Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Gerard Mor Martinez
Presentation of the PhD Thesis
January 24th, 2022 10:00
Degrees room - Superior Polytechnical School


Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Supervisor: Daniel Chemisana Villegas
Thesis outline


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez

Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- Chapter 1 -
Introduction
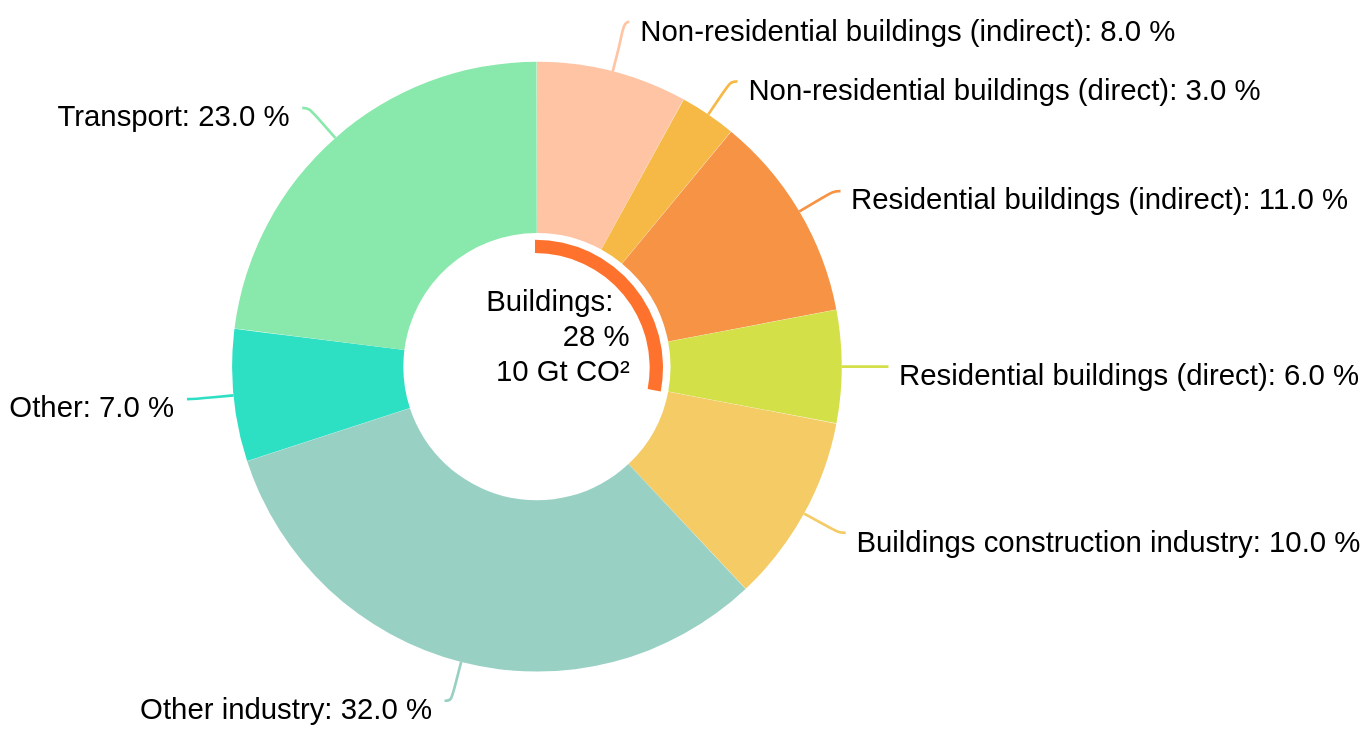
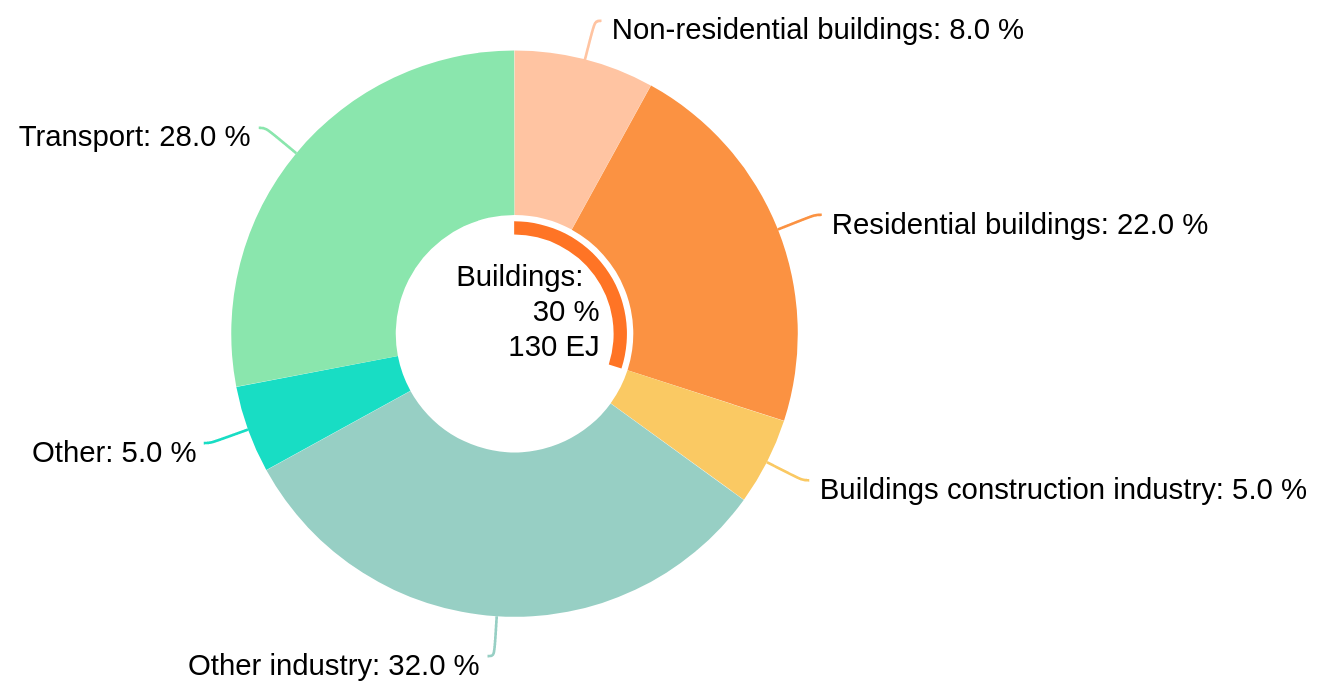
Building sector final energy use, 2019:
10 Gt CO2
28% of the total emissions
130 EJ (1EJ = 2.77 x 10⁵ GWh)
30% of total consumption
Source: International Energy Agency (IEA)
Main cause:
Usage of fossil fuel sources


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
Evolution of the energy mix in building sector

Source: IEA
Natural gas increases a the demand a 12% since 2010


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
Evolution of the energy mix in building sector

Source: IEA
Oil is maintaining the demand since 2010


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
Evolution of the energy mix in building sector

Source: IEA
Coal demand decreases a 18% since 2010


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
Reasons to boost the energy transition
Sustainability aspects
- Climate change issues with dramatic consequences:
- Rising seas (disappearance risk for some coastal regions or islands)
- Increase amount of disruptive events (floods, incidents)
- Extreme weather (desertification, shifting rainfalls)
- Unhealthy air conditions (affectance in people's health)
Economical aspects
- We are living the end of an era (Cheap fossil fuels):
- Actual fossil fuels needs to be used to produce the future renewables generators.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
The end of an era - Oil supply vs. demand
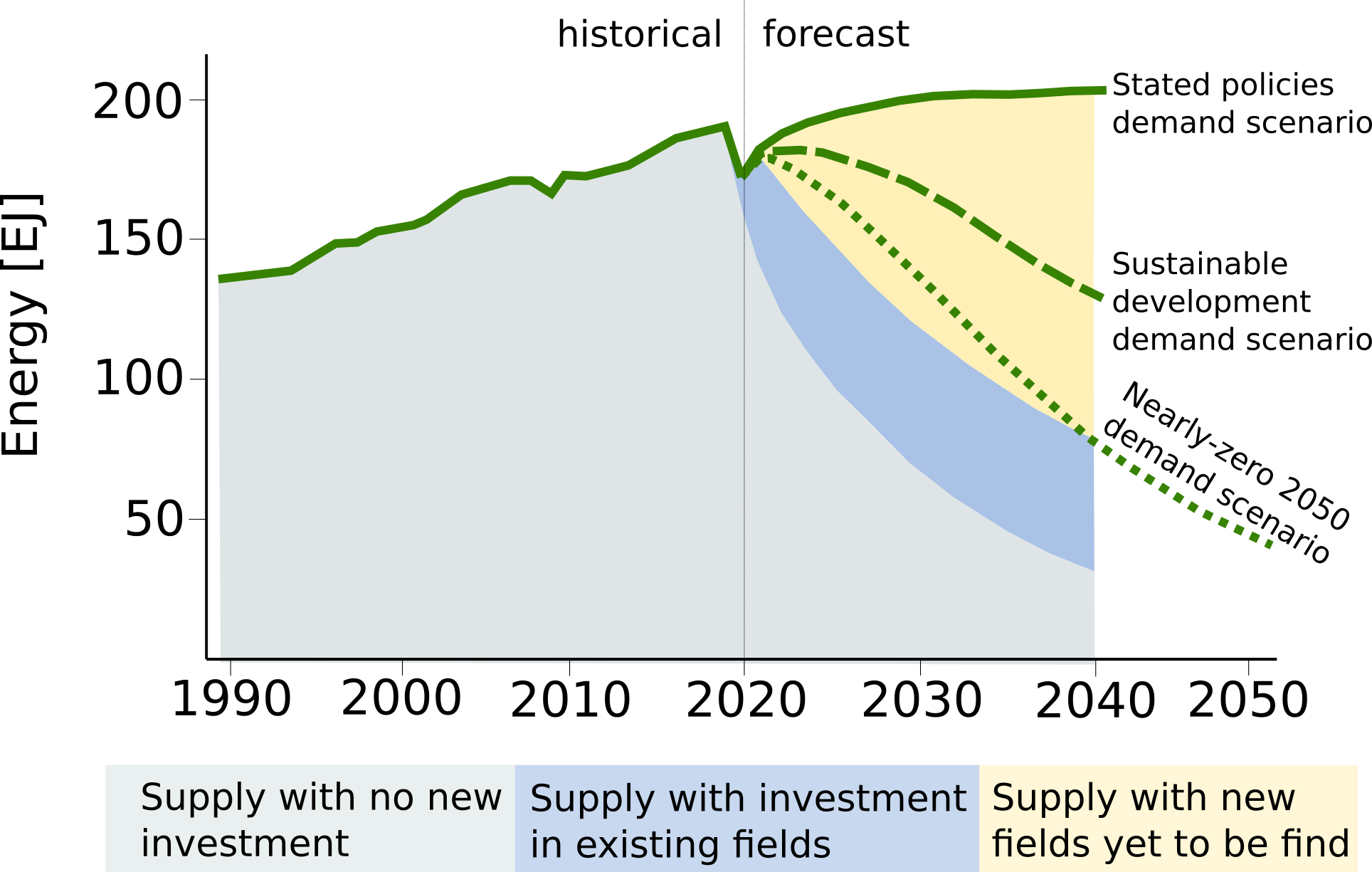
All sectors, demand sourced by oil
Source: IEA


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
The end of an era - Oil supply vs. demand

Source: IEA


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
The end of an era - Oil supply vs. demand

Source: IEA
$
$
$
$


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
The end of an era - Oil supply vs. demand

Source: IEA
$
$
$
$


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
Building Climate Tracker (BCT) Index
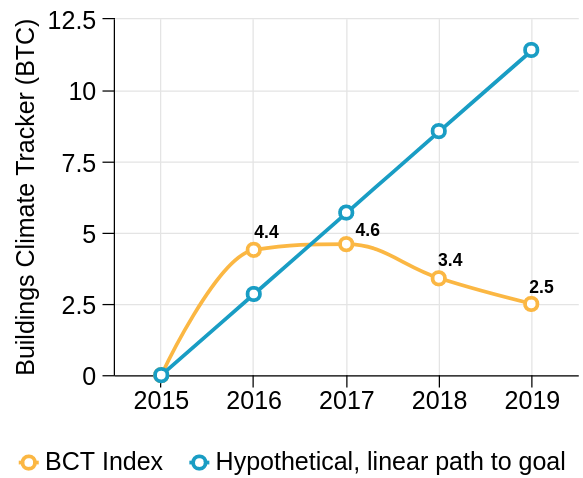
Global Alliance for Buildings and Construction (GlobalABC) tracks the buildings sector progress in decarbonisation worldwide
- Impact indicators (results of actions)
- Final energy demand
- Share of renewables
- Energy use intensities
- Action indicators (initiatives to reduce)
- Environmental policies
- Green building certifications
- Energy-efficiency efforts
- Industry actions
Source: GlobalABC
We need to change this tendency and return to the path of energy transition.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
SL methods and decarbonisation objectives
Statistical Learning (SL) and Machine Learning (ML) methods can help boosting efficiency in energy demand:
- At building level:
- Provide the intelligence of smart control systems.
- Characterisation assessment of buildings (e.g. consumption drivers, thermal characteristics).
- Evaluate the implementation of new HVAC systems (e.g. electrification).
- At consumer level:
- Empower users to rationalise their energy consumption.
- Assess the indoor thermal comfort conditions.
- Provide better consumption scenarios by changes in their behaviour.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C1 - Introduction
Driving the usage of renewables energy supply
- Renewables generation
- Allowing more accurate short- and long-term generation forecasts
- Planning new locations for renewable parks
- Assessing renewables self-consumption in microgrids or buildings
- Improve the primary transformation
- Optimisation of fuel sources mix, based on CO2 or sustainability indicators
SL methods and decarbonisation objectives
- Chapter 2 -
Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Supported by:
EMPOWERING (IEE project)
Journal: IEEE Access
JIF (2018): 4.098 - Q1


