<Hello />
React Basics
-
Components
-
JSX
-
Props
-
Rendering
-
Events
-
State
-
Context
-
useEffect
React Advanced
-
Routing
-
TypeScript
-
State Management
-
Testing
-
Forms
-
...
Setup
npx create-next-app@latest
Other Options, see: https://react.dev/learn/start-a-new-react-project
Components
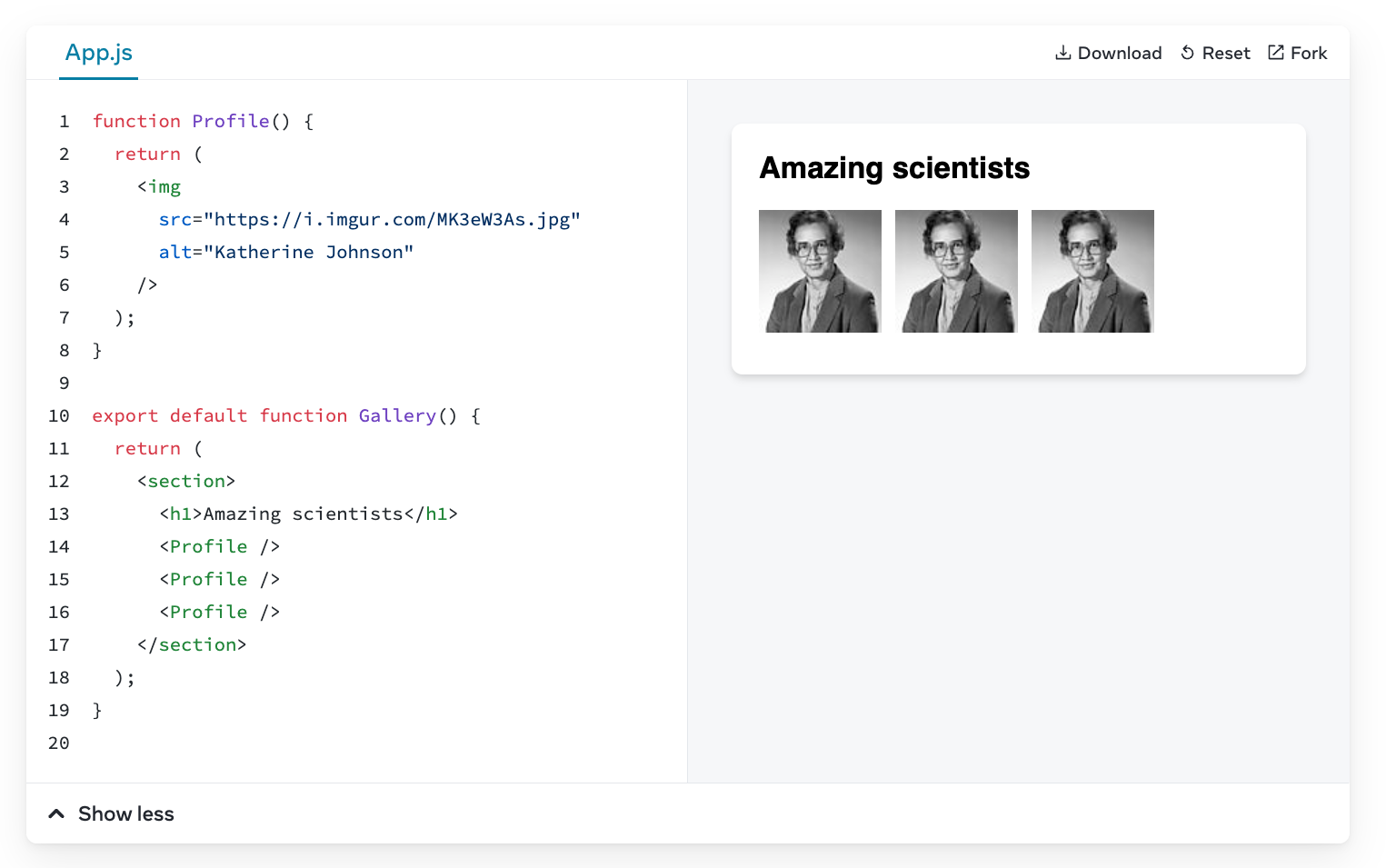
Practice 👨💻🧑💻
1. Fix the return statement
https://codesandbox.io/s/components-fix-return-f7gfnx
2. Spot the Mistake
https://codesandbox.io/s/components-profile-89h56w
Import / Export
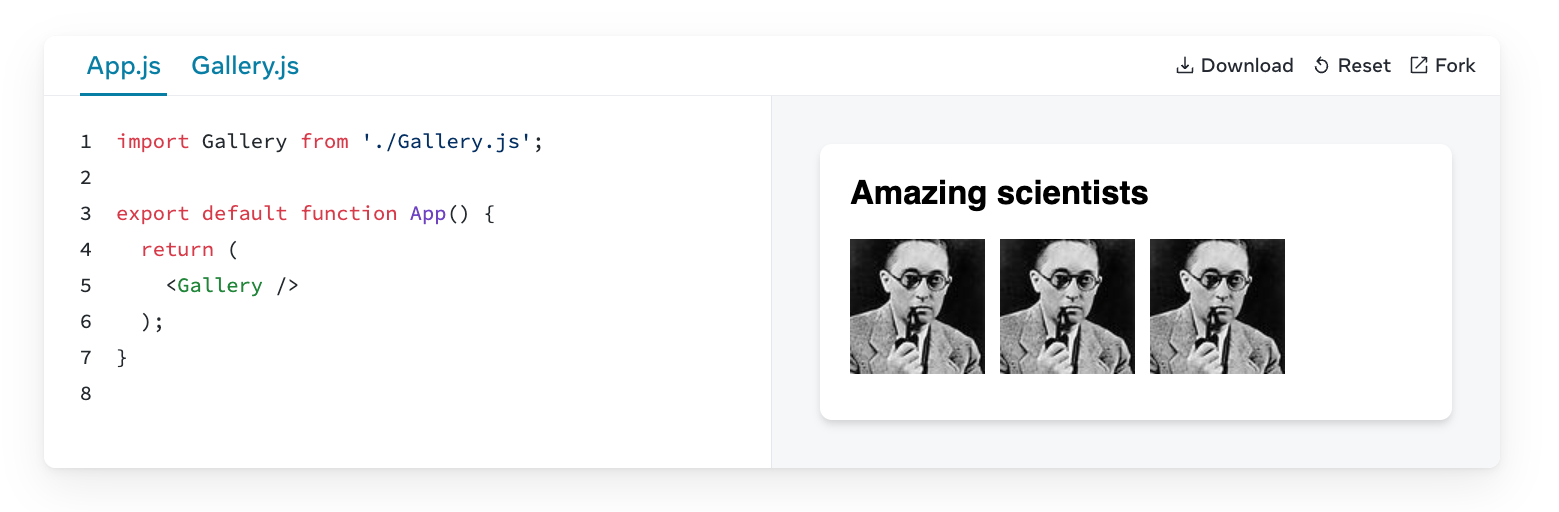
Default vs Named Exports

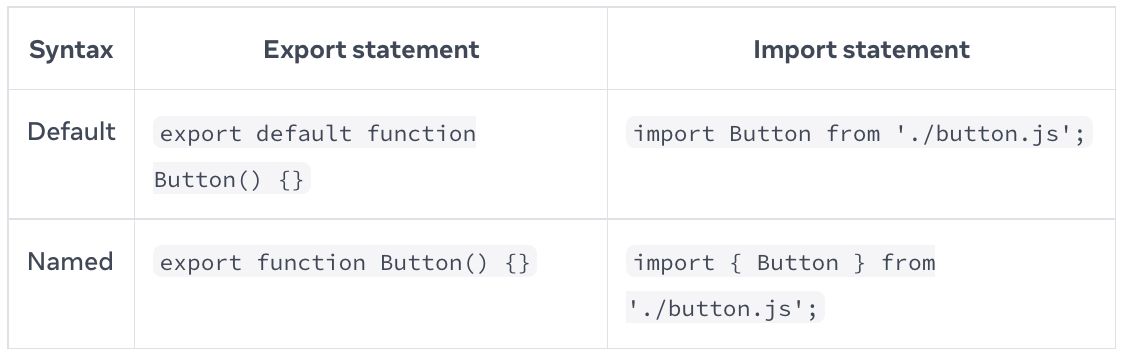
Default vs Named Exports
Recommendation: use Named Exports
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Export the Card Component
Export the Card component and place it a few times into the App Component. Try it as Default Import / Export and also as Named Import / Export.
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-components-gb0ltp
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-components-solution-82kz7i
JSX
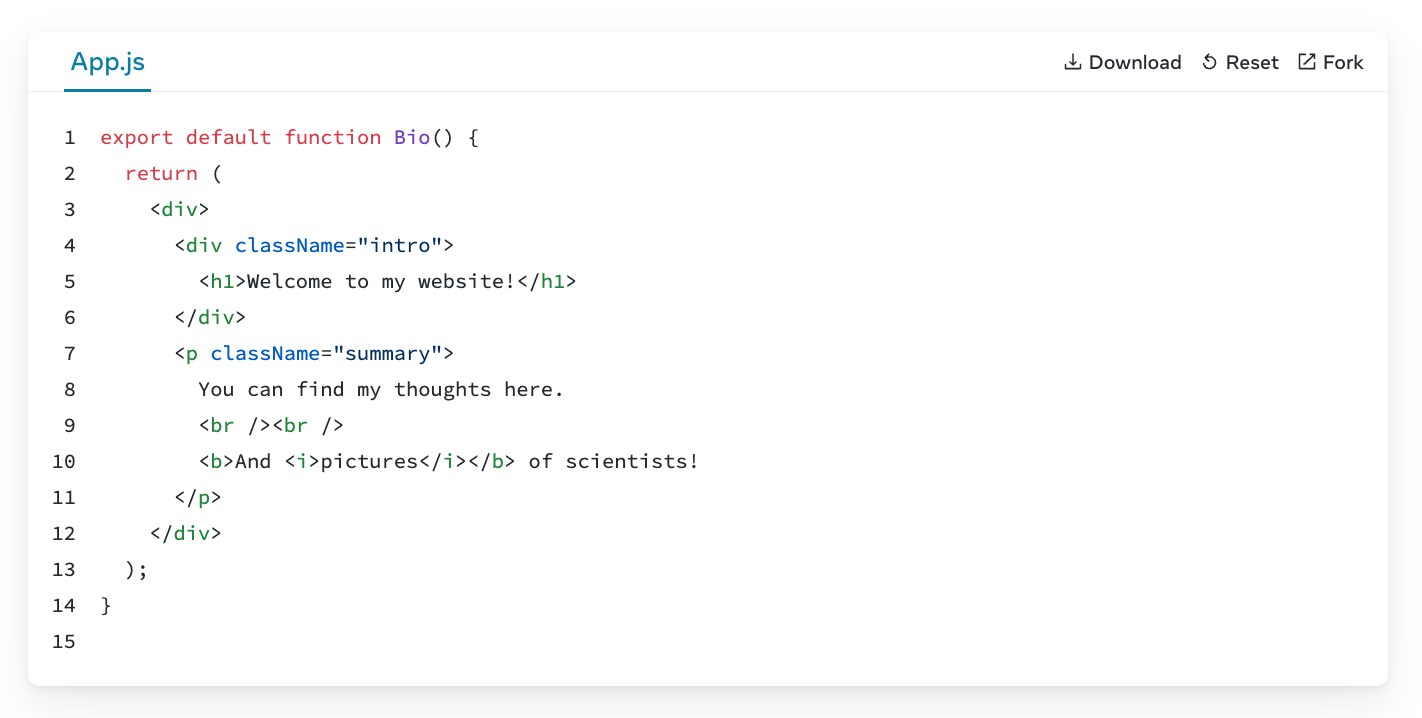
1. Return a single root element
To return multiple elements from a component, wrap them with a single parent tag.
