COMP2511
25T2 Week 10
Friday 9AM - 12PM (F09A)
Slides by Christian Tolentino (z5420628)
Agenda
- Admin Stuff
- Serverless Architecture
- Revision!
Admin Stuff
- Assignment 2 is due this Friday 3pm!
- Please complete the MyExperience ty :)
- We greatly appreciate all your feedback
- For the sample exam, please wait outside of the lab for us to log into the exam environment
Congrats on also making it to the end of the term!

Serverless Architecture
Serverless
Definition: Allows developers to build and run applications without managing infrastructure
- Apps are built as a collection of functions deployed to a cloud provider who automatically provision, scale and manage the infrastructure
- Code is deployed as small, stateless functions (FaaS) which are triggered by events (e.g. HTTP request, file upload)
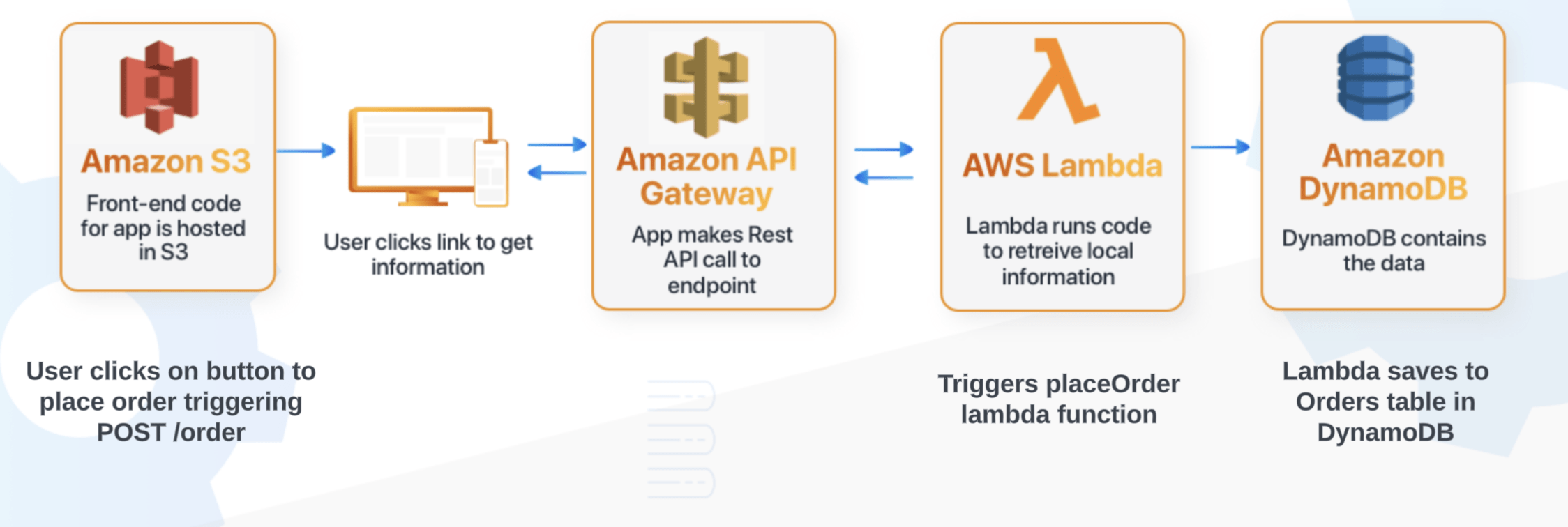
Serverless
- Developers only need to worry about writing code and are billed for execution time, to the millisecond
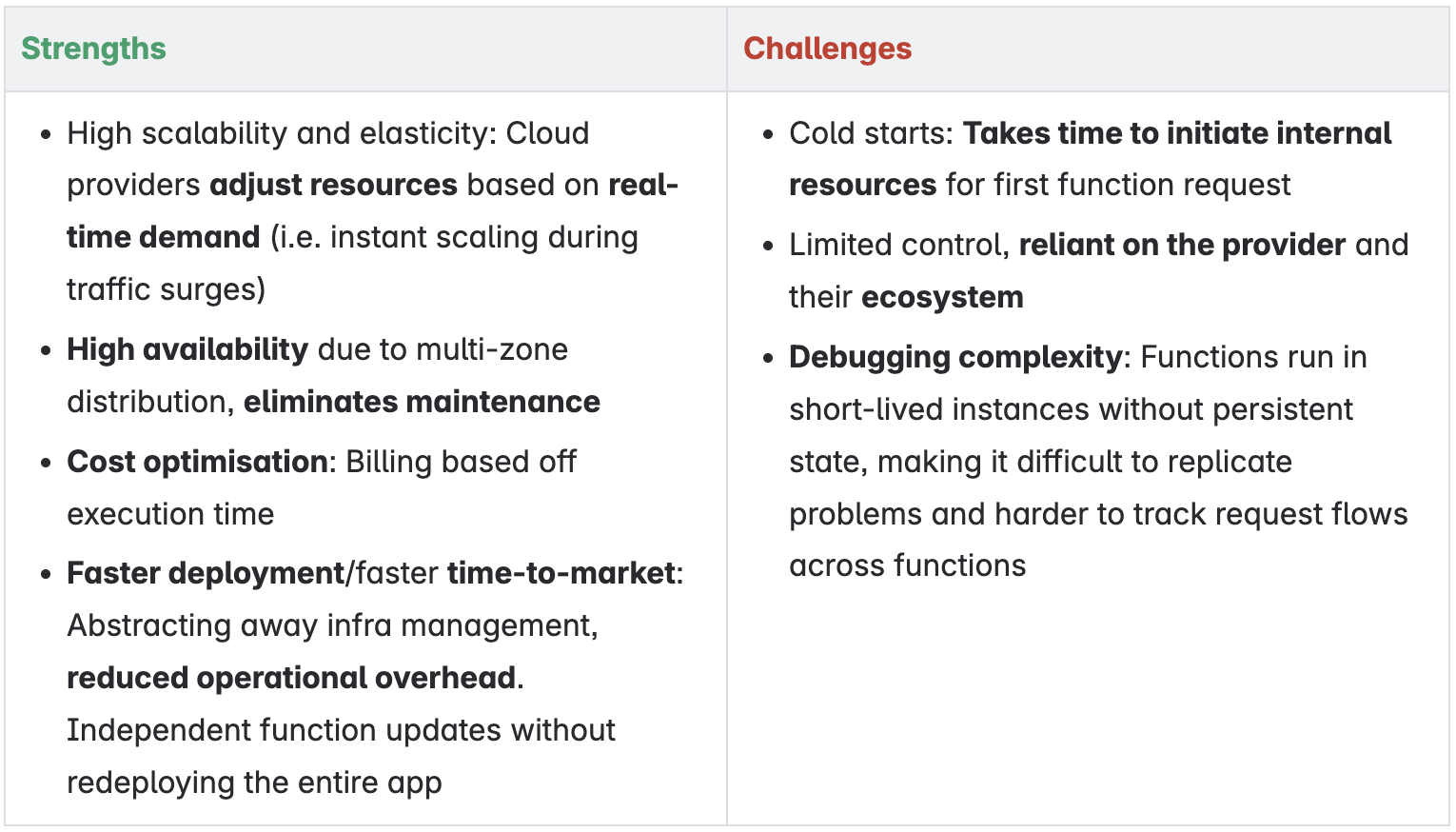
Explain how serverless functions could be used in an IoT health monitoring system.
IoT devices i.e. smart watches can send users' health data to the cloud periodically (e.g. this is why it takes a while to sync your fitness data between devices).
Each incoming data packet can trigger a serverless function that checks the data for anomalies such as a dangerously high heart rate and sends a push notification to the user.



Serverless MCQs
1. What is the primary benefit of serverless computing for developers?
- a) Complete control over the operating system
