SPLUNK
Operations
Application Monitoring
Analytics
Extensibility
BACKGROUND
- Splunk provides technology that indexes and analyzes the increasingly large amounts of customer and transaction data generated by modern systems and applications.
- Splunk launched in 2006, after 4 years of research and development, and has since built a customer base of 3,700 customers - including many of the Fortune 500 companies.
- 3 main products - Splunk Enterprise, HUNK and Splunk Cloud.
Splunk Enterprise Basics
- Splunk - a software platform that accepts data from many different sources, such as files or network streams. Splunk stores a unique copy of this data in what's called an index. Once the data is there, you can connect to Splunk with a web browser and run searches across that data.
- splunkd - a distributed C/C++ server that accesses, processes and indexes streaming IT data and also handles search requests. splunkd processes and indexes your data by streaming it through a series of pipelines, each made up of a series of processors.
- splunkweb - a Python-based application server providing the Splunk Web user interface. It allows users to search and navigate IT data stored by Splunk servers and to manage your Splunk deployment through the browser interface. splunkweb communicates with your web browser via REST and communicates with splunkd via SOAP.
Splunk Architecture
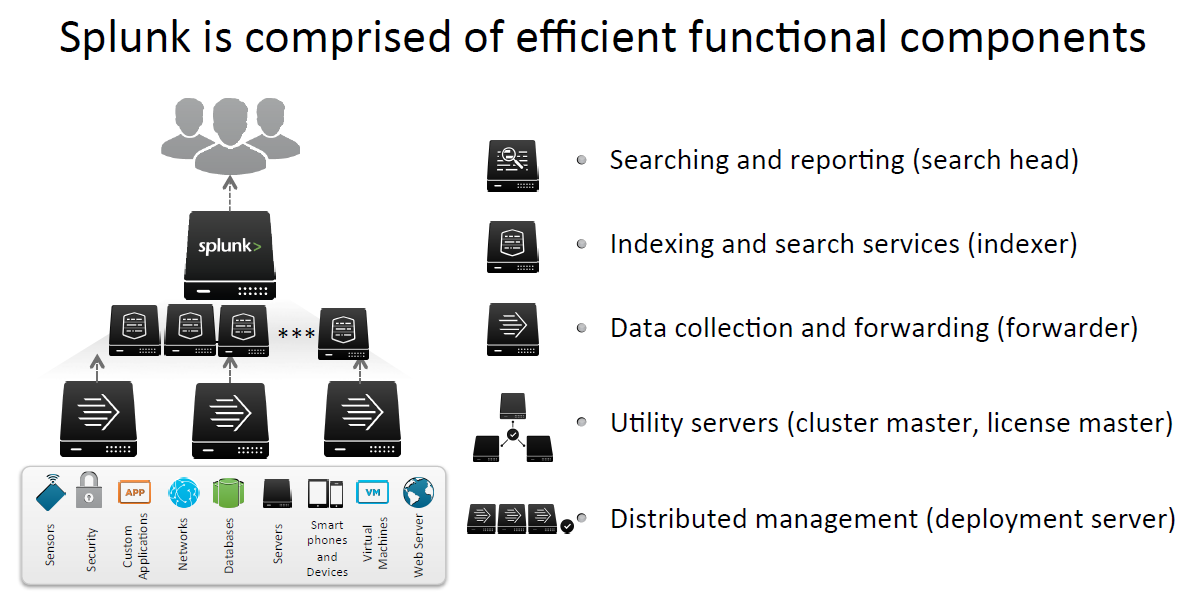
Architecture cont..
- Forwarder: Forwarders forward data to remote indexers. They may also index it locally. Data can be taken in via many different methods – monitoring log files, syslog, TCP, WMI, running scripts, querying a database, etc. Data can be forwarded to multiple indexers, or split.
- Indexer: This is the heart of the Splunk setup – it stores and indexes data, and responds to search requests.
-
Search Head: This is the main front-end, commonly accessed via the Splunk web interface. Search Heads can run searches across multiple Indexers, so you can scale out.
Architecture cont..
