Ben Combee
Hackaday Supercon 2023
A Hacker's Guide to Audio and Video Formats
- How much CPU processing can you do?
- How much RAM can you afford?
- How much storage space do you have?
- Do you just need to decode or also encode?
- What kind of latency is allowed?
- Are there licensing or patent costs?
- Can this be supported using available tools?
Questions to Ask Before Picking a Format
Audio
Audio Questions
- How large is the audio?
- Does it have metadata?
- Is it complex to decode?
- Does it support multiple channels?
- Does your hardware directly support it?
- Bitrate (samples / second)
- Sample size (8/16/24)
- Channels
- Separate vs joint stereo
Audio Formats
- Raw audio (PCM, PWM)
- aLaw / uLaw
- MP3 (MPEG-1 Layer 3)
- AAC (Advanced Audio Format)
- Dolby Digital (AC3/EAC3/AC4)
- Vorbis
- Opus
Deep Dive on MP3
- Most common audio file format ever!
- Patents ran out in 2018, so free to use
- Can go down to low bitrates
- Lots of software to decode
- Hardware solutions may be best for low-power or low-volume, but hard to justify a $12 VS1053B over a $4 Pico
- C library libhelix-mp3
- RealNetworks Public Source License
(BSD-like with patent grant) - about 20K code, 32K RAM on 32-bit ARM

Deep Dive on Opus
- Great open-source royalty-free format
- Especially designed for speech
- Supports low bitrates
- C library libopus (BSD 3-clause)
- ~200K for 32-bit ARM library with encode/decode

Images
Image Formats
- Raw memory dumps (BMP, TGA)
- Tile-based formats
- RLE compression
- Dictionary-based compression (GIF, PNG)
- DCT-based compression (JPEG)
- Based on video codes (WebP, AVIF)
- Memory for encoded form
- Complexity to decode
- Compatibility with display hardware
- Color space (RGB vs YUV)
- Indexed vs Direct Color
- Planar vs Interleaved
- Required width/height restrictions
- Alpha support
- Patent Encumbrance
Deep Dive on RLE and Indexed Color
- Image formats are often custom designed for the application
- Run Length Encoding (RLE) is a simple, low-code technique for compressing large areas of one color
- Indexed color is a way of mapping a small number of color values to a custom palette
- Find The Story (Arduboy)
- RLE compressed 2x2 screen (256x128x8) image
- Index colors mapped to B/W at runtime
- 32K reduced to 15K
Deep Dive on PNG
- Lossless bitmap format with lots of tool support
- Has index color and alpha channel support
- Uses zlib as compression for picture chunks
- Can add arbitrary metadata to images
- PNGdec library (Apache 2.0) by Larry Banks
- uses about 48K of RAM, small code size
- Designed for small projects
- Line-by-line decoding
- OptiPNG (zlib license)
- desktop tool to make PNG files smaller
- also does conversion from other formats

Deep Dive on JPEG
- JPEGDEC (Apache 2.0) by Larry Banks
- embedded-optimized decoder
- Floyd-Steinberg dithering

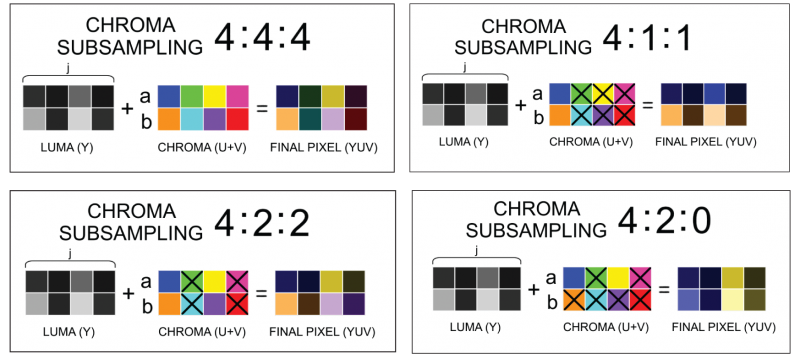
Deep Dive on YUV
- RGB colors map to how displays emit color with separate red/green/blue elements
- YUV, aka YCrCb, encodes brightness and color differences
- Native output format of JPEG and video codecs
- Since eyes are more sensitive to brightness changes, you can reduce resolution of UV planes by chroma subsampling
- libyuv (BSD) from Chromium for fast conversion
Video
- Motion JPEG
- MPEG-1 / MPEG-2
- H.264 / AVC
- H.265 / HEVC
- VP8 & VP9 & AV1
- Hardware support
- Memory required to decode
- Reference frames
- I frames / P frames / B frames
- Patent Encumbrance
Video Formats
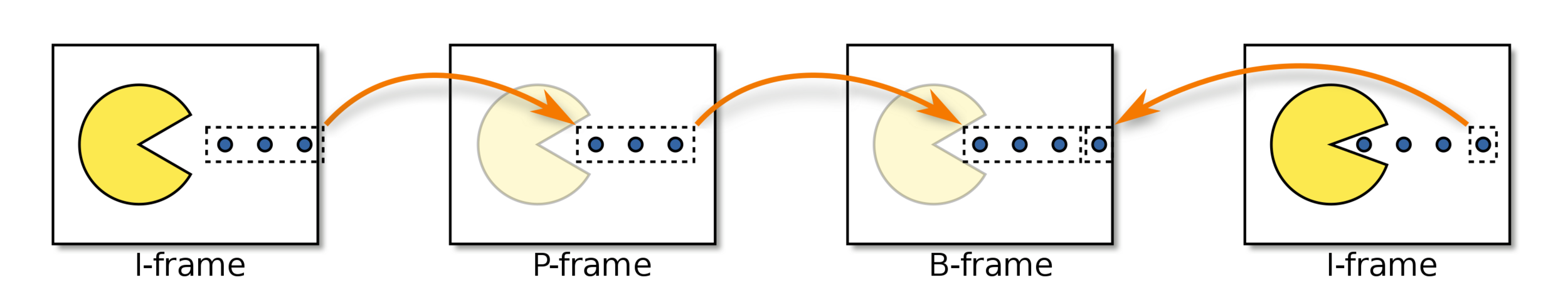
Deep Dive on MPEG-1
- Invented in late 1980's for delivering video on CDs
- Supports I, D, and B frames, but usually I and D only
- MPEG-2 is an extension of this format for broadcast use with higher bitrates and interleaved video support
- MPEG-1 is patent-free since 2008, at least
- pl_mpeg - single C header MPEG-1 decoder!
- also supports MPEG-1 layer 1/2 audio
- outputs Y/U/V planes for your code to process
- used in my BadgerMovie project