- b) No need to write functions
- c) No infrastructure management required
- d) Permanent server allocation
- Answer: C
2. In a serverless system, when does a function typically execute
- a) At scheduled time intervals only
- b) Continuously e.g. a background process
- c) Only when the server is restarted
- d) In response to specific events e.g. API calls or file uploads
- Answer: D
3. Which of the following is NOT a serverless platform?
- a) AWS Lambda
- b) Azure Functions
- c) Docker Lambda
- d) Google Cloud Functions
- Answer: C
4. What best describes the cost model of serverless computing?
- a) Fixed monthly fee
- b) Per second of CPU usage
- c) Based on RAM usage only
- d) Usage-based micro-billing
- Answer: D
- Which of the following best describes the correct order of operations in a typical serverless function workflow?
- a) A function stores data, triggers an event, and then receives a user request
- b) A user request is sent, the function processes data, then an event is triggered
- c) A user request is received, an event triggers a function, and the function processes and returns a result
- d) A function runs continuously, waiting to trigger an API Gateway response
- Answer: C
6. Which of the following best describes the correct order of operations in a typical serverless function workflow?
- a) A function stores data, triggers an event, and then receives a user request
- b) A user request is sent, the function processes data, then an event is triggered
- c) A user request is received, an event triggers a function, and the function processes and returns a result
