Async/Await and the Call Stack
What all the cool kids are doing


What is the Call Stack?
It is a current snapshot of where the JavaScript engine is in our code

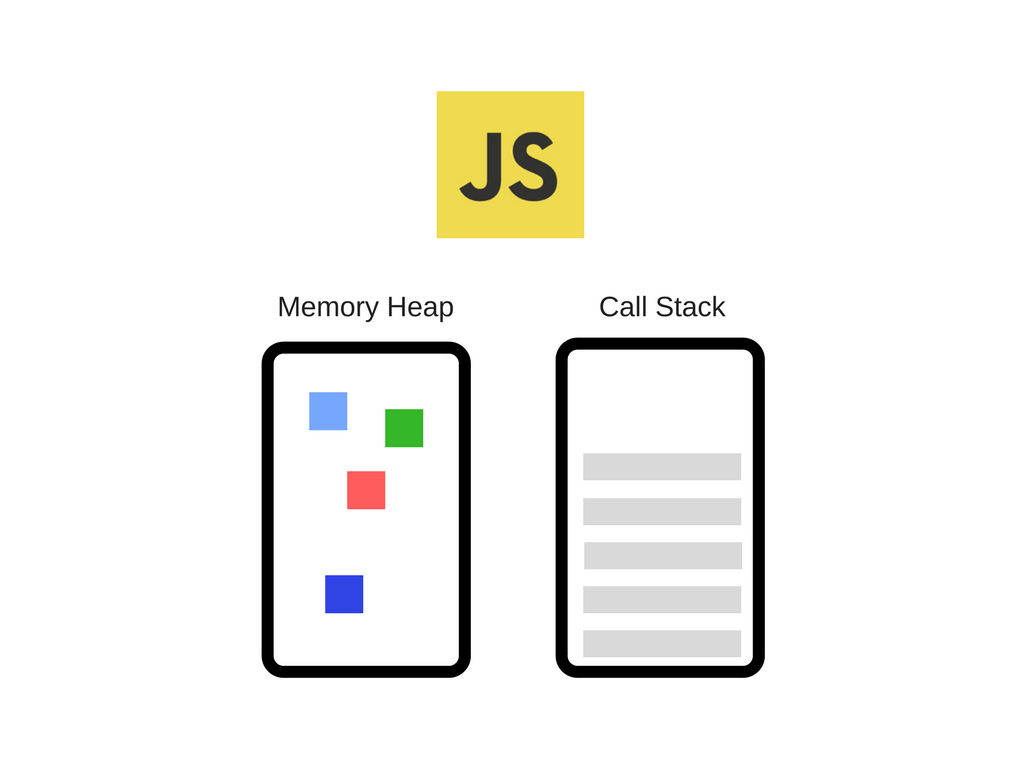
This is a JavaScript engine. vroom.
Event Loop
The Event Loop is how the runtime environment tells the engine which block of code to run at what time

Until ES6 there wasn't really a built-in way to execute JavaScript asynchronously
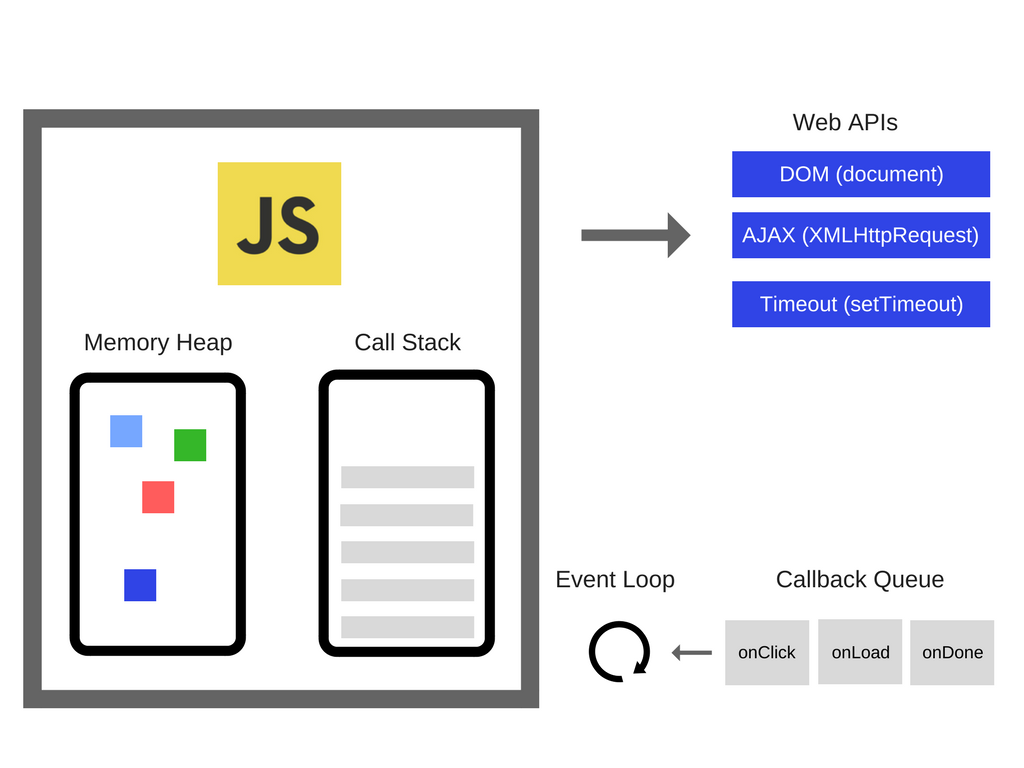
Engine from the previous slide
Let's get GIFfy!