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters
Goals
- To design and implement a IT platform to:
- Massive gathering of utilities' data and online services:
- Consumption data (whatever frequency)
- Tariffs
- Consumers information
- Weather data
- Efficiently store and analyse the data.
- Implement services for:
- Empower users about their electricity consumption.
- Infer valuable information for utilities.
- Massive gathering of utilities' data and online services:
- To validate the effect of these services: 3 pilots in Europe.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
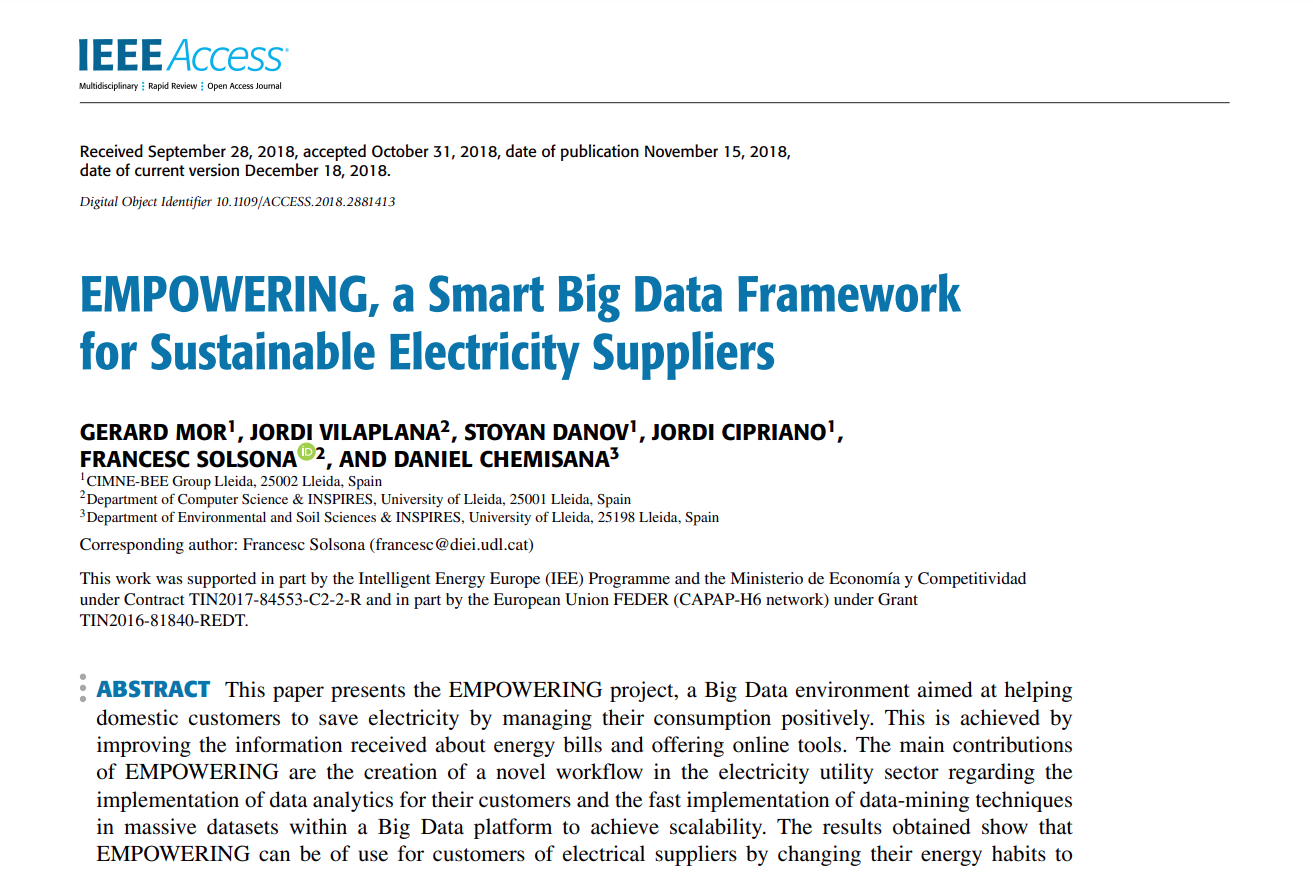
IT architecture
Advanced Programming Interface (API) REST:
- Bidirectional communication with utilities/online services
- Technology used: Python Flask
Short-term DataBase (DB):
- Real-time DB connected to the API
- Stores analytical modules results and last pushed data from utilities
- Technology used: MongoDB
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
IT architecture

Task management system:
- Queue system for managing the execution of analytical modules and Extract, Transform and Load functions (ETLs)
- Technology used: RabbitMQ and Celery
Batch processing system:
- Technology: Hadoop infrastructure
- Long term DB: contains all the historical data (Tech.: HBase)
- ETL's and analytical modules programmed in Map Reduce algorithms (Tech.: Python and R)
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Services (1/4): weather-dependence analysis
Determination whether a consumer has or not cooling or heating dependence based on energy signatures:
Monthly data
Daily and hourly data
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Electricity consumption (kWh) | |
| Cooling Degree Days (ºC) | |
| Heating Degree Days (ºC) | |
| Outdoor temperature (ºC) | |
| Optimised heating balance temperature (ºC) | |
| Optimised cooling balance temperature (ºC) | |
| timestep | |
| Error |


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Services (2/4): clustering algorithms
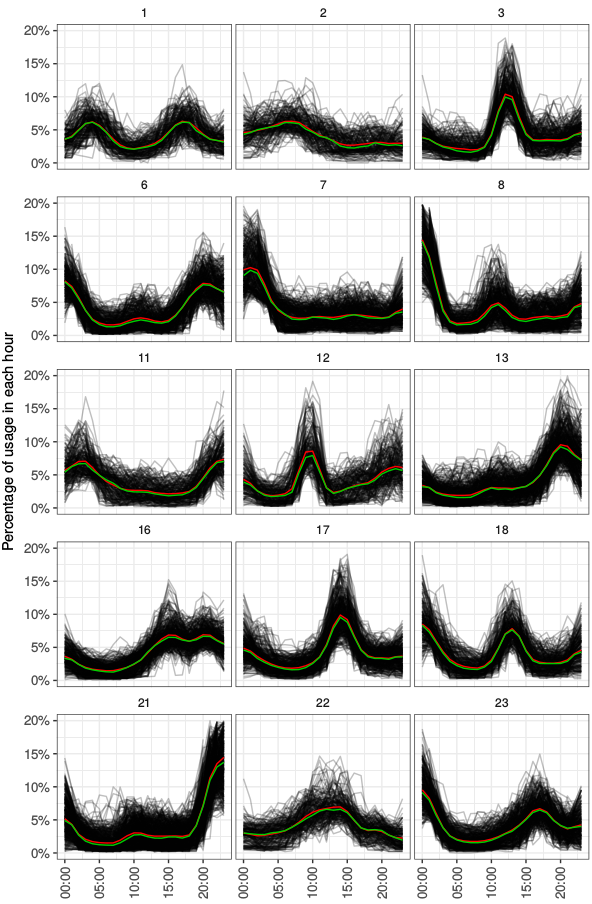
Daily load curves clustering
- Input:
- Daily load curves matrices
- Outdoor temperature, calendar features, ...
- Applications:
- Known common activity profiles
- New tariff schemas
- Boost the accuracy of characterisation models
- Techniques:
- Gaussian Mixture Models
- Spectral Clustering
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Services (2/4): clustering algorithms
Customers clustering
- Input:
- Monthly profiles
- Annual consumption
- Contracted power
- Weather dependence
-
Application:
- Benchmarking
- Utility customer segmentation
-
Techniques:
- Self-Organizing Maps + K-Means
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Services (3/4): consumption forecasting
- Types:
- Individual (for end-user applications)
- Aggregated (for utility applications)
- Short-term and long-term depending on requirements and input data.
- Used techniques: Regression models, Machine Learning and stacked ensembles.
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Services (4/4): personalised energy-saving tips
Recommender system based on:
- User most common daily load curves.
- Consumer information (weather dependence, contracted power, ...).
- Selection of tips based on consumer profile and the tips bible.
- Get feedback from the user for increase user acceptance
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Pilots
Spain (Utility: ElGas - City: Sóller)
- Control group: 3129, experimental group: 1582, daily data.
-
Grouping:
- G1: online reports
- G2: monthly billing reports
France (Utility: GEG - City: Grenoble)
- Control group: 4632, experimental group: 60, 3-months data.
-
Grouping:
- G1: Low contracted power
- G2: High contracted power
- G3: HVAC systems sourced by electricity
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Pilots
Austria (Utility: LINZ AG - City: Linz)
- Control: 45423, experimental: 115, 15-min data.
-
Grouping:
- G1: online reports
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters
Period of evaluation of the 3 pilots: November 2013 - December 2015


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Pilot evaluation methodology
Difference-in-difference multi-parameter regression method
Average baseload of the all utility customers
Effect on belonging to experimental group
Effect of the evaluation period
Effect of the end-user services received
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Average Daily Consumption (kWh) | |
| Is it in the experimental group? | |
| Is in the evaluation period? | |
| Error | |
| Year-Month and customer id. |
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Pilot evaluation results
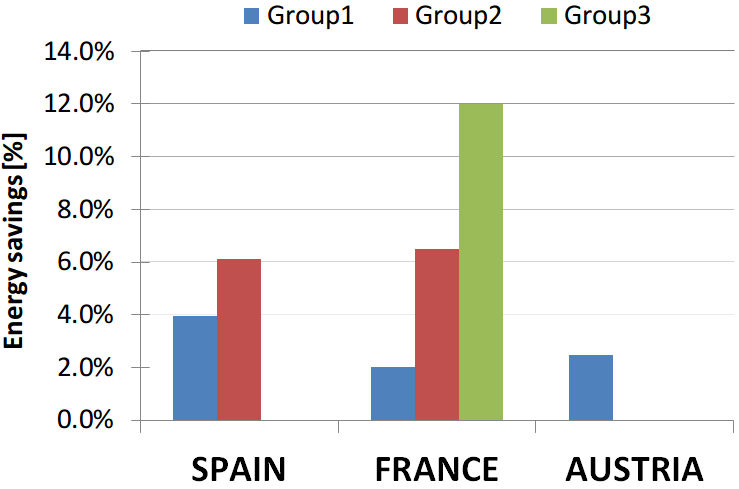
Relative energy savings (Es) by pilot
Online
Billing
Low power
High power
Electric HVAC
Online
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Conclusions
- An scalable and efficient platform for the massive analysis of energy utilities data was presented
- The usage of short- and long-term DB allow different types of processing scenarios
- Applications presented in this Thesis:
- Use the Short-term DB as their storage system.
- And the analytics toolbox implemented.
- Applications presented in this Thesis:
- The usage of short- and long-term DB allow different types of processing scenarios
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C2 - Big data infrastructure for the massive analysis of energy smart meters
Conclusions
- During 2013-2015, from 2 to 12% energy saving were achieved, depending on the pilot site and consumers grouping.
-
An startup (beedata) was created from the seed of the project.
- Nowadays, up to +350k clients are receiving online and billing reports.
- Chapter 3 -
Data-driven virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Supported by:
REFER (RIS3CAT project)
Journal: Energies
JIF (2020): 3.004


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Goal
To design and implement a methodology for simulating control scenarios in smart thermostats
- Based on data-driven models
- AutoRegressive with eXogenous variables (ARX) models for indoor temperature and gas consumption
- Model coupler algorithm
- Model optimiser framework
- Executed in a cloud-based infrastructure
- Using legacy equipment already installed:
- Robust
- Cheap
- But less accurate measurements compared to on-site monitoring systems


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
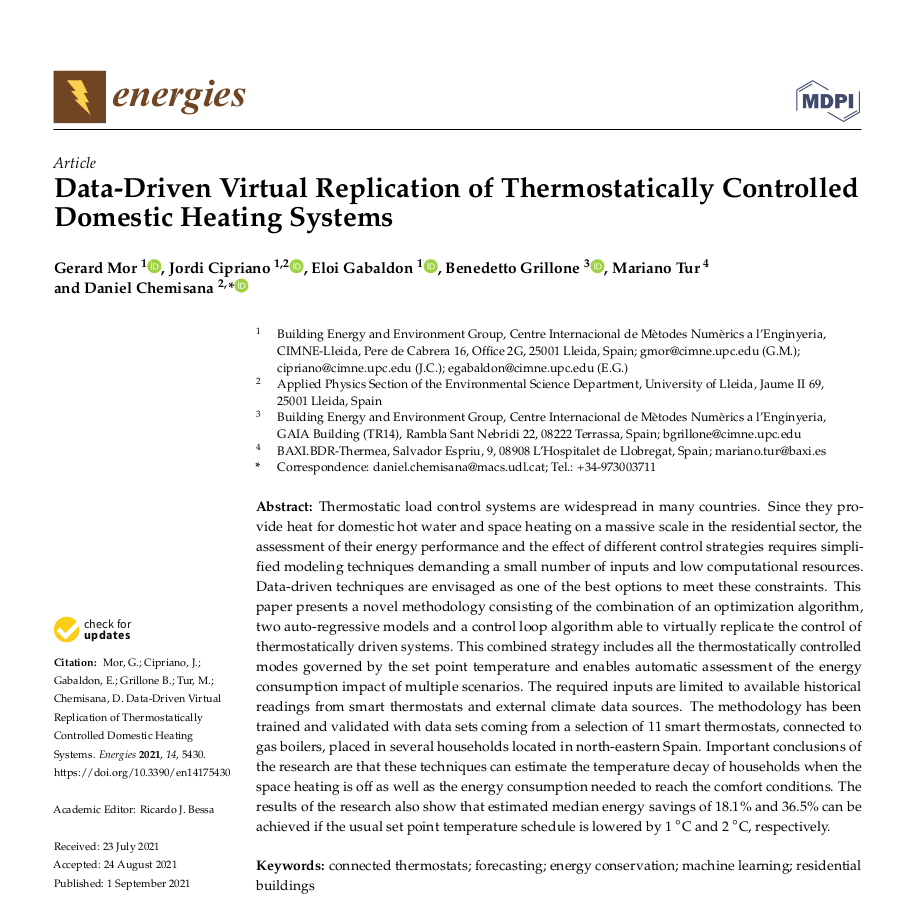
General steps and applications
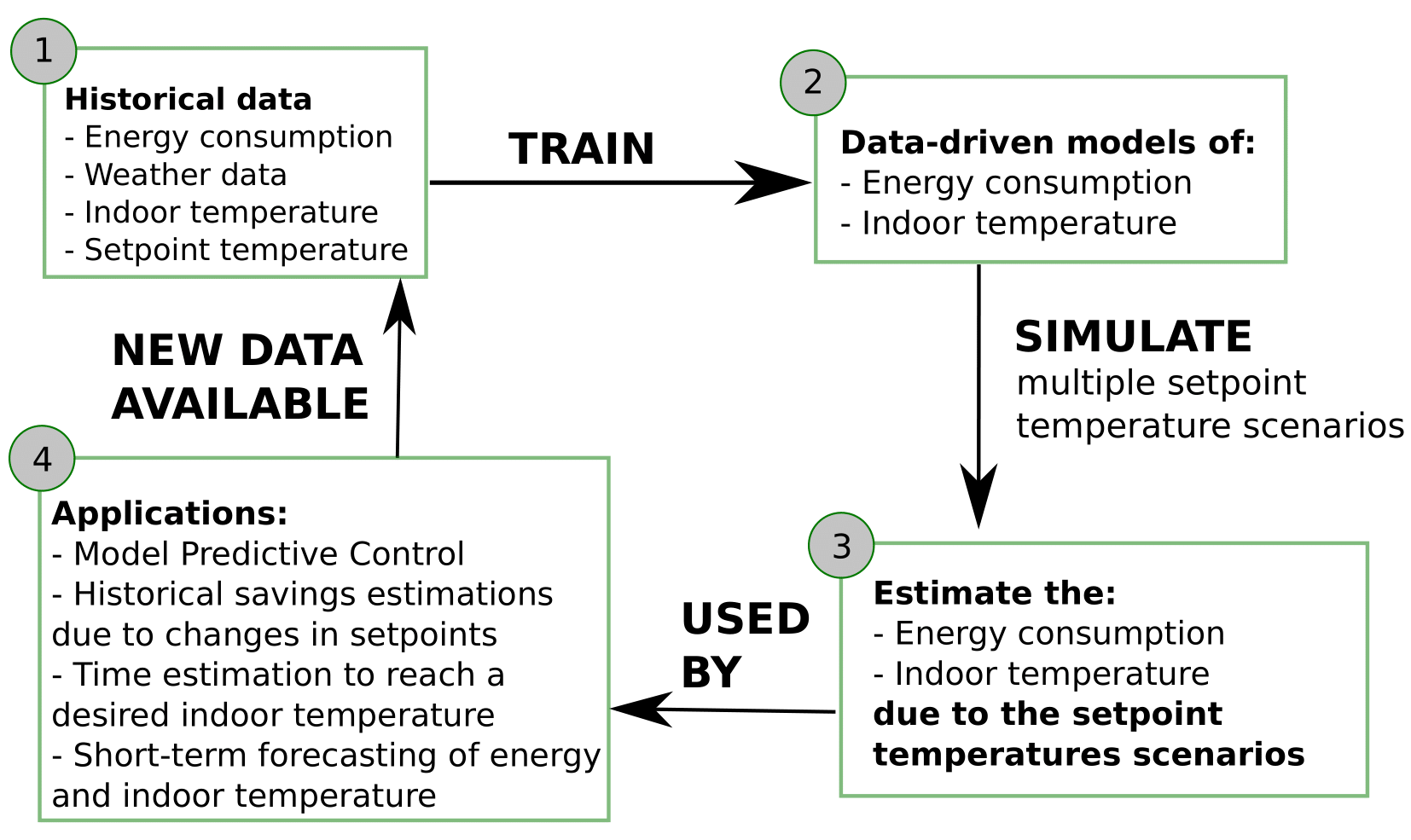


