Version Control
using Git
Faisal P P
Product Engineer @ Styl

Hrishikesh K B
Secretary , SMC
Text
Typical Developer
- Create
- Save
- Edit
- Repeat
- Collaborate
Project X
Project X - Old
Project X - Latest
Project X - 2000/12/12
Project X - 2001/05/01
Version control is a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later
Benefits
- Backup
- Undo
- Monitor
- Collaborate
Types
- Centralized (Subversion)
- Distributed (Git)

Setup GIt
- sudo apt-get install git
- Install Git Bash
Configure Git
- git configure --global user.name "Username"
- git configure --global user.email "hello@example.com"
Initialize Repository
- git init
The three states
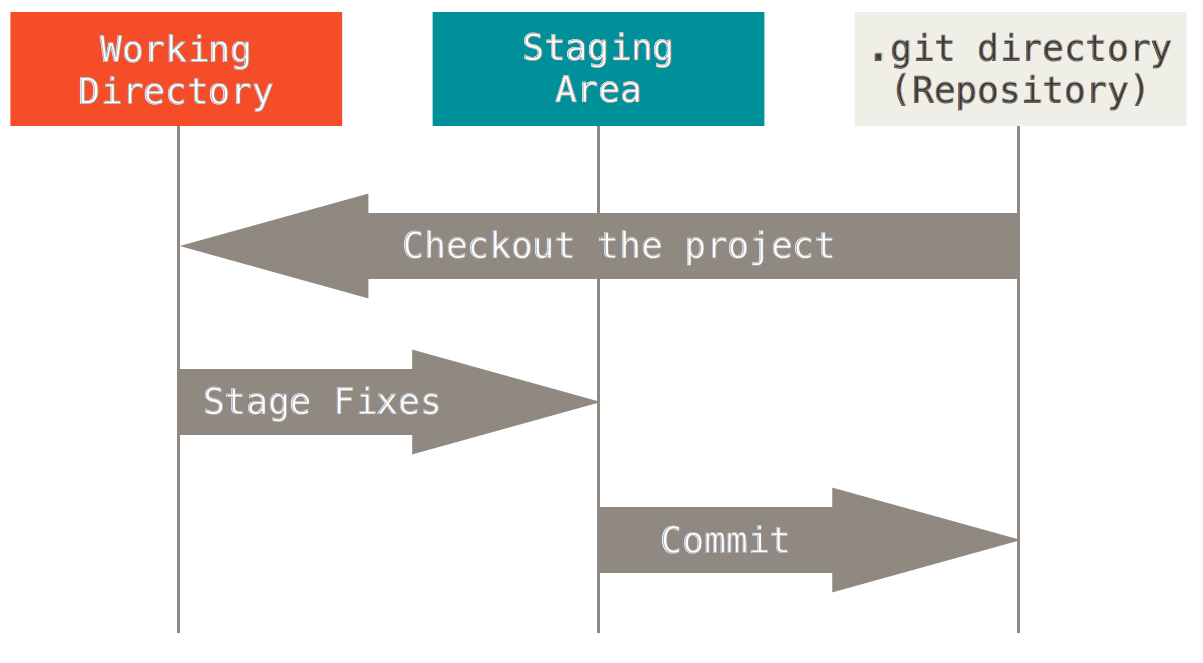
Start Coding
HelloWorld.c
Check Status
- git status
Track New File
- git add helloworld.c
- git add .
Commit Changes
- git commit -m "first commit"
You like projectx?
- git clone https://github.com/faisalp4p/projectx.git
Commit History
- git log
- Each commit is a snap shot
Collaborate by working remote
- git remote
- git remote add <name> <url>
- git remote rm <remote-name>
- git fetch <remote-name>
- git push <remote-name> <branch>
Homework
- Where all these info are stored?
- ls .git
- git init on .git
Branching
- You are working on master
- git branch testing
- what is HEAD?
