PHC7065 CRITICAL SKILLS IN DATA MANIPULATION FOR POPULATION SCIENCE

NoSQL Databases
Hui Hu Ph.D.
Department of Epidemiology
College of Public Health and Health Professions & College of Medicine
April 1, 2019
NoSQL Databases and Semi-structured Data Models
Introduction to MongoDB
Lab: MongoDB
NoSQL Databases and Semi-structured Data Model
NoSQL
- NoSQL: "non SQL", "non relational" or "not only SQL"
- It provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data which is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases
- NoSQL systems are also sometimes called "Not only SQL" to emphasize that they may support SQL-like query languages.
Types of NoSQL Databases
-
Column: Accumulo, Cassandra, Druid, HBase, Vertica, SAP HANA
-
Document: Apache CouchDB, ArangoDB, Clusterpoint, Couchbase, DocumentDB, HyperDex, IBM Domino, MarkLogic, MongoDB, OrientDB, Qizx, RethinkDB
-
Key-value: Aerospike, ArangoDB, Couchbase, Dynamo, FairCom c-treeACE, FoundationDB, HyperDex, MemcacheDB, MUMPS, Oracle NoSQL Database, OrientDB, Redis, Riak, Berkeley DB
-
Graph: AllegroGraph, ArangoDB, InfiniteGraph, Apache Giraph, MarkLogic, Neo4J, OrientDB, Virtuoso, Stardog
- Multi-model: Alchemy Database, ArangoDB, CortexDB, Couchbase, FoundationDB, MarkLogic, OrientDB
Semi-structured Data
- A form of structured data that does not conform with the formal structure of data models associated with relational databases or other forms of data tables
- It contains tags or other markers to separate semantic elements and enforce hierarchies of records and fields within the data
- Also known as self-describing structure
- The data model behind the web
html
- Semi-structured data are usually tree-structured


