ES6+ Deep Dive
Prathik Shetty
awebdeveloper
Why ES6?


Deep Dive
-
Variables and Scoping
-
Strings
-
Destructuring
-
Parameter Handling
-
Arrow Functions
-
Classes
-
Modules
-
Generators
-
Promise
-
Async Await
Running ES6








Variables and Scoping
var vs. let / const
var snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
if (food) {
var snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
// undefined
var vs. let / const
var snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
var snack;
if (food) {
snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
// undefined
var vs. let / const
let snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
if (food) {
let snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
// A
// B
// 'Meow Mix'
var vs. let / const
let snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
if (food) {
let snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
// A
// B
// 'Meow Mix'
(function () {
var food = 'Meow Mix';
}());
console.log(food);
// Reference Error
var vs. let / const
{
let food = 'Meow Mix';
}
console.log(food);
// Reference Error
var vs. let / const
const food = 'Meow';
{
const food = 'Meow 2';
console.log(food);
}
console.log(food);
// Meow 2
var vs. let / const
// Meow
Scoping
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map(function (character) {
return this.name + character;
});
};
// Cannot read property 'name' of undefined
// A
// B
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
var that = this;
return arr.map(function (character) {
return that.name + character;
});
};
// Store this
Scoping
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map(function (character) {
return this.name + character;
}, this);
}
Scoping
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map(function (character) {
return this.name + character;
}.bind(this));
}Scoping
Arrow Functions
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map((character) => this.name + character );
}
Arrow Functions
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const squares = arr.map(x => x * x);
const squares = arr.map(function (x) { return x * x });
// Function Expression
// Terse
Strings
String.prototype.contains
var string = 'food';
var substring = 'foo';
console.log(string.indexOf(substring) > -1);
const string = 'food';
const substring = 'foo';
console.log(string.contains(substring));
// true
// true
String.prototype.repeat
function repeat(string, count) {
var strings = [];
while(strings.length < count) {
strings.push(string);
}
return strings.join('');
}
'meow'.repeat(3);
// meowmeowmow
Template Literals: Escaping Characters
var text = "This string contains \"double quotes\" which are escaped."
let text = `This string contains "double quotes" which are escaped.`
Template Literals: Interpolation
const name = 'Tiger';
const age = 13;
console.log(`My cat is named ${name} and is ${age} years old.`);
var name = 'Tiger';
var age = 13;
console.log('My cat is named ' + name + ' and is ' + age + ' years old.');
Template Literals: Multi-line Strings
var text = (
'cat\n' +
'dog\n' +
'nickelodeon'
)
var text = [
'cat',
'dog',
'nickelodeon'
].join('\n')
var text = (
`cat
dog
nickelodeon`
)
Template Literals: Expressions
let today = new Date()
let text = `The time and date is ${today.toLocaleString()}`
Template Literals: Multi-line Strings
let book = {
title: 'Harry Potter and The Sorcercers Stone',
summary: 'Much magic. Such depth.',
author: 'J.K. Rowling'
}
let html = `<header>
<h1>${book.title}</h1>
</header>
<section>
<div>${book.summary}</div>
<div>${book.author}</div>
</section>`
Destructuring
Destructuring
var luke = { occupation: 'jedi', father: 'anakin' }
var {occupation, father} = luke;
console.log(occupation); // 'jedi'
console.log(father); // 'anakin'
var [a, b] = [10, 20]
console.log(a); // 10
console.log(b); // 20
Destructuring
function getCoords () {
return {
x: 10,
y: 22
}
}
var {x, y} = getCoords()
console.log(x); // 10
console.log(y); // 22
Modules
Exporting in CommonJS
module.exports = 1
module.exports = { foo: 'bar' }
module.exports = ['foo', 'bar']
module.exports = function bar () {}
export default 1
export default { foo: 'bar' }
export default ['foo', 'bar']
export default function bar () {}
Named Exports
module.exports.name = 'David';
module.exports.age = 25;
export var name = 'David';
export var age = 25;
Exporting in ES6
// math/addition.js
function sumTwo(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function sumThree(a, b) {