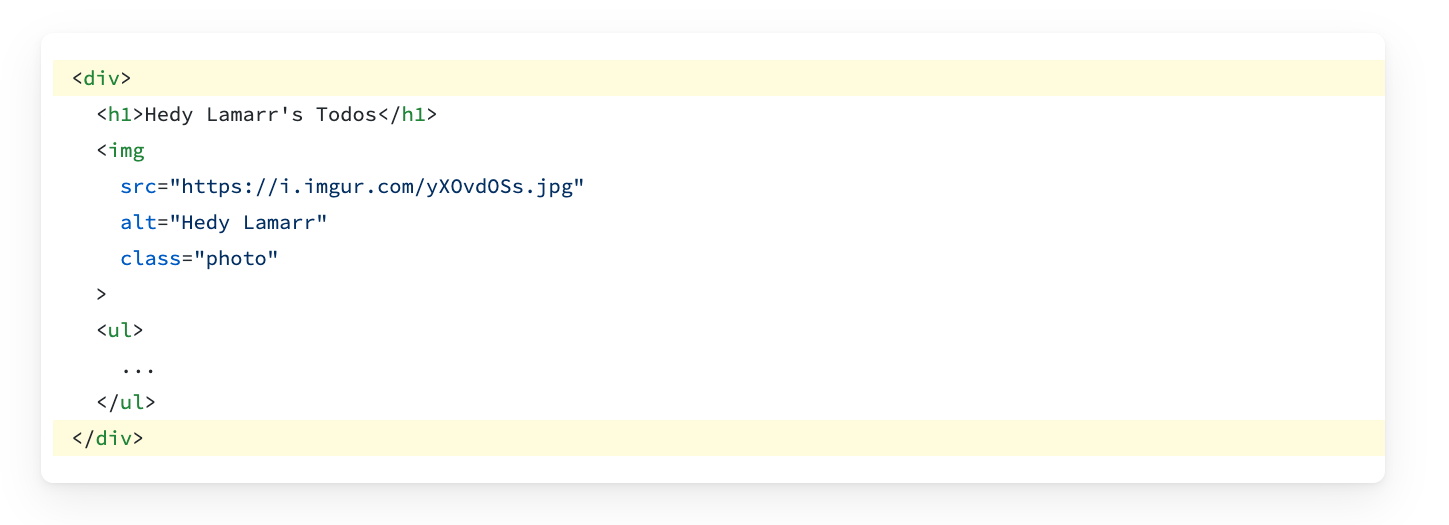
If you don’t want to add an extra <div> to your markup, you can write <> and </> instead:
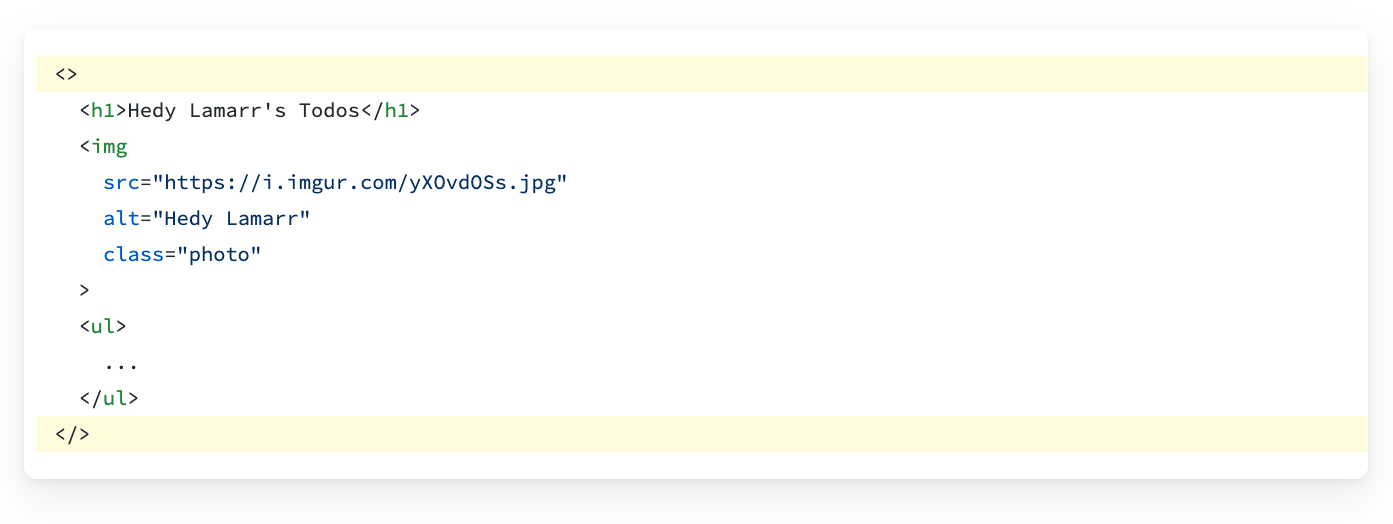
2. Close all the tags
JSX requires tags to be explicitly closed: self-closing tags like <img> must become <img />
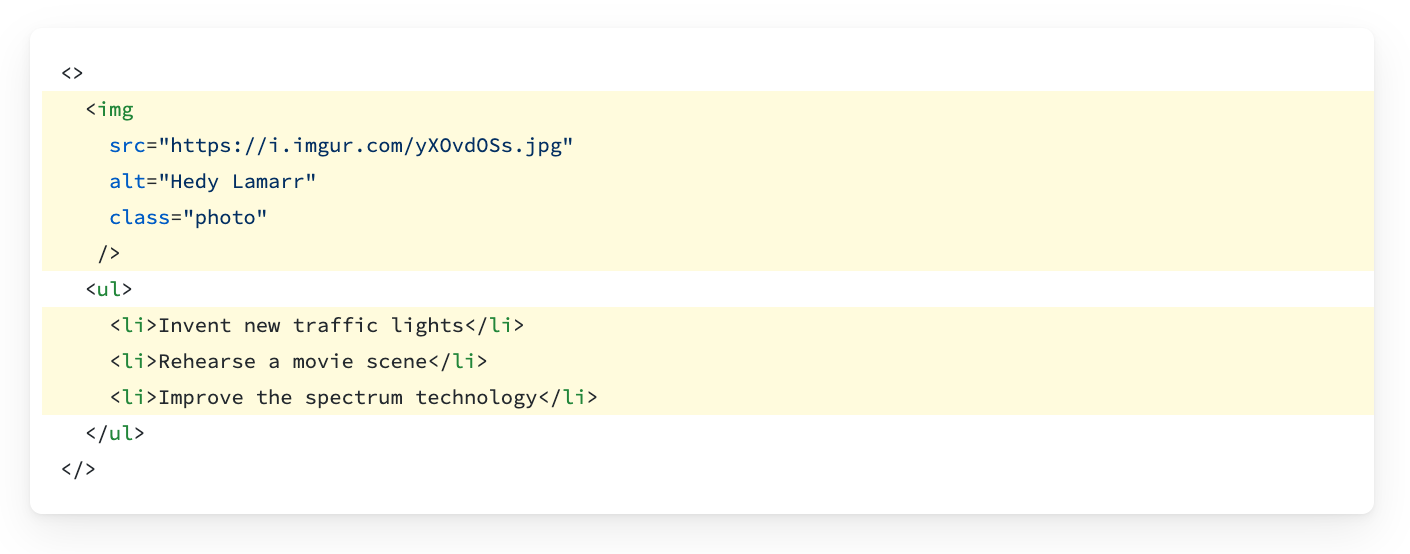
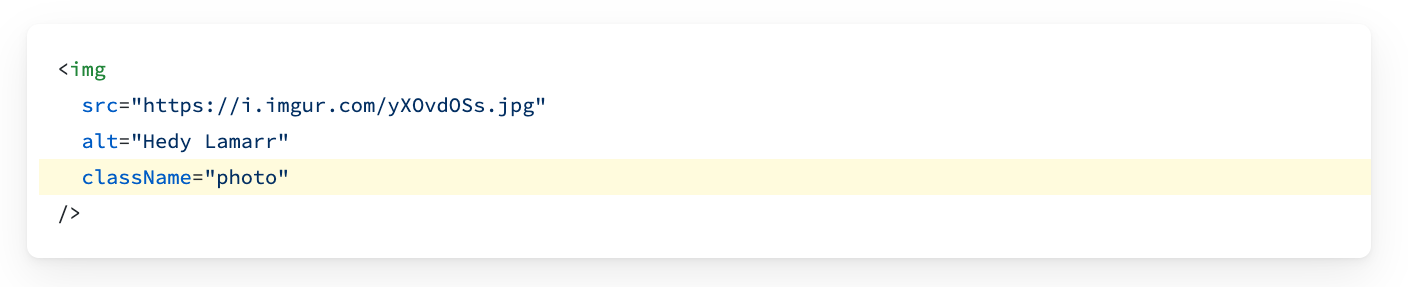
3. camelCase most of the things!
Pro-tip: Use a JSX Converter
Converting all these attributes in existing markup can be tedious!
https://transform.tools/html-to-jsx
Practice 👨💻🧑💻
JavaScript in JSX with Curly Braces
When you want to pass a string attribute to JSX, you put it in single or double quotes.