- git checkout testing
Before Branching
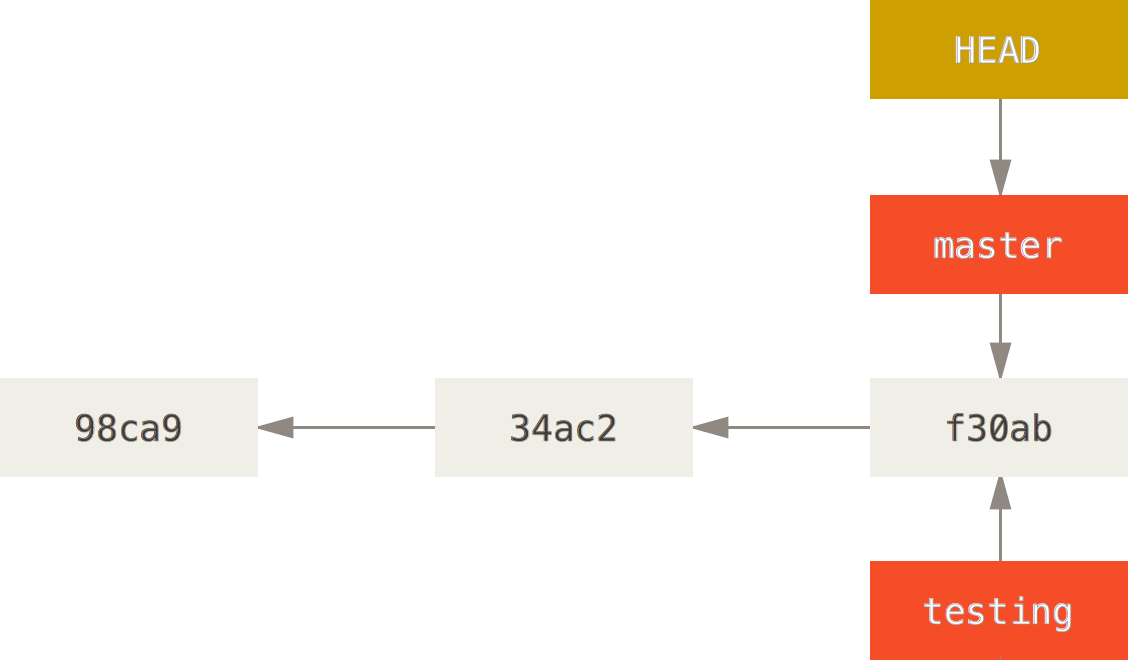
Created Branch testing

Switch Branch

When new Commit
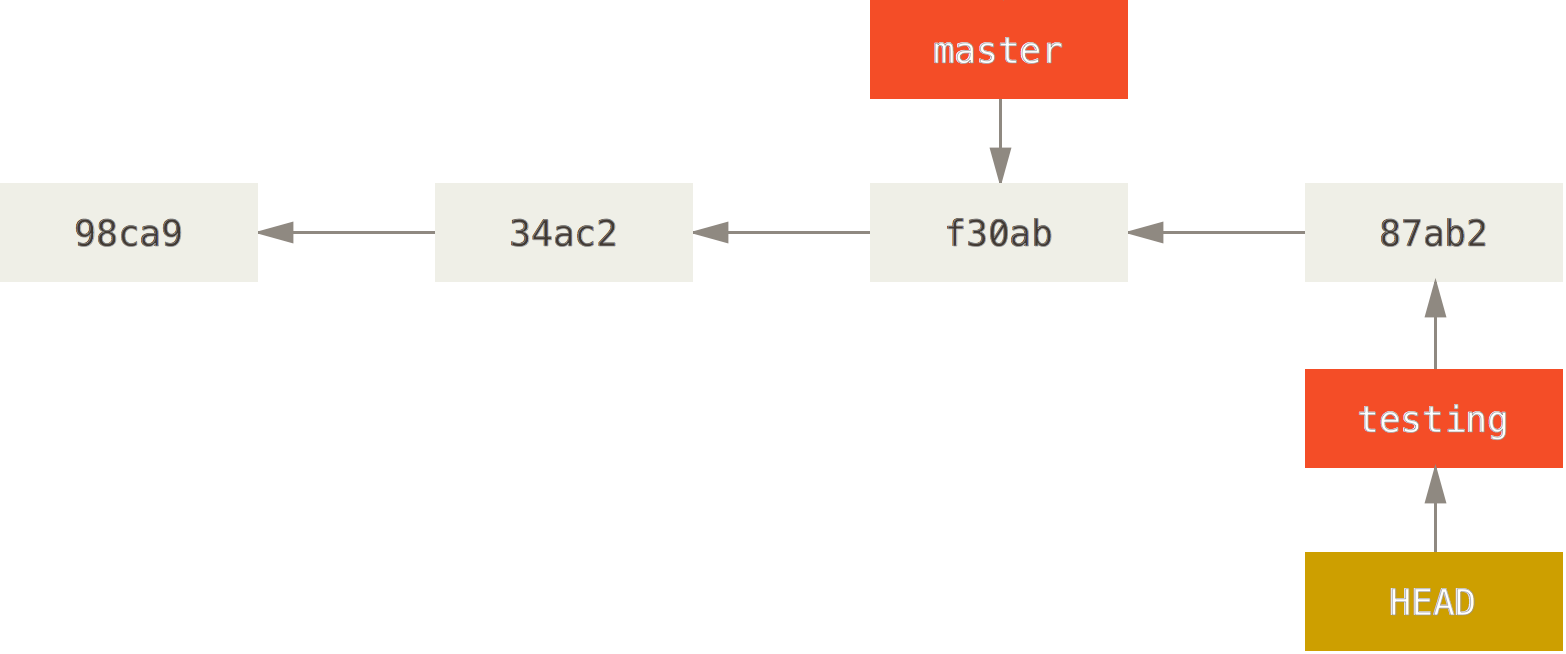