• Scalability – Horizontal, vertical
• Load and Performance
– Users
– Data
- volumes
– Searches
– Use-‐cases
• Resilience
– Availability
– Data safety
– Disaster recovery
SplunkWEB
- Inputs
-
Search
-
Pivot
-
Reports
-
Alerts
-
Dashboards
BUCKETS
-
Each of the index directories is known as a bucket.
-
An "index" contains compressed raw data and associated index files.
-
An index resides across many age-designated index directories.
-
An index directory is a bucket.
- A bucket moves through several stages as it ages (hot, warm, cold, frozen).
-
Each of the index directories is known as a bucket.
-
An "index" contains compressed raw data and associated index files.
-
An index resides across many age-designated index directories.
-
An index directory is a bucket.
- A bucket moves through several stages as it ages (hot, warm, cold, frozen).
Buckets cont..
| Bucket type | Default location | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Hot | $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk/defaultdb/db/* |
There can be multiple hot subdirectories. Each hot bucket occupies its own subdirectory, which uses this naming convention:
|
| Warm | $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk/defaultdb/db/* |
There are separate subdirectories for each warm bucket. These are named as described below in "Warm/cold bucket naming convention". |
| Cold | $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk/defaultdb/colddb/* |
There are multiple cold subdirectories. When warm buckets roll to cold, they get moved into this directory, but are not renamed. |
| Frozen | N/A: Frozen data gets deleted or archived into a directory location you specify. | Deletion is the default; see "Archive indexed data" for information on how to archive the data instead. |
| Thawed | $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk/defaultdb/thaweddb/* |
Location for data that has been archived and later thawed. See "Restore archived data" for information on restoring archived data to a thawed state. |
Archiving
- The indexer rotates old data out of the index based on your data retirement policy
- Data moves through several stages, which correspond to file directory locations. Data starts out in the hot database, located as subdirectories ("buckets") under $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk/defaultdb/db/.
- It then moves to the warm database, also located as subdirectories under $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk/defaultdb/db.
- Eventually, data is aged into the cold database $SPLUNK_HOME/var/lib/splunk/defaultdb/colddb.
- Finally, data reaches the frozen state. At this point, the indexer erases the data from the index. If you want the indexer to archive the frozen data before erasing it from the index, you must specify that behavior.
- This can be done in two ways. Let the indexer perform the archiving automatically. Specify an archiving script for the indexer to run.
Extensibility
-
CLI - External scripted lookups
-
REST API
-
6 language SDKs - Tools , utilitys and librarys
-
Splunkbase Apps
/ Add-ons
-
Custom search commands
-
Scripted Inputs
-
Modular Inputs
-
The Web Framework
-
Standard HTML/Javascript/CSS
-
Data Models
Custom Commands
Authoring a search command involves 2 main steps, first specify parameters for the search command, second implement the generate() function with logic which creates events and returns them to Splunk.
import sys, time
from splunklib.searchcommands import dispatch, GeneratingCommand, Configuration, Option, validators
@Configuration()
class GenerateHelloCommand(GeneratingCommand):
count = Option(require=True, validate=validators.Integer())
def generate(self):
for i in range(1, self.count + 1):
text = 'Hello World %d' % i
yield {'_time': time.time(), 'event_no': i, '_raw': text }
dispatch(GenerateHelloCommand, sys.argv, sys.stdin, sys.stdout, __name__)
Modular Inputs
- Extend the Splunk framework to define a custom input capability, just like the standard inputs (TCP/UDP/File etc…)
- Splunk treats your custom input definitions as if they were part of Splunk's native inputs, totally integrated first class citizen objects in Splunk
- Users interactively create and update your custom inputs using Splunk manager, just as they do for native inputs.
- All the properties are fully manageable via the REST API
-
Version 5.0 +
Modular Input contd..
- My preference is to use Python, however any language can be used.
- http://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/AdvancedDev/ModInputsIntro
- There is a lot of “plumbing” to put in place . The SDKs that take care of this for you, so you can just focus on the business logic.
- Java,Python,C# SDKs also have Modular Input APIs
-
Eclipse plugin has a wizard for creating Modular Inputs in Java
SPLUNK
By Polkan
SPLUNK
- 1,784



