
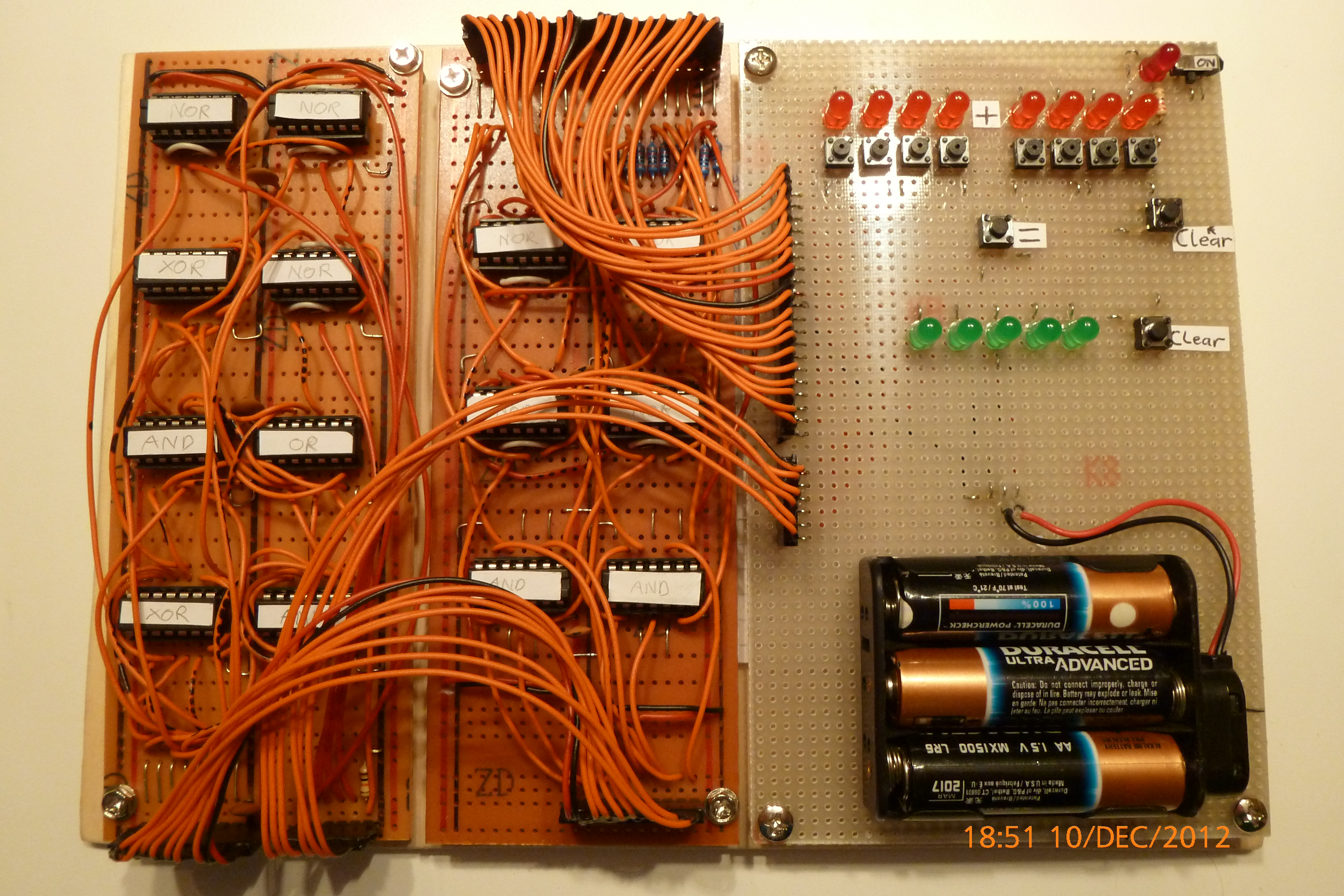
Logic
NOTES from google drive
Logic II

STOP+THINK.
How many rows in the truth table for this expression?
VW!XY || !VWZ || VWYZ || VW!XYZ
5031
STOP+THINK.
How many rows in the truth table for this expression?
VW!XY || !VWZ || VWYZ || VW!XYZ
Count the variables: V, W, X, Y, and Z - five total.
Therefore we need 25=32 rows.
Motivation
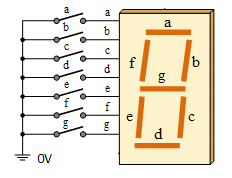
you want to build a number displaying machine
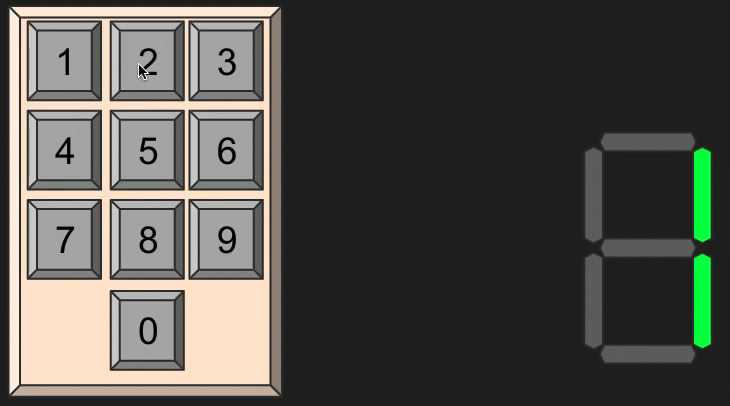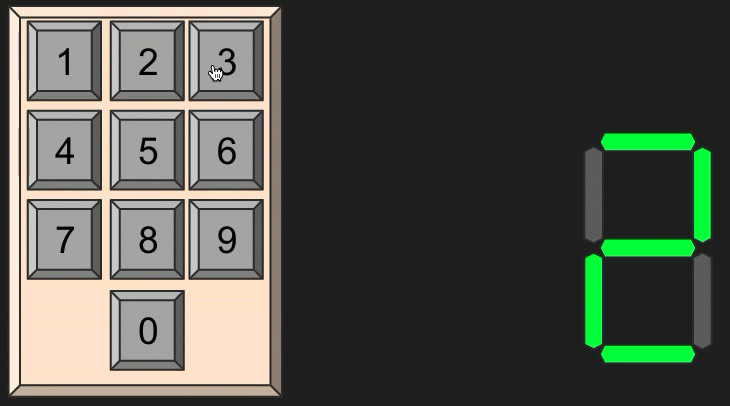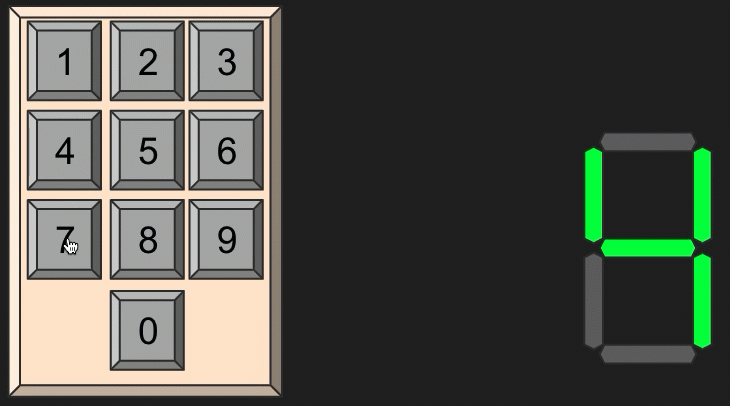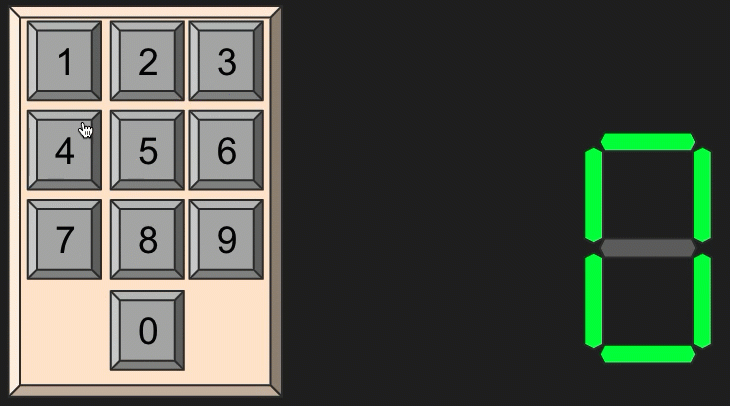
Tutorial
Prep
- y = f(x)
- CSS classes
- another page element property (classname)
- JavaScript "switch"
We have set up a shell with some HTML, CSS, and JS. Here's what happened behind the scenes:
Create 10 buttons in the <div> each of which sends a single digit to a function called "display(x)"
Create a <div> ("division") element to contain our button pad
Add <br /> ("line break") tags to create "line breaks" so we see three buttons per line
Create a table in HTML with 5 rows and 3 columns that we can use for the seven segment display.
Give the seven table cells that will be part of the 7 segment display the ids A through G.
Give the table cells A, G, and D the class "horizontal" and cells B, C, E, F the class "vertical" so that we can use CSS to style them
Instructions 1
Create the classes vertical and horizontal in CSS
.vertical {
width: 20;
height: 60;
background-color: red;
}.horizontal
{
width: 60;
height: 20;
background-color: red;
}