console.log('Hi');
setTimeout(function cb1()
{
console.log('cb1');
}, 5000);
console.log('Bye');
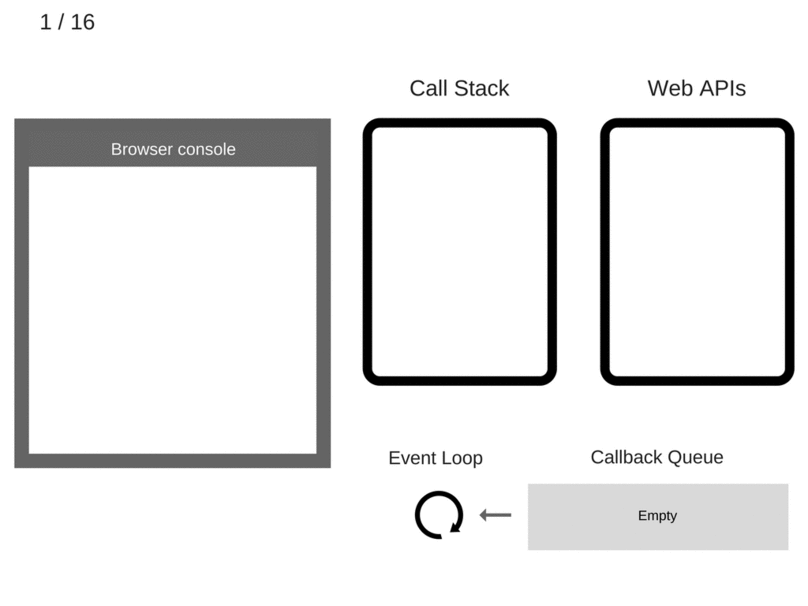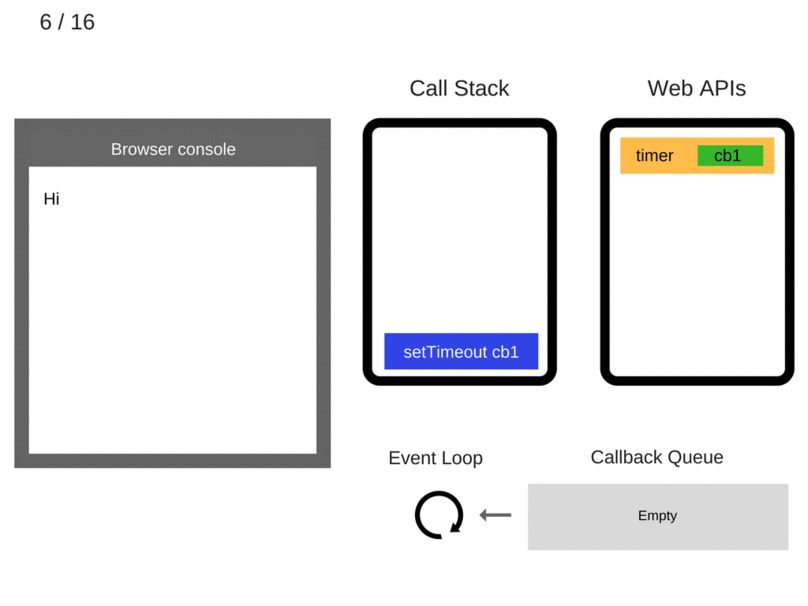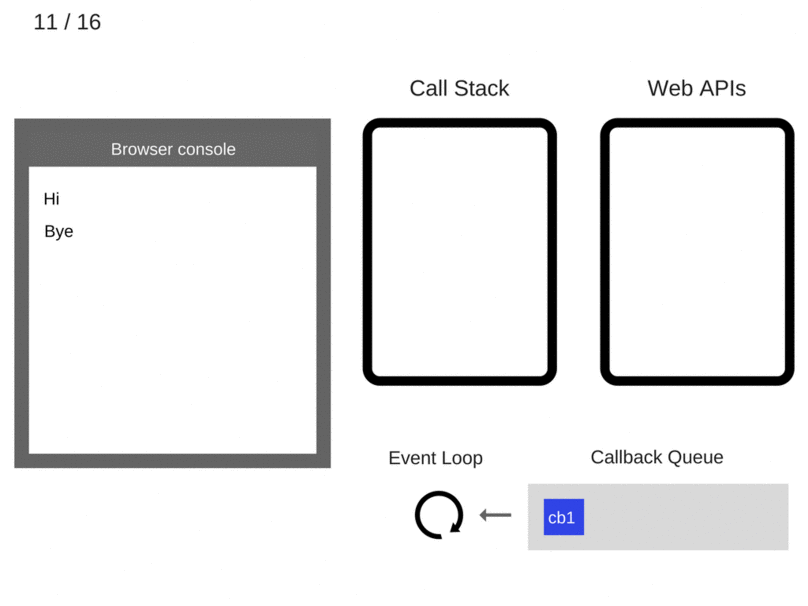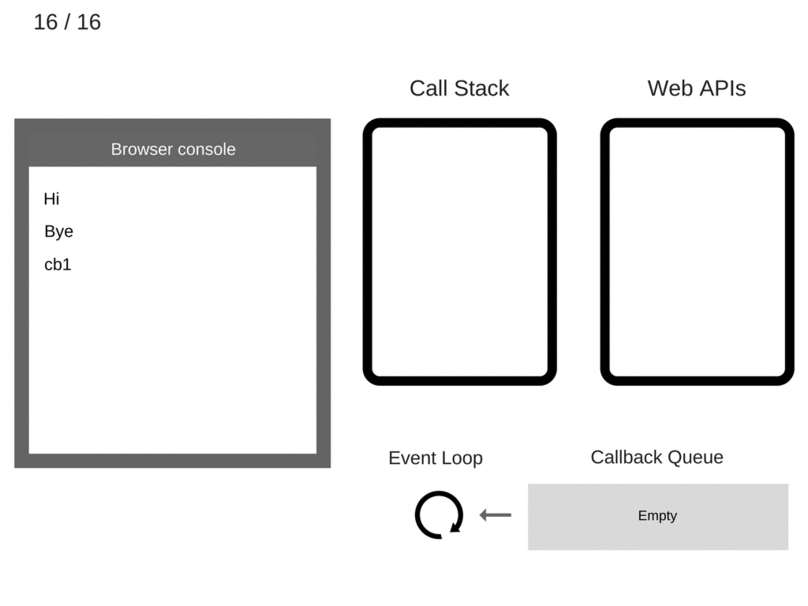
Making it Even More Complex

