Arrow of outrageous fortune


Functional Programming in Kotlin
David Rawson
What is Kotlin?

class Author(val firstName: String,
val lastName: String) extends Comparable[Author] {
override def compareTo(that: Author) = {
val lastNameComp = this.lastName compareTo that.lastName
if (lastNameComp != 0) lastNameComp
else this.firstName compareTo that.firstName
}
}
object Author {
def loadAuthorsFromFile(file: java.io.File): List[Author] = ???
}
What is Kotlin?
class Author(val firstName: String,
val lastName: String) extends Comparable[Author] {
override def compareTo(that: Author) = {
val lastNameComp = this.lastName compareTo that.lastName
if (lastNameComp != 0) lastNameComp
else this.firstName compareTo that.firstName
}
}
object Author {
def loadAuthorsFromFile(file: java.io.File): List[Author] = ???
}
What is Kotlin?
import java.io.File
class Author(
val firstName: String,
val lastName: String
) : Comparable<Author> {
override fun compareTo(that: Author) {
val lastNameComp = this.lastName.compareTo(that.lastName)
return if (lastNameComp != 0) {
lastNameComp
} else {
this.firstName.compareTo(that.firstName)
}
}
}
object Authors {
fun loadAuthorsFromFile(file: File): List<Author> = TODO()
}

What is Kotlin?
import java.io.File
class Author(
val firstName: String,
val lastName: String
) : Comparable<Author> {
override fun compareTo(that: Author) = compareValuesBy(
this,
that,
Author::lastName,
Author::firstName
)
}
object Authors {
fun loadAuthorsFromFile(file: File): List<Author> = TODO()
}
Why Kotlin?

- Tooling

Why Kotlin?

- Tooling

Why Kotlin?

- Tooling

plugins {
java
kotlin("jvm") version "1.4.10"
}
group = "org.example"
version = "1.0-SNAPSHOT"
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation(kotlin("stdlib"))
testCompile("junit", "junit", "4.12")
}

Why Kotlin?

- Tooling

- Compilation targets
Why Kotlin?

- Tooling


- Compilation targets
Why Kotlin?

- Tooling

- Targets

Why Kotlin?

- Tooling

- Targets
- Sympathetic to FP
Why Kotlin?

- Sympathetic to FP
Why Kotlin?

- Sympathetic to FP

Why Kotlin?

- Sympathetic to FP


Why Kotlin?

- Sympathetic to FP




Why Kotlin?

- Sympathetic to FP





Why Kotlin?

- Sympathetic to FP
fun main() {
val immutable = listOf(1, 2, 3)
val mutable = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3)
val david = Person(Name("David"), Age(21))
val olderDavid = david.copy(age = Age(22))
}Why Kotlin?

- Sympathetic to FP

Why Kotlin?

- Sympathetic to FP


Why not Kotlin?

Why not Kotlin?

- Slower builds than POJ
Why not Kotlin?

- Must be carefully introduced into Java project
- Slower builds than POJ
Why not Kotlin?

- Must be carefully introduced into Java project
- Language features can be abused
- Slower builds than POJ
FP in Kotlin?

FP in Kotlin?


https://arrow-kt.io/
FP in Kotlin?



Our initial positive impressions of Arrow were confirmed when using it to build applications that are now in production.
FP in Kotlin?


core
FP in Kotlin?



fx
FP in Kotlin?




optics
FP in Kotlin?





meta
FP in Kotlin?


Arrow Core
FP in Kotlin?


-
Typeclass-o-pedia
Arrow Core
FP in Kotlin?


-
Typeclass-o-pedia
Arrow Core
FP in Kotlin?


-
Typeclass-o-pedia
Arrow Core
FP in Kotlin?


-
Typeclass-o-pedia
Arrow Core
FP in Kotlin?


-
Typeclass-o-pedia
Arrow Core

FP in Kotlin?


-
Typeclass-o-pedia
Arrow Core
-
Error handling
data class Name(val name: String)
data class Age(val age: Int)
data class Person(val name: Name, val age: Age)
object TestClassic {
fun makeName(name: String?): Name {
if (name == null || name == "") {
throw IllegalArgumentException("Name cannot be null or empty")
}
return Name(name)
}
fun makeAge(age: String): Age {
val parsedAge = age.toInt()
require(0 <= parsedAge) {
"Ages must be non-negative"
}
return Age(parsedAge)
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
try {
val name = TestClassic.makeName(args[0])
val age = TestClassic.makeAge(args[1])
val person = Person(name, age)
println(person)
} catch (e: Exception) {
println("Could not make a person!")
}
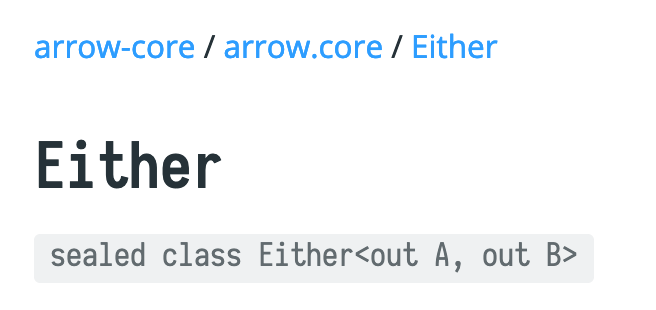
}import arrow.core.Either
object TestEither {
fun makeName(name: String?): Either<Throwable, Name> {
return when (name) {
null, "" -> return Either.Left(IllegalArgumentException())
else -> Either.Right(Name(name))
}
}
fun makeAge(age: String): Either<Throwable, Age> =
Either.catch {
age.toInt()
}.flatMap {
when {
it <= 0 -> Either.Left(IllegalArgumentException())
else -> Either.Right(it)
}
}.map {
Age(it)
}
}import arrow.core.Either
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
TestEither.makeName(args[0]).flatMap { name ->
TestEither.makeAge(args[1]).map { age ->
Person(name, age)
}
}.fold(
ifLeft = {
"Could not make a person!"
},
ifRight = {
it.toString()
}
).let {
println(it)
}
}import arrow.core.computations.either
suspend fun main(args: Array<String>) {
either<Throwable, Person> {
val name = TestEither.makeName(args[0]).bind()
val age = TestEither.makeAge(args[1]).bind()
Person(name, age)
}.fold(
ifLeft = {
"Could not make a person!"
} ,
ifRight = {
it
}
).let {
println(it)
}
}