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Demand-side model
Heat input terms
Raw outdoor temperature terms
Outdoor temperature term affected by envelope characteristics
Air infiltrations term
Solar gains term
Indoor temperatures terms (Thermal inertia)
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Indoor temperature (ºC) | |
| Gas consumption (kWh) | |
| Outdoor temperature (ºC) | |
| Wind speed (m/s) | |
| Wind direction (º) | |
| Solar irradiance (W/m²) | |
| Solar azimuth (º) | |
| Solar elevation (º) | |
| timestep | |
| Error |


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Supply-side model
Indoor temperature terms (Thermal inertia)
Raw outdoor temperature terms (ventilation)
Outdoor temperature term affected by envelope characteristics
Air infiltrations loses
Solar gains
Historical gas consumption
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Indoor temperature (ºC) | |
| Gas consumption (kWh) | |
| Outdoor temperature (ºC) | |
| Wind speed (m/s) | |
| Wind direction (º) | |
| Solar irradiance (W/m²) | |
| Solar azimuth (º) | |
| Solar elevation (º) | |
| timestep | |
| Error |


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Model coupler algorithm



PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Inputs transformation
First order low-pass filter (LPF)
- Inputs better represent the dynamics of the system, eliminating high frequencies of data, smoothening the input variable


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Inputs transformation
Fourier series
- Transformation to linearise the relationship between cyclic features (e.g. hour of day, solar position, wind direction) and other features.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Optimisation of the parameters
Based on a binary genetic algorithm:
- Optimise the model:
- Auto-regressive orders
- Low-pass filter coefficients
- Number of harmonics
- Hysteresis
- Solar and air infiltration terms mode
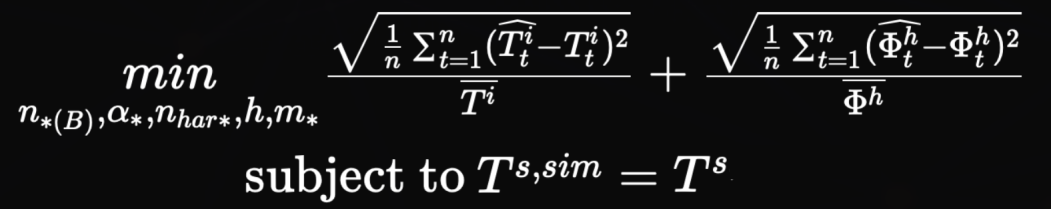


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Case study
- 15 households placed in the north-west of Spain (11 valid for our purposes)
- Valid datasets from march to may 2019
- Equipped with a condensing gas boiler and BAXI Connect thermostats
- Hourly consumption (Res. 2 kWh) and indoor temperatures (Res. 0.5ºC)
- Weather data from Darksky and Copernicus


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Results in one household
- Model results
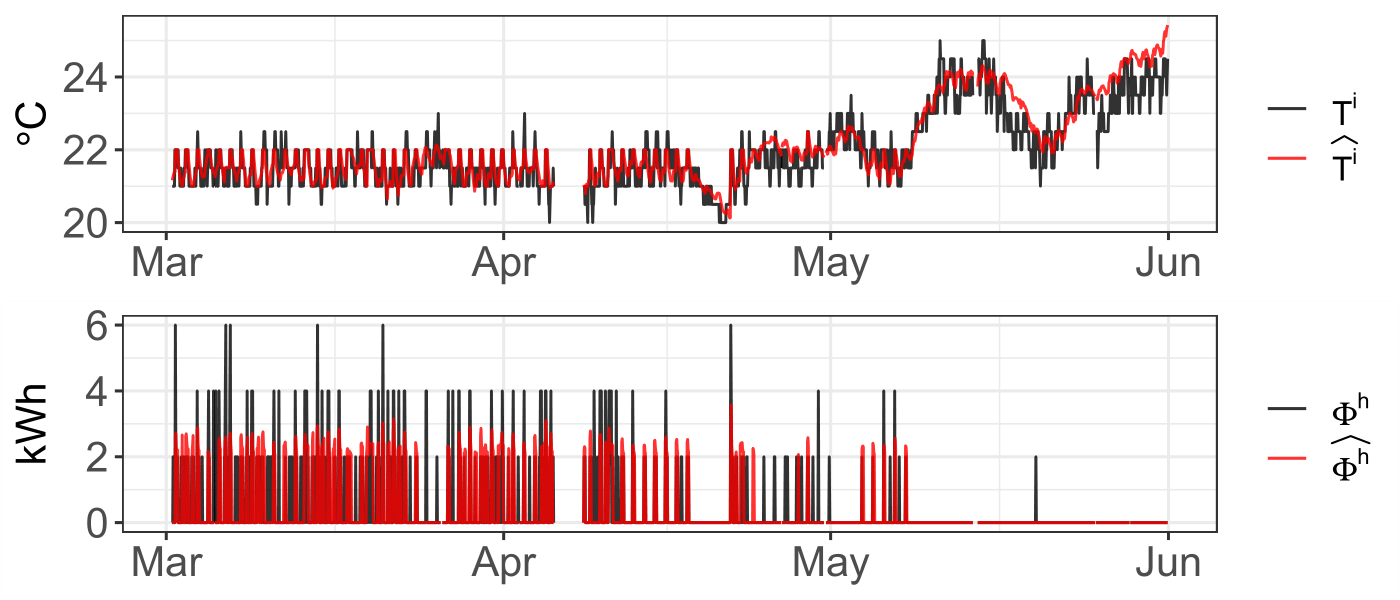
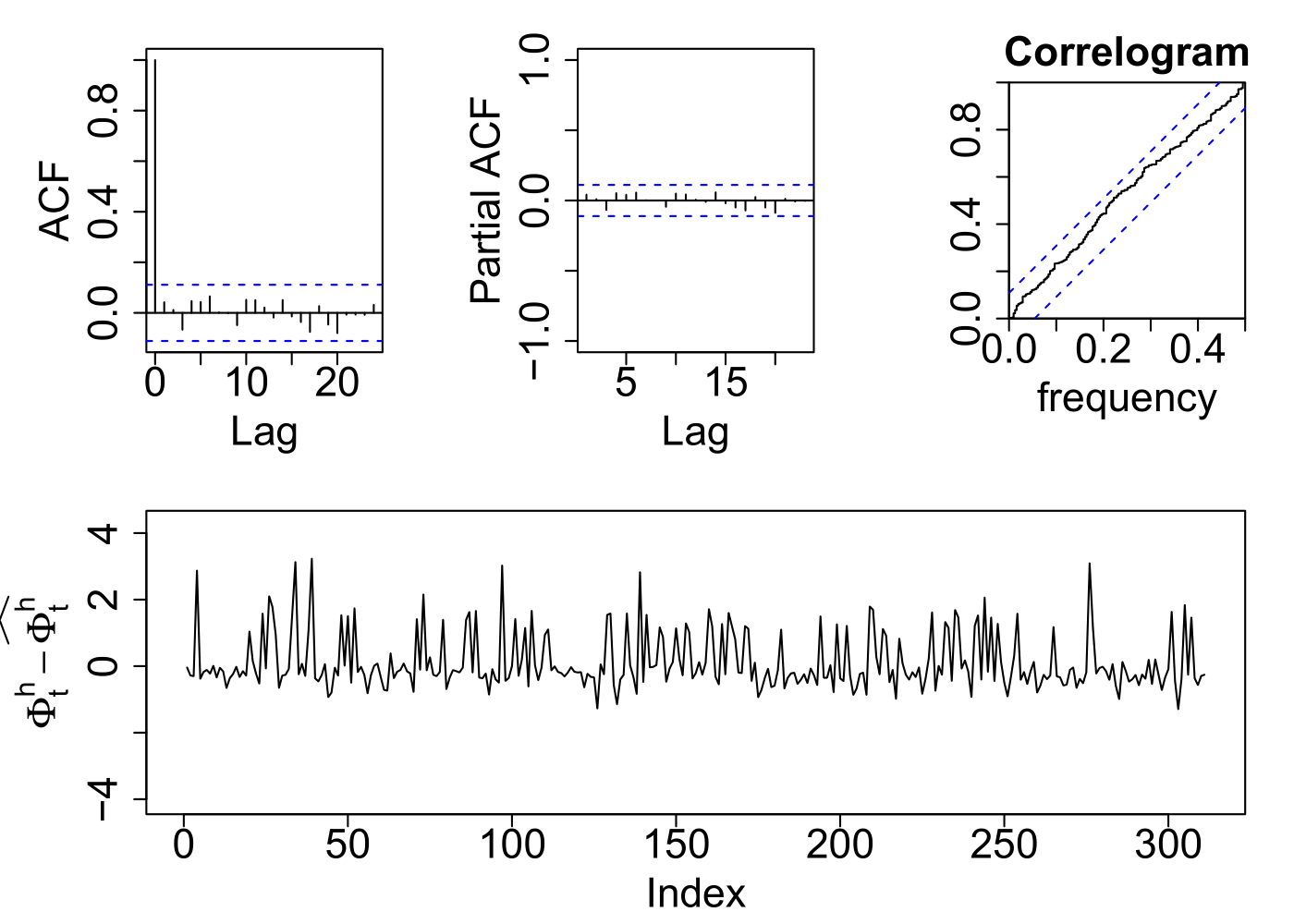
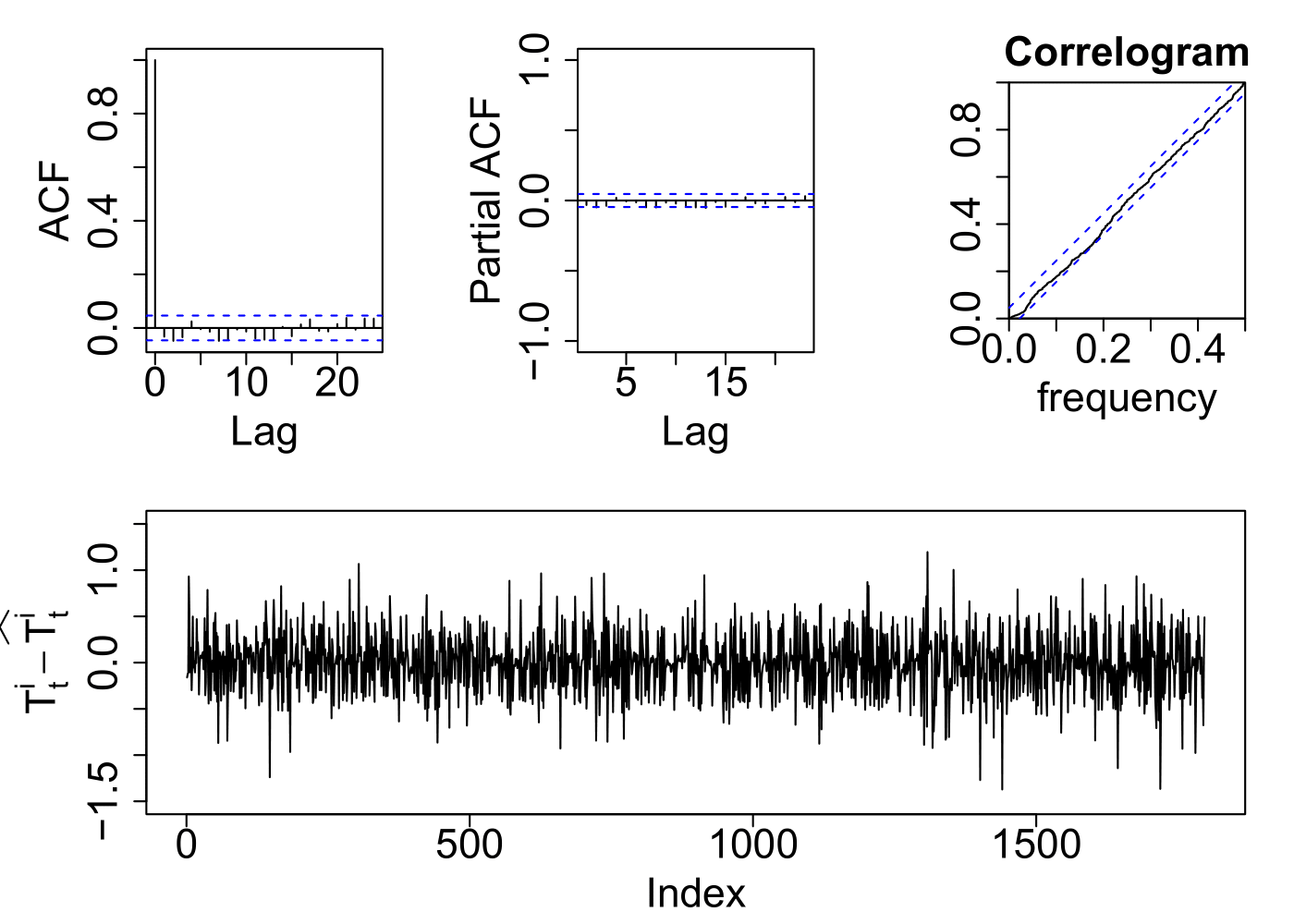


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Results in one household
Demand-side model
RMSE: 0.45ºC
MAPE: 1.4%
Supply-side model
(daily results)
RMSE: 4.72 kWh
MAPE: 37.1%
Cumulative consumption March 1st - May 31st
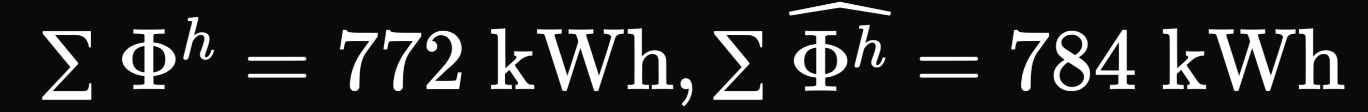
Real
Predicted
+1.5%
| Acronym | Description |
|---|---|
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| CVRMSE | Coefficient of Variation of the RMSE |
| MAPE | Mean Average Percentage Error |


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Case study model results
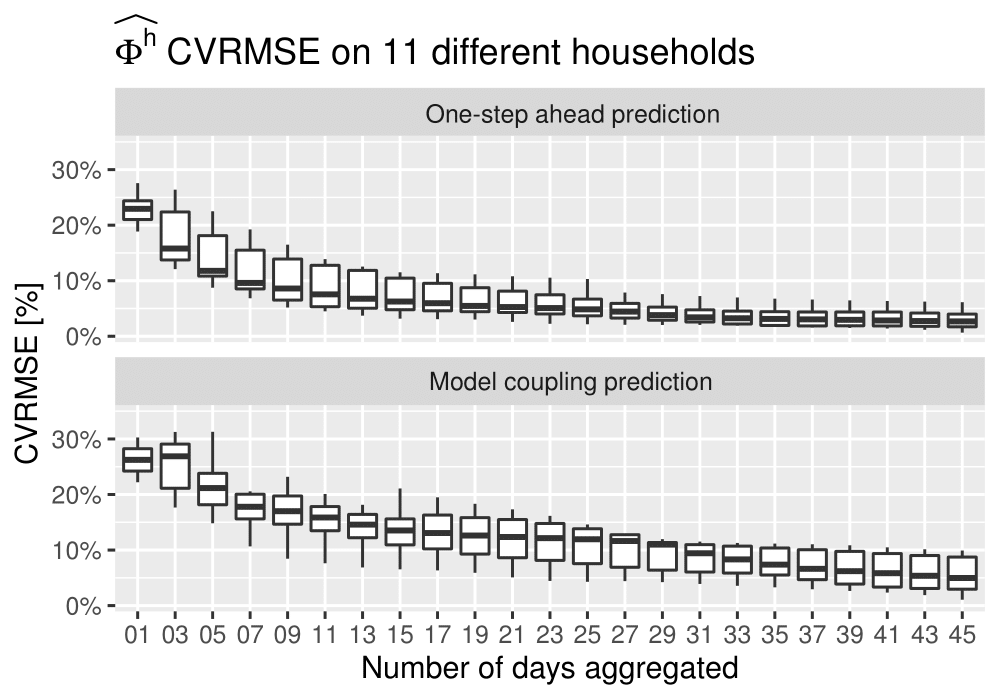
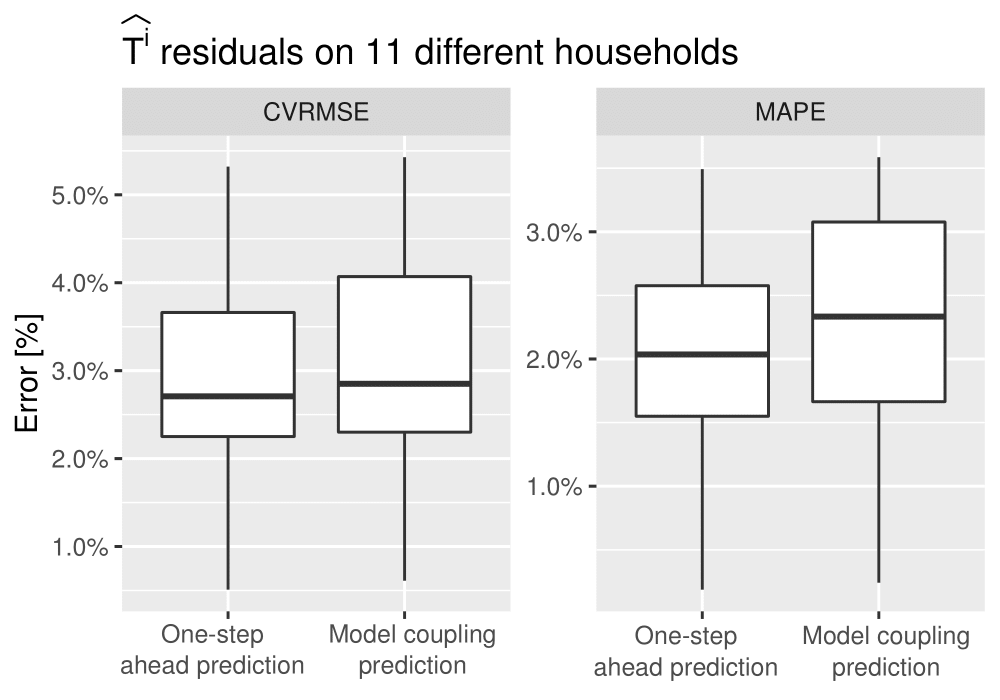
Supply-side model
Demand-side model