off on on off off off off
on off on on off on on
on on on on on on on
Think Slowly
Start Simply
Can we design a digital electronic machine to do this?
Imperfect Analogy




ANALOG - CONTINUOUS
DIGITAL - DISCRETE
ANALOG - CONTINUOUS
DIGITAL - DISCRETE



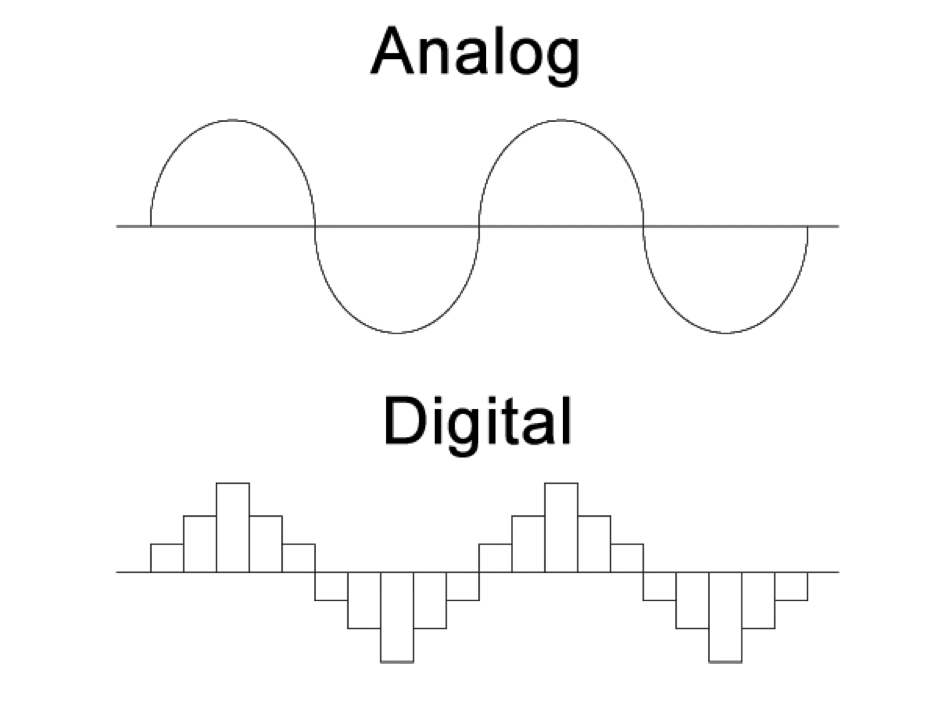
analog
digital
input
output









4 input bits
4 input bits
5 output bits
push button switches
Tools We Already Have
- Binary output from each key


?
Agenda
- Logic
- Circuits
Review
Review
Statement: sentence that can be true or false
Logical expression: combination of logical variables and operators
LOGIC 101
My name is Dan.


My name is Dan.
value = TRUE
value = FALSE
A = it is sunny out
A?
A = it is sunny out
A?
A is a logical variable. A name that stands for a statement or condition that can be true or false.
A LOGICAL VARIABLE CAN TAKE ON ONE OF TWO LOGICAL VALUES
TRUE
FALSE
1
0
LOGICAL VARIABLES can be combined
with LOGICAL OPERATORS
such as AND, OR, and NOT
to form LOGICAL EXPRESSIONS
which also can only be TRUE or FALSE

