Visualizing app logic with
state machines
David Khourshid · @davidkpiano
stately.ai
Frontend Friday


Code
+ Features
- Bugs
+/- Devs
+ Changes
+ Shiny new things
Time
Complexity
The path to
legacy code

Left to right
Top to bottom
File by file
Code is linear,
programs are not
📚
User stories
🖼
Mockups
🔀
User flows
💻
Code
🧪
Tests
👩🏫
Tutorials
💥
📚
User stories
🖼
Mockups
🔀
User flows
💻
Code
🧪
Tests
👩🏫
Tutorials
Designers
Stakeholders
Developers
Logged out
Logged in
LOG IN
[correct credentials]
- Make API call to Supabase
- Initiate OAuth flow
- Ensure token is valid
- Persist token as cookie
- Redirect to logged in view
Given a user is logged out,
When the user logs in with correct credentials
Then the user should be logged in
All programs are
directed graphs
cart
shipping
contact
payment
confirmation
CHECKOUT
NEXT
NEXT
ORDER
PAYPAL
- Initial state
- Finite set of states
- Finite set of events
- Transitions
- Final states
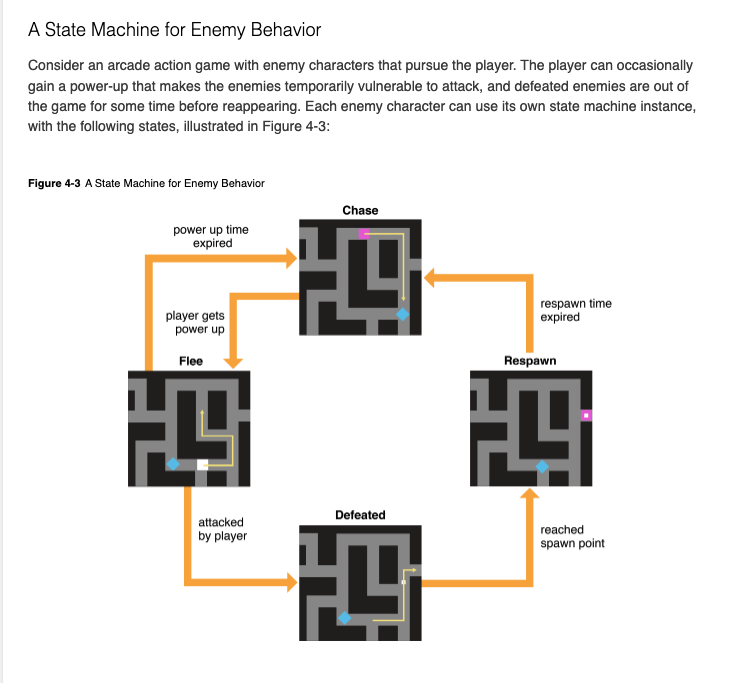