There is now something called the Job Queue! This is like a priority Event Loop queue.
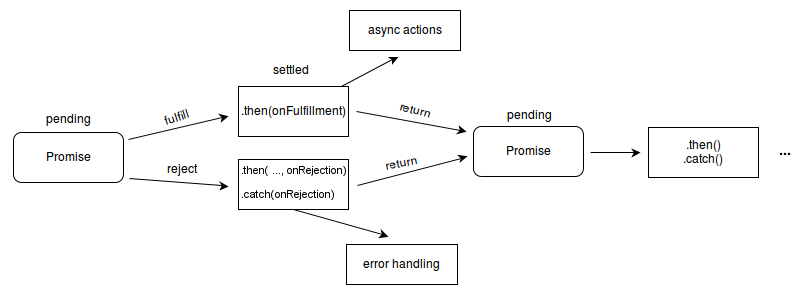
And Introducing Promises
At their most basic, promises are a bit like event listeners except:
- A promise can only succeed or fail once. It cannot succeed or fail twice, neither can it switch from success to failure or vice versa.
- If a promise has succeeded or failed and you later add a success/failure callback, the correct callback will be called, even though the event took place earlier.
- Promises can be: fulfilled, rejected, pending, and is also considered settled if rejected or fulfilled

Async/Await
The purpose of async/await is to simplify working with promises

function getNumber1() {
return Promise.resolve('374');
}
// This function does the same as getNumber1
async function getNumber2() {
return 374;
}function f1() {
return Promise.reject('Some error');
}
async function f2() {
throw 'Some error';
}- making a function async causes it to return a Promise
- if you return something from an async function it's the same as returning a "fulfilled" promise
- if you throw and error in an async function it's the same as returning a "rejected" promise
Async/Await
await tells the async function which values to wait for

const asyncFun = async function(req, res) {
const data = await axios.get('some url goes here');
res.status(200).send(data)
}- making a function async causes it to return a Promise
- if you return something from an async function it's the same as returning a "fulfilled" promise
- if you throw and error in an async function it's the same as returning a "rejected" promise

module.exports = {
getStuffAsync: async (req, res) => {
const db = req.app.get("db");
try {
const data = await db.get_my_data();
res.status(200).send(data);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).send(error);
}
},
getStuffThen: (req, res) => {
const db = req.app.get("db");
db.get_my_data()
.then((data) => {
res.status(200).send(data);
})
.catch((err) => {
res.status(500).send(err);
});
},
};
Async/Await and Call Stack
By Cole Finlayson
Async/Await and Call Stack
- 394