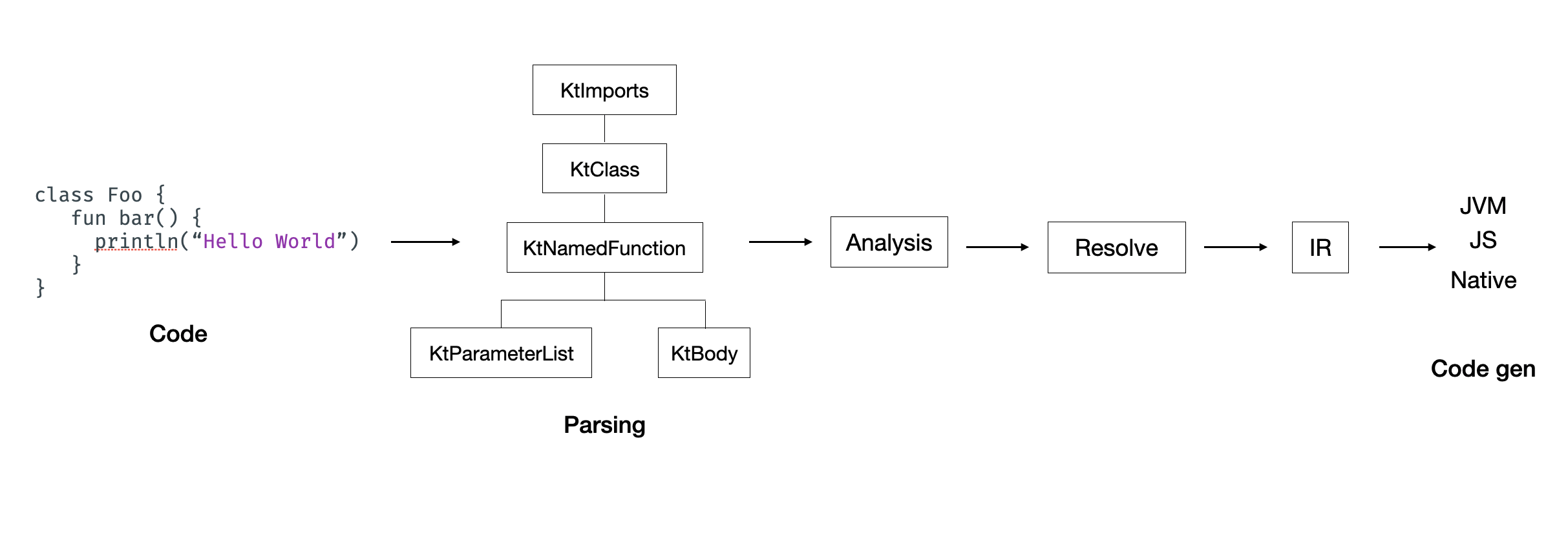
https://medium.com/@heyitsmohit/writing-kotlin-compiler-plugin-with-arrow-meta-cf7b3689aa3e


https://medium.com/@heyitsmohit/writing-kotlin-compiler-plugin-with-arrow-meta-cf7b3689aa3e
intercepts

data class Age(val age: Int)
object TestClassic {
fun makeAge(age: String): Age {
val parsedAge = age.toInt()
require(0 < parsedAge) {
"Ages must be positive"
}
return Age(parsedAge)
}
}
data class PositiveInt(val value: Int) {
init {
require(0 < value) {
"Should be positive"
}
}
}@Refinement
inline class PositiveInt(val value: Int) {
companion object : Refined<Int, PositiveInt> {
override val target : (Int) -> PositiveInt = ::PositiveInt
override val validate: Int.() -> Map<String, Boolean> = {
mapOf(
"Should be > 0" to (this > 0)
)
}
}
}
@Coercion
fun Int.positive(): PositiveInt? =
PositiveInt.from(this)Functional Programming in Kotlin
By David Rawson
Functional Programming in Kotlin
- 1,051