return a + b + c;
}
export { sumTwo, sumThree };
Exporting in ES6
export function sumTwo(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
export function sumThree(a, b) {
return a + b + c;
}
Exporting default bindings
function sumTwo(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function sumThree(a, b) {
return a + b + c;
}
var api = {
sumTwo : sumTwo,
sumThree: sumThree
}
export default api
Importing Modules
var _ = require('underscore');
import _ from 'underscore';
import { sumTwo, sumThree } from 'math/addition'
import {
sumTwo as addTwoNumbers,
sumThree as sumThreeNumbers} from
} from 'math/addition'
import * as util from 'math/addition'
Parameters
Default Parameters
function addTwoNumbers(x, y) {
x = x || 0;
y = y || 0;
return x + y;
}
addTwoNumbers(2, 4); // 6
addTwoNumbers(2); // 2
addTwoNumbers(); // 0
Default Parameters
function addTwoNumbers(x=0, y=0) {
return x + y;
}
addTwoNumbers(2, 4); // 6
addTwoNumbers(2); // 2
addTwoNumbers(); // 0
Rest Parameters
function logArguments() {
for (var i=0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
console.log(arguments[i]);
}
}
function logArguments(...args) {
for (let arg of args) {
console.log(arg);
}
}
Named Parameters
function initializeCanvas(options) {
var height = options.height || 600;
var width = options.width || 400;
var lineStroke = options.lineStroke || 'black';
}
function initializeCanvas(
{ height=600, width=400, lineStroke='black'}) {
...
}
function initializeCanvas(
{ height=600, width=400, lineStroke='black'} = {}) {
...
}
Spread Operator
Math.max(...[-1, 100, 9001, -32]) // 9001
var arr = [1, ...[2,3], 4];
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
var arr1 = [0, 1, 2];
var arr2 = [3, 4, 5];
arr1.push(...arr2);
Math.max(-1, 100, 9001, -32) // 9001
Classes
Base Classes
function Person(name, age, gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
Person.prototype.incrementAge = function () {
return this.age += 1;
};
Extended Classes
function Personal(name, age, gender, occupation, hobby) {
Person.call(this, name, age, gender);
this.occupation = occupation;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
Personal.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Personal.prototype.constructor = Personal;
Personal.prototype.incrementAge = function () {
return Person.prototype.incrementAge.call(this) += 1;
}
Base Classes in ES6
class Person {
constructor(name, age, gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
incrementAge() {
this.age += 1;
}
}
Extended Classes in ES6
class Personal extends Person {
constructor(name, age, gender, occupation, hobby) {
super(name, age, gender);
this.occupation = occupation;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
incrementAge() {
super.incrementAge();
this.age += 20;
console.log(this.age);
}
}
// Calls parent incrementAge()
Maps
(Hash) Maps in ES5
var map = new Object();
map[key1] = 'value1';
map[key2] = 'value2';
Maps in ES6
let map = new Map();
> map.set('name', 'david');
> map.get('name'); // david
> map.has('name'); // true
// key
// value
Keys can be more than strings!
Arbitrary values as keys
let map = new Map([
['name', 'david'],
[true, 'false'],
[1, 'one'],
[{}, 'object'],
[function () {}, 'function']
]);
for (let key of map.keys()) {
console.log(typeof key);
// > string, boolean, number, object, function
};
.entries( )
for (let entry of map.entries()) {
console.log(entry[0], entry[1]);
}
for (let [key, value] of map.entries()) {
console.log(key, value);
}
WeakMaps
Classes 101
class Person {
constructor(age) {
this.age = age;
}
incrementAge() {
this.age += 1;
}
}
Private data?
Naming Conventions
class Person {
constructor(age) {
this._age = age;
}
_incrementAge() {
this._age += 1;
}
}
WeakMaps to the rescue!
(Maybe they're not so weak)
WeakMaps for Privacy
let _age = new WeakMap();
class Person {
constructor(age) {
_age.set(this, age);
}
incrementAge() {
let age = _age.get(this);
if(age > 90) {
console.log('Midlife crisis');
}
}
}
> const person = new Person(90);
> person.incrementAge(); // 'Midlife crisis'
> Reflect.ownKeys(person); // []
Promises
Callback Hell
func1(function (value1) {
func2(value1, function(value2) {
func3(value2, function(value3) {
func4(value3, function(value4) {
func5(value4, function(value5) {
// Do something with value 5
});
});
});
});
});
D
O
O
M
Promises
func1(value1)
.then(func2(value1) { })
.then(func3(value2) { })
.then(func4(value3) { })
.then(func5(value4) {
// Do something with value 5
});
Promises