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Case study potential savings
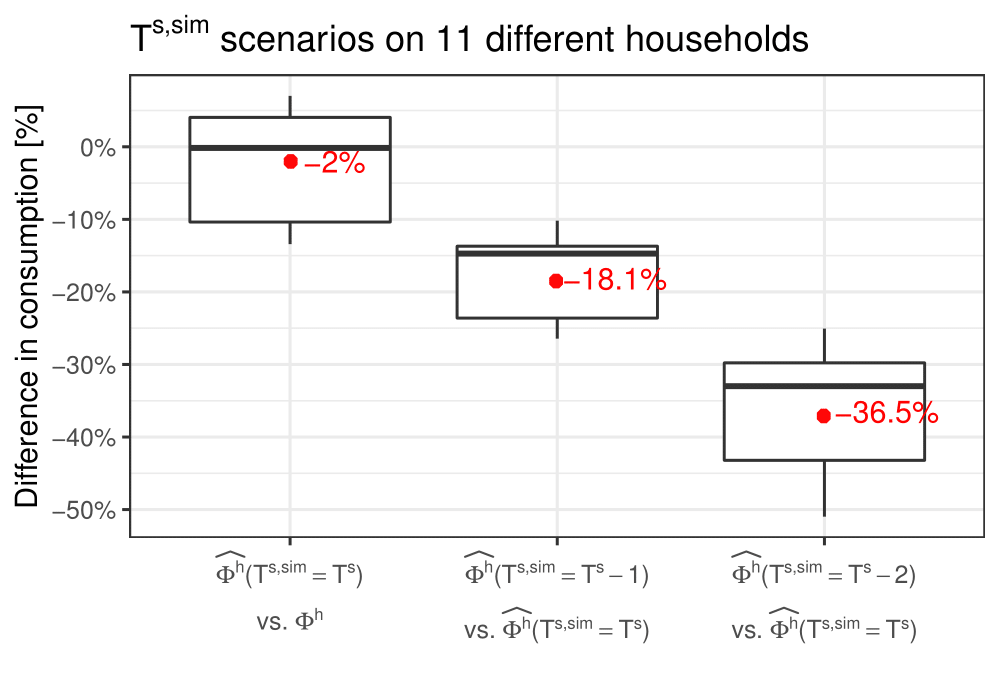
Warm period - Considering March 1st to May 31st period


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C3 - Virtual replication of domestic thermostatically controlled loads
Conclusions
- The method provides good accuracy for simulating control scenarios.
- Supply-side model was highly affected by the heating consumption readings
-
- A 0.1 kWh data resolution is needed, at least, for DR or MPC applications.
- If not possible, simpler supply-side models should be used
- A 0.1 kWh data resolution is needed, at least, for DR or MPC applications.
- Potential usage of this modelling infrastructure for many applications (characterisation, forecasting, anomaly detection, ...)
- During warm periods in Spain, high energy savings can be achieved decreasing 1-2ºC the actual setpoints (avg. 18.1%-36.5%, respectively)
- Chapter 4 -
Operation and flexibility assessment of Direct Load Control (DLC) systems in buildings


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels

Supported by:
Sim4blocks (H2020 project)
Journal: Energy and Buildings
JIF (2020): 5.879 - Q1


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Goal
- To design and implement a methodology to assess the operation of Direct Load Control (DLC) systems in buildings.
- Through the estimation of the Flexibility Models (FM) and Flexibility Functions (FF) using ARX techniques.
- This characterisation needs to addresses multiple flexibility markets, with use cases located in Germany, Switzerland and Spain.
- Hence, the FM needs to consider different penalty or activation signals for Demand Response (DR).


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
General methodology
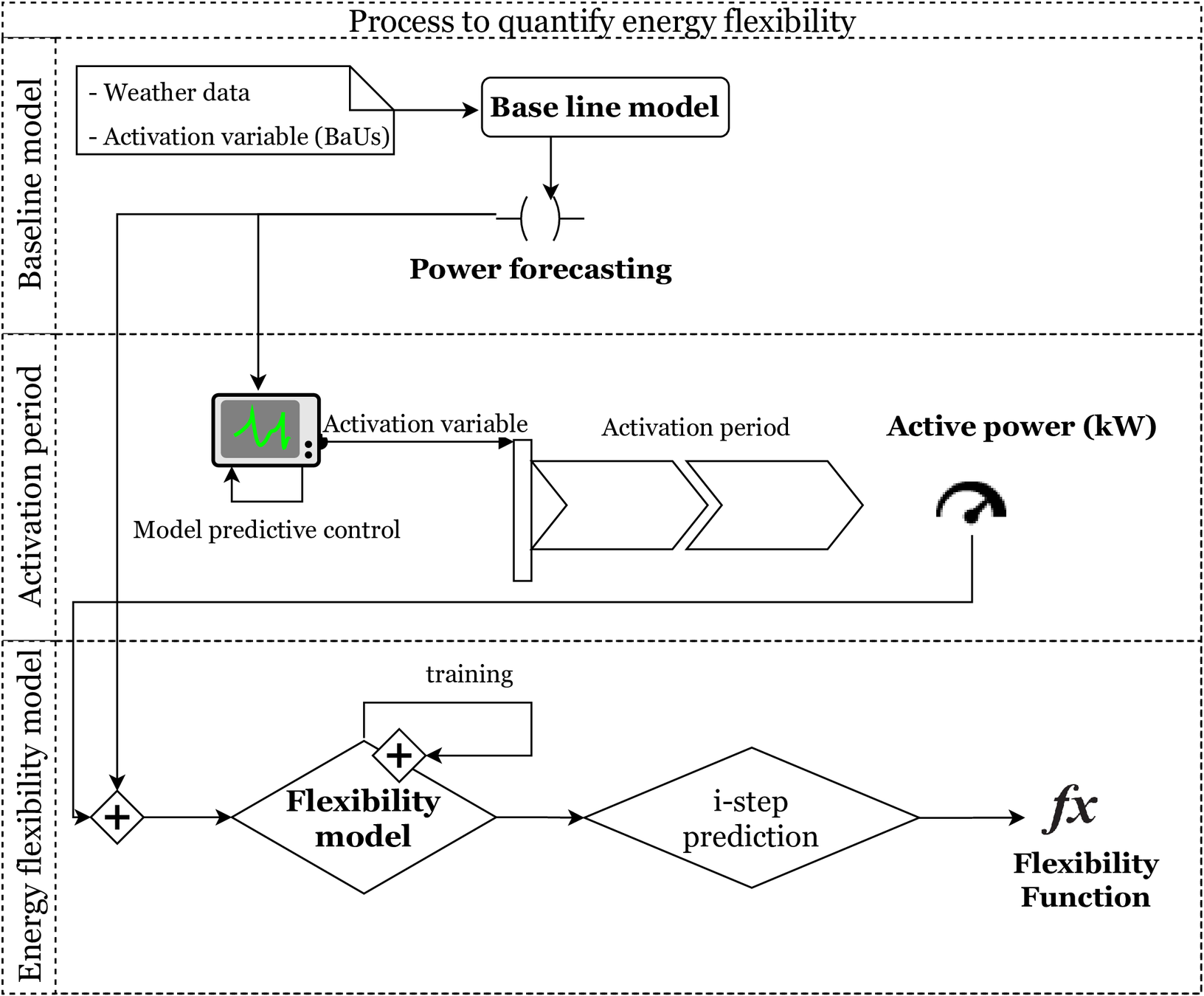
1 . Predicted 'Business as Usual (BaU)' consumption scenario
$$(P^b)$$
2. Optimise the consumption based on some penalty or activation signal (sending proper control to the system)
4. Periodically, both signals $$P^e \:and\:P^b$$ are given to the flexibility model
3. The building uses the control signal sent by the controller, and consume certain amount of energy $$(P^e)$$
5. To estimate the Flexibility Function (FF)
DR operation


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Spanish pilot site
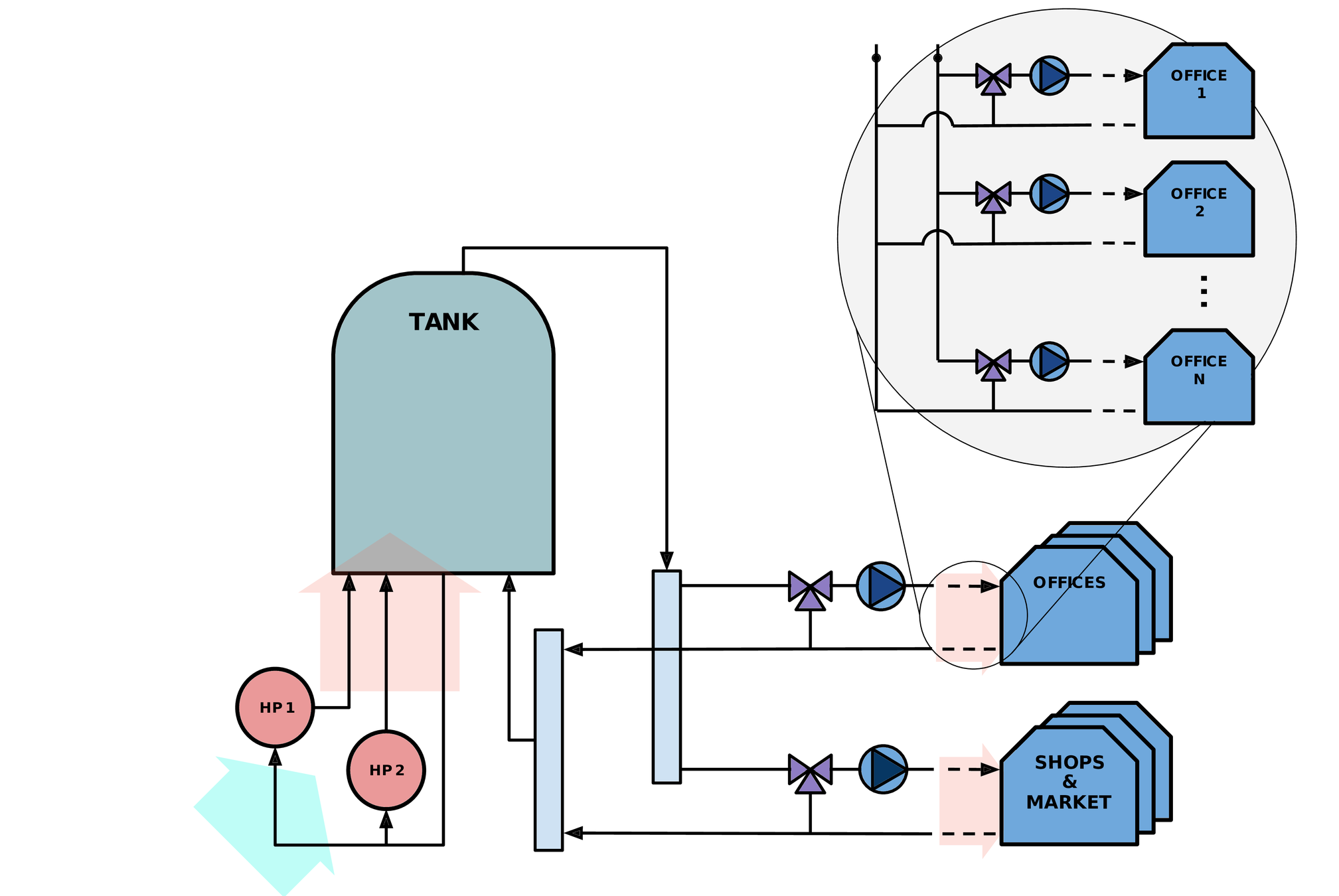
Sant Cugat (Barcelona)
- Large building with 32 offices, 3 shops, a local market
- Consumption rings connected to a hot buffer tank of 3500 litres of capacity.
- 2 air-to-water electric Heat Pumps (HP).
- Aggregated HP peak power = 60 kWe


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Swiss pilot site
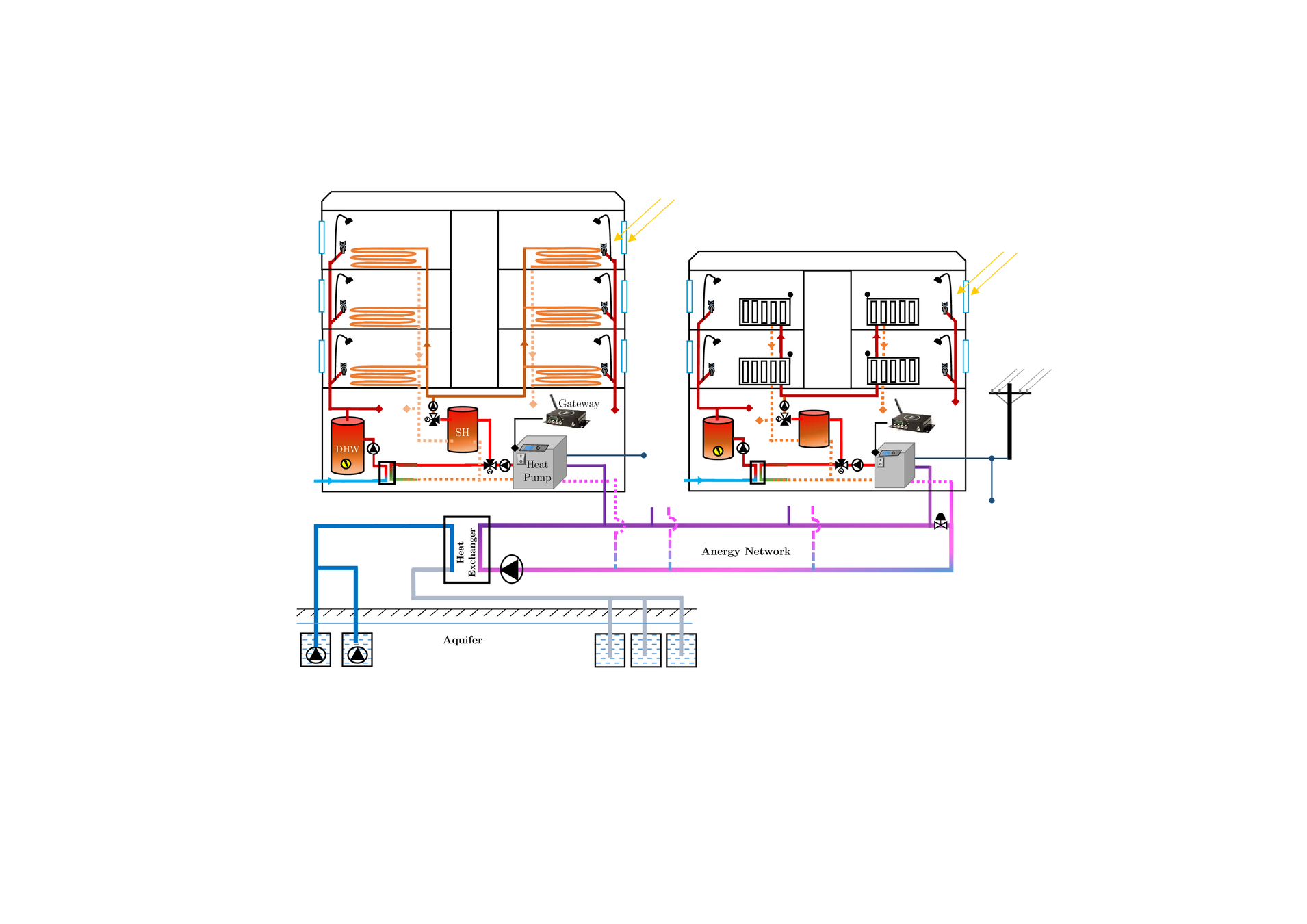
Naters (Valais)
- 5 multi-family residences sourced by water-to-water HP
- Aggregated HP peak power = 34.3 kWe
- Year of construction 1919-2015
- HPs are connected to a geothermal district heating


