Fibonacci Numbers & Recursion

Fibonacci Numbers
with
Human Computers
Instructions
Each student receives algorithmic instructions:
when you are asked for fib(n):
if n is 1 or 2 return 1
otherwise return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2)
To compute fib(n-1) or fib(n-2) find another student and give them this task. Wait for their response. When you get both responses, respond to whomever asked you for fib(n).
Instructor starts process by asking one student for, say, fib(7).
Text

function fibonacci(n) {
if (n < 3) {
return 1}
else {
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)}
}

fib(22)
fib(19)
fib(20)
fib(21)
fib(18)
fib(19)
fib(20)
fib(18)
fib(17)
fib(18)
fib(19)
fib(17)
fib(18)
fib(17)
fib(18)
Calculating the 22nd Fibonacci number recursively
What about fib(22)?
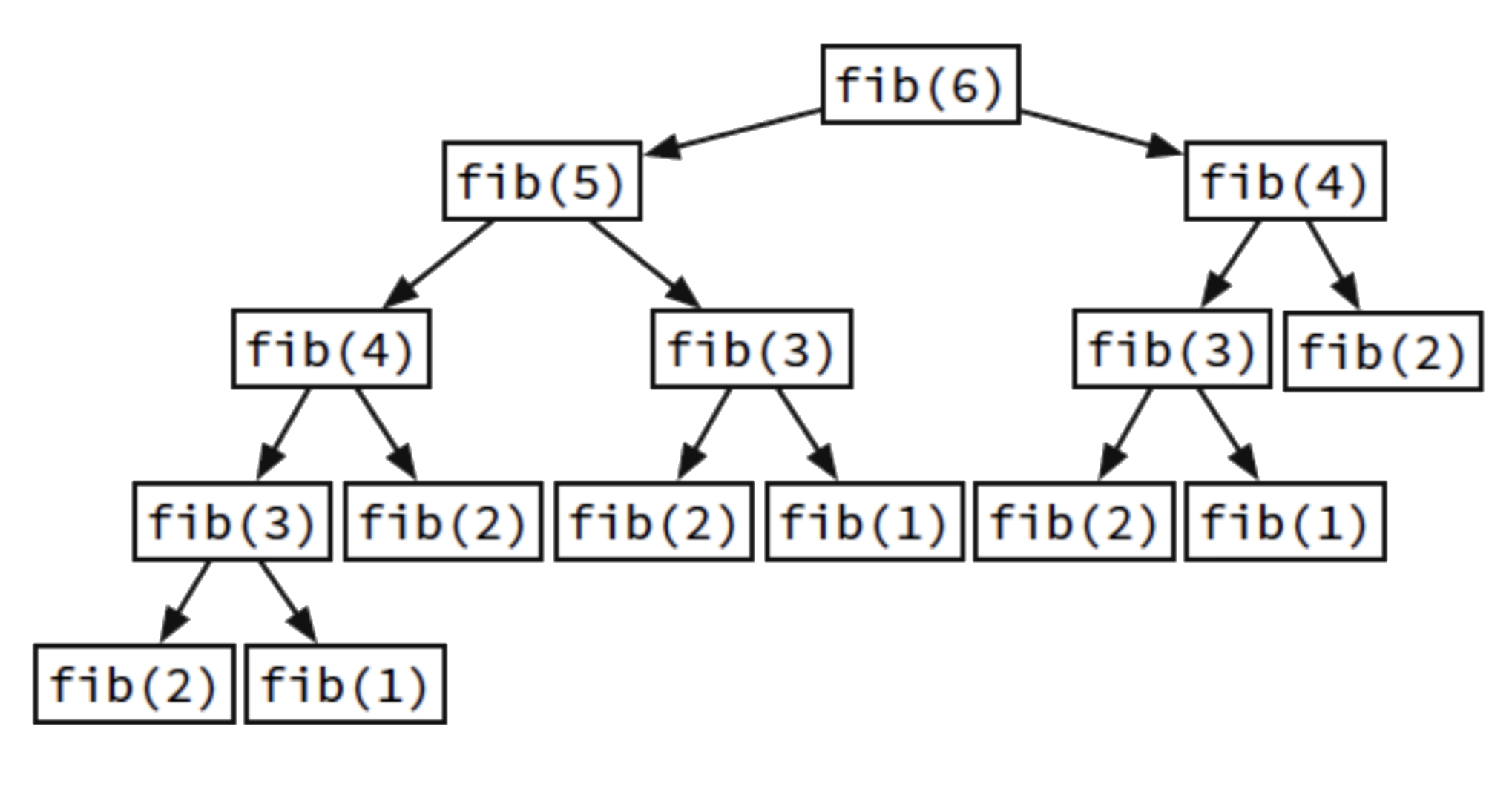
F6 calls F5 and waits...
F5 calls F4 and waits...
F4 calls F3 and waits...
F3 calls F2 and waits...
F2 returns 1
F3 calls F1 and waits...
F1 returns 1
F3 returns 2=1+1
F4 calls F2 and waits...
F2 returns 1
F4 returns 3=2+1
F5 calls F3 and waits...
F3 calls F2 and waits...
F2 returns 1
F3 returns 2=1+1
F3 calls F1 and waits...
F1 returns 1
F5 returns 5=3+2
F6 calls F4 and waits...
F6 returns 8=5+3
1,1,2,3,5,8
F4 calls F3 and waits...
F3 calls F2 and waits...
F2 returns 1
F3 calls F1 and waits...
F1 returns 1
F3 returns 2=1+1
F4 calls F2 and waits...
F2 returns 1
F4 returns 3=2+1
Repetition-Fibonacci
By Dan Ryan
Repetition-Fibonacci
Module for "Problem Solving with Repetition"
- 227