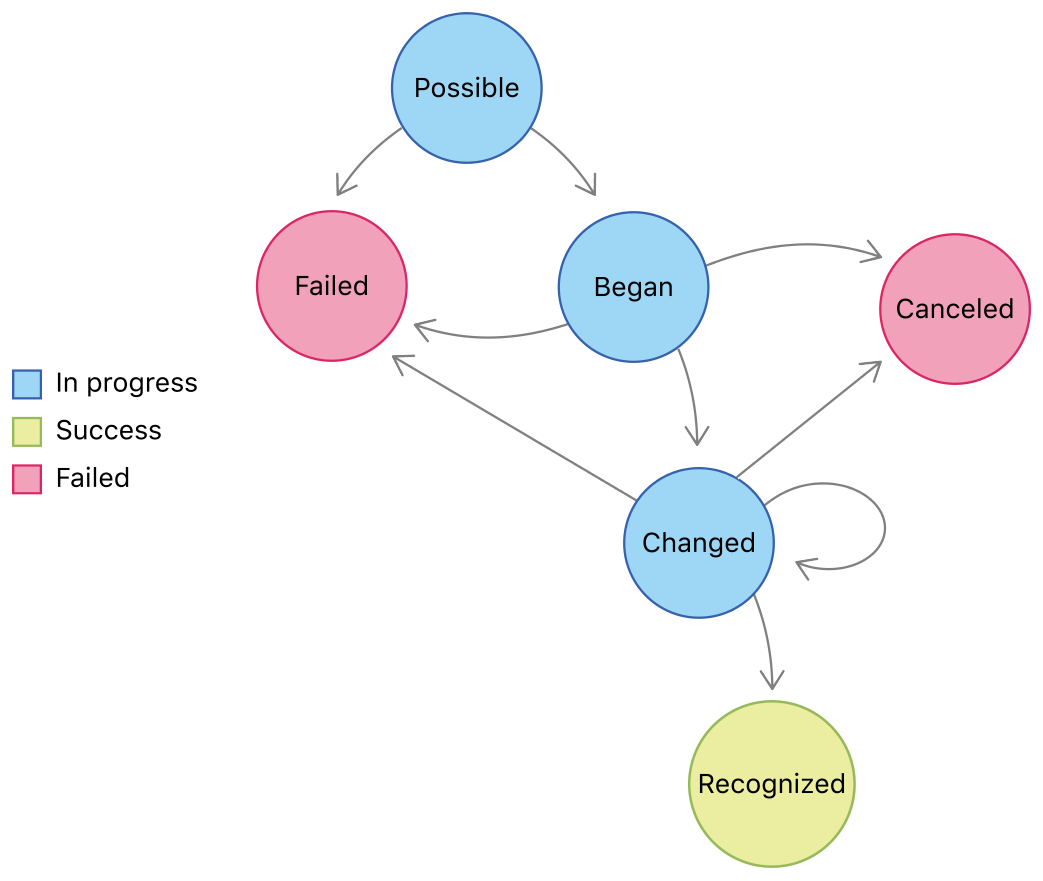
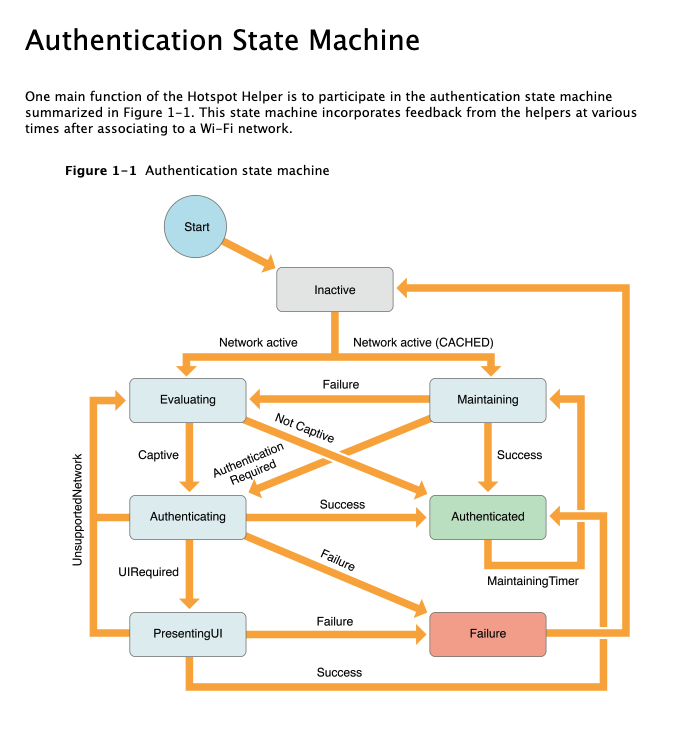
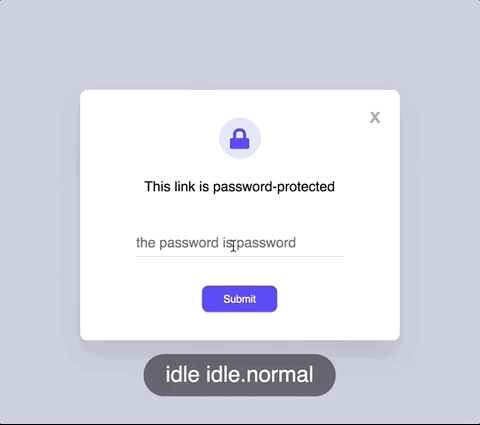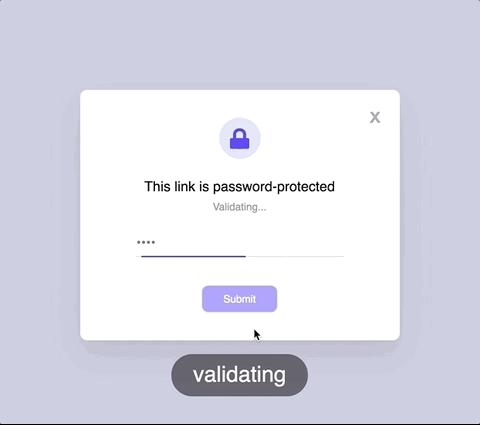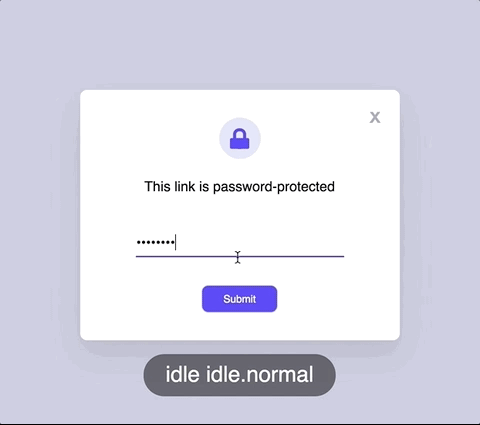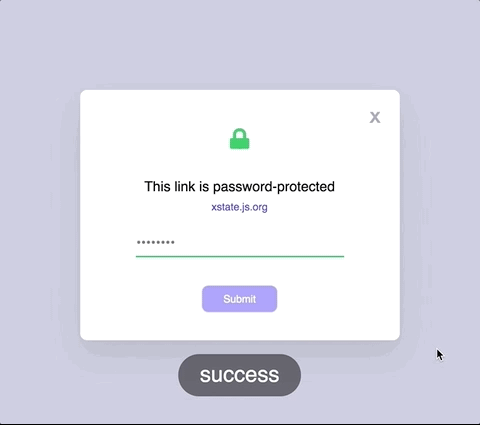

State machines prevent
impossible states.
isLoading isSuccess hasErrors
type Status = | 'loading' | 'error' | 'success'
function transition(state, event) {
switch (state.value) {
case 'cart':
if (event.type === 'CHECKOUT') {
return { value: 'shipping' };
}
return state;
case 'shipping':
// ...
default:
return state;
}
}State machines
with switch statements
State
Event
const machine = {
initial: 'cart',
states: {
cart: {
on: {
CHECKOUT: 'shipping'
}
},
shipping: {
on: {
NEXT: 'contact'
}
},
contact: {
// ...
},
// ...
}
}function transition(state, event) {
const nextState = machine
.states[state]
.on?.[event.type]
?? state;
}
transition('cart', { type: 'CHECKOUT' });
// => 'shipping'
transition('cart', { type: 'UNKNOWN' });
// => 'cart'State machines
with objects
import { createMachine } from 'xstate';
const machine = createMachine({
initial: 'cart',
states: {
cart: {
on: {
CHECKOUT: 'shipping'
}
},
shipping: {
on: {
NEXT: 'contact'
}
},
contact: {
// ...
},
// ...
}
});import { interpret } from 'xstate';
const actor = interpret(machine).start();
actor.send({ type: 'CHECKOUT' });
// => { value: 'shipping' }
actor.send({ type: 'NEXT' });
// => { value: 'contact' }
npm install xstate
xstate.js.org/docs
cart
shipping
contact
payment
confirmation
CHECKOUT
NEXT
NEXT
ORDER
PAYPAL
BACK
BACK
CANCEL
Identify
logical flaws
cart
shipping
contact
payment
confirmation
CHECKOUT
NEXT
NEXT
ORDER
PAYPAL
As a user, when I'm in the cart and I click the checkout button, I should be on the shipping page.
cart
shipping
contact
payment
confirmation
CHECKOUT
NEXT
NEXT
ORDER
PAYPAL
As a user, when I'm in the cart and I checkout via PayPal, I should be taken directly to the payment screen.