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
German pilot site
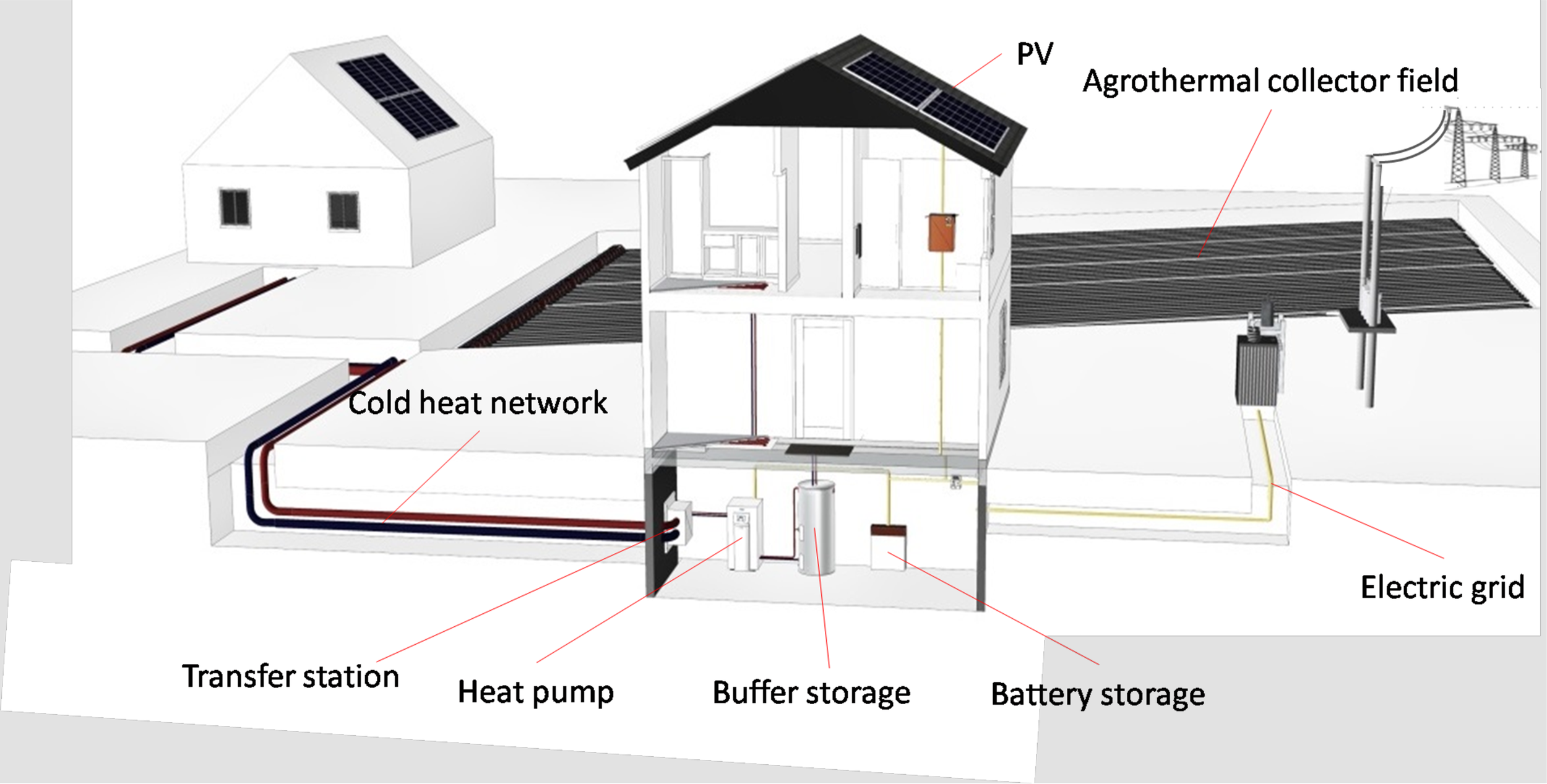
Wüstenrot (Stuttgart)
- Newly-built positive energy settlement (4 buildings were tested supplied by water-to-water HP)
- Aggregated HP peak power = 12.4 kWe
- HP are connected to a low-temperature district heating


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
DLC operation methodology
Spanish pilot:
- Hot water tank and consumption heat pumps: ARX models
- Consumption rings: Generalised Additive Model
-
Control: Genetic algorithm
- Setting setpoint temperature of the hot water tank
- Launched every day at 00:00 (Horizon 24h) - Minimising the cost
Swiss pilot:
- Grey-box model of each residential building
- Baseline based on a Seasonal AutoRegressive model of past 3 days of data
- Control: Scheduling Optimization problem (ON/OFF of multiple HP's)
- Developed by Hes-so Valais-Wallis


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
DLC operation methodology
German pilot:
- Calibrated white-box model based on a system of differential equations and heat transfer functions
- Control: Scheduling Optimization problem (ON/OFF of multiple HP's)
- Developed by HFT Stuttgart


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
DLC operation results in Spanish pilot site
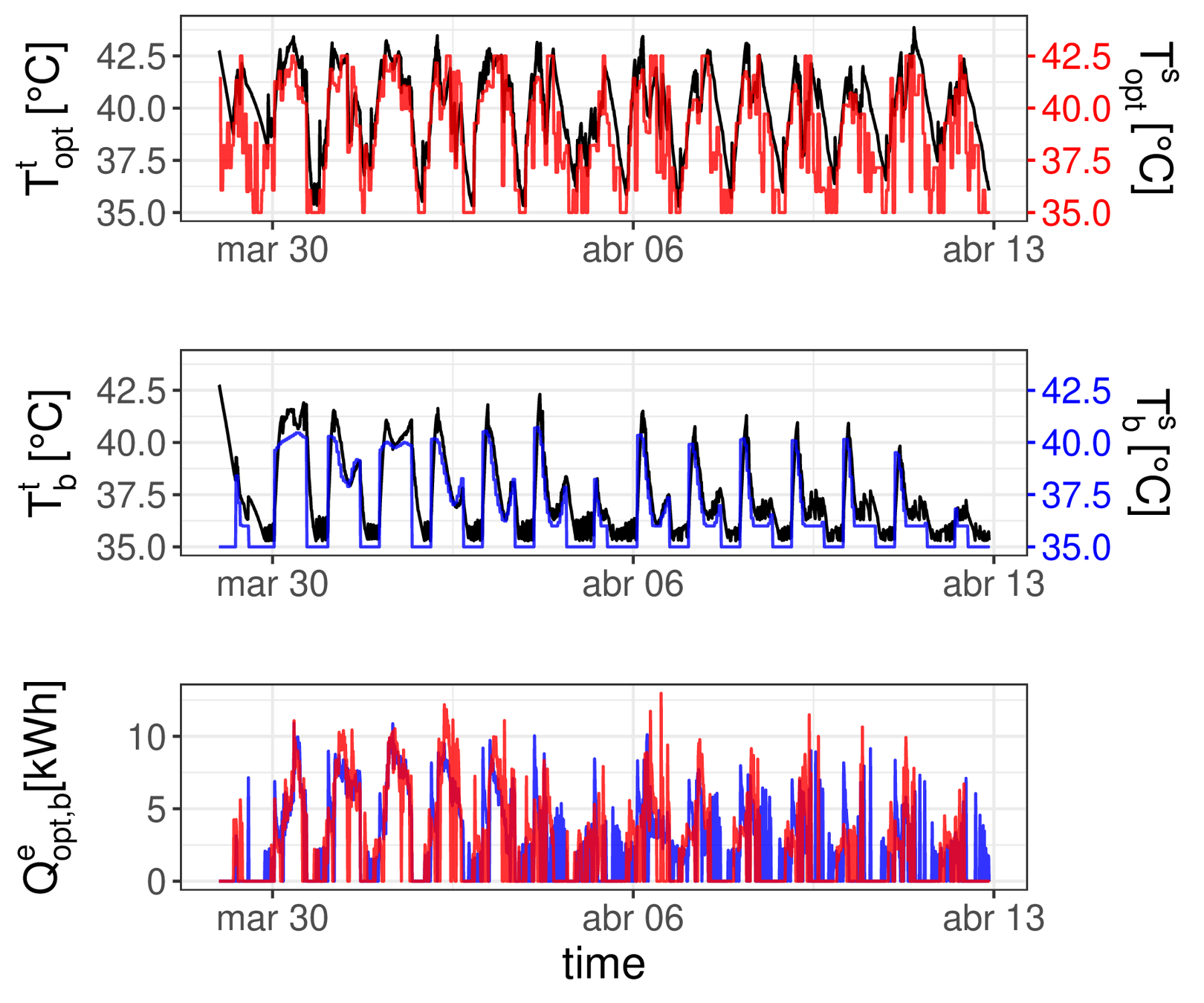
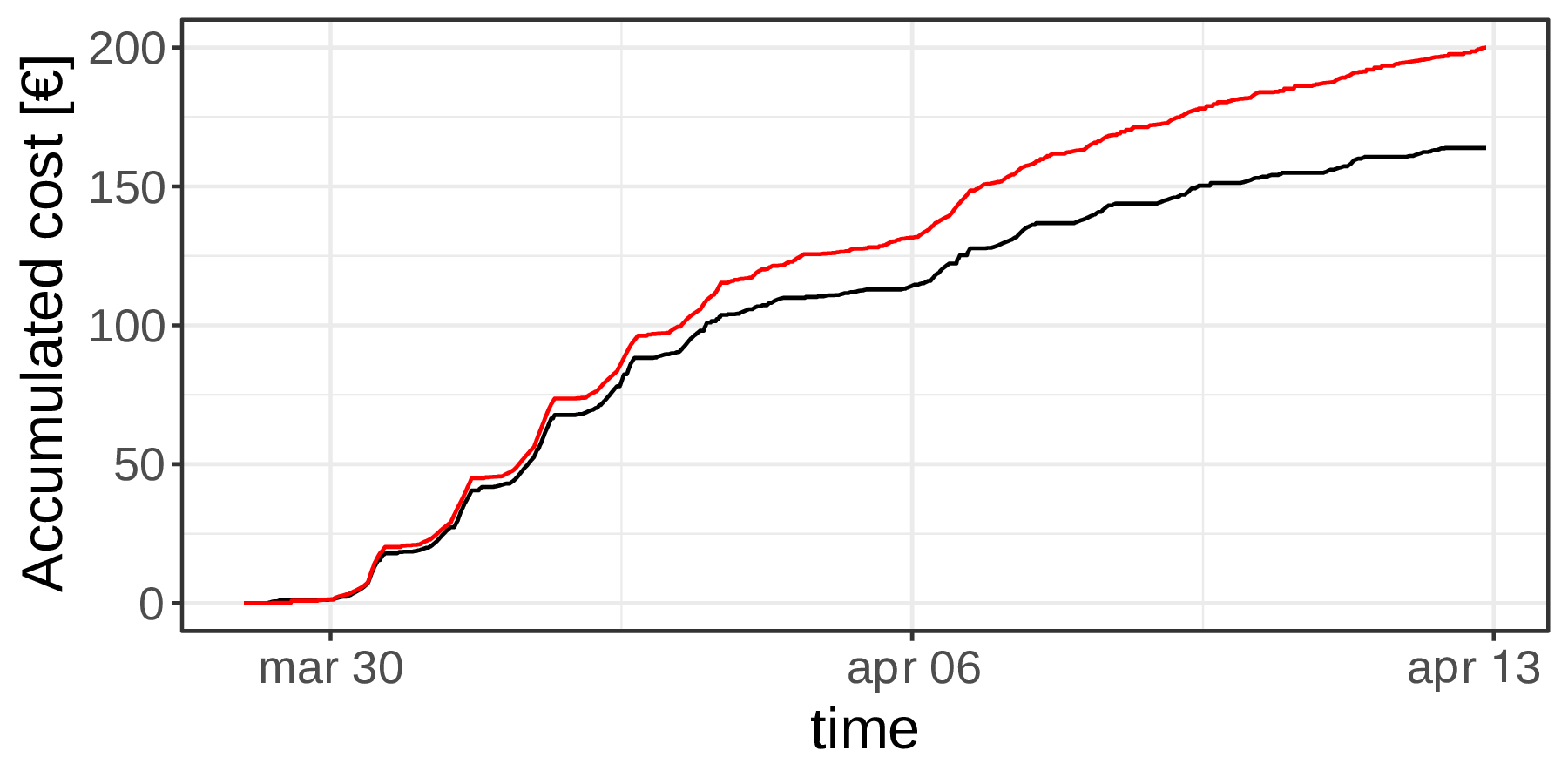
-18% in accumulated cost
$$T^t_{opt}$$ Actual tank temperature
$$T^s_{opt}$$Setpoint temperature provided by the controller
$$T^t_b$$ Simulated tank temperature
$$T^s_b$$Setpoint temperature setting the minimal temperature to feed comfort requirements
$$Q^e_{opt}$$Actual HP electric consumption
$$Q^e_b$$Simulated HP electric consumption using the minimal tank temperature to feed comfort requirements
Evaluation period: March 29th to April 12th 2019, both included


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Methodology - Flexibility model estimation
Flexibility Model (FM) when activation variable is the day-ahead price of the wholesale spot market
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Active power (kW) | |
| Simulated baseline power (kW) | |
| Electricity Spanish spot price (€/kWh) | |
| Error | |
| timestep | |
| FF evaluation period | |
| FF activation period |


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Methodology - Flexibility model estimation
Flexibility Model (FM) when activation variable is the day-ahead price of the wholesale spot market
Active power terms
Baseload power terms
Activation signal terms
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Active power (kW) | |
| Simulated baseline power (kW) | |
| Electricity Spanish spot price (€/kWh) | |
| Error | |
| timestep | |
| FF evaluation period | |
| FF activation period |


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Methodology - Flexibility model estimation
Flexibility Model (FM) when activation variable is the day-ahead price of the wholesale spot market
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Active power (kW) | |
| Simulated baseline power (kW) | |
| Electricity Spanish spot price (€/kWh) | |
| Error | |
| timestep | |
| FF evaluation period | |
| FF activation period |


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Methodology - Flexibility model estimation
FM when activation variable is a percentage of activation time within each time step
FM when activation variable is a trace to be tracked
German pilot
Swiss pilot


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Methodology - Flexibility model estimation
FM when activation variable is a percentage of activation time within each time step
FM when activation variable is a trace to be tracked
Difference between:
- Trace to track
- Baseline
Percentage of activation during each timestep
German pilot
Swiss pilot