LOGICAL EXPRESSIONS
for example
A = "my name is Dan."
B = "I am in Toronto."
C = "I am a dog."
D = A and B
E = A and C
F = A or B
G = not C
H = B and not C
I = not A or not C
TRUE
TRUE
TRUE
TRUE
TRUE
FALSE
LOGICAL OPERATORS
- "Binary" Operators (connecting two values)
- AND
- OR
- "Unary" Operator (works on just one value)
- NOT
Alternative Notations
A and B also written AB, A∧B, A·B
A or B also written A+B, A∨B
not A also written ~A, !A, ¬A, Ā
Definitions I
W is true if both A, B are true
W is true when A is false, false when A is true
W = A or B
W = A and B
W is true if either or both A,B truee
W = not A
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
- akin to multiplication
- AB, A∧B, A·B
-
1 or TRUE is identity
- X AND TRUE = X
- X·1=X for any X
Only two "numbers": 0 and 1
Three "operations":
AND
- akin to addition
- A+B, A∨B
-
0 or FALSE is identity element
- X or FALSE = X
- X+0=X
- akin to negation
- ~A, !A, ¬A, Ā
- not 0 = 1, not 1 = 0
OR
NOT
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
AND takes precendence over OR
AB + C
means "A and B ... or C"
not "A and ... B or C"
but use parentheses to say otherwise
A(B + C)
means "A and ... B or C"
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
AND "distributes" over OR
A(B + C) = AB + AC
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
common vars can be "factored out: of ORs
AB + AC = A(B + C)
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
Since 1/0 are exhaustive
A + !A = TRUE
Since 1/0 are mutually exclusive
A · !A = FALSE
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
Summary so far
A + !A = TRUE
A · !A = FALSE
AB + AC = A(B + C)
A(B + C) = AB + AC
X·1 = X for any X
X+0 = X for any X
TRUTH TABLES
A logical expression is DEFINED by its truth table which shows its value for every possible combination of inputs
TRUTH TABLES
A truth table is simply a listing of all possible combinations for an expression along with the value of the expression for each combination.
Suppose an expression includes three variables A, B, and C.
A can be true or false
B can be true or false
C can be true or false
B can be true or false
C can be true or false
C can be true or false
C can be true or false
1
0
11
10
01
00
111
110
101
100
011
010
001
000
A
C
B
exp
TRUTH TABLES
A truth table is simply a listing of all possible combinations for an expression along with the value of the expression for each combination.
Suppose an expression includes three variables A, B, and C.
0 0 1
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
A
C
B
exp
"expression" - we'll put the value of the expression for each input combination here
TRUTH TABLES
| A | B | A+B |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
row for each
input combination
row for each
input combination
column
for each
variable
column
for "output"
TRUTH TABLES
| A | B | A+B |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
all the 1's for the first varible
{
all the 0's for the first varible
{
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A |
|---|
| 1 |
| 0 |
| A | B |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 |
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Definitions II
| A | B | AB |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
AND
| A | B | A+B |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
OR
| A | !A |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
NOT
Example: Build Truth Table for !A + B
A
B
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
!A
!A+B
1
B
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
| A | B | C | !A!B | + | BC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
Build Truth Table for !A!B + BC
1
| A | B | C | !A!B | + | BC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Build Truth Table for !A!B + BC
1
2
3
| A | B | C | !A!B | + | BC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Build Truth Table for !A!B + BC
1
2
3
4
Example: Build Truth Table for !A!B + BC
A
B
C
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
!A
!B
!A·!B
B·C
!A!B+BC
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
AND "distributes" over OR
A(B + C) = AB + AC
| A | B | C | A | and | B+C | AB | + | AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Laws
- DeMorgan
- !(AB) = !A+!B
- !(A+B) = !A!B
- Distributive
- A(B+C) = AB + AC
- Double negation
- !!A = A
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
Summary so far
A + !A = TRUE
A · !A = FALSE
AB + AC = A(B + C)
A(B + C) = AB + AC
X·1 = X for any X
X+0 = X for any X
!(A+B) = !A!B
!(A · B) = !A + !B
}
}
}
}
identity elements
distributive property
mutual exclusive + exhaustive
definition of NOT
DeMorgan's Laws
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
Truth table for expression can be written as
"or of ands"
where the ands are the inputs of each row a 1 in the last column
| A | B | C | EXP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
| A | B | C | EXP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
1
1
1
1
+
+
+
B
A
C
1
1
1
A
!C
!B
1
0
0
C
!A
!B
1
0
0
!C
!A
!B
0
0
0
Boolean Algebra: the "math" of logic
And, finally:
Truth table for an expression can be written as an "or of ands" where the ands are the inputs of each line of the truth table that yields a 1
| A | B | C | EXP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
+
+
+
+
+
+
B
A
C
A
!C
!B
C
!A
!B
!C
!A
!B
Logic and Circuits
-
logical values and electricity
-
AND, OR
-
Basic Logic Gates
-
Simple expressions and circuits
Logic 2 Storyboard
Black Boxes
for logic
Gates
controlling switches
Electricity
switches as logic
Electricity
what is a volt?
Review
Truth Tables
stepwise refinement
logic circuits
Circuit Cost
Expression
Equivalence
Logic Reduction
Best Solutions?
Electricity
but first...
"potential" (energy)
but first...
1 kg
1 m
"potential" (energy)
but first...
1 kg
1 m
9.8 joules
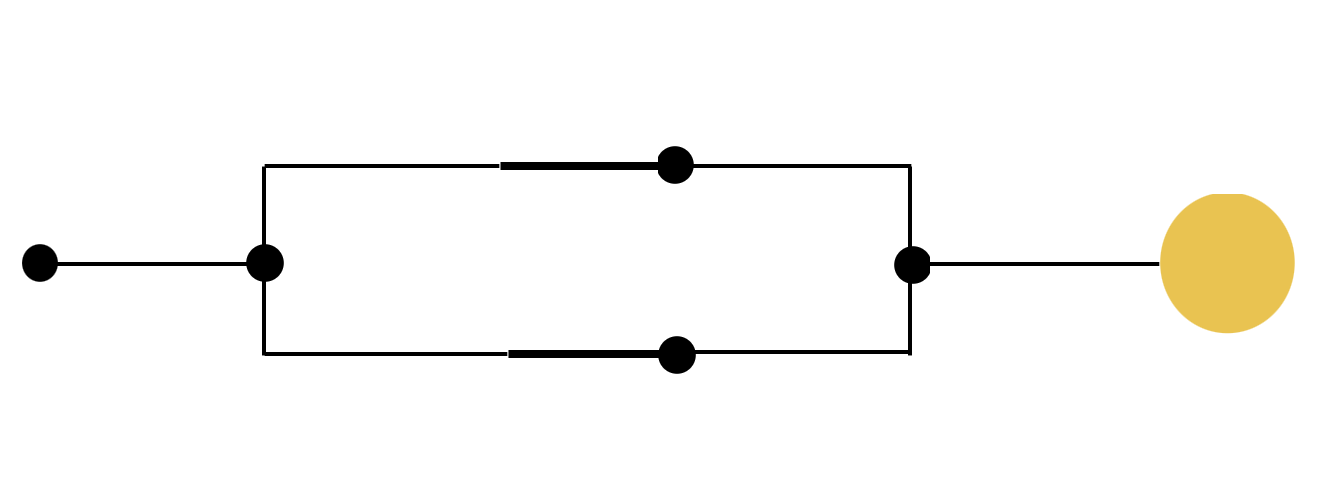
Electrical Potential Energy VOLTS
positive and negative electric charges are attracted to one another
-
+
potential (volts)
Electrical Potential Energy VOLTS
separating positive and negative charges increases potential
-
+
potential (volts)