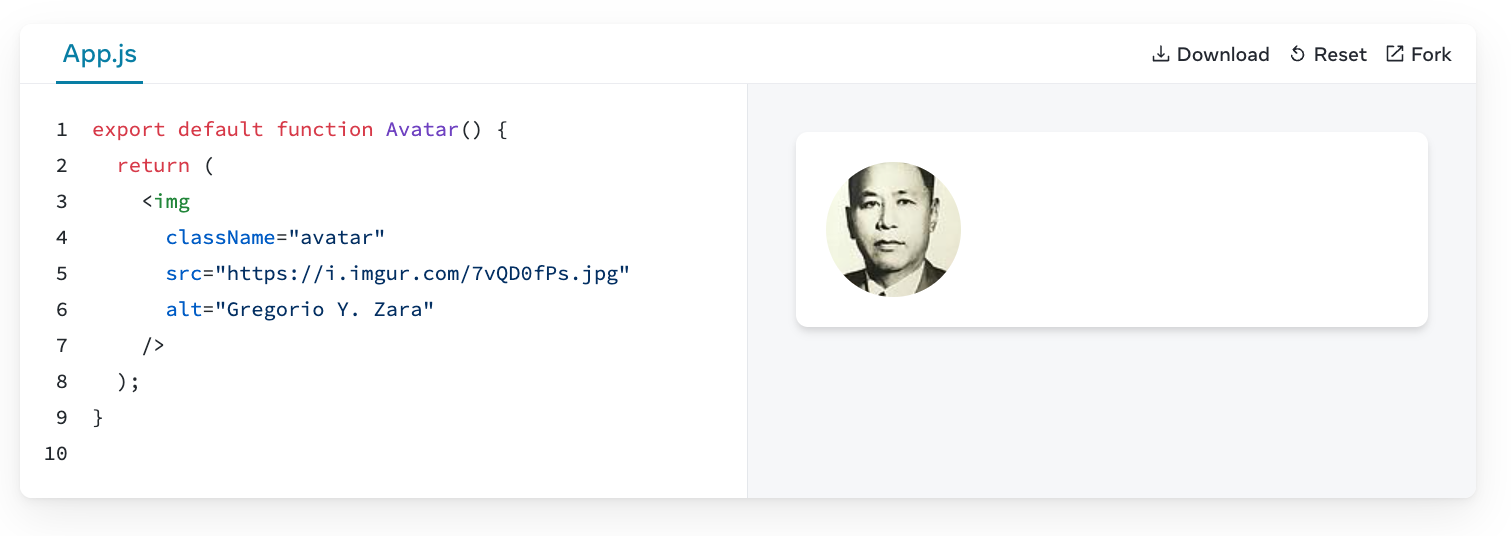
If you want to dynamically specify the src or alt text, you could use a value from JavaScript by replacing " and " with { and }:
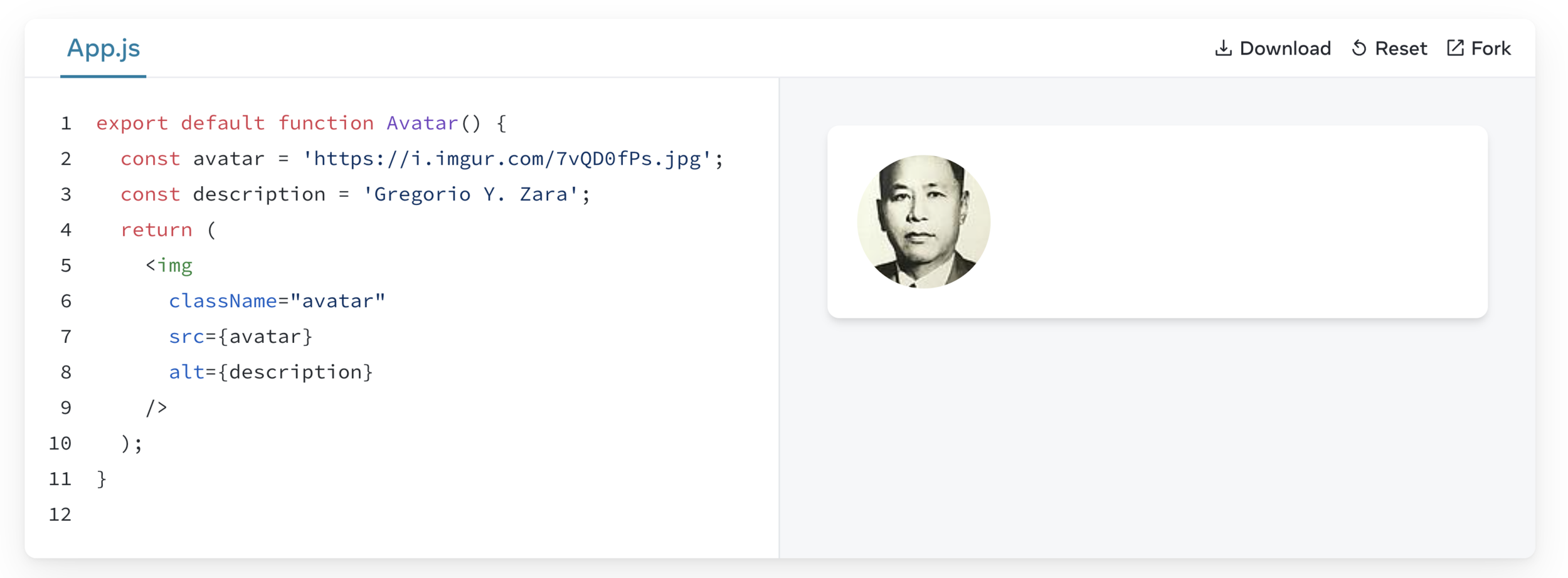
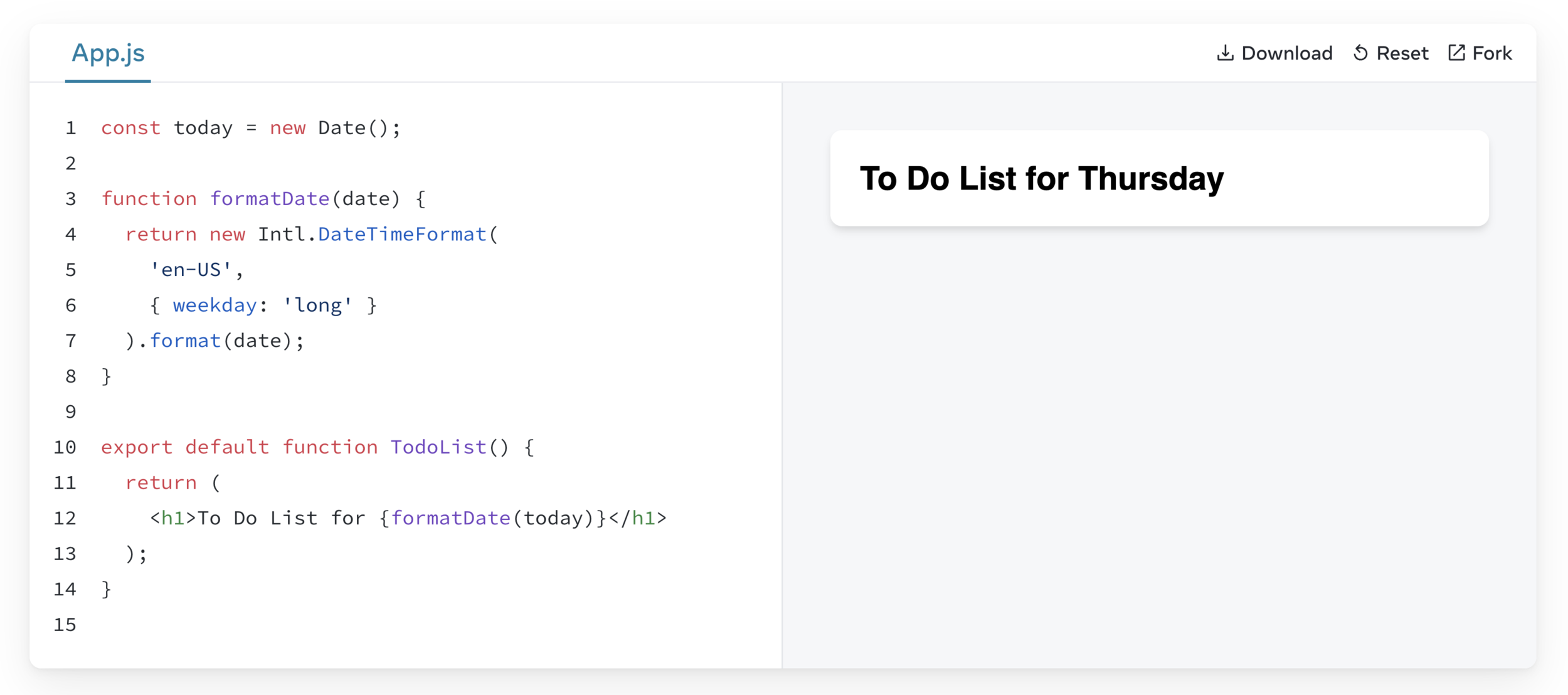
Any JavaScript expression will work between curly braces, including function calls like formatDate():
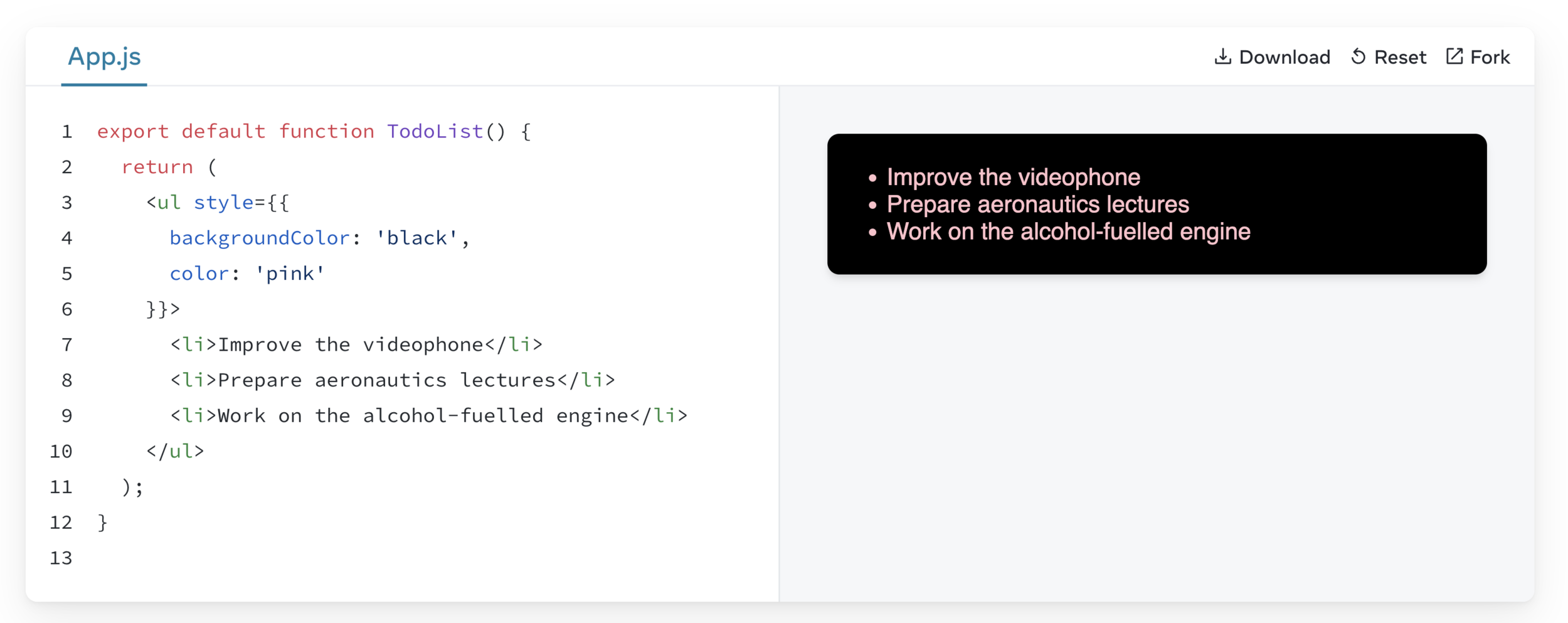
Using “double curlies”: CSS and other objects in JSX
In addition to strings, numbers, and other JavaScript expressions, you can even pass objects in JSX.
Practice 👨💻🧑💻
Fix the mistake
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Extract some Data
In the <Card> Component, extract the Image URL, Title, Price and Availability into Variables or an Object. Then use them in the JSX markup using Curly Brackets.
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-components-solution-82kz7i
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-jsx-solution-jyjv0k
Passing Props to a Component
React components use props to communicate with each other.
Every parent component can pass some information to its child components by giving them props.
