Python for 3D image analysis using qim3d
Felipe Delestro
Senior Research Software Specialist
fima@dtu.dk
slides.com/delestro/dtu-skylab-october-2024

QIM Center
Center for Quantification of Imaging Data from MAX IV





supported by



Rebecca
Engberg
Center Manager
Anders Bjorholm Dahl
Head of the QIM Center
Jon
Sporring
Deputy Head of the QIM Center
















an open-source Python library, that focuses on 3D volumetric data

Getting started is easy:
pip install qim3d
Full documentation at https://platform.qim.dk/qim3d/




&
Cortical (or compact)
The rigid, dense outer layer of the bone that provides most of its strength and support. It's designed to handle stress and protect the inner bone.
Trabecular (or spongy/cancellous)
The less dense, porous inner part of the bone. It has a honeycomb-like structure, which helps to absorb shock and reduce the weight of the bone.
Bone structure
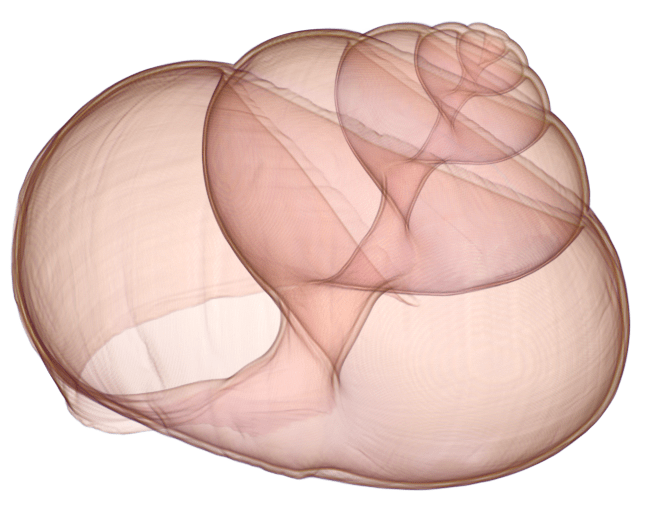
Can you locate a crack in the shell by exploring the volume?
Escargot shell
This dataset represents a Gastropod shell, stored in a multi-scale format called OME-Zarr. This format allows the data to be saved at multiple resolutions, which are streamed to the visualization tool dynamically, as needed.
Qim platform & jupyter notebooks
We provide a Jupyter notebook launcher that makes it easy to start new servers on the DTU HPC cluster. You can find here a tutorial for using the launcher.
Notebooks and data for exercises

Ensure that your notebooks are saved in a location where you have permission to modify and run them, such as your home directory.
If you're using the Qim Platform, there's no need to upload the data, it’s already stored there.
dtu-skylab-october-2024
By Felipe Delestro
dtu-skylab-october-2024
- 323