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Operation - Flexibility model in Spanish pilot
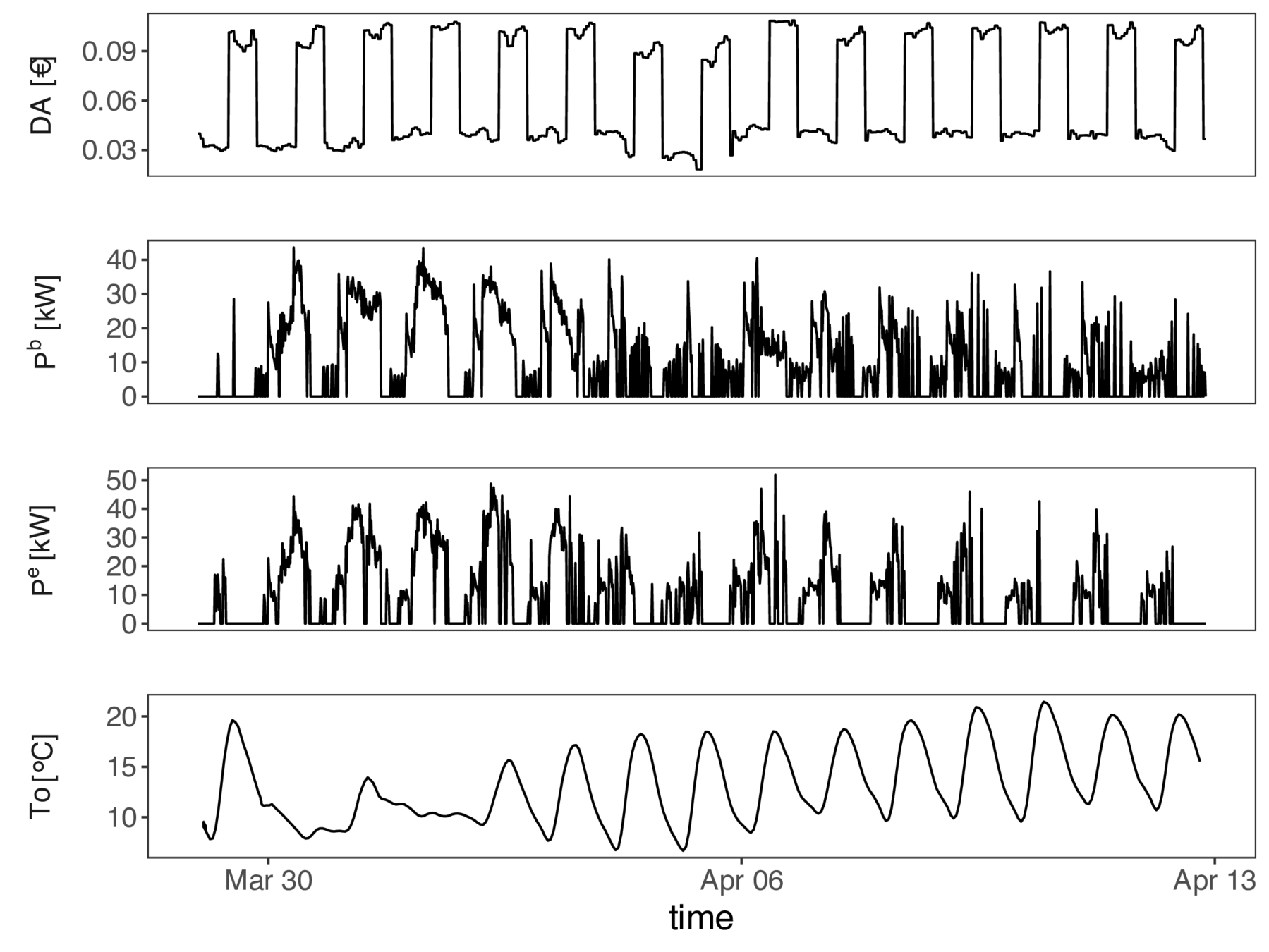
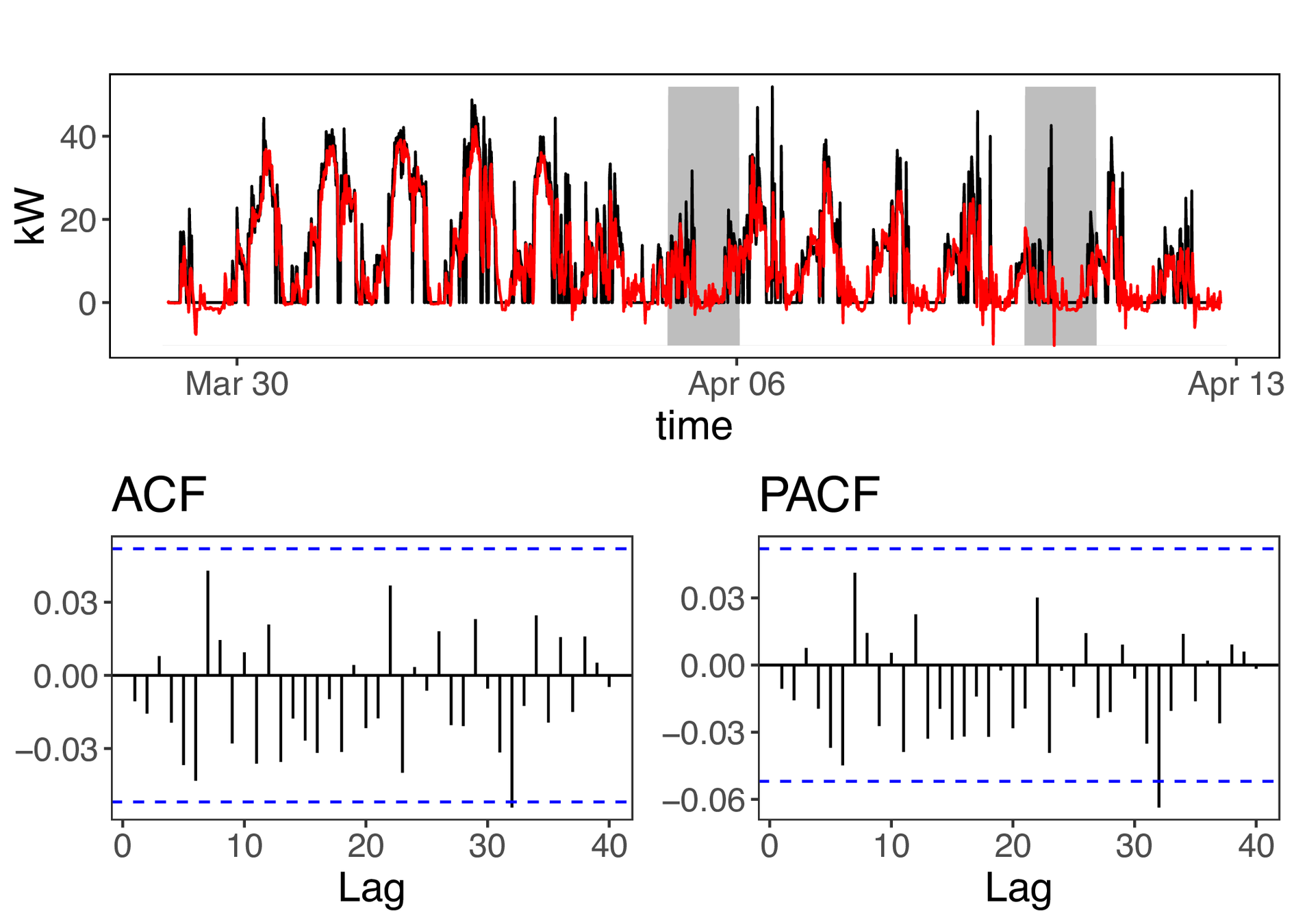
Models inputs
Model fitting


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Operation - FF Spanish pilot site
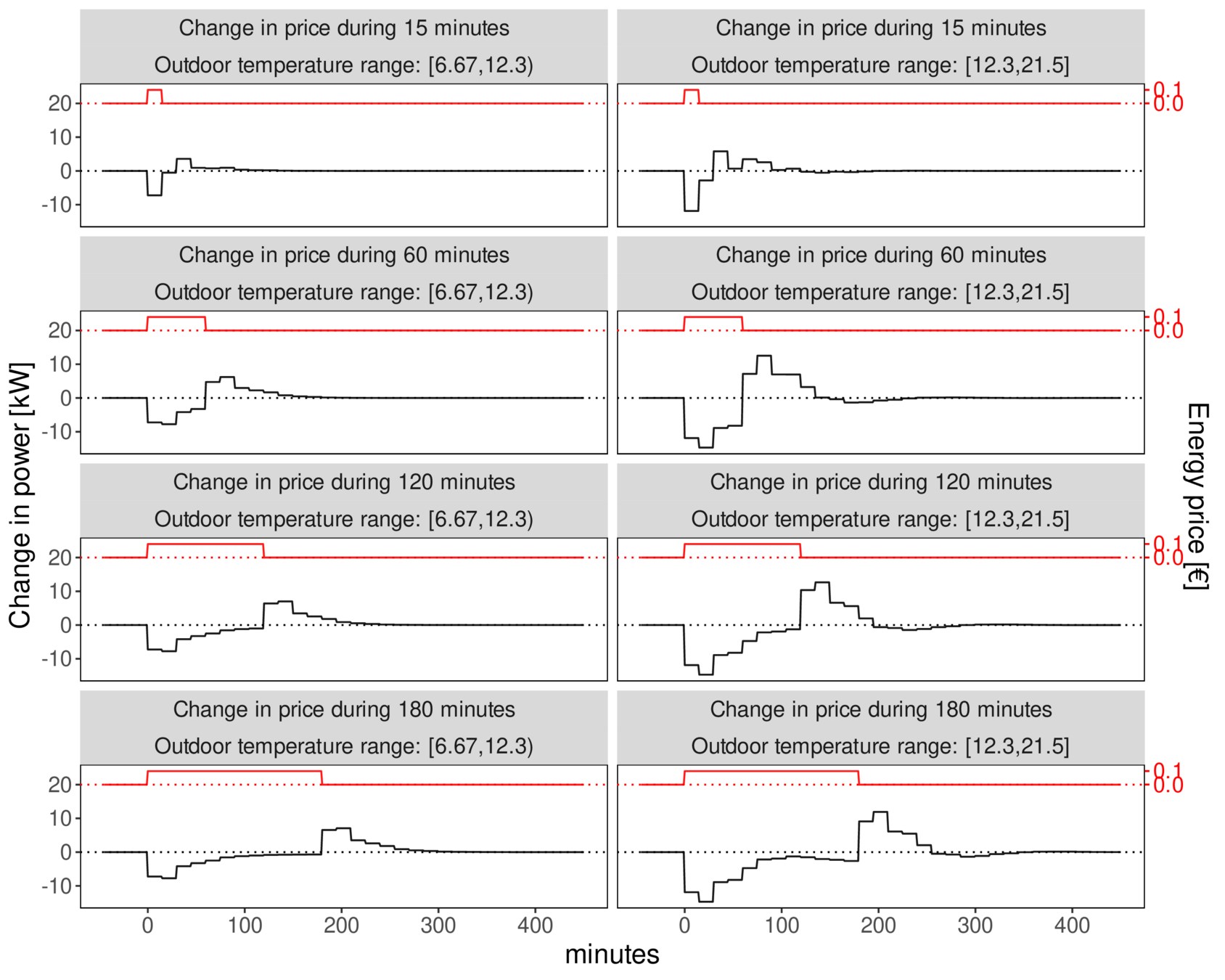
Low outdoor temperatures:
- After increase in price of 0.1 €/kWh:
- 30' of 6-7 kW of reduction.
- After it, decreases until no affection after 1h 45'.
- Price return to normal
- Similar rebound effect.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Operation - FF Spanish pilot site

Warm temperatures:
- After increase in price of 0.1 €/kWh:
- 60' of an average of 10 kW of reduction (Peak of 13kW between 15' and 30' from activation)
- After it, decreases until no affection after 2h.
- Price return to normal
- Shorter rebound effect of 8kW on average, during 1h 15'.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C4 - Operation and flexibility assessment of DLC systems in buildings
Conclusions
The Flexibility Model can be used:
- To estimate feasible optimal consumption scenarios that a certain system historically did.
- Applications:
- Anomaly detection of DR operations in DLC systems.
- Improve the negotiation process between aggregators and cluster/building managers.
- Applications:
The Flexibility Function helps to:
- Understand the historical DLC operations in buildings according to a certain DR activation signal.
- Infer the energy flexibility characteristics of a system.
- Chapter 5 -
Electricity load characterization of districts


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels

Supported by:
ELISE (ISA2 project) and Joint Research Center (Ispra)
Journal: Energy Reports
JIF (2020): 6.870 - Q1


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Goals
- To design and implement a visual tool for the characterisation of energy consumption at local scale (districts, regions)
- To benchmark different parts of the territory with radically different conditions:
- Built area
- Activity sectors
- Weather conditions
- To evaluate the interoperability and potential of using INSPIRE-harmonised datasets with energy-related datasets


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Data inputs (2018-2020)
- Aggregated hourly electricity consumption
- By tariff
- By similar-to-district geographical level (Spain: postal code)
- By type of usages (Industrial, residential, tertiary)
- Building information (INSPIRE harmonised)
- Typology
- Built area
- Year of construction
- Geometry
- Weather data
- Outdoor temperature and wind speed


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Optional data inputs
- Aggregated socio-economical information
- Annual net incomes per household
- Incomes sources (salary, pension, benefits,...)
- Gini index (inequality)
- Population age
- People per household
- Population
Consumption data Socio-economic data Buildings information
Postal code ~ Census tract > Building level
Aggregation


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Methodology
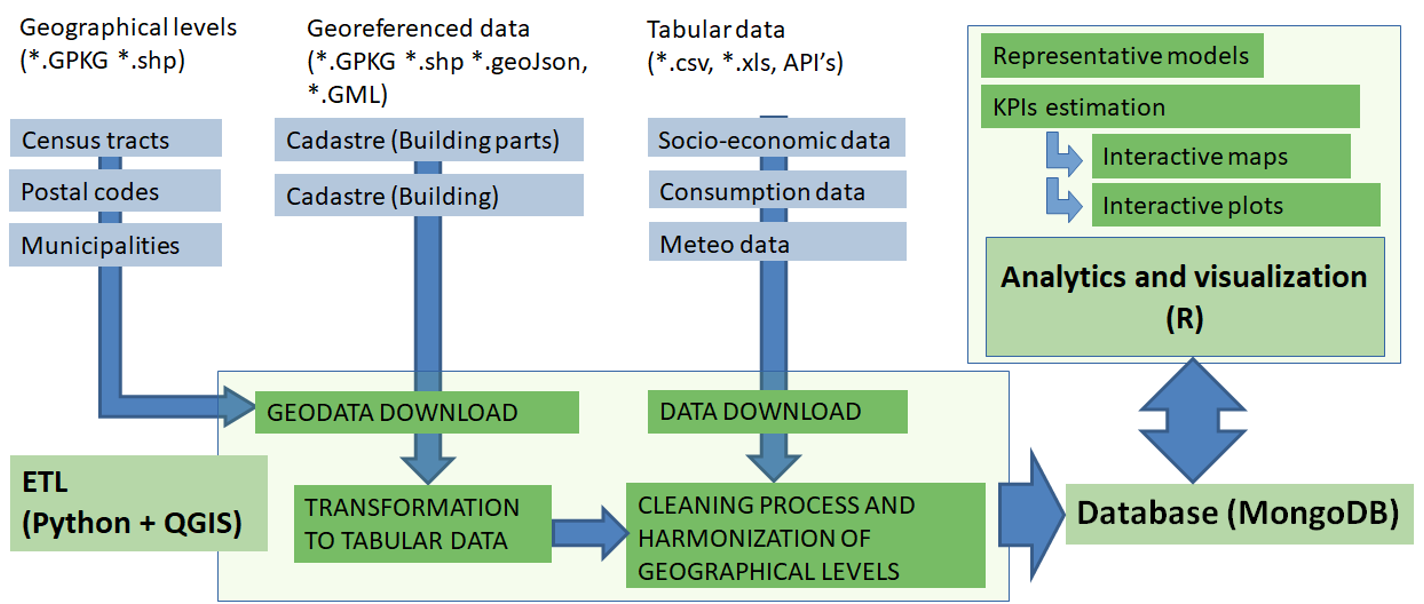