Step 1: Pass props to the child component
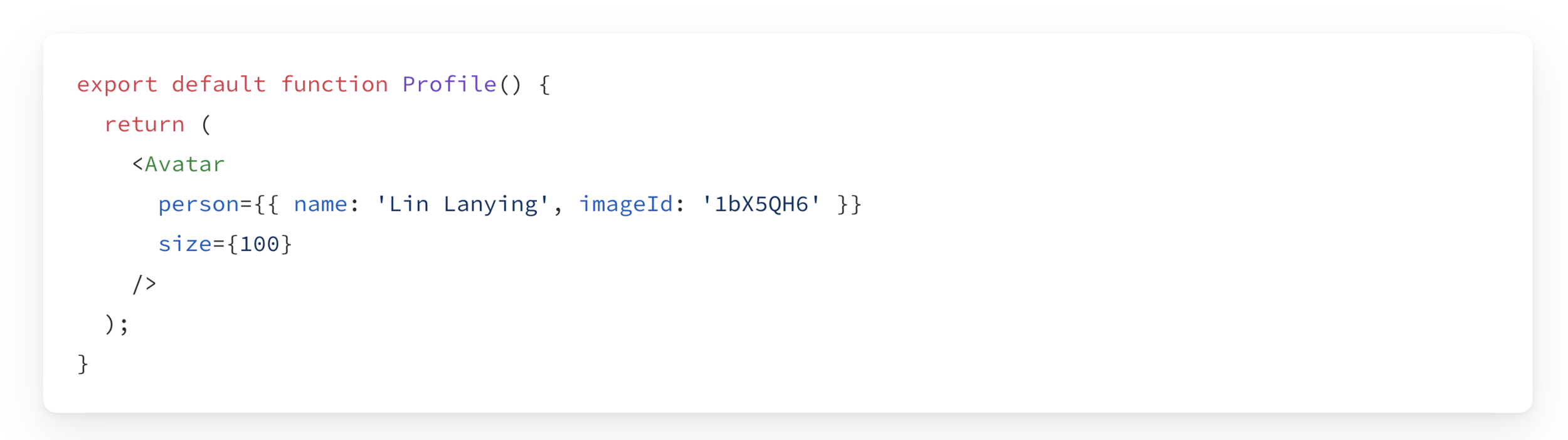
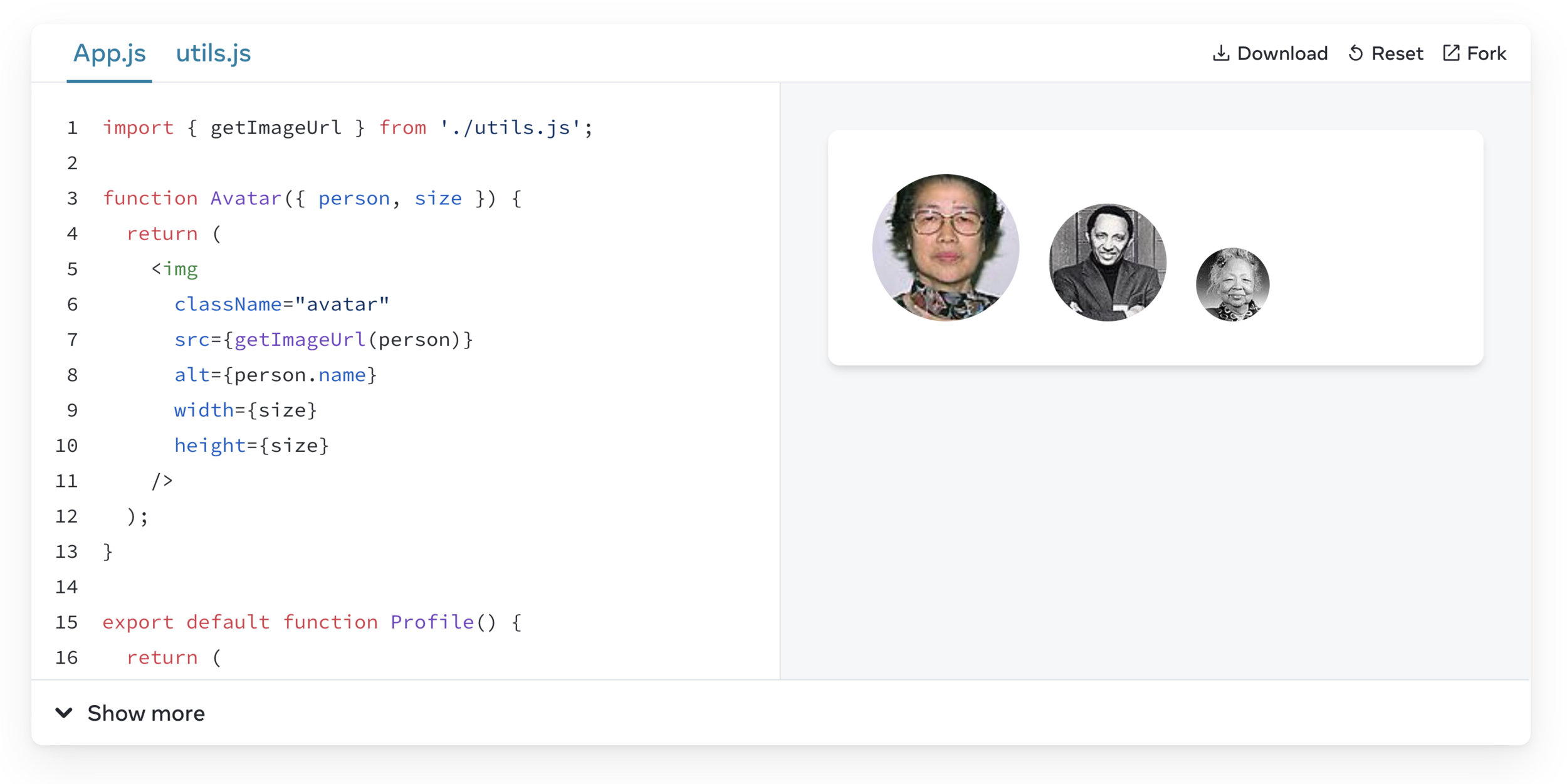
Step 2: Read props inside the child component
Specifying a default value for a prop
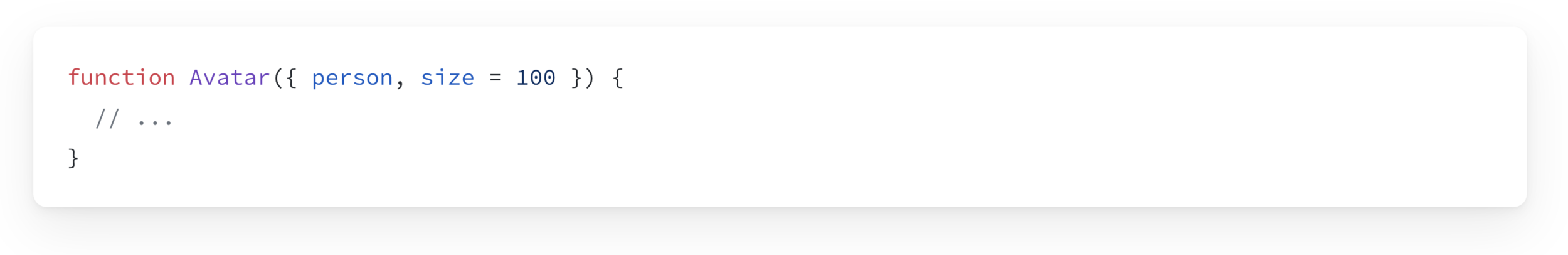
If you want to give a prop a default value to fall back on when no value is specified, you can do it with destructuring by putting = and the default value right after the parameter:
Forwarding props with the JSX spread syntax
Sometimes, passing props gets very repetitive.
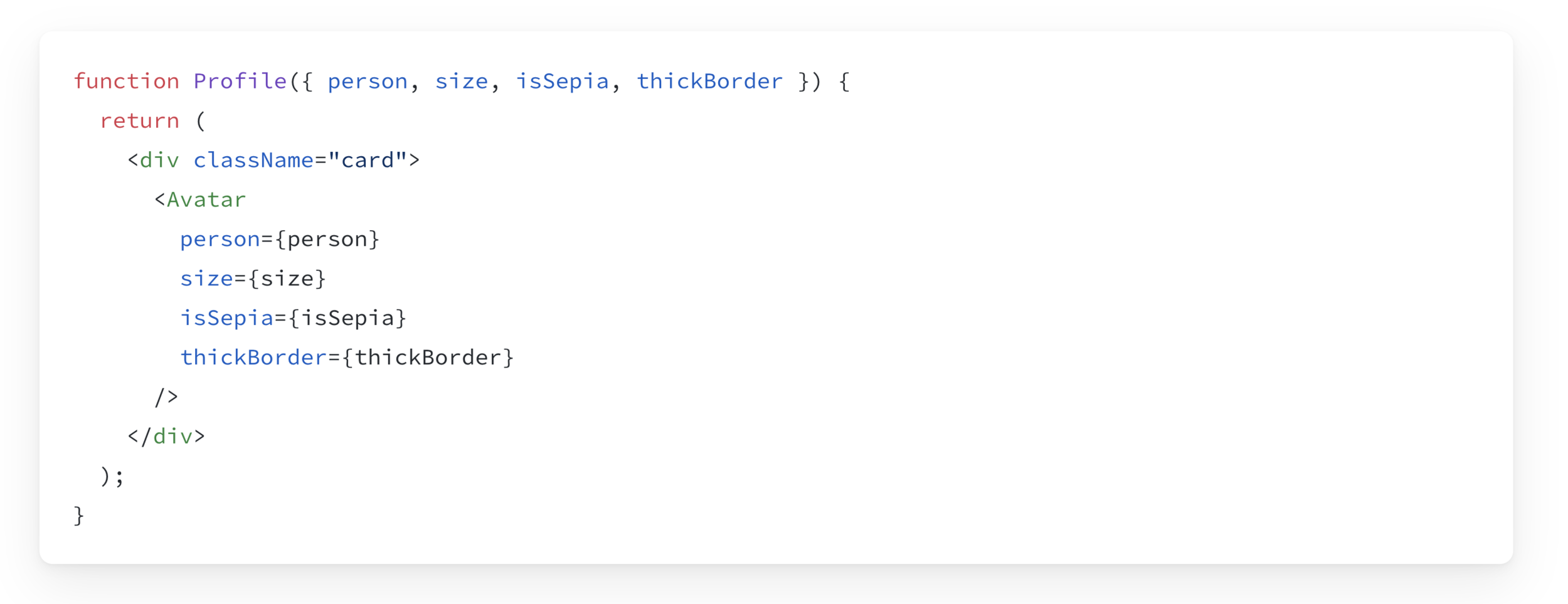
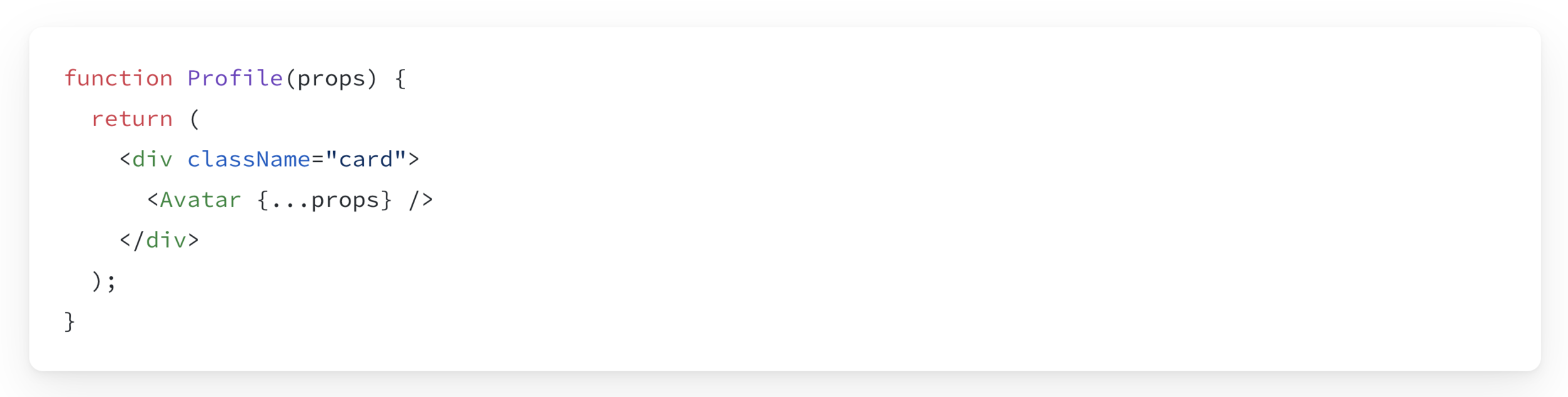
In those cases you can use the Spread Operator to forward all your props.