HEAD moves on checkout
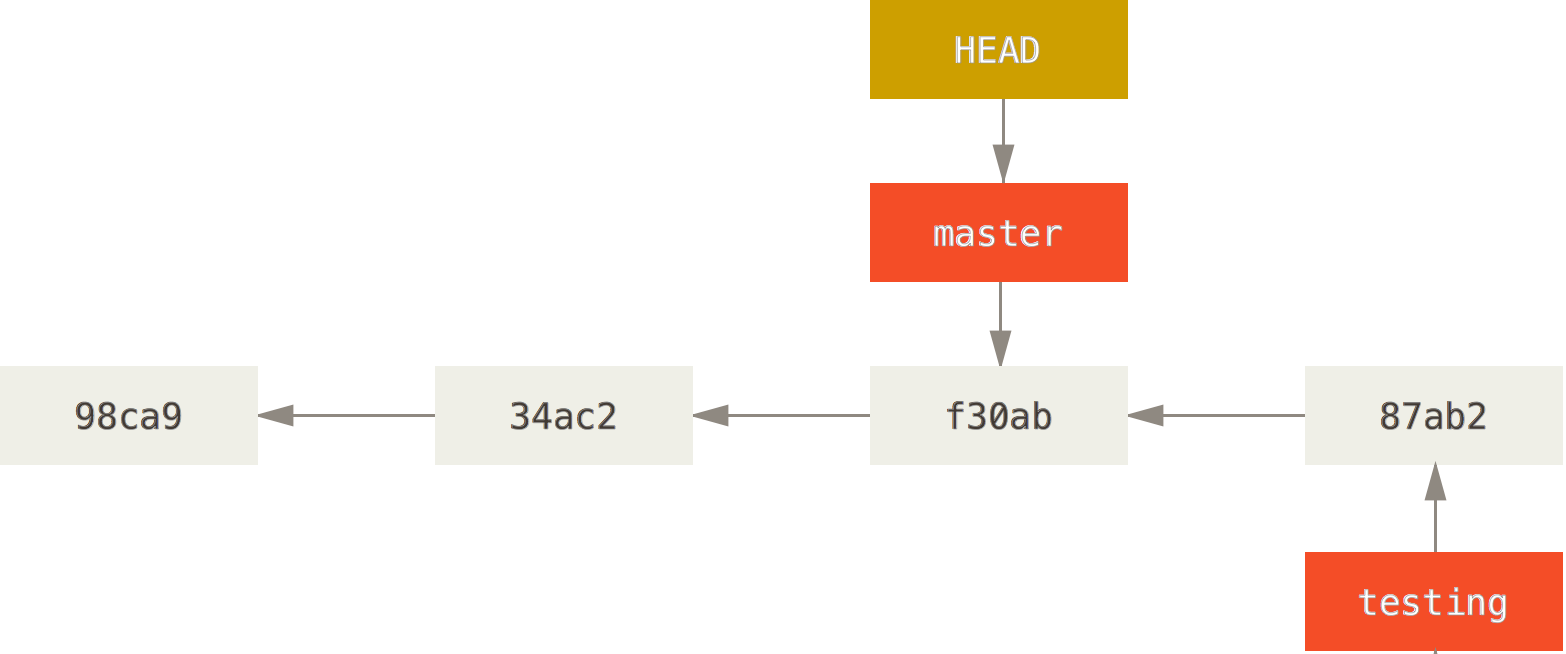
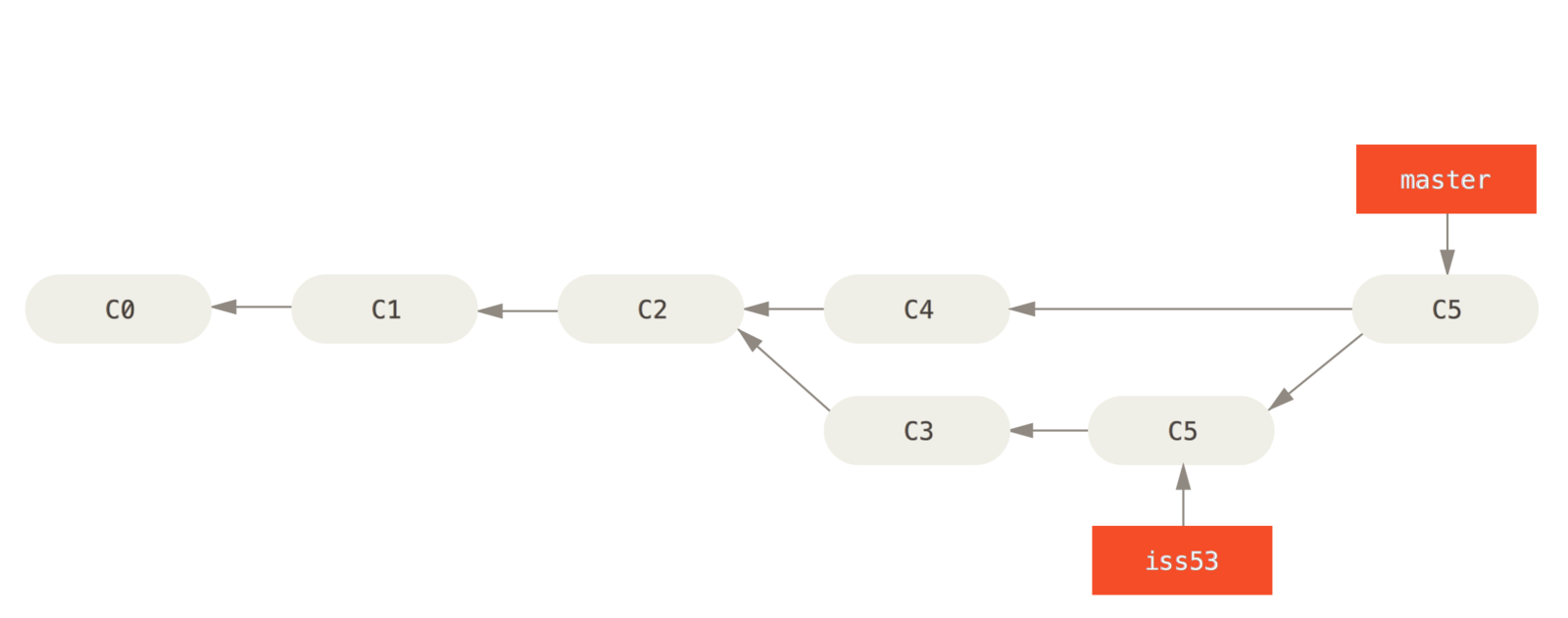
Merging
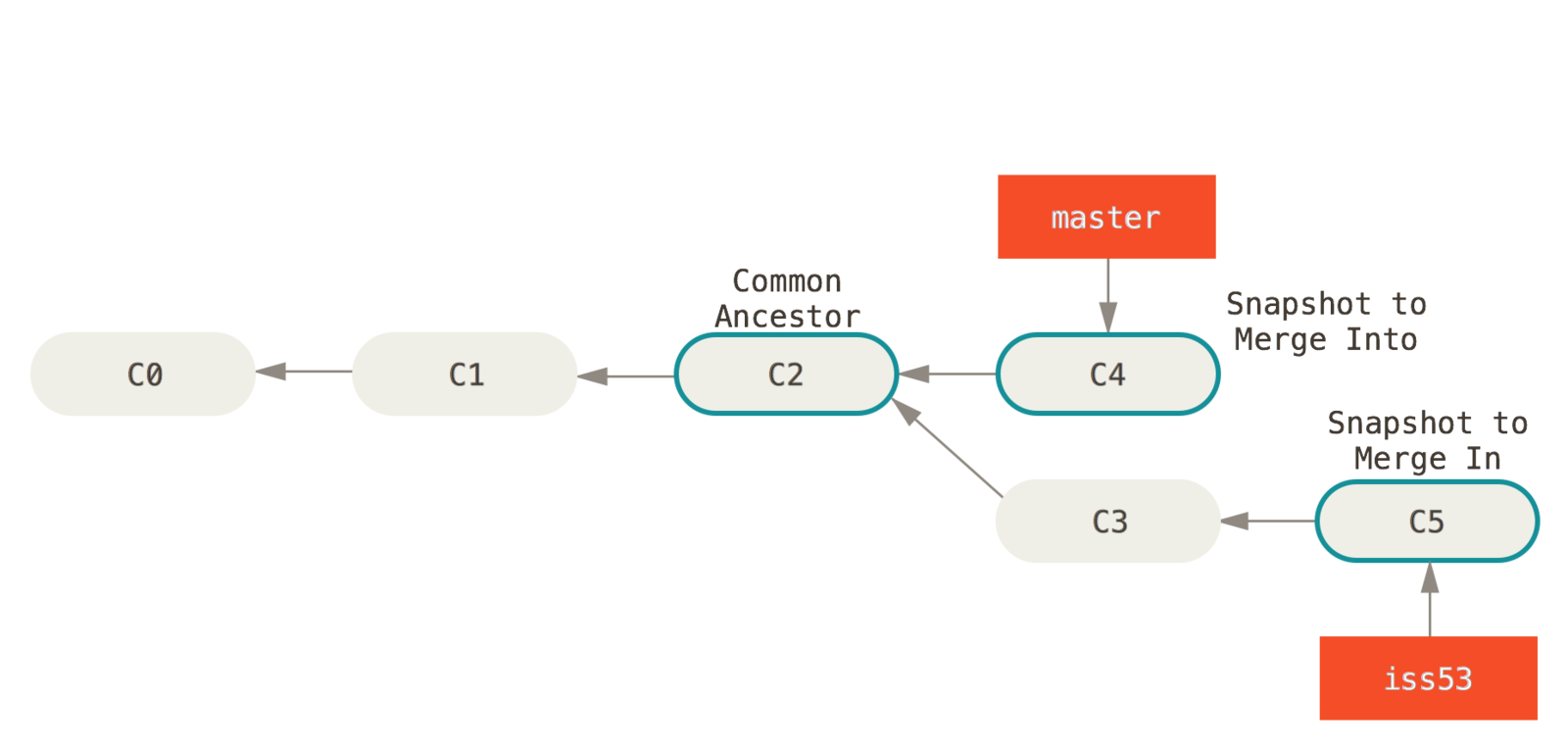
Merging
Merge Conflict- If you changed the same part of the same file differently in the two branches you’re merging together, Git won’t be able to merge them cleanly.
- Need to fix it manually
- Commit again
git tag
- tag at any point
- git tag -a "v1"
What Next?
- git is awesome - practice
- Github, Bitbucket
- Collaborate
Thank You!
Copy of deck
By Developers Bay
Copy of deck
- 1,071