Promises
new Promise(resolve => resolve(data))
.then(result => console.log(data));
new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
reject(new Error('Failed to fufill Promise')))
.catch(reason => console.log(reason));
Promises

Promises
var fetchJSON = function(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
$.getJSON(url)
.done((json) => resolve(json))
.fail((xhr, status, err) => reject(status + err.message));
});
}
Parallelizing using Promises
var urls = [
'http://www.api.com/items/1234',
'http://www.api.com/items/4567'
];
var urlPromises = urls.map(fetchJSON);
Promise.all(urlPromises)
.then(function(results) {
results.forEach(function(data) {
});
})
.catch(function(err) {
console.log("Failed: ", err);
});
Generators
Syntax
function* sillyGenerator() {
yield 1;
yield 2;
yield 3;
yield 4;
}
var generator = sillyGenerator();
var value = generator.next();
> console.log(value); // { value: 1, done: false }
> console.log(value); // { value: 2, done: false }
> console.log(value); // { value: 3, done: false }
> console.log(value); // { value: 4, done: false }
What about using return?
Return in a Generator
function* sillyGenerator() {
yield 1;
yield 2;
yield 3;
yield 4;
return 5;
}
for(let val of sillyGenerator()) {
console.log(val); // 1, 2, 3, 4
}
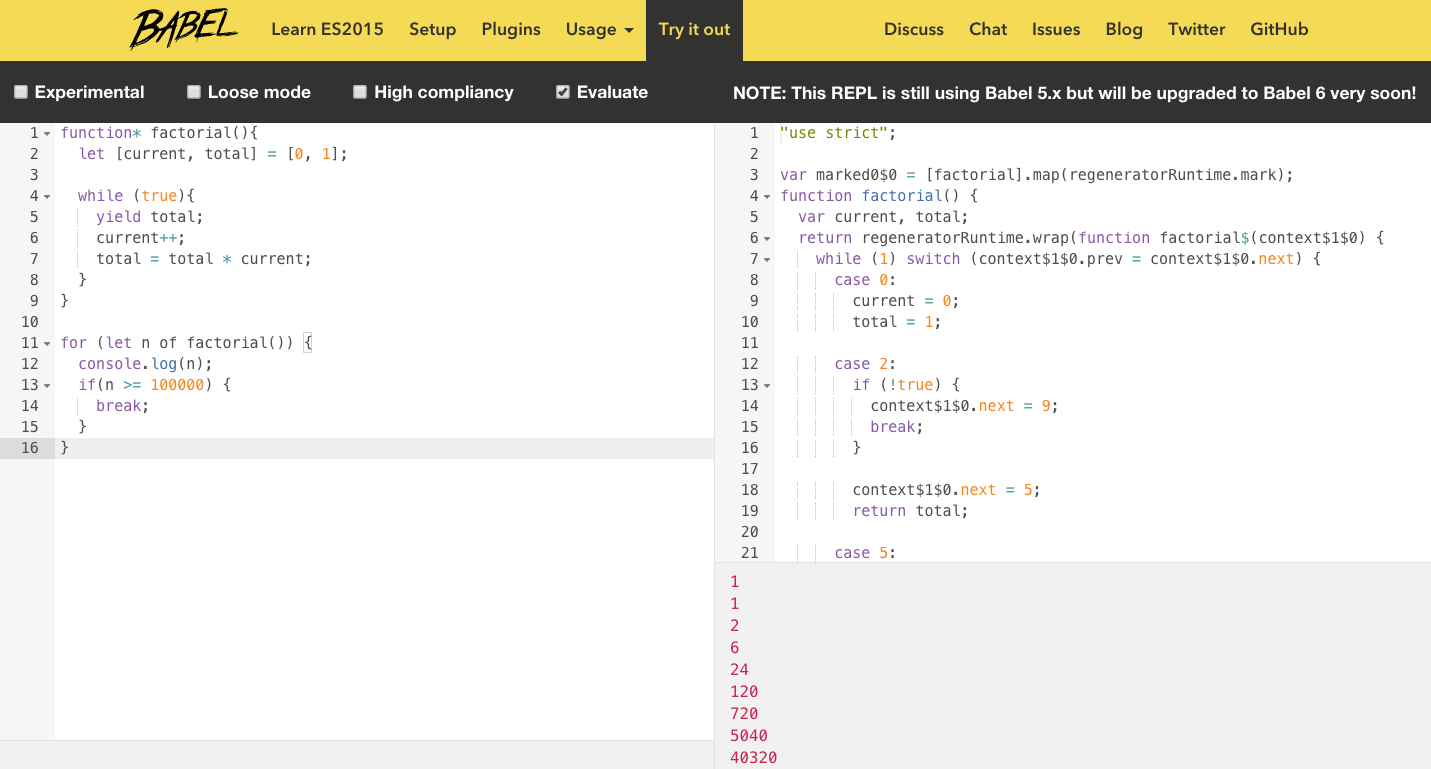
Real Generator Function
function* factorial(){
let [current, total] = [0, 1];
while (true){
yield total;
current++;
total = total * current;
}
}
for (let n of factorial()) {
console.log(n);
if(n >= 100000) {
break;
}
}
Alternate Solution?
Beyond ES6
Async / Await (ES6+)
var request = require('request');
function getJSON(url) {
request(url, function(error, response, body) {
return body;
});
}
function main() {
var data = getJSON('http://some_api/item1');
console.log(data); // Undefined
}
main();
Async / Await (ES6+)
var request = require('request');
function getJSON(url) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
request(url, function(error, response, body) {
resolve(body);
});
});
}
async function main() {
var data = await getJSON();
console.log(data); // NOT undefined!
}
main();
console.log('The data is: ');
Thank you everyone!
Symbols
Seems functional, right...?
Get Own Properties
function getOwnProperty(object, propertyKey) {
return (object.hasOwnProperty(propertyKey) ? object[propertyKey]: undefined);
}
We should be safe...right?
> getOwnProperty({ hasOwnProperty: 'Hah, overwritten'}, 'Pwned');
> TypeError: Propery 'hasOwnProperty' is not a function