Optional Practice 👨💻🧑💻
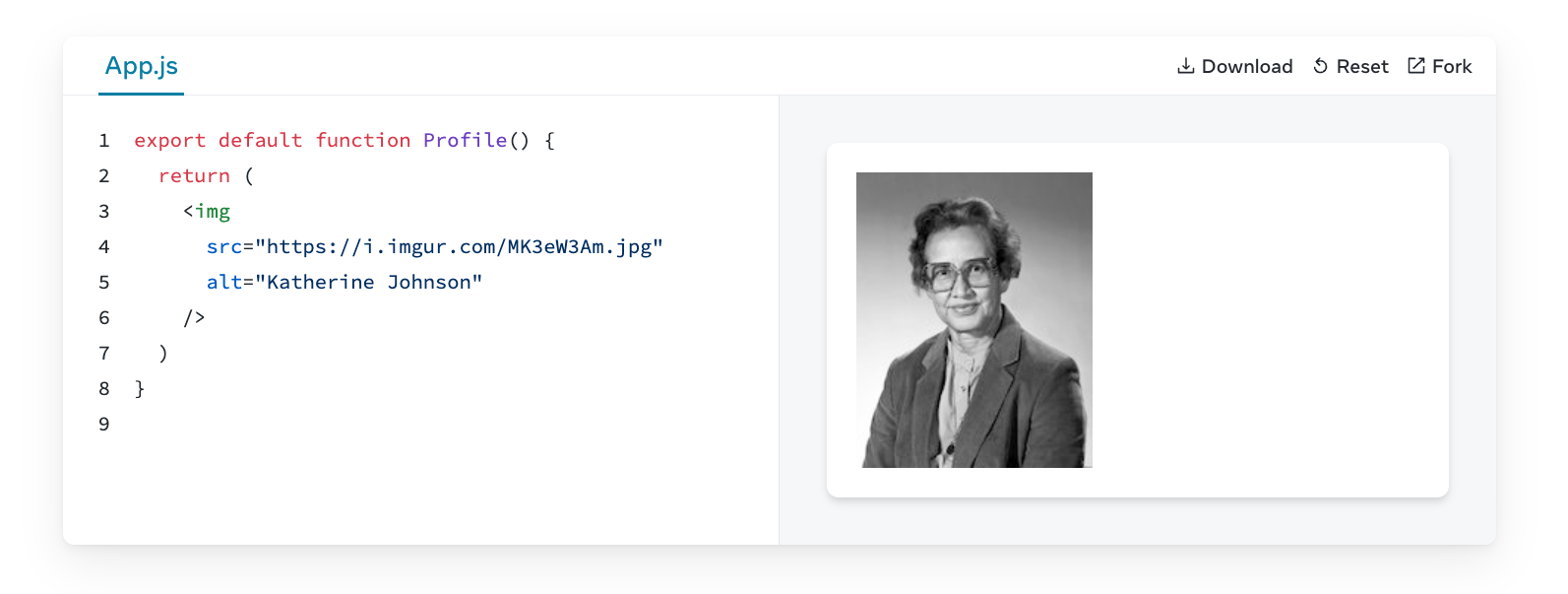
Extract a component
This Gallery component contains some very similar markup for two profiles. Extract a Profile component out of it to reduce the duplication. You’ll need to choose what props to pass to it.
https://codesandbox.io/s/props-extract-wnwrwh
Hint: Start by extracting the markup for one of the scientists. Then find the pieces that don’t match it in the second example, and make them configurable by props
How props change over time
A component may receive different props over time.
Props are not always static!
In the following example, the time prop changes every second, and the color prop changes when you select another color. And whenever props change, the React Component re-renders
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Pass Data down as Props
Move the Card Data (Title, Price etc.) into the App Component and pass it down to the Cards as Props. In the Card component, define default values for each prop.
Bonus: add a new Prop isFavorite to show the Heart in Pink color (text-pink-400) for certain products.
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-jsx-solution-jyjv0k
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-props-solution-zu6wmh
Rendering
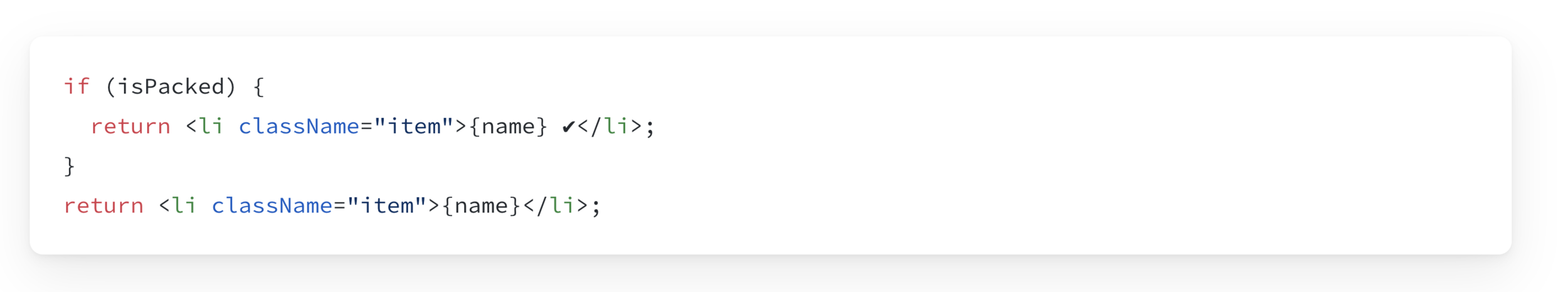
Conditional (ternary) operator
Instead of this:
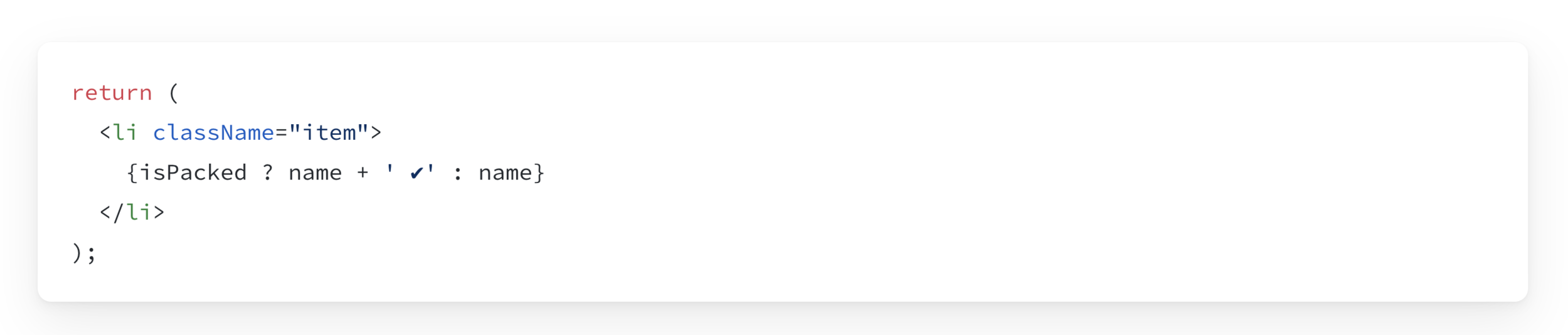
You can write this:
Logical AND operator (&&)
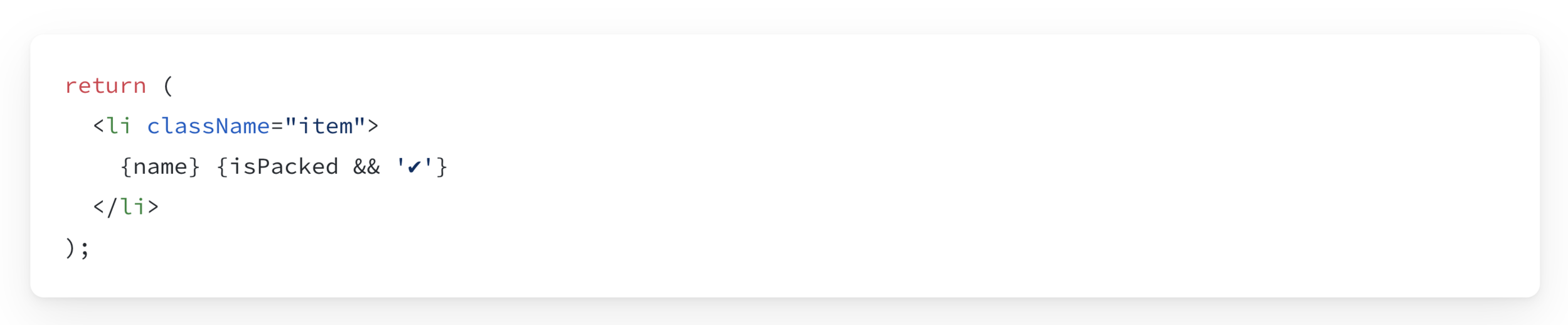

Rendering Lists
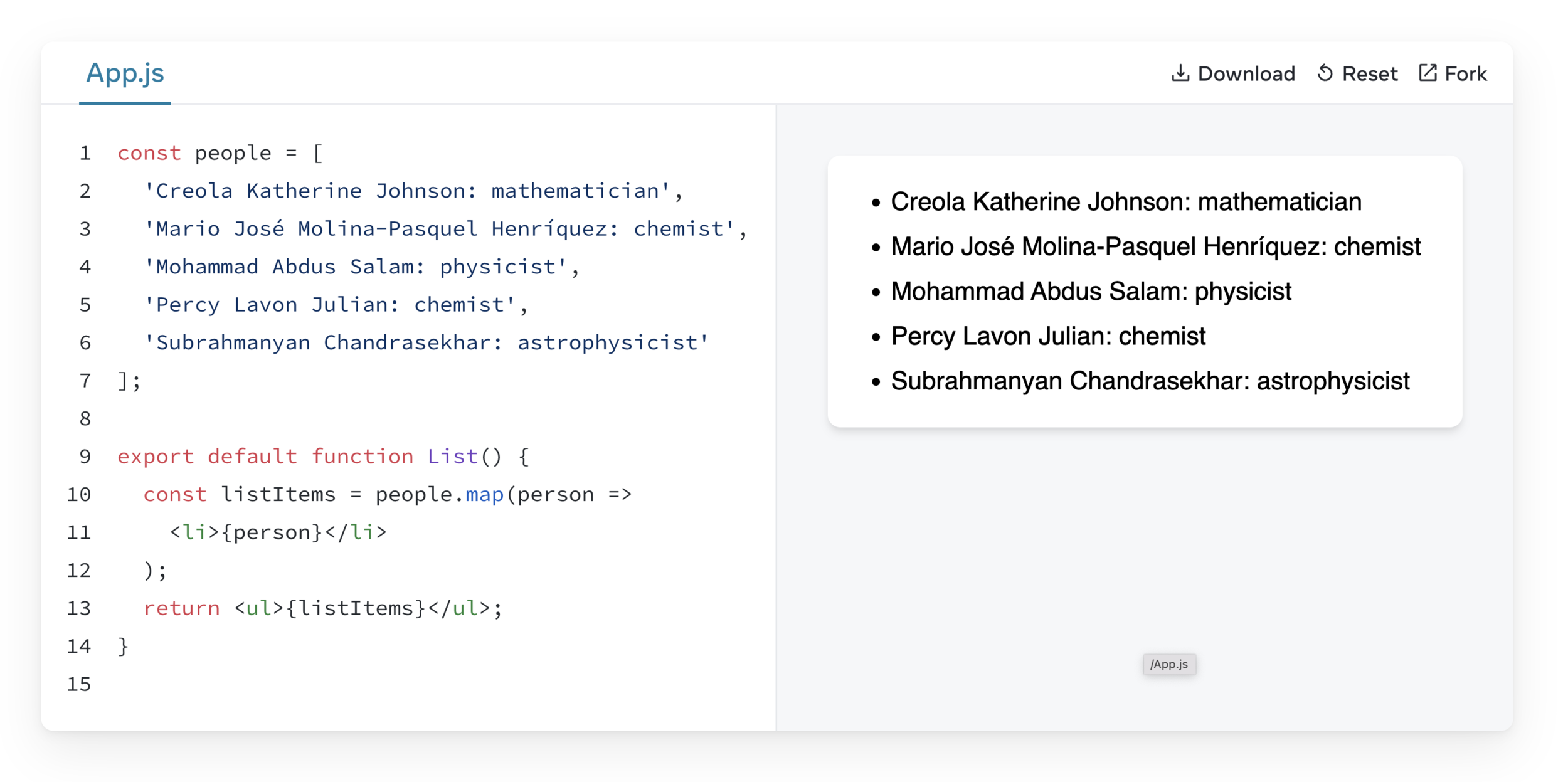
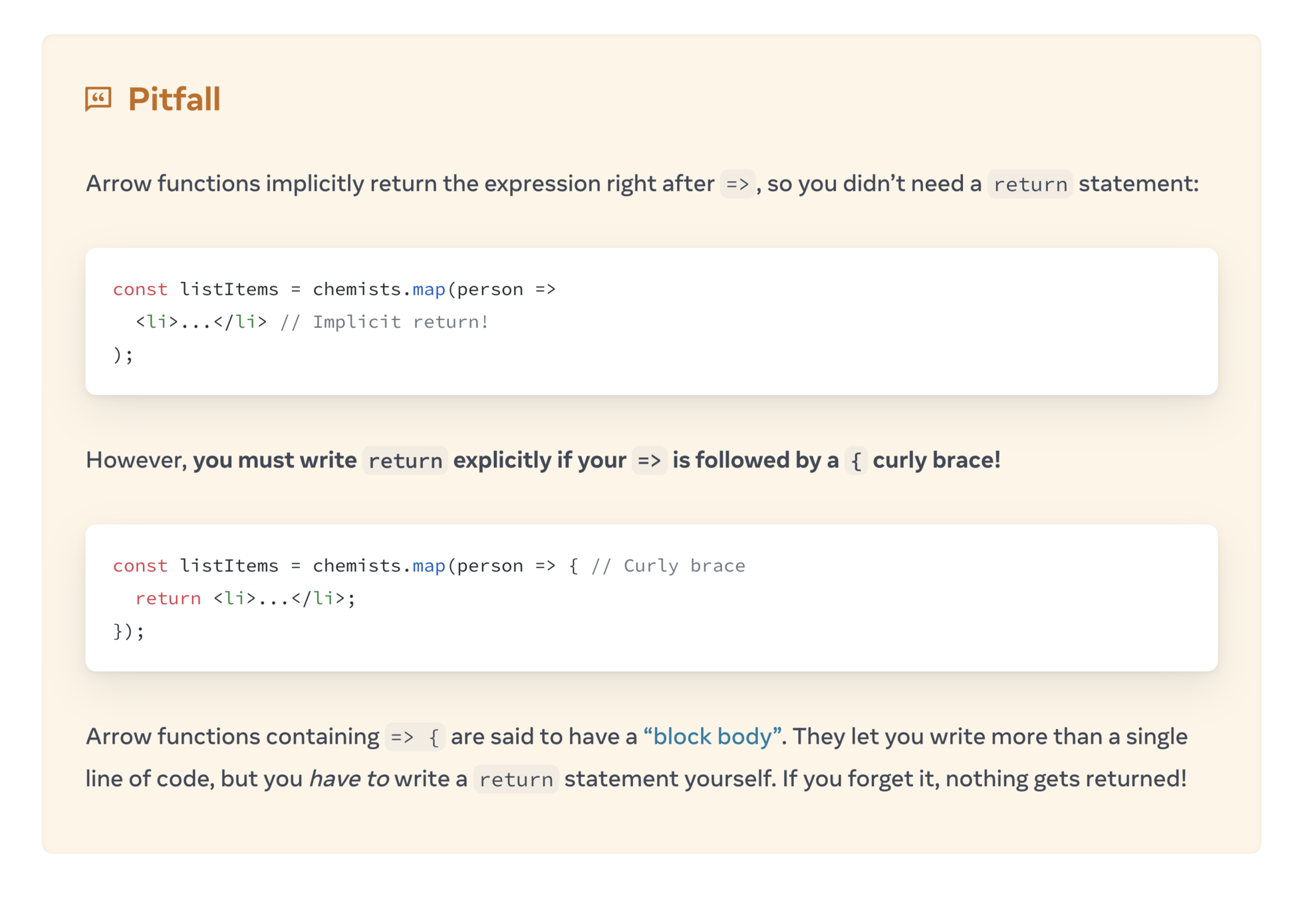
Arrow Functions
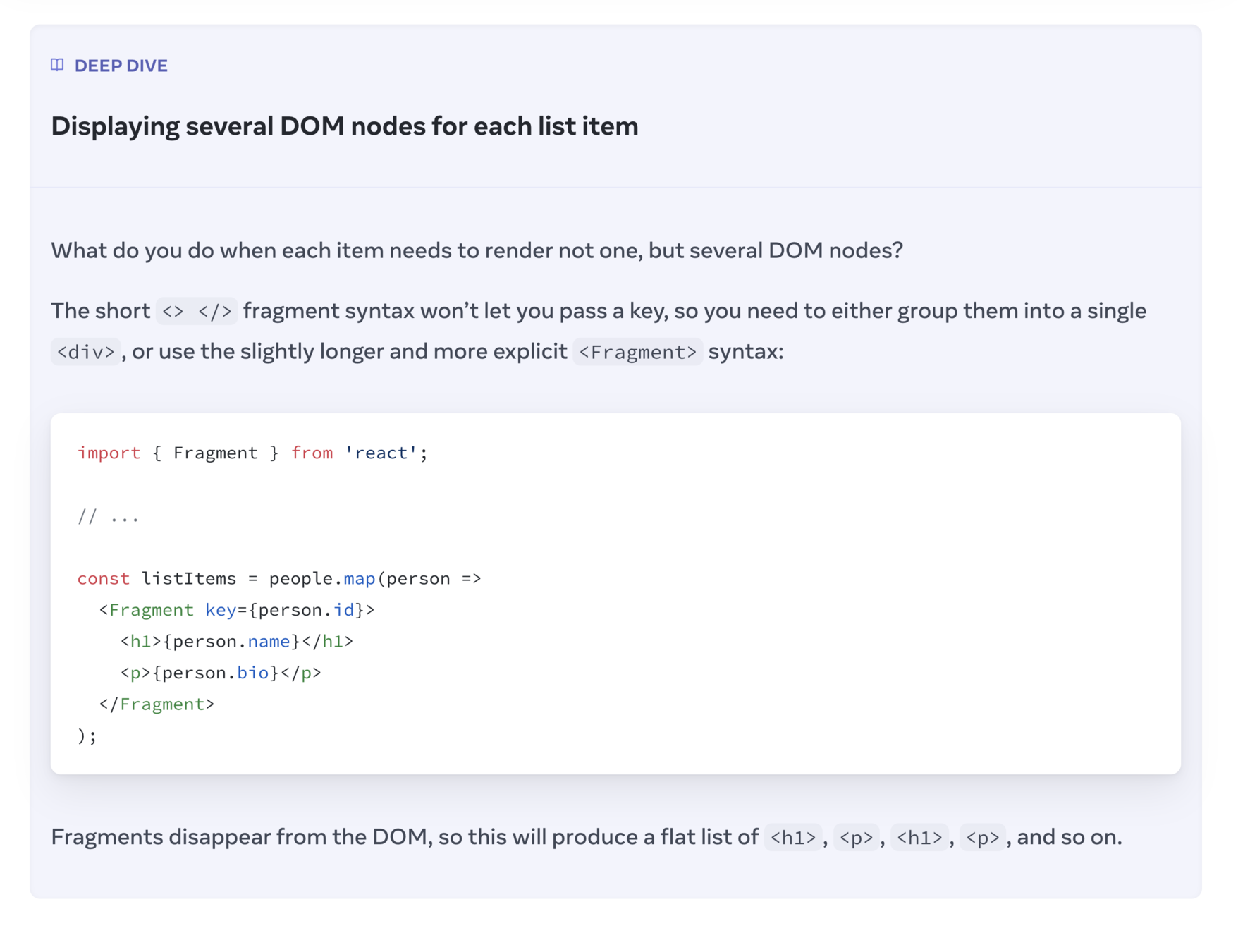
React Fragment
Practice 👨💻🧑💻
Splitting a list in two
This example shows a list of all people. Change it to show two separate lists one after another: Chemists and Everyone Else. You can determine whether a person is a chemist by checking if person.profession === 'chemist'.
https://codesandbox.io/s/rendering-persons-xfyzw3
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/rendering-persons-solution-7ymvgw