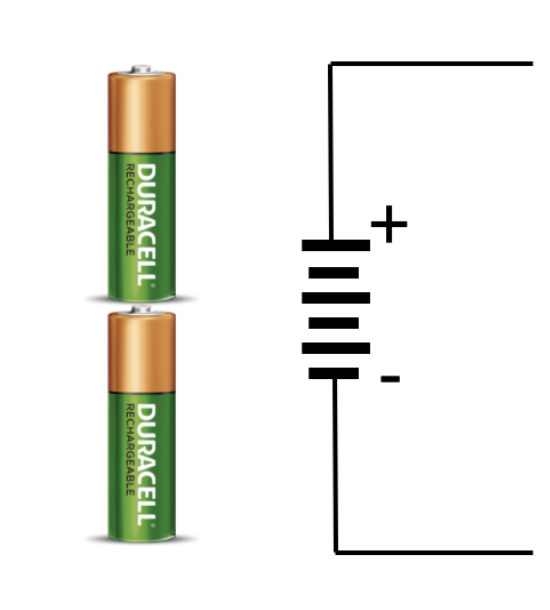
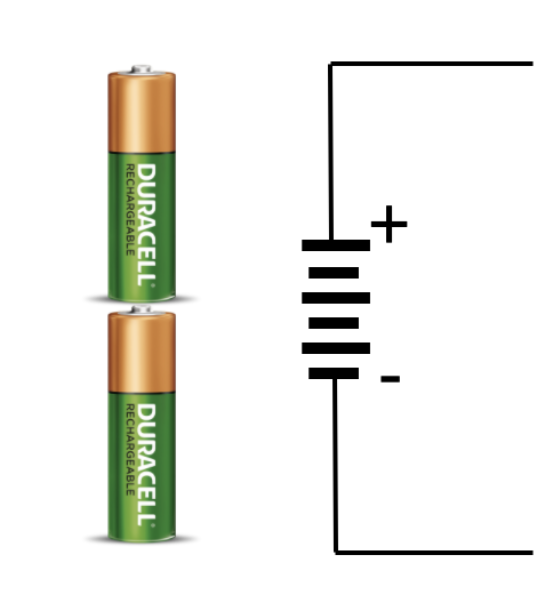
Volt

+
-
3V

Logical Values + Electricity
+3 or +5 volts
0 volts
1
0
true
false

+
-
3V

Logical Operators + Switches
Logical Values + Switches
+3-5 volts
+3-5 volts
logical 0
logical 1
OPEN SWITCH
CLOSED SWITCH
For what it's worth: the usual value of digital "1" is +3-5 volts DC
AND, OR
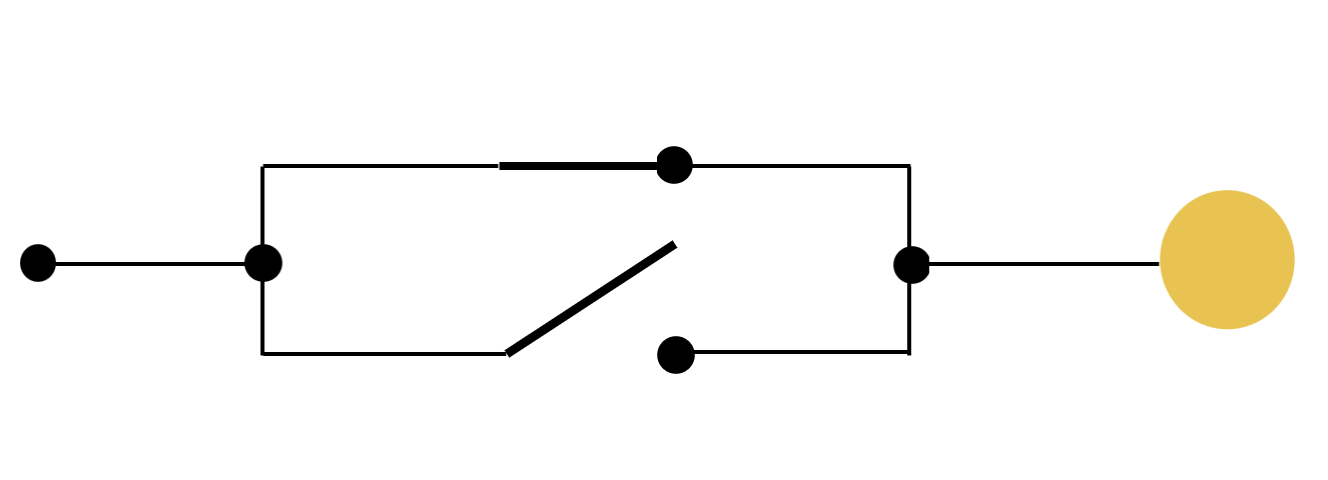
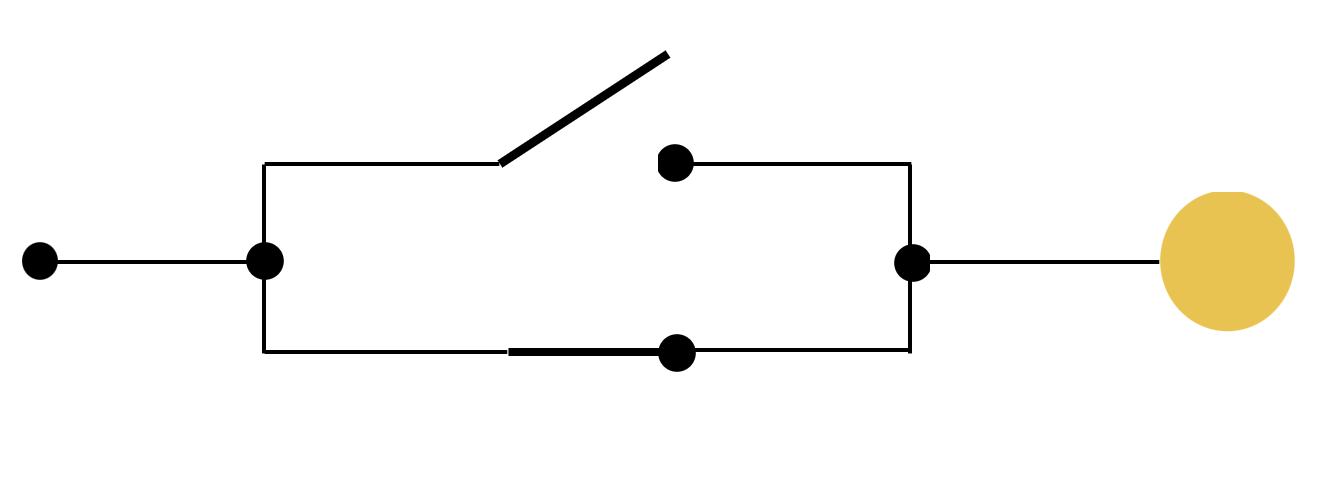
A and B