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Energy characterisation method
Once datasets are harmonised to postal code level:
- Data cleaning
- Inference of usage patterns
- Model consumption based on built area, calendar features, usage patterns and weather data.
- Disaggregate consumption
- Baseload
- Heating
- Cooling
- Holidays
- Covid-19 lockdown
- Obtain benchmarking indicators


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Inference of usage patterns
- Based on relative daily load curves during:
- March to May + September to November
- Avoid COVID-19 lockdown periods and holidays
- Using Spectral clustering technique
- Kernel: Polynomial of degree=2
- Best K: Gap in the eigenvalue spectrum
- Classification of non-clustered days:
- Using a multinomial logistic regression model
- Based on calendar features
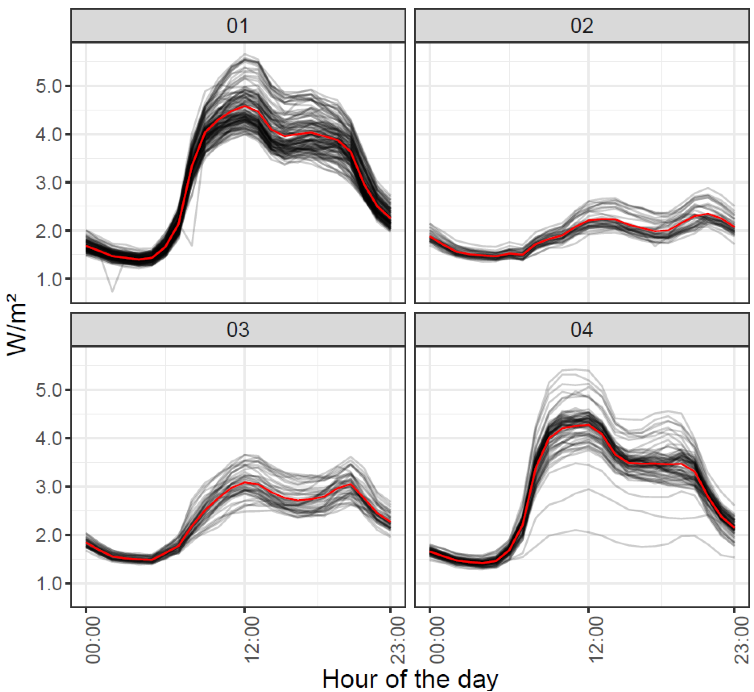
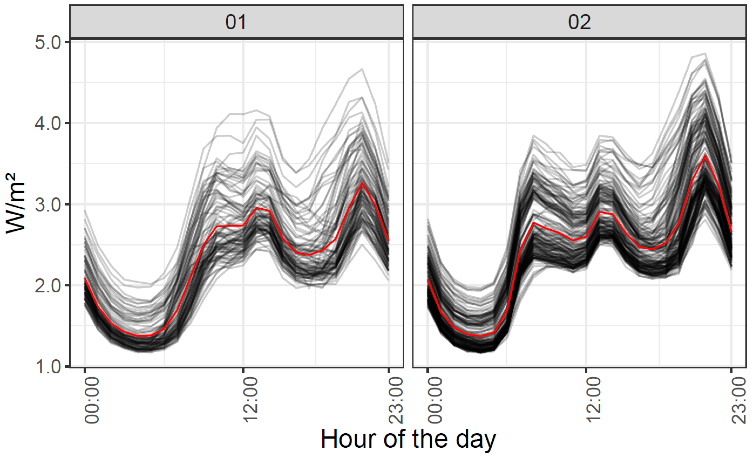


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Energy modelling
Baseload terms
Weather dependence terms
Technique: Penalised regression model
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy use intensity (kWh/m²) | |
| DLC cluster | |
| Hour of the day | |
| Timestep | |
| Error |


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Energy modelling - Baseload
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| hour of the day | |
| hour of the week |
Fixed baseload
Influence of the daily seasonality
Influence of the weekly seasonality


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Energy modelling - Weather dependence
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Outdoor temperature (ºC) | |
| Balance temperature of heating demand (ºC) | |
| Wind speed (m/s) | |
|
|
|
| Low-pass filter coefficient [0-1] | |
|
|
Inertia-affected indoor-outdoor temperature (Envelope transfer)
Raw indoor-outdoor temperature (Ventilation, windows operation transfers)
Interaction of indoor-outdoor temperature and wind speed (Air infiltrations transfer)


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Energy modelling - Holidays and lockdowns
- Holidays influence
- Avoid holidays in training periods
- Then, when predicting:
- Covid-19 lockdown (March 15th - June 21th 2020) influence
- Re-fit coefficients during that period
- Force no holidays influence
If CVRMSE ( \( Q^e \), \( \widehat{Q^e} \) ) > 20%, consider that difference due to holidays


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Training procedure
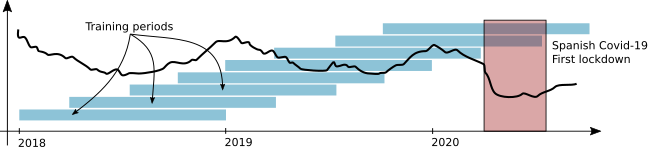
Each training period:
75% training
25% validation
Days randomly distributed

Coefficients estimated using maximum likelihood method + a genetic algorithm


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Results of a single district
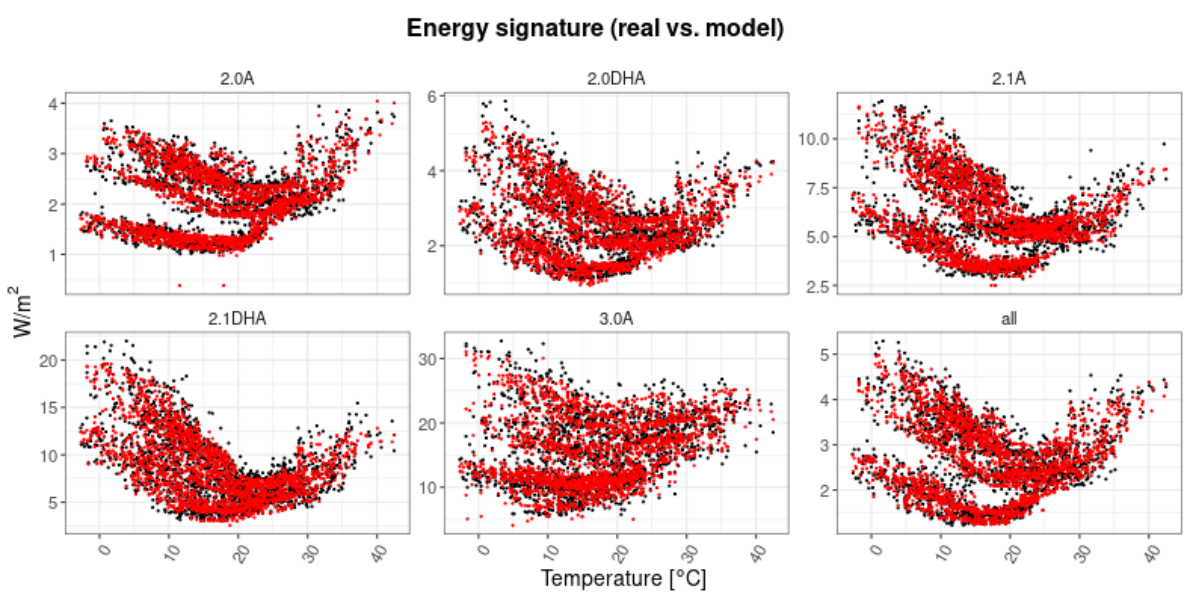
A district in the city of Lleida
(Zona alta neighborhood)
Residential sector
Average accuracy
MAPE: 5.04%
CVRMSE: 6.51%


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Results of a single district
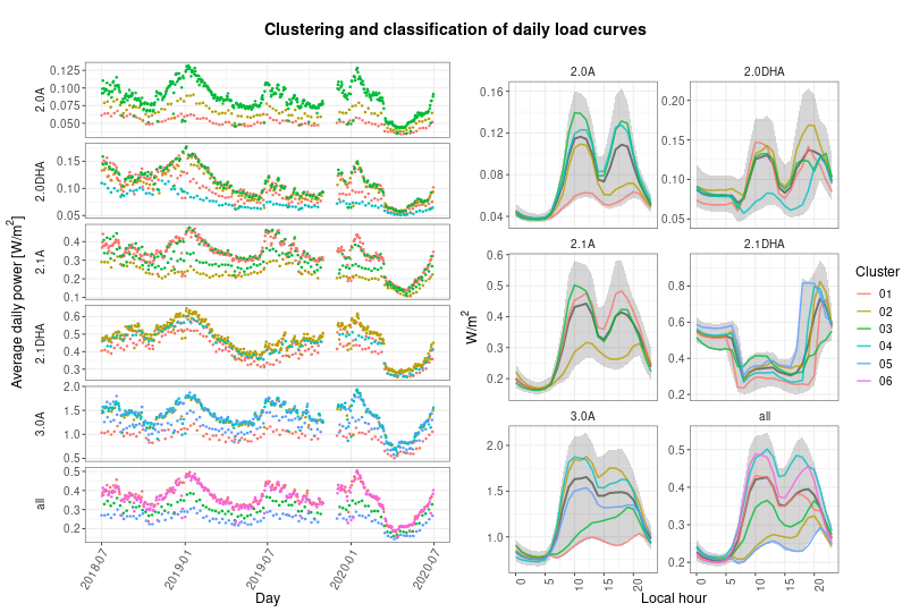
Estimation of most common daily load curves:
Detection of high and low activity periods depending Spanish tariff


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Results of a single district
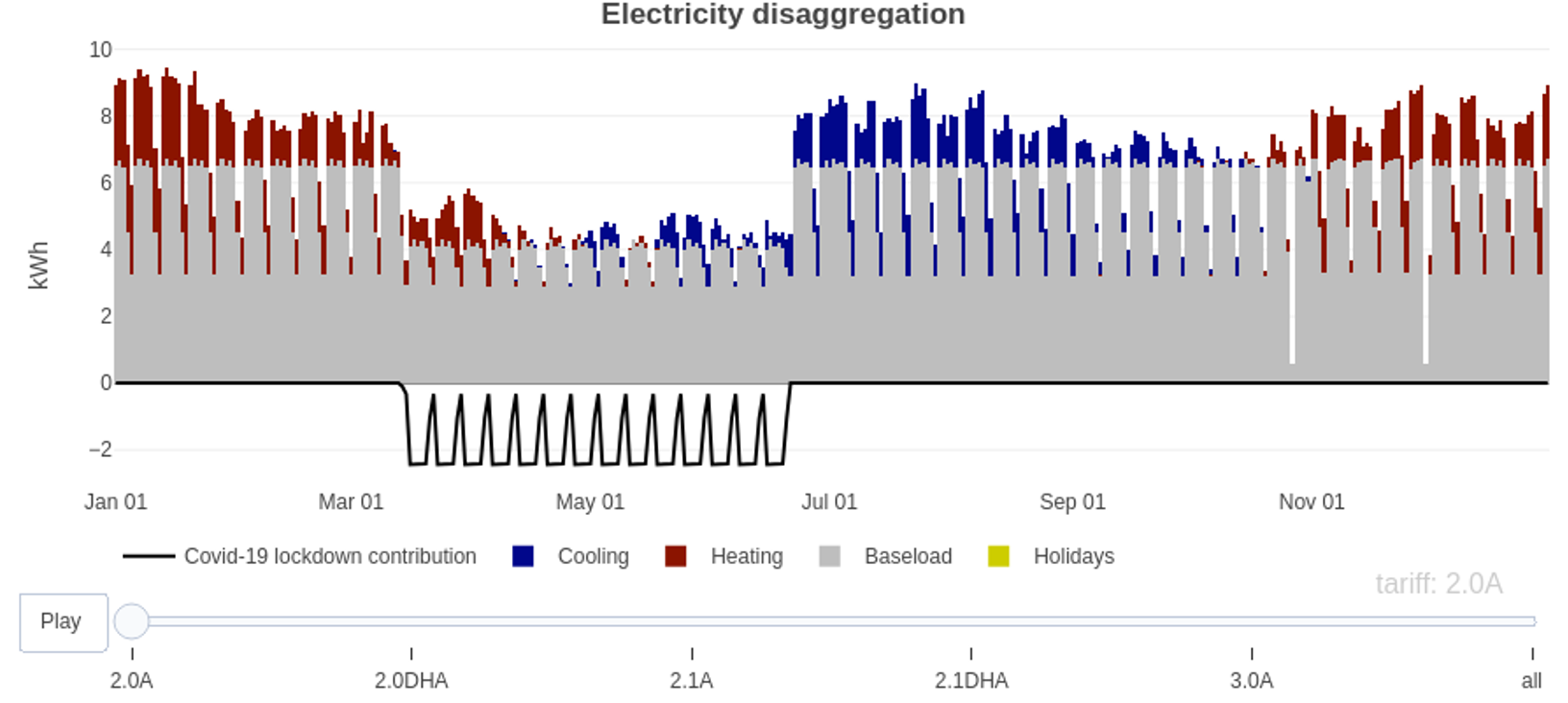
Detailed daily consumption components during a standardised year


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Results for the province of Lleida
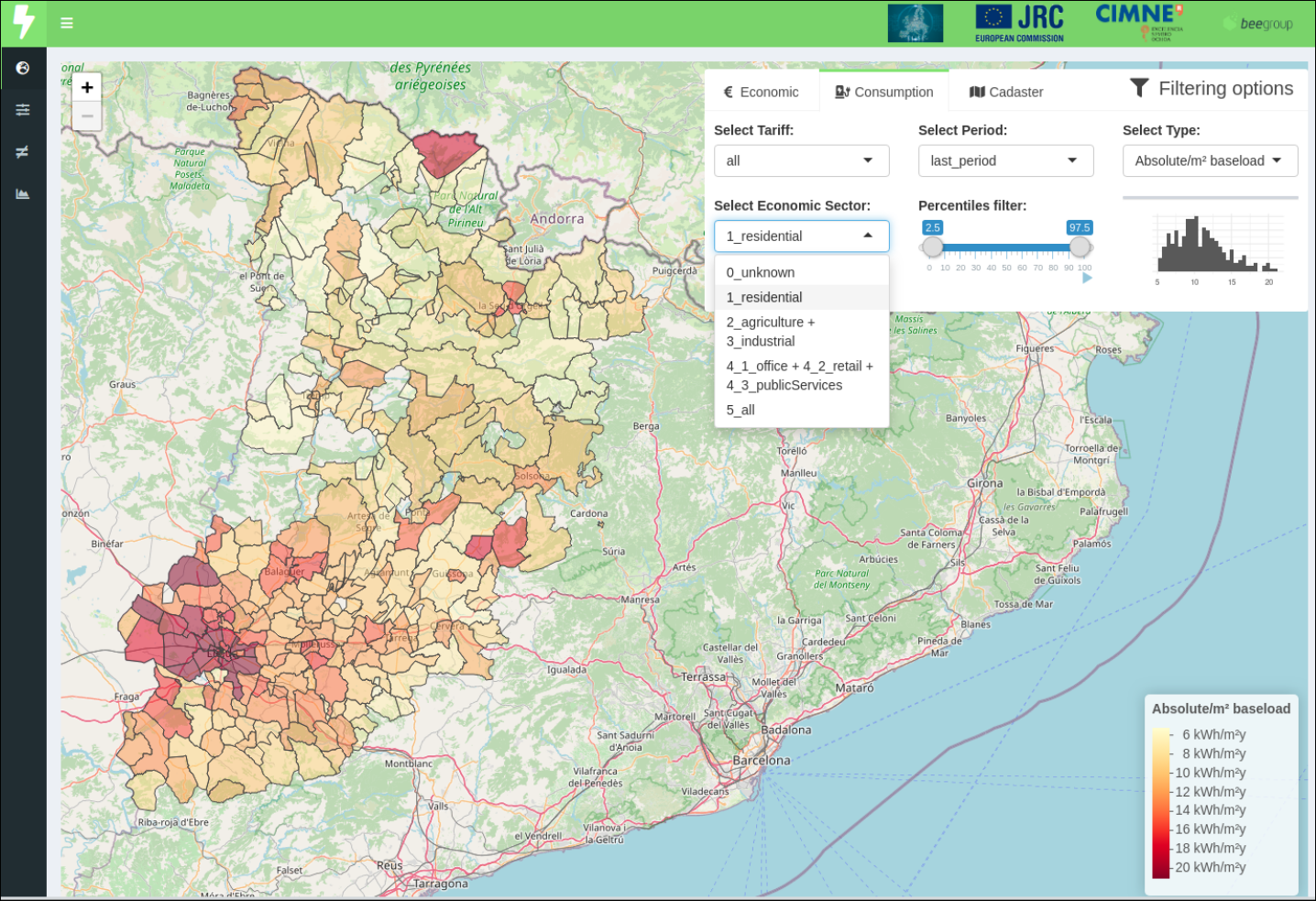
All results and harmonised data can be represented on the map
Online filtering capabilities using quantiles
Tab: Indicators on a map