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Render Cards as a List
Create an Array with different Card Data (Title, Price etc.) for each Card. Loop over the Array to render the Cards. You can find images for your products in the public/images folder.
Bonus: add a new Prop showSizes to hide the available Sizes on the Card if the product does not have a size (i.e. Tequila)
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-props-solution-zu6wmh
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-rendering-solution-jhqp0g
Events
React lets you add event handlers to your JSX. Event handlers are your own functions that will be triggered in response to interactions like clicking, focusing and so on.

Alternative Syntax
Instead of passing a function, you can write the Event Handler inline:
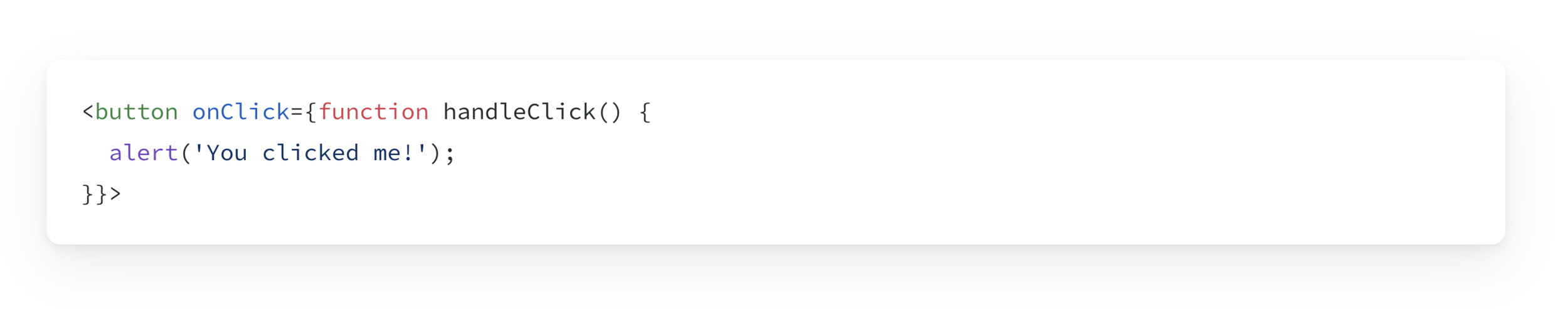
Or using an Arrow Function:
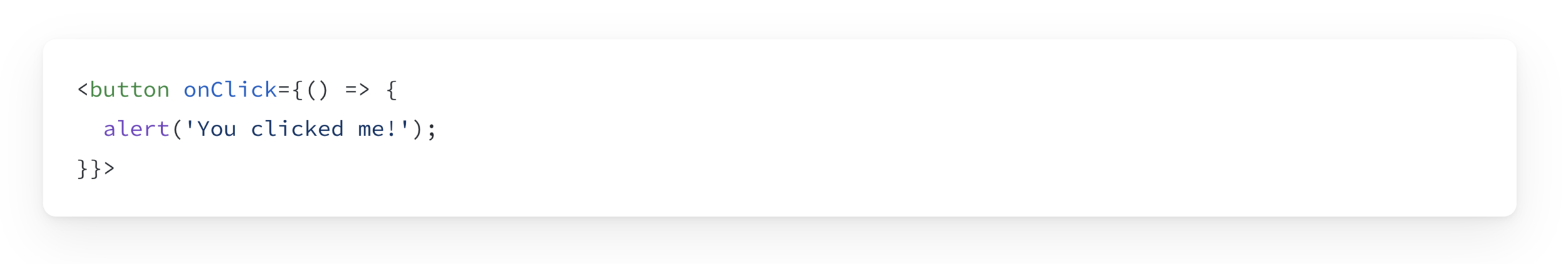
Practice 👨💻🧑💻
Fix an Event handler
Clicking the button is supposed to switch the page background between white and black. However, nothing happens when you click it. Fix the problem. (Don’t worry about the logic inside handleClick — that part is fine.)
https://codesandbox.io/s/events-toggle-the-lights-gky5xy
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/events-toggle-the-lights-solution-wpf9qj
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Add Event Listener
In the Card Component, add onClick Events for the Add to Cart button and the Favorite Button. The Events should just log to the Console (console.log) what was clicked i.e. Add to Cart: Dom Perignon.
Bonus: add onChange Event Listener to the Sizes Selection and save which size was selected.
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-rendering-solution-jhqp0g
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-events-solution-7736rz
State
Components often need to change what’s on the screen as a result of an interaction.
For example, typing into the form should update the input field. Clicking “next” on an image carousel should change which image is displayed etc.