+
-
3V

A or B
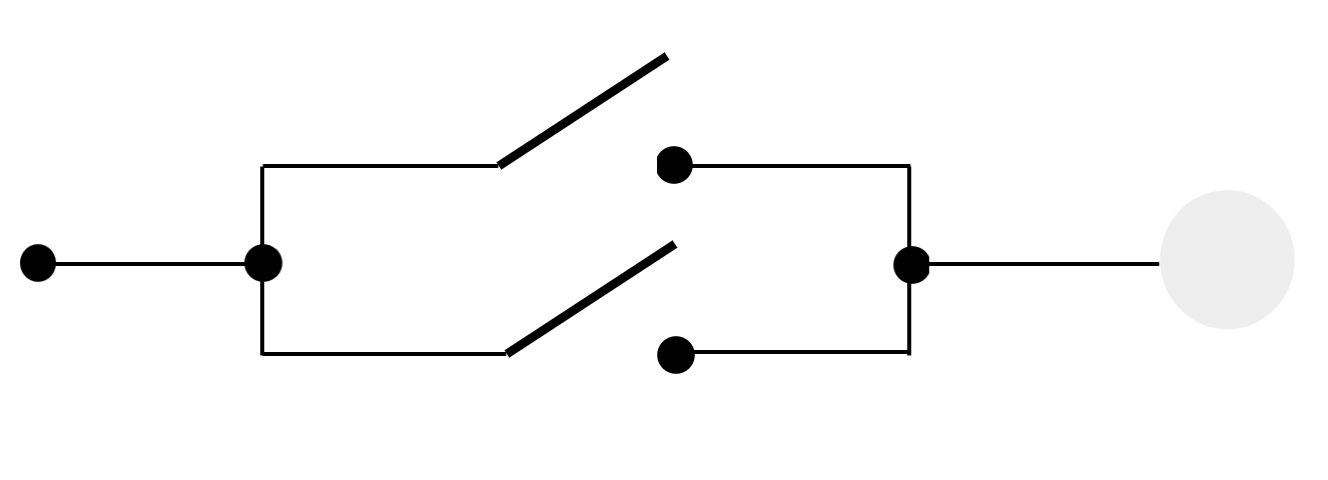
Logical Operators + Switches

+
-
3V

A
B
A
B
AND as black box
A
B
3V
AND
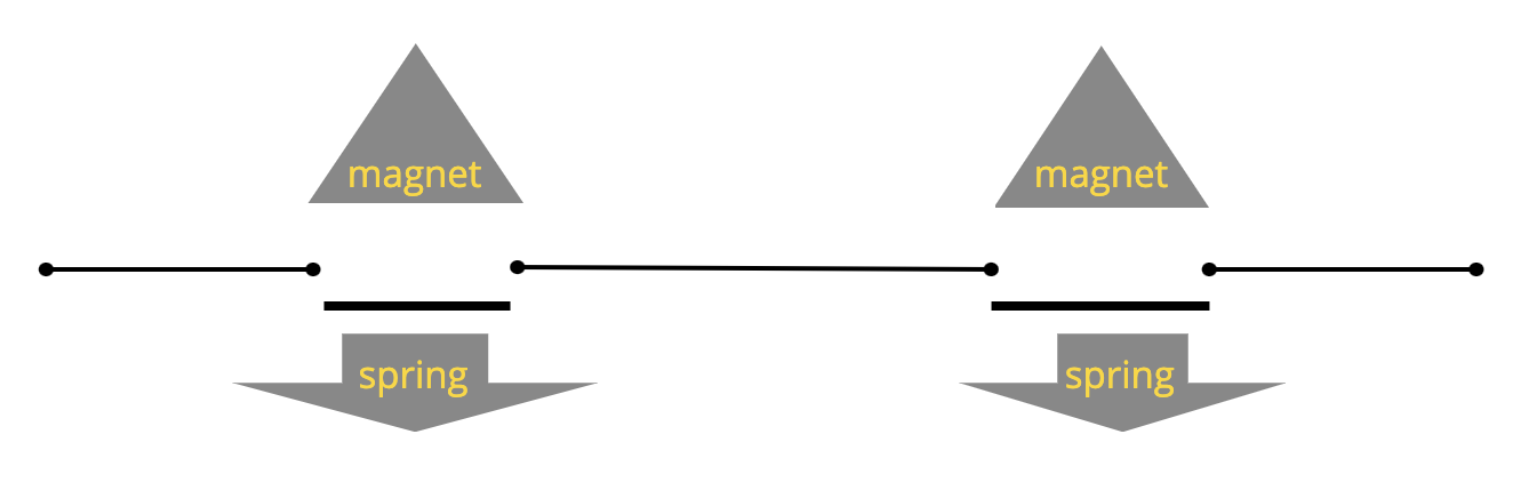
magnet
spring
magnet
spring
A
B
3V

output
AND
magnet
spring
magnet
spring
A
B
3V
AND

+
-
3V

magnet
spring
magnet
spring
A
B
AND

+
-
3V

magnet
spring
magnet
spring
A
B
AND
3V

A
B
Y
A
B
Y
A
B
Y
A
B
Y
A
B
Y
OR

A
B
Y
OR

A
B
Y
OR

A
B
Y
OR

A
B
Y
OR



A
B
C
D
What is the output if the inputs are TFTF?



