2?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
- Performant code (docs close to code)
- Automatically generates all man files
- Simple to use
- Handles NAMESPACE
- Similar to JavaDoc and DOxygen
roxygen2 syntax

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Unit testing with testthat

Why unit testing?

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Fewer bugs
Better code structure
Faster restarts
Robust code - correct a bug only once
A must in complicated projects!
Types of testing

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
- White box testing
- Black box testing
- Probabilistic testing
testthat

Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
R-Studio debugger


Advanced R Programming
Måns Magnusson
Advanced R - Lecture 3
By monsmagn
Advanced R - Lecture 3
Lecture 3 in the course Advanced R programming at Linköping University.
- 1,550