When a regular variable isn’t enough
1. Local variables don’t persist between renders. When React renders this component a second time, it renders it from scratch—it doesn’t consider any changes to the local variables.
2. Changes to local variables won’t trigger renders. React doesn’t realize it needs to render the component again with the new data.
Example https://codesandbox.io/s/state-local-variable-xgkjgz
Adding a state variable
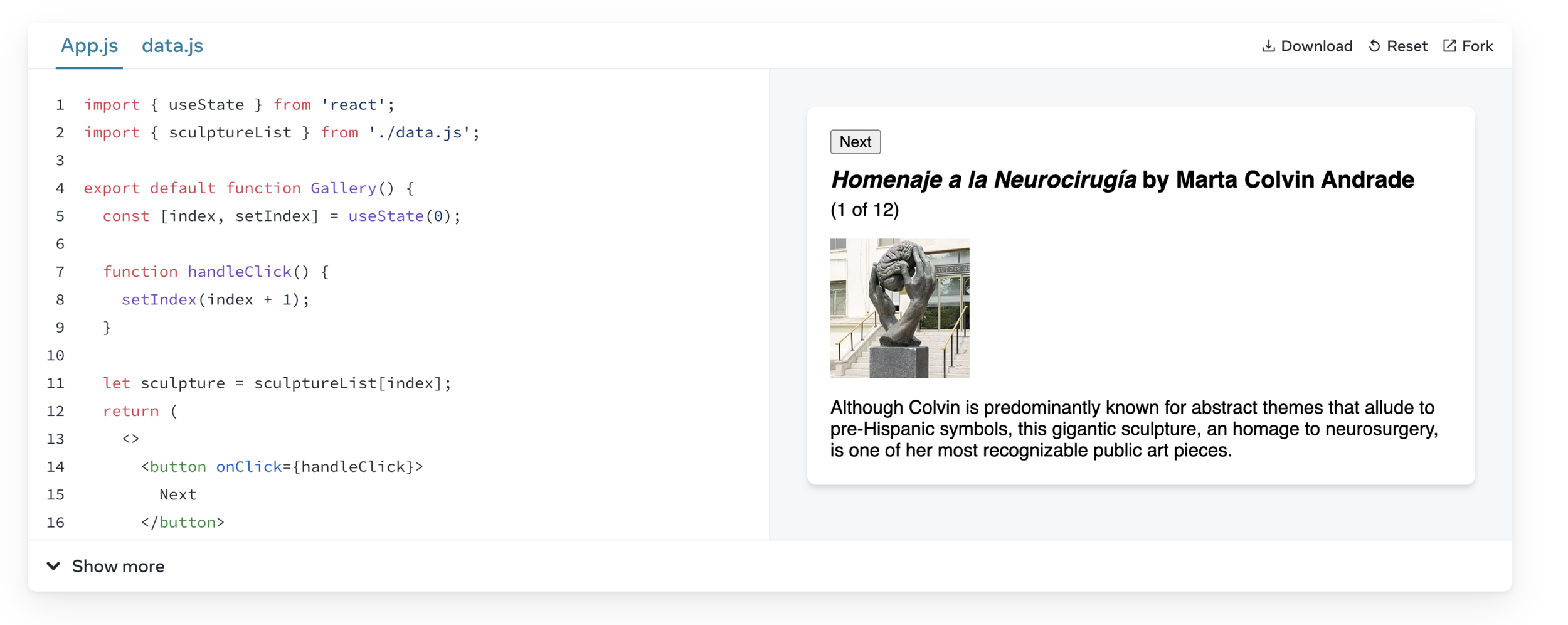
Meet your first Hook
In React, useState, as well as any other function starting with ”use,” is called a Hook.

A simple Example

Practice 👨💻🧑💻
Complete the gallery
When you press “Next” on the last sculpture, the code crashes. Fix the logic to prevent the crash. You may do this by adding extra logic to event handler or by disabling the button when the action is not possible.
After fixing the crash, add a “Previous” button that shows the previous sculpture. It shouldn’t crash on the first sculpture.
https://codesandbox.io/s/state-gallery-jc8m4m
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/state-gallery-solution-l6wmmf
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Use State in the Card Component
Use one useState Hook to save for each Card if it is in the Cart and if it is a Favorite. Bonus: save which Size is selected.
Use that State to toggle the buttons i.e. show "✓ Added to Cart" and change the color of the Favorite Button.
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-events-solution-7736rz
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/galaxus-mini-state-solution-jpljqp
React batches state updates
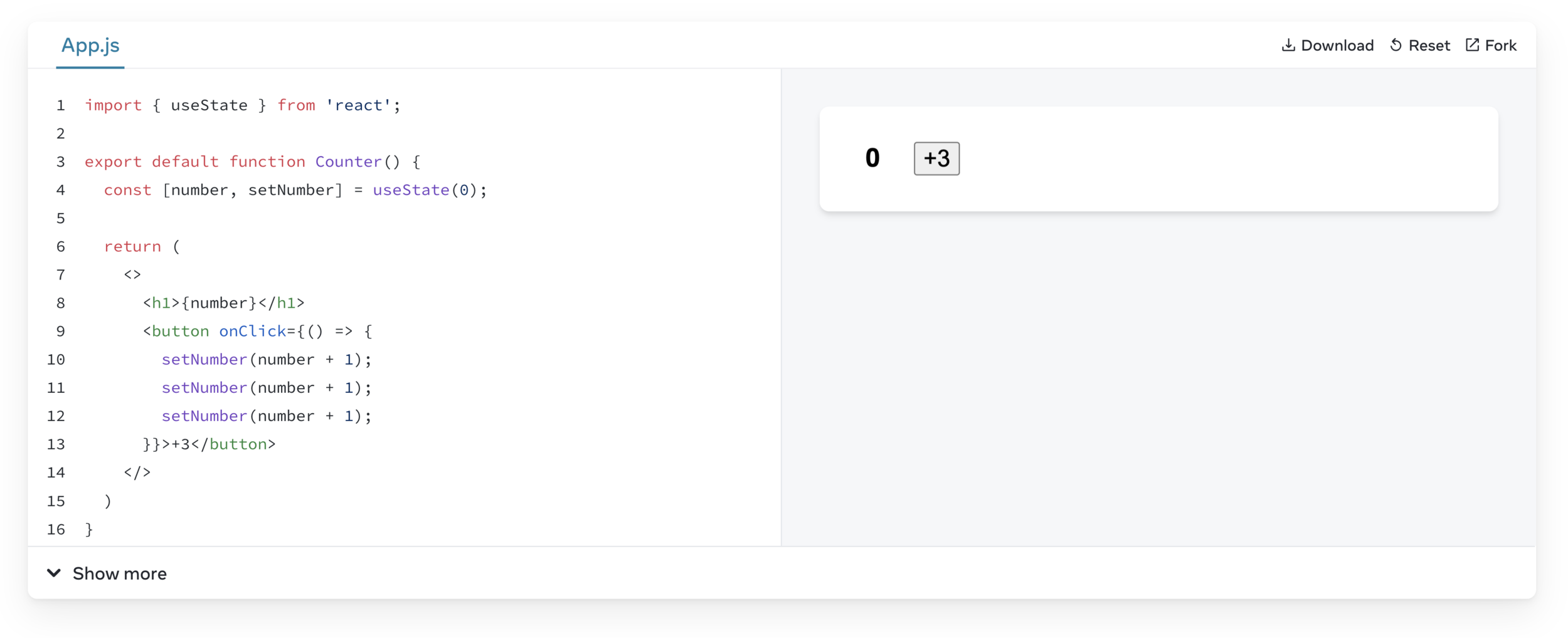
Updating the same state variable multiple times
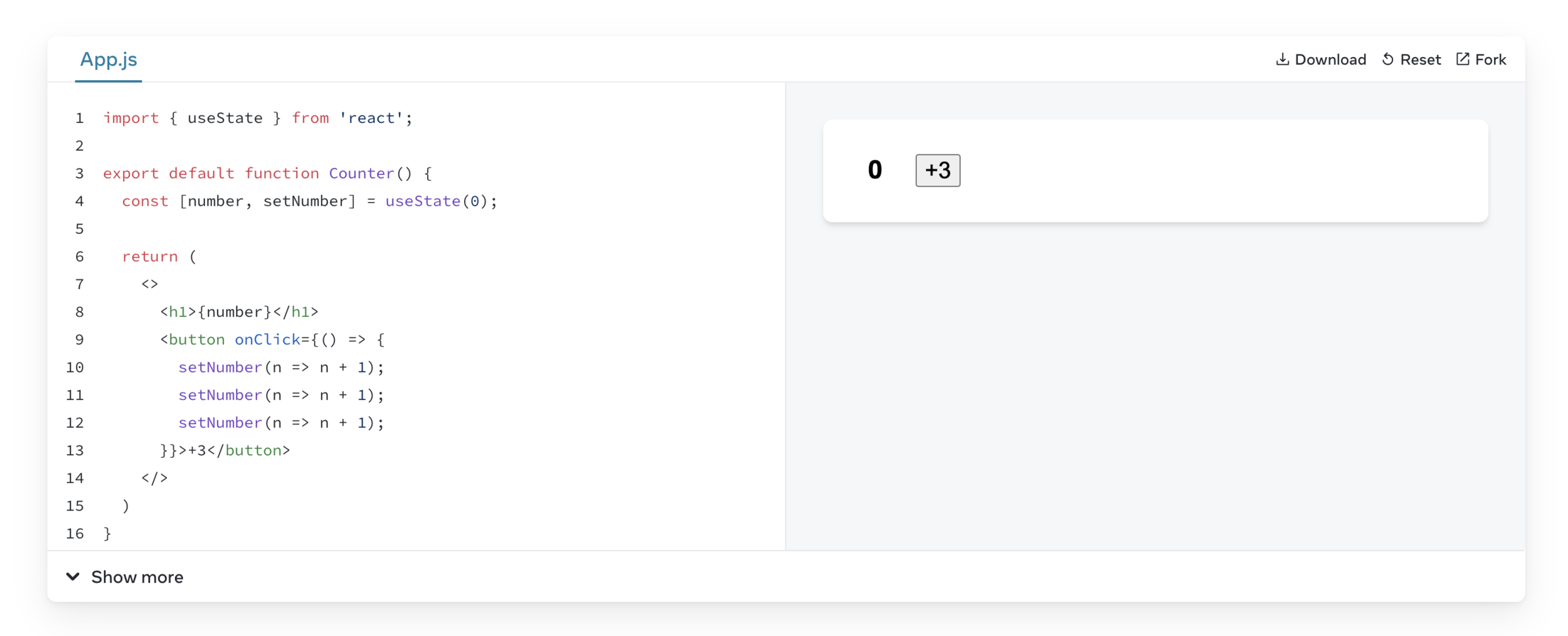
useState Updater Function
Overall, using an updater function with setState provides flexibility, ensures the most up-to-date state, and allows for complex state updates or performance optimizations.
When the next State depends on the previous State it's best to use an updater function.
Counter Example https://codesandbox.io/s/counter-updater-function-dpkxdh
More Info: https://react.dev/reference/react/useState#setstate-caveats
Updating Objects in State
State can hold any kind of JavaScript value, including objects. But you should not change objects that you hold in the React state directly.
Instead, when you want to update an object, you need to create a new one (or make a copy of an existing one), and then set the state to use that copy.
Example Mutating the State directly does not work
https://codesandbox.io/s/state-mutating-objects-j3hs62
Copying objects with the spread syntax
We need to use the setState Function to Update the state. And we need to copy the existing data into it.