A
B
C
D
AB + CD



A
B
C
D
AB + CD



A
B
C
D
AB + CD



A
B
C
D



A
B
C
D
AB + CD

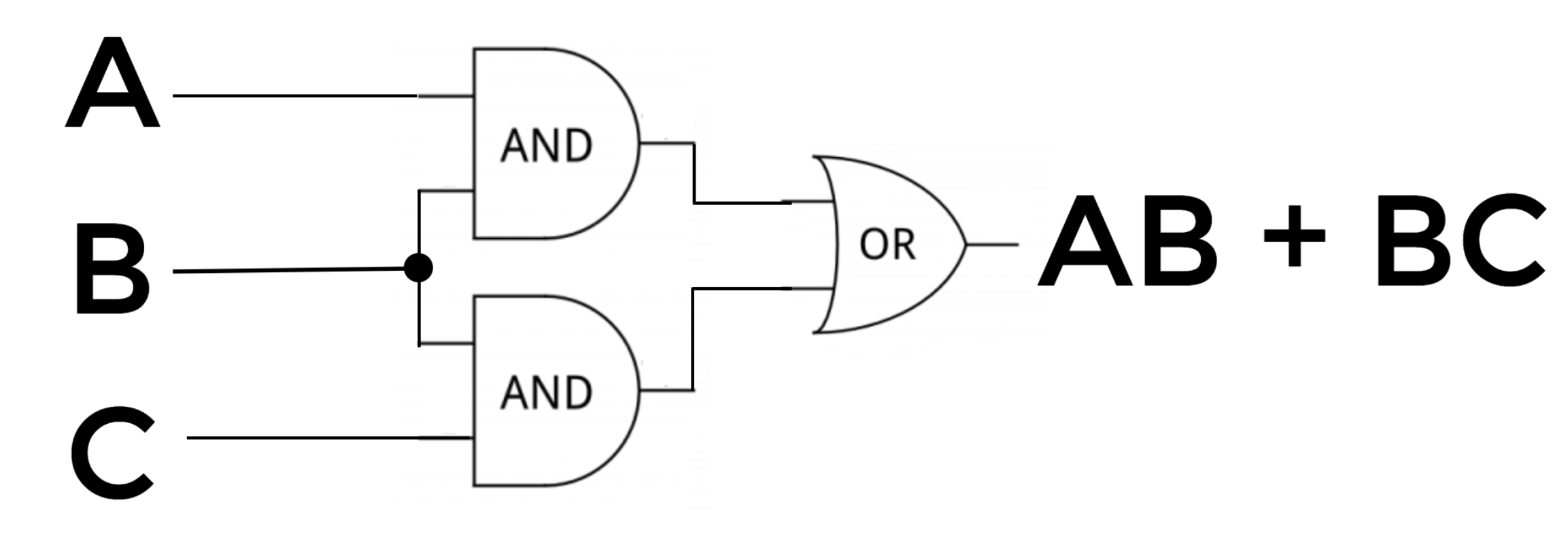
Simple expressions + circuits
AB + BC
A
B
C

Simplifying Logic Expression = Simplifying Logic Circuits
AB + BC=B(A+C)
A
B
C



Simple expressions + circuits
C
B
A
B
C
C
C
1
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
Simplifying Logic Expression = Simplifying Logic Circuits
AB + BC=B(A+C)
B
A
C


33% savings!
A
B
C



Simplifying Logic Expression = Simplifying Logic Circuits
AB + BC=B(A+C)
A B C AB + BC B and A+C
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1
1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Simple expressions + circuits
A
B
C




!A!B + BC
Pause
Binary
Arithmetic
1 Bit Addition
1
+0
01
0
+1
01
0
+0
00
1
+1
10
A
+B
WX
1 Bit Addition
1
+0
01
0
+1
01
0
+0
00
1
+1
10
A
+B
WX
| A | + | B | = | W | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
1 Bit Addition as black box with two inputs and two outputs
A
+B
WX
| A | + | B | = | W | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
A
B
W
X
1 Bit Addition
1
+0
01
0
+1
01
0
+0
00
1
+1
10
A
+B
WX
| A | + | B | = | W | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
looks like
A and B
1 Bit Addition
| A | + | B | = | W | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
looks like
A and B
1 Bit Addition
| A | + | B | = | W | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
what
about
this?

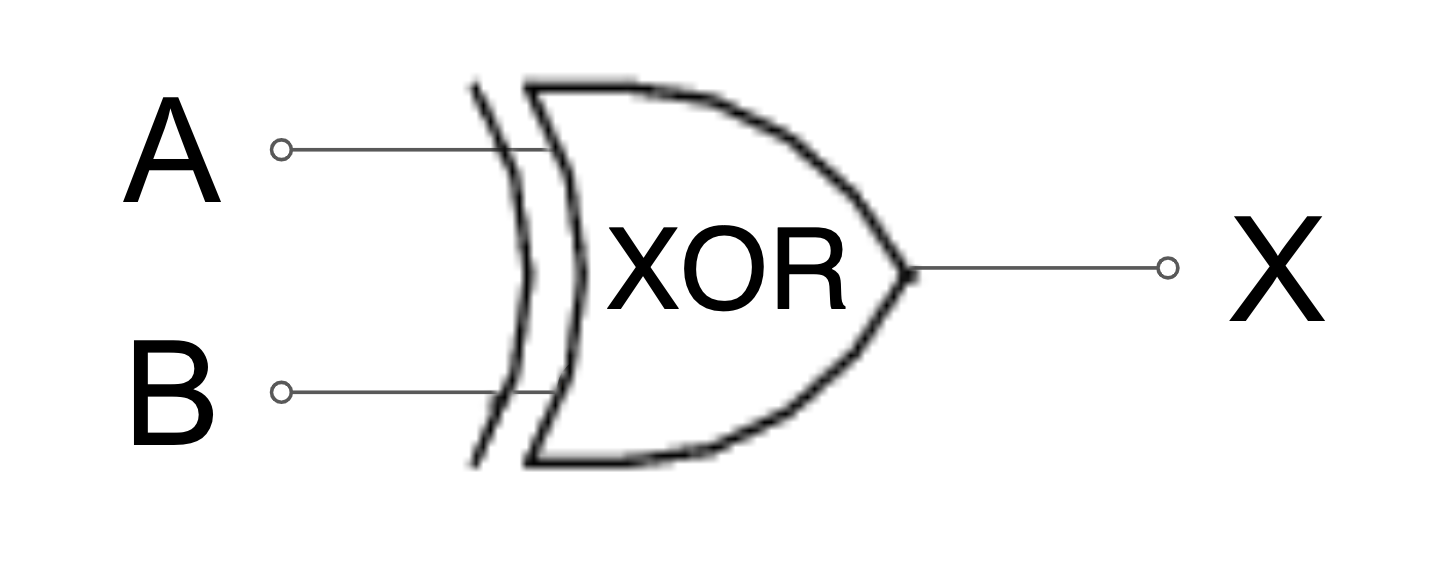
Introducing XOR
"exclusive or"
XOR
exclusive or
aka
or but not and
| A | B | A XOR B |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
BinaryArithmetic
1
+0
01
0
+1
01
0
+0
00
1
+1
10
A
+B
WX
| A | + | B | = | W | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
looks like
A XOR B
BinaryArithmetic
| A | + | B | = | W | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
looks like
A XOR B