Credit: http://memesvault.com/nooo-meme-darth-vader/
Second time is the charm.
function getOwnProperty(object, propertyKey) {
return (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty(object, propertyKey) ? object[propertyKey]: undefined);
}

credit: http://deloiz.blogspot.com/2014/01/Pusheen.html
Unique Property Keys
const key = Symbol();
const keyTwo = Symbol();
const object = {};
>> key === keyTwo
>> false
object.key = 'Such magic.';
object.keyTwo = 'Much Uniqueness'
Symbols as Concepts
const anakin = 'jedi';
const yoda = 'jedi master';
const luke = 'jedi';
const anakin = Symbol();
const yoda = Symbol();
const luke = Symbol();
Writing Sync-Async
function request(url) {
getJSON(url, function(response) {
generator.next(response);
});
}
function* getData() {
var entry1 = yield request('http://some_api/item1');
var data1 = JSON.parse(entry1);
var entry2 = yield request('http://some_api/item2');
var data2 = JSON.parse(entry2);
}
Not without problems though...
-
How do we handle errors?
-
getJSON not in control
-
Parallelize?

Generators & Promises
function request(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
getJSON(url, resolve);
});
}
Generators & Promises
function iterateGenerator(gen) {
var generator = gen();
var ret;
(function iterate(val) {
ret = generator.next();
if(!ret.done) {
ret.value.then(iterate);
} else {
setTimeout(function() {
iterate(ret.value);
});
}
})();
}
Generators & Promises
iterateGenerator(function* getData() {
var entry1 = yield request('http://some_api/item1');
var data1 = JSON.parse(entry1);
var entry2 = yield request('http://some_api/item2');
var data2 = JSON.parse(entry2);
});
ES6+ Deep Dive
By Prathik S
ES6+ Deep Dive
An overview of ES6+ features.
- 1,040