Synchronization
Keeping Audio & Video in Sync
- Presentation Time Stamp (PTS)
- 90kHz clock
- Clock rollover
- Device's realtime/system clock unreliable for sync
- Device speed can be subtly different from playback speed
- Video may also be decoded out-of-order

Not Just Audio/Video Synchronization
- Closed captions
- Animations
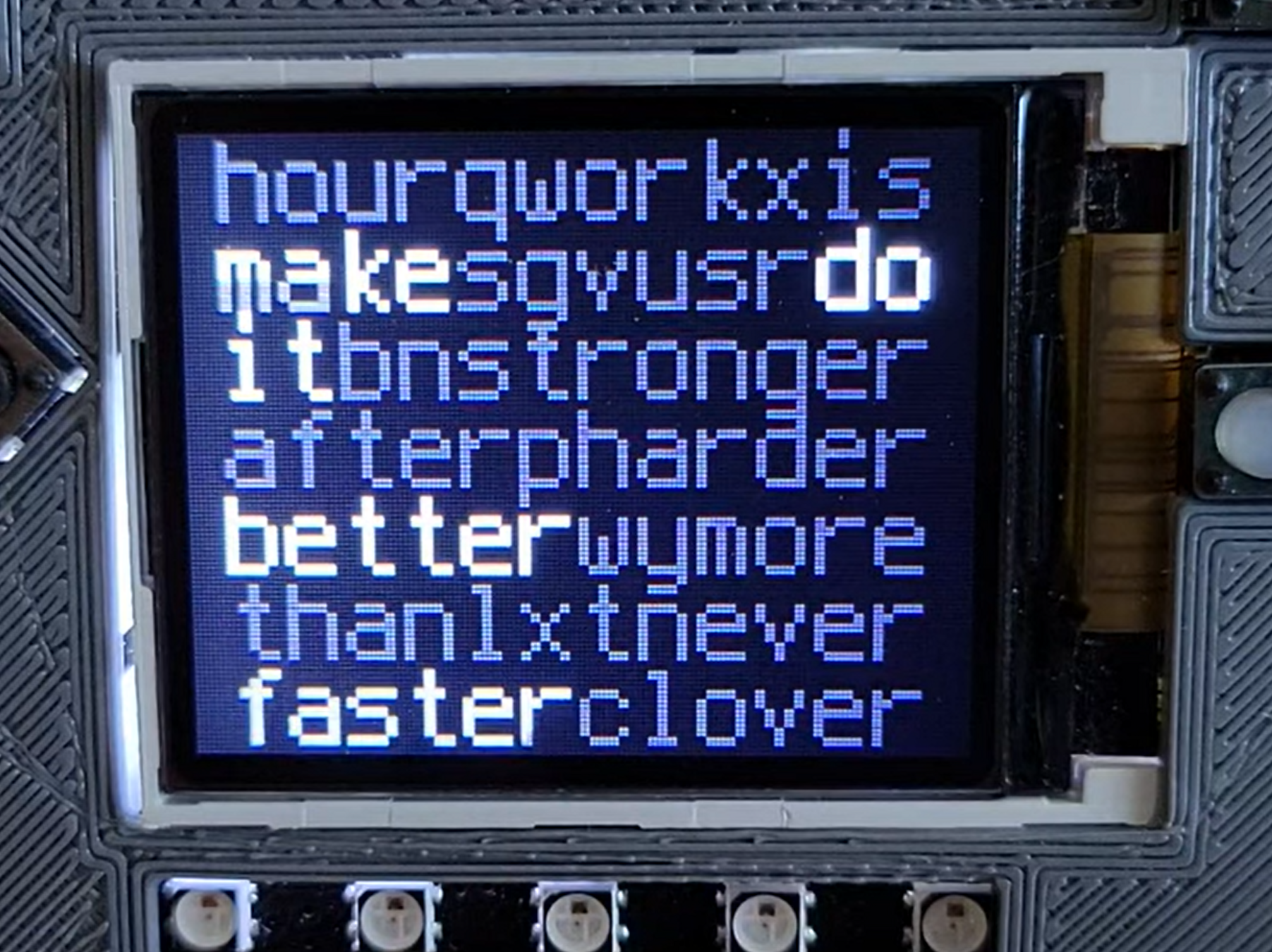
- DaftPunkWordClock
- synced highlighting of lyrics with timestamps to MP3
- drifted terribly until I modified CircuitPython to expose decoded audio frame count allowing better sync
Thanks!
Creative Commons Acknowledgements
Creative Commons Acknowledgements
Code Links
A Hacker's Guide to Audio and Video Formats
By Ben Combee
A Hacker's Guide to Audio and Video Formats
- 546