1 Bit Addition with Carry
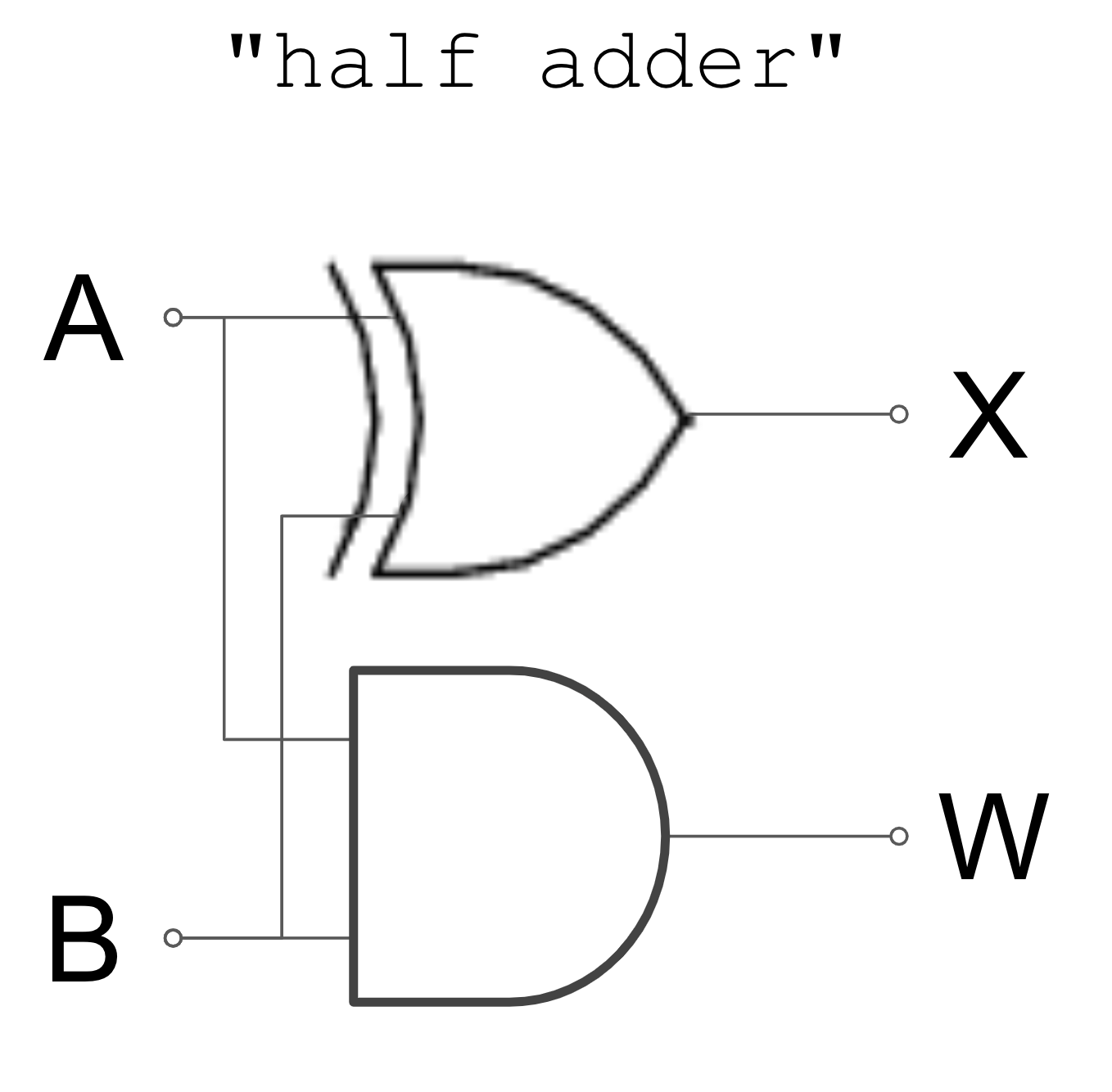
STOP+TRY: build the half adder circuit. Use switches for inputs and bulbs for outputs.
What
about
this?
ab
+cd
wxy
STOP+THINK
What would the truth table look like?
ab
+cd
wxy
ab
+cd
wxy
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | 1 | |||||
| 1 | ||||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 0 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | |||||
| 0 |
11
+11
110
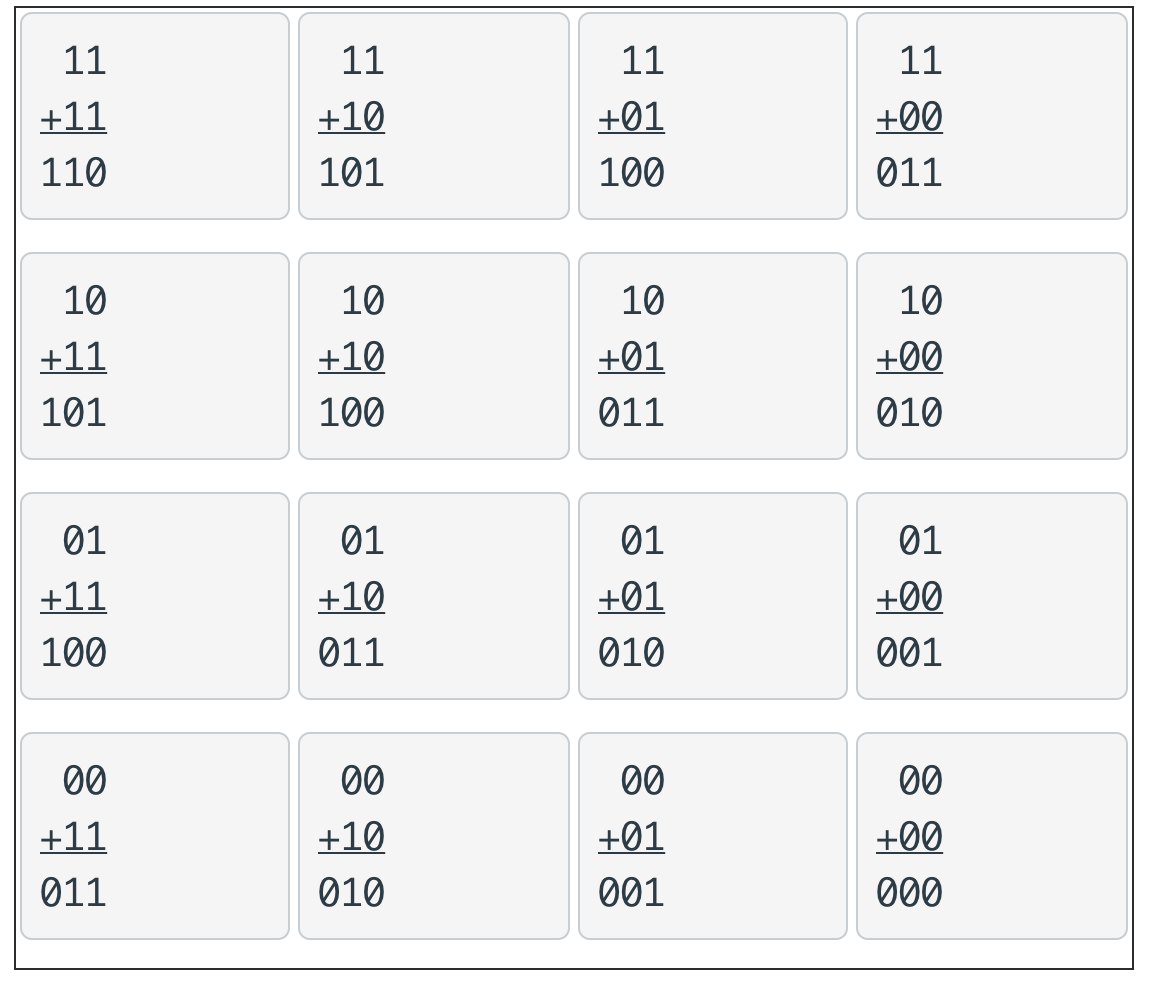
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
When is W true?
ABCD
or
ABC!D
or
AB!CD
or
A!BCD
or
A!BC!D
or
!ABCD
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
W=ABCD+ABC!D+AB!CD+A!BCD+!ABCD+A!BC!D
We could just build this as a circuit but it would be...complicated.
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
W=ABCD+ABC!D+AB!CD+A!BCD+!ABCD
We wonder if there is a simpler but equivalent version of this expression.
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
W=ABCD+ABC!D+AB!CD+A!BCD+!ABCD
Equivalent means it would have the same truth table.
| A | B | C | D | W | X | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
W=ABCD+ABC!D+AB!CD+A!BCD+!ABCD
Simpler means fewer terms and fewer operators.
e.g.
P=ABCD + ABC!D + AB!C + A!B
P=ABC(D+!D) + AB!C + A!B
P=ABC(TRUE) + AB!C + A!B
P=ABC + AB!C + A!B
P=AB(C+!C) + A!B
P=AB + A!B
P=A(B+!B)
P=A
| A | B | C | D | ABCD | ABC!D | AB!C | A!B | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Pause
Logic Reduction
AB + A!B = A(B+!B) = A and TRUE = A
A may be a compound expression:
PQR + PQ!R = (PQ)(R+!R) = PQ
P=ABCD + ABC!D + AB!C + A!B
ABC(D+!D)
ABC
AB(C+!C)
AB
A(B+!B)
A
change A
ABCD
A!BCD
ABC!D
AB!CD
!ABCD
change C
change B
change D
A B C D Y 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
AB
CD
ABCD
ABC!D
AB!CD
AB!C!D
A!BCD
!ABCD
!A!BCD
ABC
AB!C
ACD
!ACD
| CD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | ||
| AB |
00 |
!A!B!C!D |
!A!B!CD |
!A!BCD |
!A!BC!D |
|
01 |
!AB!C!D |
!AB!CD |
!ABCD |
!ABC!D |
|
|
11 |
AB!C!D |
AB!CD |
ABCD |
ABC!D |
|
|
10 |
A!B!C!D |
A!B!CD |
A!BCD |
A!BC!D |
|
Karnaugh Map
| CD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | ||