cart
shipping
contact
payment
confirmation
CHECKOUT
NEXT
NEXT
ORDER
PAYPAL
Shortest path
confirmation state
cart
shipping
contact
payment
confirmation
CHECKOUT
NEXT
NEXT
ORDER
PAYPAL
Shortest path
confirmation state where
shipping address is provided

Statecharts
Extended state machines
idle
loading
LOAD / fetchData
success
RELOAD / fetchData
RESOLVE / assign
Actions
idle
loading
LOAD
success
RELOAD
RESOLVE / assign
entry / fetchData
exit / logTelemetry
- ➡️ Transition actions
- 📥 Entry actions
- 📤 Exit actions
Actions
start
Send for approval
sending
Invocations
awaiting approval
invoke / sendInvoice
invoke / waitForApproval
done (sendInvoice)
done (waitForApproval)
error
error (sendInvoice)
Retry
Compound states
loading
ready
playing
paused
loaded
next
⏸
▶️
Parallel states
music
player
volume
playing
paused
muted
unmuted
PAUSE
PLAY
UNMUTE
MUTE
Other features
🛑 Guarded transitions ⬆️ Raised events ⏱ Delayed (after) transitions ▶️ Eventless (always) transitions ⏳ History states ...
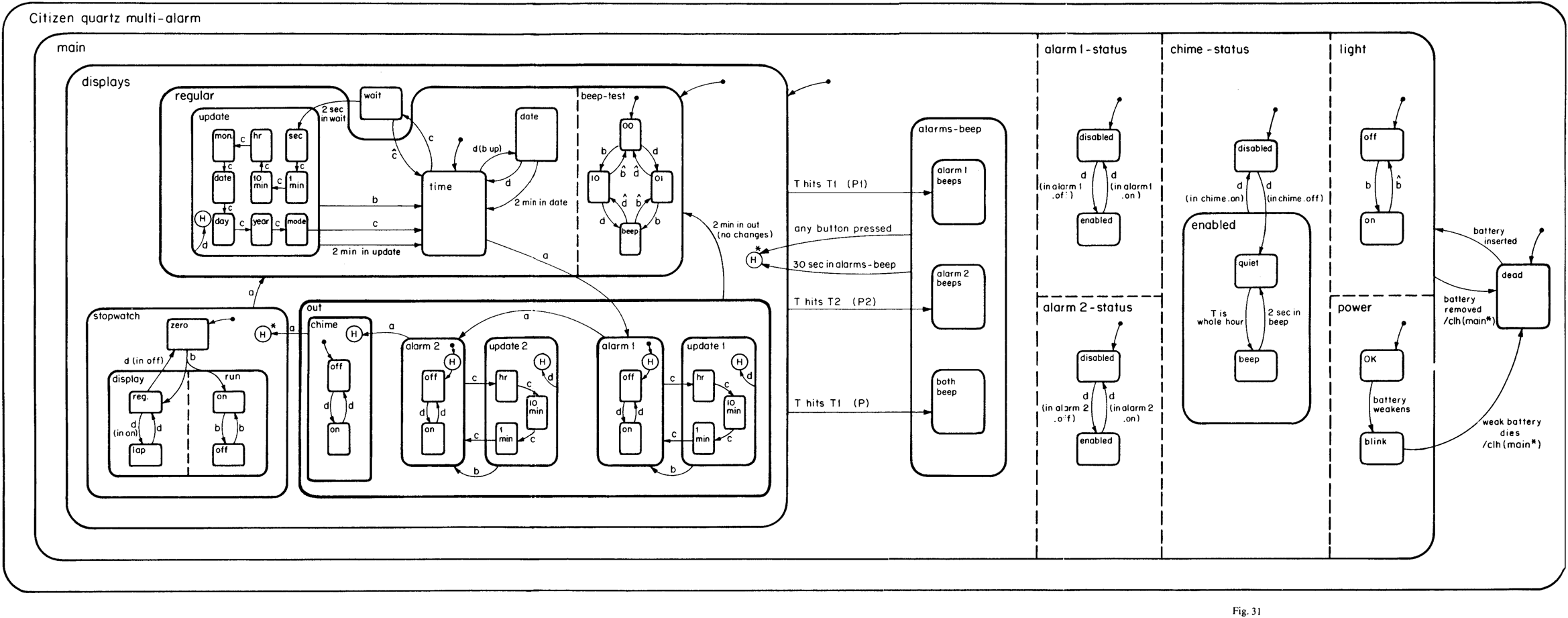
Map requirements to code
1
Code independently of frameworks
2
Make interfaces simple (read, send)
3
Use a common visual language
4
Takeaways
Final presentation state.
Questions?

Visualizing app logic with state machines
By David Khourshid
Visualizing app logic with state machines
- 1,428