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Results for the province of Lleida
Detailed and interactive visualisations for each case
Aggregated results to understand tendencies
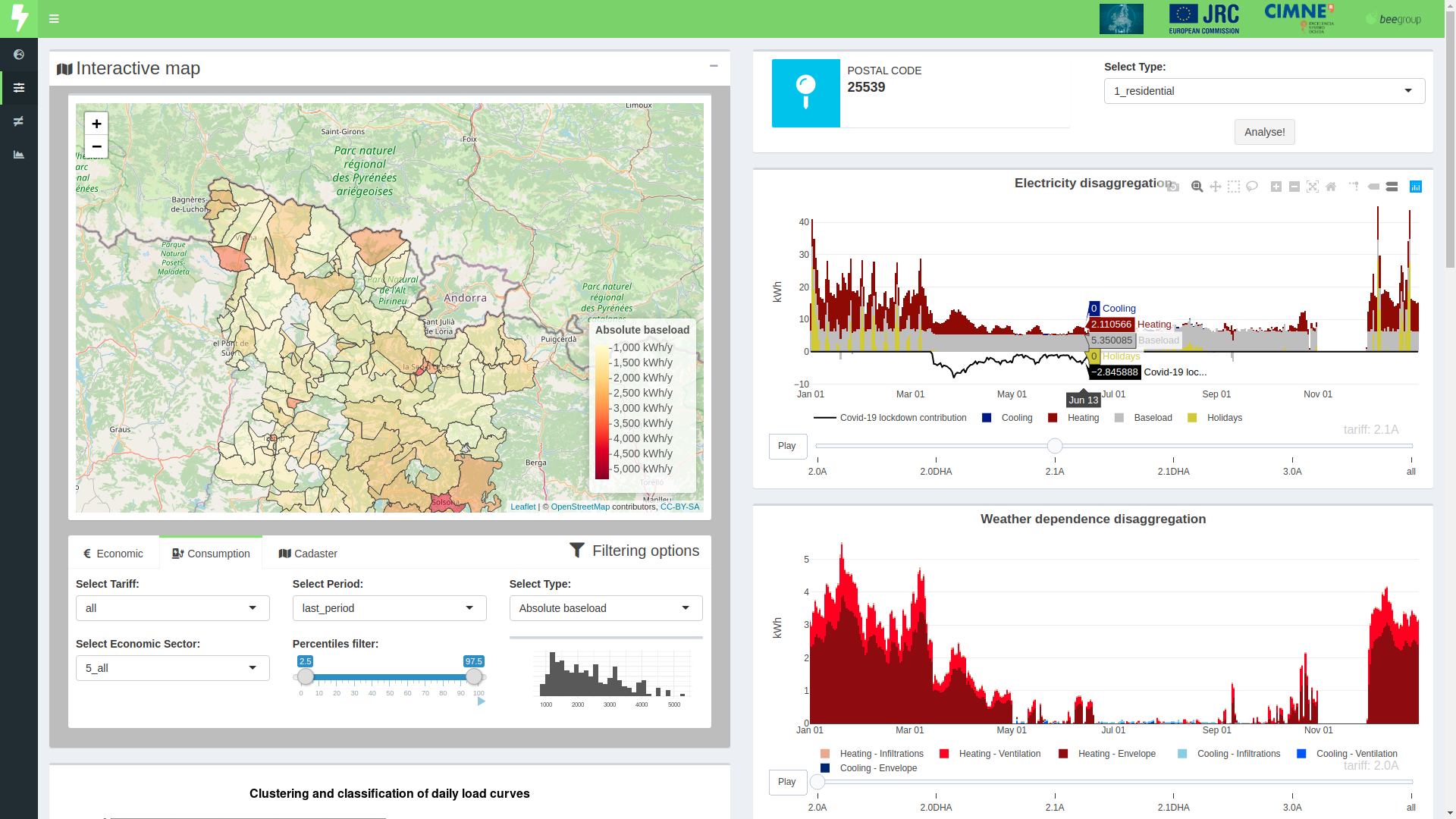
Tab: Detailed energy characterisation
... more plots are included


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Results for the province of Lleida
Weather-normalised comparison between two different groups
Intraday time-varying benchmarking
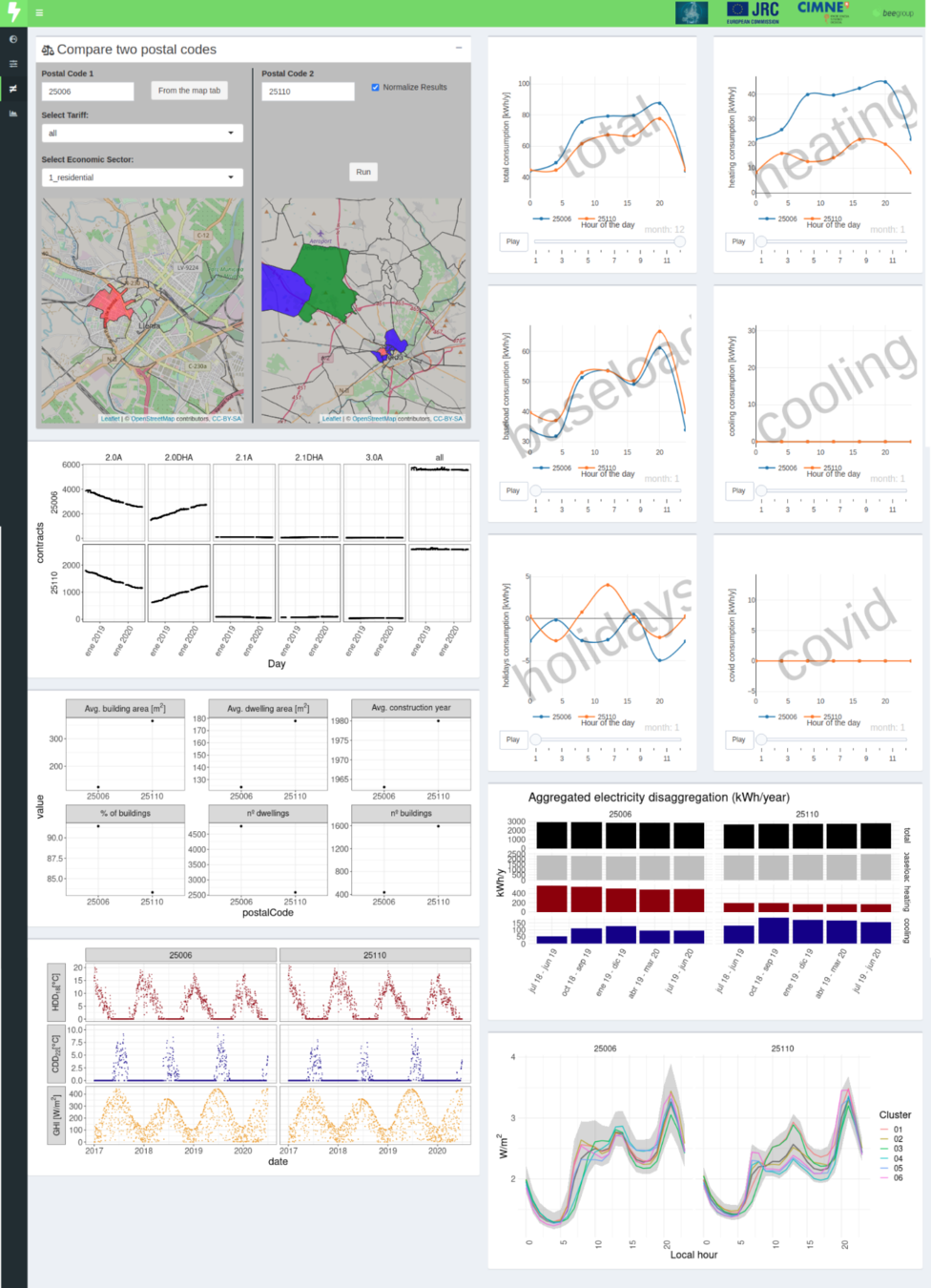
Tab: Benchmarking of two postal codes


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Results for the province of Lleida
It help to understand between characterisation indicators and harmonised data
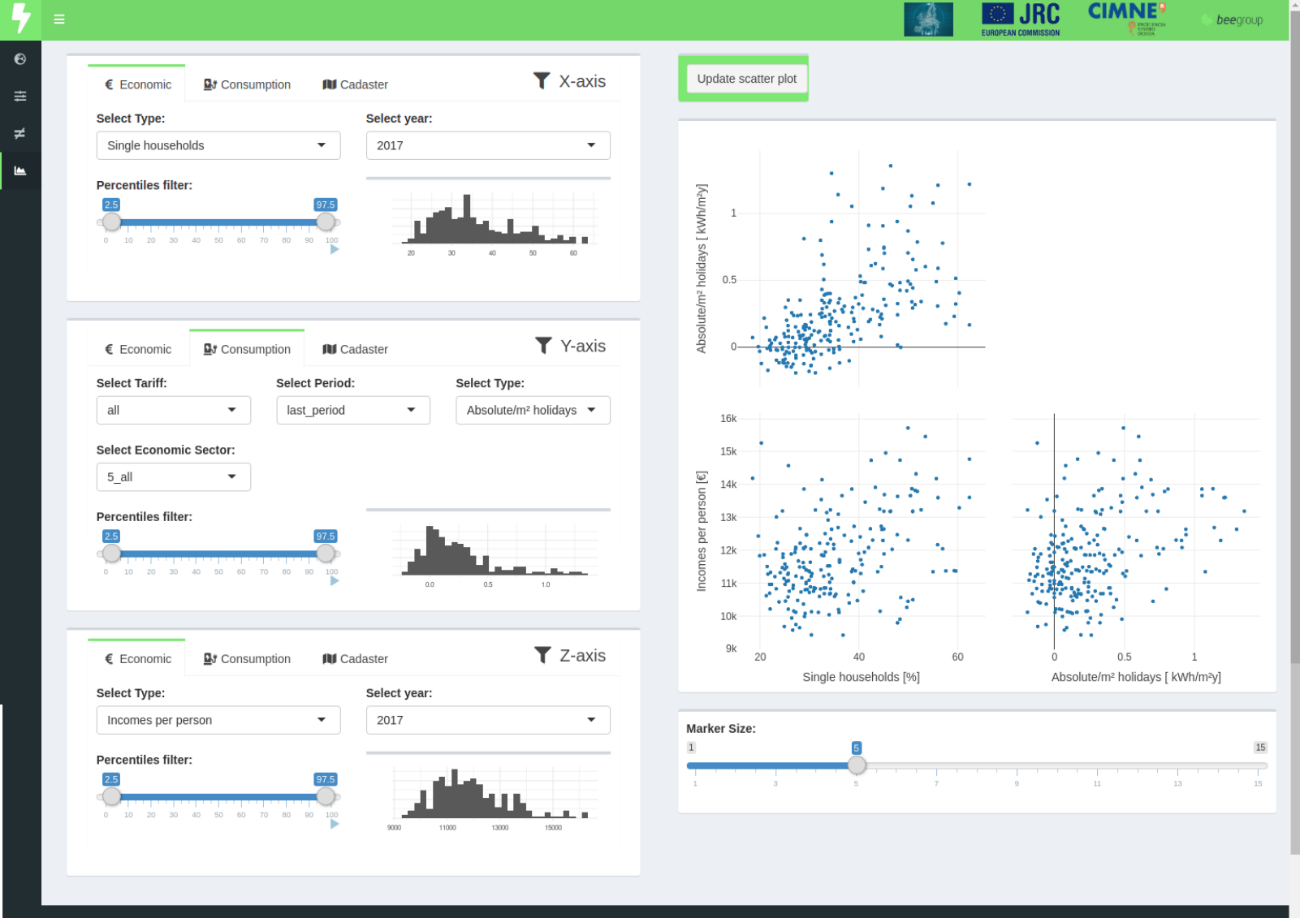
Tab: Regional correlations


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C5 - Electricity load characterization of districts
Conclusions
This methodology is:
- Capable to infer the drivers of consumption in building sector and their occupants.
- Demonstrates the potential of using open data and INSPIRE harmonised datasets
Applications:
- Detect potentialities for in-situ renewables generation
- Assessing Energy Performance of Buildings
- Estimate the electric equipment installed along the territory
- Chapter 6 -
General discussion and conclusions


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
In this PhD Thesis, an IT infrastructure was implemented for the massive analysis of consumption data in building sector.
- A set of analytical services were implemented and validated during 2 years.
- End-users savings from 2 to 12% were estimated due to the reporting services received.
Future work
- The creation of a general harmonised data model that could integrate the vast majority of existent monitoring platforms and open datasets.
- The integration in the architecture of the last technologies for real-time and batch processing of data (Spark, Kafka, Spark Streaming, ...) and also, software to simplify the horizontal scalability of the cluster (Kubernetes)


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C6 -
General discussion and conclusions
Secondly, a methodology was implemented and validated for the simulation of thermostatically load control based uniquely in data coming from smart thermostats.
- The long-term results of the BaU scenarios, both in terms of actual consumption and indoor temperature perform accurately.
- End-users savings from 18 and 36% were estimated during warm periods in Spain, decreasing 1 or 2ºC the thermostat setpoint temperature.
Future work
- Test of the methodology in a Model Predictive Control (MPC) framework.
- Obtain a better resolution for the heat consumption data and re-run the analysis, optimising those parts that may be affected by actual validation conditions.
- Simplifying the supply-side model, if no better data resolution is gathered.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C6 -
General discussion and conclusions
Thirdly, a methodology to assess the operation of DR in buildings and clusters of buildings through the estimation of the FF and FM.
- Based on the analysis of baseline estimated consumption and actual DR operation.
- Three different types of activation signals where considered: price-based, full activation petition, and trace to follow.
Future work
- To test the FF and FM over longer periods of operation, and implement improvements in the methodology (e.g. time-varying model coefficients, or introduce other exogenous variables).
- To investigate if the FM could be used by aggregators to quickly predict what a CM would respond to a certain activation signal.


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C6 -
General discussion and conclusions
Fourthly, and last, a data-driven methodology and a web dashboard for the energy characterisation of districts was created.
- It is based on massive gathering and analysis of open datasets, freely available.
- Public administrations need these methods to take decisions in energy transition plans and urban planning
-
Private companies may require these data driven methods to substantiate their energy services


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
- C6 -
General discussion and conclusions
Future work
- Transform the electricity characterisation method to a thermal characterisation method, based on the inclusion of:
- Aggregated gas consumption
- Technical inspections of buildings, and energy performance certificates datasets.
- Include systems performance in the model formula.
Acknowledgements


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
Thanks for your attention


PhD Defense Presentation - January 24th, 2022
Gerard Mor Martinez
Statistical learning methods for energy assessment in buildings with applications at different geographic levels
PhD presentation Gerard Mor
By CIMNE BEE Group
PhD presentation Gerard Mor
- 108