| AB | 00 | !A!B!C!D 0 |
!A!B!CD1 | !A!BCD 3 |
!A!BC!D 2 |
| 01 | !AB!C!D 4 |
!AB!CD 5 |
!ABCD 7 |
!ABC!D 6 |
|
| 11 | AB!C!D 12 |
AB!CD 13 |
ABCD 15 |
ABC!D 14 |
|
| 10 | A!B!C!D 8 |
A!B!CD 9 |
A!BCD 11 |
A!BC!D 10 |
|
Karnaugh Map
| CD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | ||
| AB | 00 |
|
|
|
|
| 01 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 11 | AB!C!D 1 |
AB!CD 1 |
ABCD 1 |
ABC!D 1 |
|
| 10 | A!B!C!D 1 |
A!B!CD 1 |
A!BCD 1 |
A!BC!D 1 |
|
P=ABCD + ABC!D + AB!CD + A!BCD + AB!C!D +A!B!CD + A!B!C!D + A!BC!D
| CD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | ||
| AB | 00 |
|
|
|
|
| 01 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 11 | AB!C!D 1 |
AB!CD 1 |
ABCD 1 |
ABC!D 1 |
|
| 10 | A!B!C!D 1 |
A!B!CD 1 |
A!BCD 1 |
A!BC!D 1 |
|
P=ABCD + ABC!D + AB!CD + A!BCD + AB!C!D +A!B!CD + A!B!C!D + A!BC!D
| CD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | ||
| AB | 00 |
|
|
|
|
| 01 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 11 | AB!C!D 1 |
AB!CD 1 |
ABCD 1 |
ABC!D 1 |
|
| 10 | A!B!C!D 1 |
A!B!CD 1 |
A!BCD 1 |
A!BC!D 1 |
|
P=ABCD + ABC!D + AB!CD + A!BCD + AB!C!D +A!B!CD + A!B!C!D + A!BC!D
| CD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | ||
| AB | 00 |
|
|
|
|
| 01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
|
10 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
P=ABCD + ABC!D + AB!C + A!B
P=ABCD + ABC!D + AB!CD + AB!C!D + A!BCD + A!BC!D + A!B!CD + A!B!C!D
Finis
NOTE: X1=B, X3=A, X0=C, X2=D
C is 1 here
D is 1 here
A is 1 here
B is 1 here
KMaps & Race Conditions
A



C
B
D
1 0 1 1 1 0 1
R=!ABC!D+A!B!C!D+A!B!CD+A!BC!D+A!BCD+AB!C!D+AB!CD+ABC~D
| 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 | |
| 00 | ||||
| 01 | 1 | |||
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
AB
CD
A!C




A!B
R=A!B + A!C + BC!D
BC!D
1 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 1 0 1
1 1 1 1 1 1
Race Conditions - the race is among these AND gates. Their inputs depend on A, B, C, and D but some might be delayed by NOT
0 1 0 0
!A
0 1 0 0
!B
0 0 0 0
!C
1 1 1 0
!D
1 1 1 1
A
1 0 1 1
B
1 1 1 1
C
0 0 0 0
D

R=A!B + A!C + BC!D
R=A!B + A!C + BC!D + A!D
Logic
By Dan Ryan
Logic
- 781