body
h1
p
p
li
li
Tree Data Structure
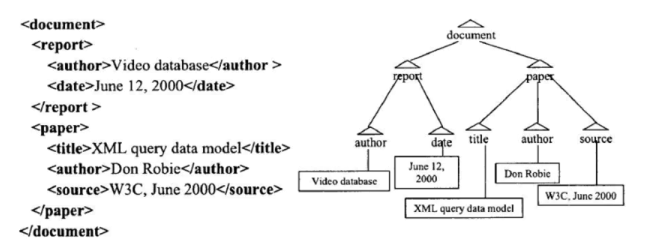
- Paper
- getParent -> document
- getChildren -> title, author, source
- getSibling -> report
- "June 12, 2000"
- root-to-node path: document/report/date/"June 12, 2000"
- Queries need tree navigation
- e.g. author of "XML query data model"
xml
- The entities belonging to the same class may have different attributes even though they are grouped together, and the attributes' order is not important
Extensive Markup Language
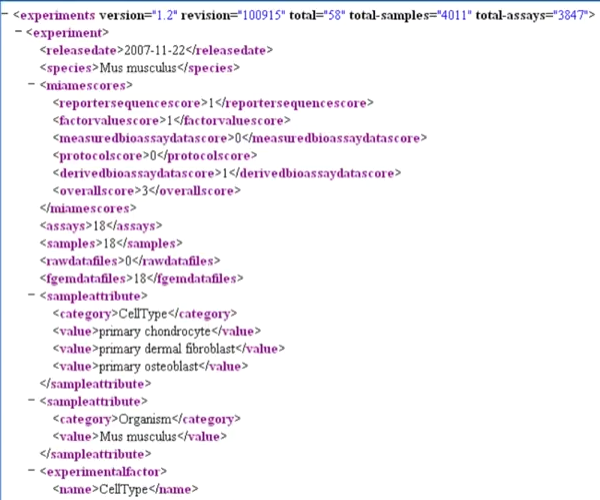
- Allows the querying of both schema and data
- What is the name of the element which contains a sub-element whose value is "CellType"?
JSON
JavaScript Object Notation
- Key-value pairs
- Tuple
- Arrays (indicated by square brackets)
[
{
_id: 1,
name: "john",
age: 21,
type: 1,
status: "A",
favorites: {artist:"Picasso",food:"pizza"},
finished: [17,3],
badges: ["blue","black"],
points: [
{points: 85, bonus: 10},
{points: 70, bonus: 5}
]
},
{
_id: 2,
name: "mike",
age: 20
}
]One structure can be embedded in another structure
Introduction to MongoDB
MongoDB
- MongoDB (from "humongous") is a cross-platform document-oriented database.
- Classified as a NoSQL database, MongoDB eschews the traditional table-based relational database structure in favor of JSON-like documents with dynamic schemas (BSON), making the integration of data in certain types of applications easier and faster
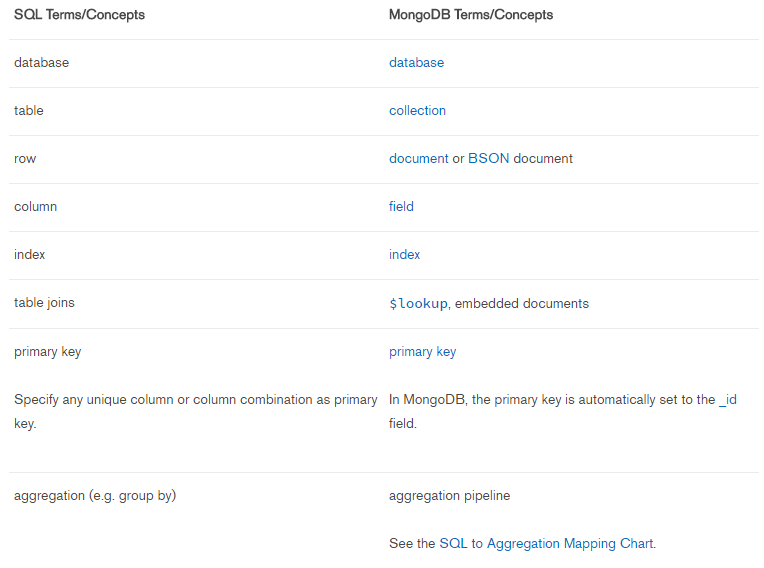
- SQL to MongoDB Mapping Chart
Connect to MongoDB using "mongolite" package in R
- MongoDB is a collection of documents
con <- mongo(collection="collectionName", db="dbName", url="url")Similar to Table in relational databases
con <- mongo(collection="Students", db="phc7065", url="mongodb://localhost:27017")- Example:
find()
SELECT
con$find()- Query 1:
- SQL: SELECT * FROM Student
- MongoDB: con$find()
- Query 2:
- SQL: SELECT a, b FROM Student
- MongoDB:
con$find(
{},
fields='{"a":1,"b":1,"_id":0}'
)
- Query 3:
- SQL: SELECT a FROM Student WHERE b="c"
- MongoDB:
con$find( '{"b":"c"}', fields='{"a":1,"_id":0}' )
Examples (continued)
- Query 4:
- SQL: SELECT DISTINCT a FROM Student WHERE c>10
- MongoDB:
unique(con$find( '{"c":{"$gt":10}}',fields: '{"a":1,"_id":0}' ))
- Some Operators of MongoDB:
$eq, $gt, $gte, $lt, $lte, $ne
$in, $nin
$or, $and, $not, $nor
Array Operations
- Find students who are taking courses "a" and "b"
- con$find( '{"courses": {"$in":["a","b"]} }' )
- Find students who are not taking courses "a" and "c"
- con$find( '{"courses": {"$nin":["a","c"]} }' )
-
Find the second and third elements of courses
- con$find( '{}', fields='{"courses": {"$slice": [1,2]} }' )
- con$find( '{}', fields='{"courses": {"$slice": -2} }' )
- Find a student whose second element in courses is "b"
- con$find('{"courses.1":"b"}')
{_id:1,
name:"John",
age:20,
courses: ["a","b","c"]}Compound Statements
- Find students with age 20 or 21 and who are taking course "a" or "b" as their first course
- SELECT * FROM Students
WHERE (age=20 OR age=21) AND (course0="a" OR course0="b")
- con$find('{
"$and":[
{"$or": [{"age":20},{"age":21}] },
{"$or": [{"courses.0":"a"},{"courses.0":"b"}] }
]
}')
{_id:1,
name:"John",
age:20,
courses: ["a","b","c"]}Queries over Nested Elements
_id:1,
points: [
{points: 90, bonus:10}
{points: 60, bonus:20}
]_id:2,
points: [
{points: 53, bonus:20}
{points: 64, bonus:11}
]_id:1,
points: [
{points: 99, bonus:17}
{points: 10, bonus:24}
]- con$find( '{"points.0.points": {"$lte": 80} }' )
-
con$find( '{"points.points": {"$lte": 80} }' )
- con$find( '{ "points.points":{"$lte":80}, "points.bonus": {"$lte": 20} }' )
Counting and Distinct
con$count('{"age":{"$exists":true}}')
SELECT COUNT(age) FROM StudentsSELECT COUNT(DISTINCT age) FROM Studentslength(con$distinct('age'))Aggregation
Aggregation
con$aggregate('[
{"$group":{"_id":"$department","meanAge":{"$avg":"$age"}}}
]')SELECT MEAN(age) FROM Students GROUP BY department;
SELECT MEAN(age) FROM Students
WHERE course0='a' OR course1='a' OR course2='a'
GROUP BY department;con$aggregate('[
{"$match":{"courses":{"$in":["a"]}}}
{"$group":{"_id":"$department","meanAge":{"$avg":"$age"}}}
]')Multi-attribute Aggregation
con$aggregate('[
{
"$group":{
"_id":{"department":"$department","college":"$college"},
"meanAge":{"$avg":"$age"}
}
}
]')SELECT MEAN(age) FROM Students GROUP BY department, college;
Aggregation with Text Search
con$aggregate('[
{"$match":{"$text":{"$search":"Miami Florida"}}},
{"$sort":{"score":{"$meta":"textScore"}}},
{"$project":{"hometown":1,"name":1}}
]')
Join
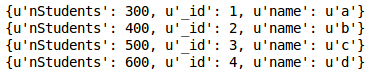
Join

Colleges
Students
con$aggregate('[
{
"$lookup":{
"from":"Students",
"localField":"name",
"foreignField":"college",
"as":"students"
}
}
]'')con$aggregate('[
{
"$lookup":{
"from":"Colleges",
"localField":"college",
"foreignField":"name",
"as":"colleges"
}
}
]')
MongoDB
git pull
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/install-mongodb-on-ubuntu/
PHC7065-Spring2019-Lecture8
By Hui Hu
PHC7065-Spring2019-Lecture8
Slides for Lecture 8, Spring 2019, PHC7065 Critical Skills in Data Manipulation for Population Science
- 1,212