- d) A function runs continuously, waiting to trigger an API Gateway response
- Answer: C
7. What is a major drawback of serverless architecture?
- a) Low availability
- b) High upfront infrastructure cost
- c) Cold start latency
- d) Poor scalability
- Answer: C
8. Which of the following principles is LEAST aligned with serverless design?
- a) Statelessness
- b) Single-responsibility functions
- c) Monolithic code blocks
- d) Event-driven logic
- Answer: C
9. What is a mitigation strategy for cold start issues?
- a) Restarting the server
- b) Using containers
- c) Using warm-up plugins or provisioned concurrency
- d) Increasing memory allocation to the function
- Answer: C
10. When comparing the serverless and microservice architecture, which is TRUE about serverless?
- a) It uses containers for deployment
- b) Monitoring is fully integrated
- c) It has fixed computational costs
- d) It is managed fully by the cloud provider
- Answer: D
11. What is a key design principle that makes serverless architecture suitable for modern applications?
- a) Complex functions with multiple responsibilities
- b) Event-driven workflows with small, composable functions
- c) Rigidly defined request and response chains
- d) Dependence on local file systems for state management
- Answer: B
12. Why can observability be a challenge in serverless systems?
- a) Functions do not support logs
- b) Functions are executed on user-managed servers
- c) The request flow may span multiple short-lived functions
- d) Serverless functions run too slowly to trace
- Answer: C
13. Which scenario is best suited for a serverless architecture?
- a) A long running background process with complex state
- b) A low traffic contact form that stores submissions in a database
- c) A high performance game server with persistent connections
- d) A legacy application requiring access to local file systems
- Answer: B
14. What role does an event play in a serverless system?
- a) It replaces the need for functions
- b) It triggers the execution of a function
- c) It controls billing rates
- d) It stores function logs for auditing
- Answer: B
15. What is a common drawback of relying too heavily on a single cloud provider particularly in serverless architecture?
- a) Decreased application performance
- b) Slower deployment across platforms
- c) Bills become expensive over time
- d) Vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility and portability
- Answer: D
Architecture Revision
You’re building a simple online ordering system for a small cafe because they would like an electronic way of managing their orders. There are only a handful of features (creating an order, marking an order as complete and deleting an order) as the owner would like to test the system out before committing to it. What architecture is most suitable?
a) Microservices
b) Event driven
c) Layered Architecture
d) Modular Monolith
Your organisation wants to scale user management, billing, and content recommendation independently for a streaming platform like Netflix. What architecture is most suitable?
a) Microservices
b) Event driven
c) Layered Architecture
d) Modular Monolith
A government tax agency needs high control over deployments and compliance enforcement. Which architecture provides easier centralised governance?
a) Microservices
b) Modular Monolith
c) Monolithic
d) Event Driven
An education platform needs clear boundaries between features like course content, assessment, and user management. Teams are aligned to business domains. What is the best fit?
a) Modular Monolith
b) Serverless
c) Layered Architecture
d) Microservices
An IoT device continuously sends JSON health data to the cloud. The system must process this data and generate alerts immediately. What is the most efficient choice?
a) Microservices
b) Event Driven
c) Layered
d) Monolithic
An image processing pipeline needs to resize photos as soon as they're uploaded to a cloud bucket. Cost is a major concern. What architecture should you use?
a) Microservices
b) Serverless
c) Modular Monolith
d) Event driven
Revision
Finding Patterns
Code and Design Smells
Code Smells
A code smell is a surface indication that usually corresponds to a deeper problem in the system.
An good list of most code smells are in Refactoring Guru. You will be tested on identifying different code smells in the assignment and final exam!
In groups, let's discuss the following examples. Identify the code smells and any underlying design problems associated with them.
Code Smell #1
Mark, Bill and Jeff are working on a PetShop application. The PetShop has functionality to feed, clean and exercise different types of animals. Mark notices that each time he adds a new species of animal to his system, he also has to rewrite all the methods in the PetShop so it can take care of the new animal.
- Code Smell: Divergent Change
-
Design Problem:
- Open-Closed Principle
- High Coupling
- How to fix: Delegate behaviour away to relevant classes which adhere to single responsibility (e.g. Strategy, Abstract Factory, etc.)
Code Smell #2
public class Person {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int age;
private int birthDay;
private int birthMonth;
private int birthYear;
private String streetAddress;
private String suburb;
private String city;
private String country;
private int postcode;
public Person(String firstName, String lastName, int age,
int birthDay, int birthMonth, int birthYear,
String streetAddress, String suburb, String city,
String country, int postcode) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = age;
this.birthDay = birthDay;
this.birthMonth = birthMonth;
this.birthYear = birthYear;
this.streetAddress = streetAddress;
this.suburb = suburb;
this.city = city;
this.country = country;
this.postcode = postcode;
}
// Some various methods below
// ....
}
- Code Smell: Data clumps, long parameter list
- Design Problem: DRY and KISS
- How to fix: Refactor by making more classes for birthday and address ("Extract Class"/ "Introduce Parameter Object")
Code Smell #3
public class MathLibrary {
List<Book> books;
int sumTitles {
int total = 0
for (Book b : books) {
total += b.title.titleLength;
}
return total;
}
}
public class Book {
// Our system just models books as titles
// (content doesn't matter)
Title title;
}
public class Title {
int titleLength;
int getTitleLength() {
return titleLength;
}
void setTitleLength(int tL) {
titleLength = tL;
}
}
-
Code Smell:
- Inappropriate intimacy (accessing public fields)
- Message chaining (Law of Demeter)
- Data/Lazy classes
- Design Problem: High coupling from encapsulation being broken
-
How to fix:
- Make attributes private and use getters and setters
-
BookandTitlecan be one class
Code and Design Smells
How do these code smells cause problems when developing code?
Affects the reusability, maintainability and extensibility. How fast does it take for a new developer to understand what is happening?
Is a code smell always emblematic of a design problem?
No - e.g "switch statements" and "comments" are often listed as code smells but are not always actually smells
Kahoot
COMP2511 Week 10 25T2
By Christian Tolentino
COMP2511 Week 10 25T2
- 75