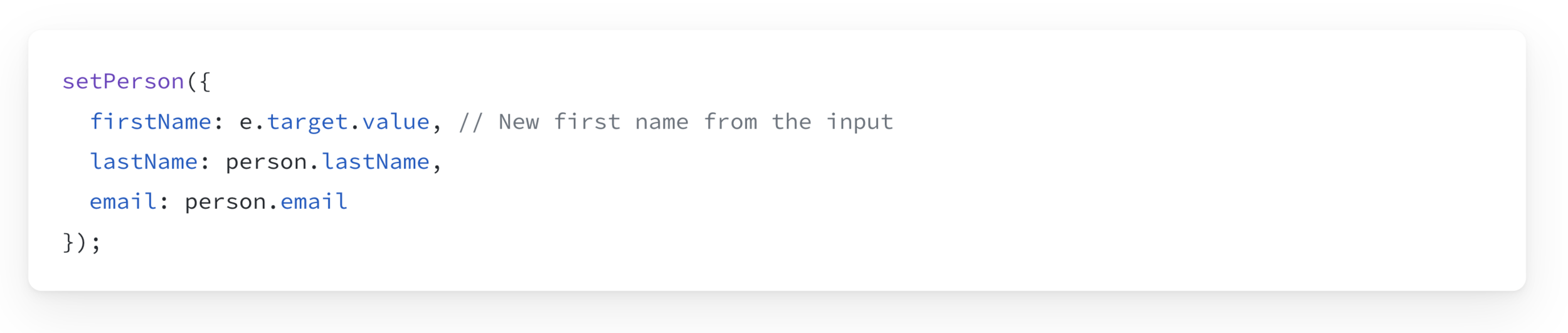
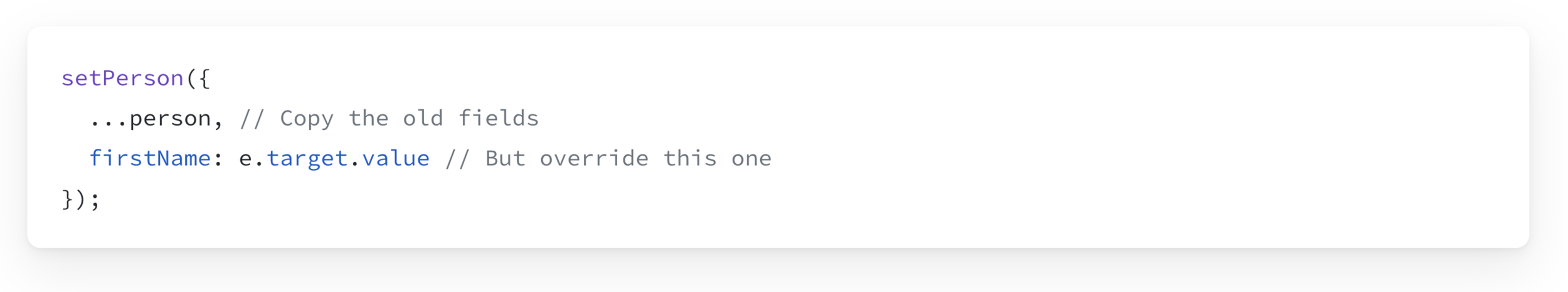
Object Spread Syntax:
Updating a nested object
To update a nested Object, we need to copy each "Level".
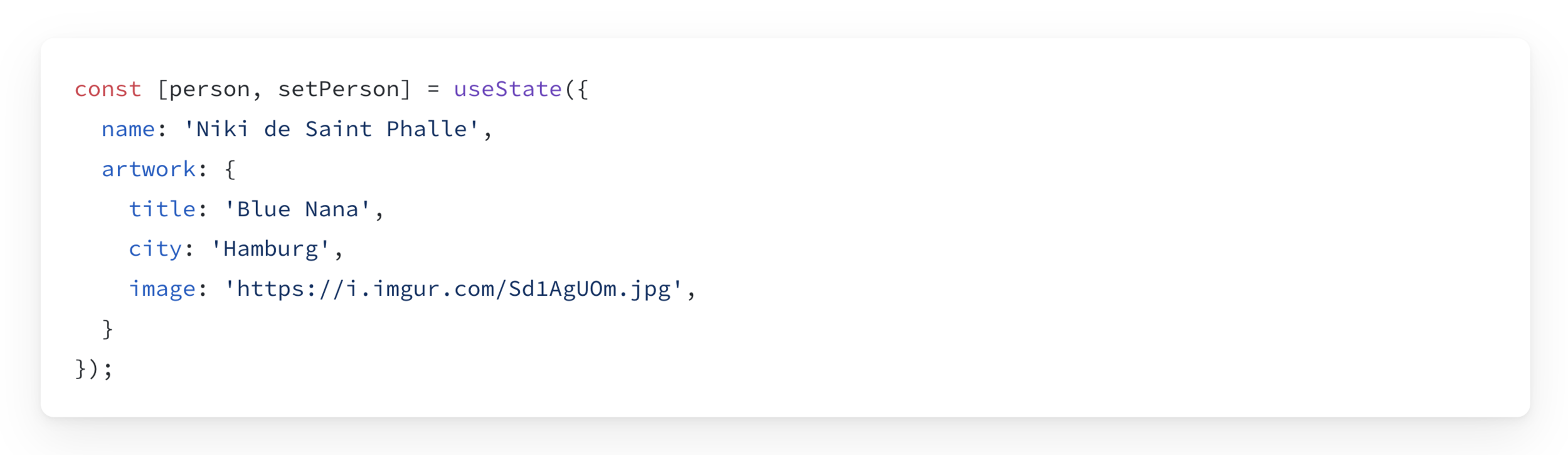
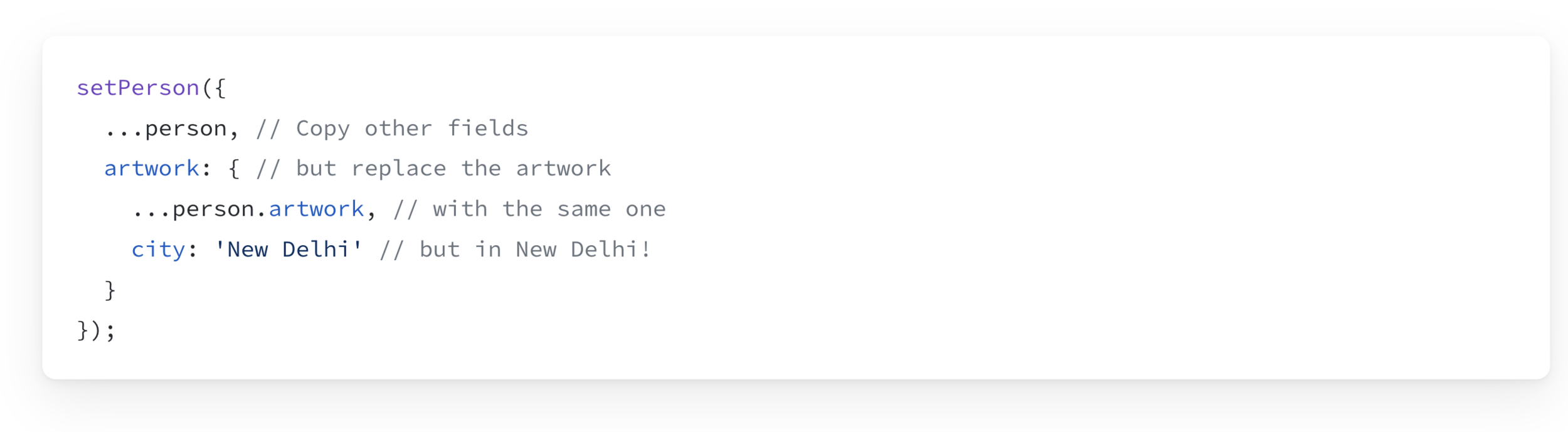
Changing the city prop:
Write concise update logic with Immer
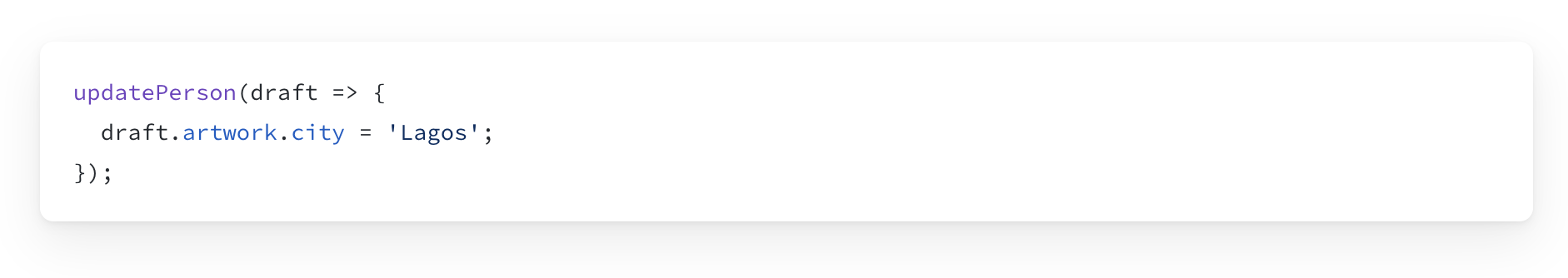

Practice 👨💻🧑💻
Replace the Updating Logic
Use Immer JS to simplify the state Updating Logic.
https://codesandbox.io/s/state-immer-kkcz78
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/state-immer-solution-2m3zw7
Updating Arrays in State
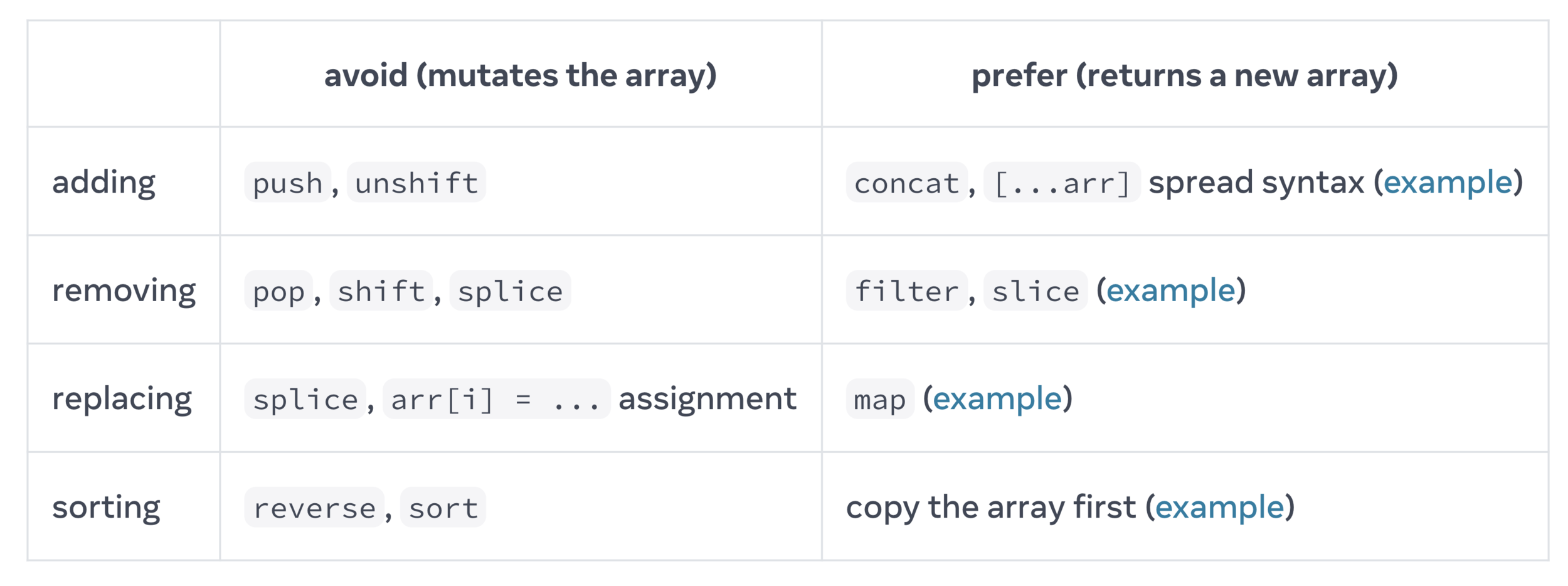
Updating an Array
Add something:
Change something:

More Examples: https://react.dev/learn/updating-arrays-in-state
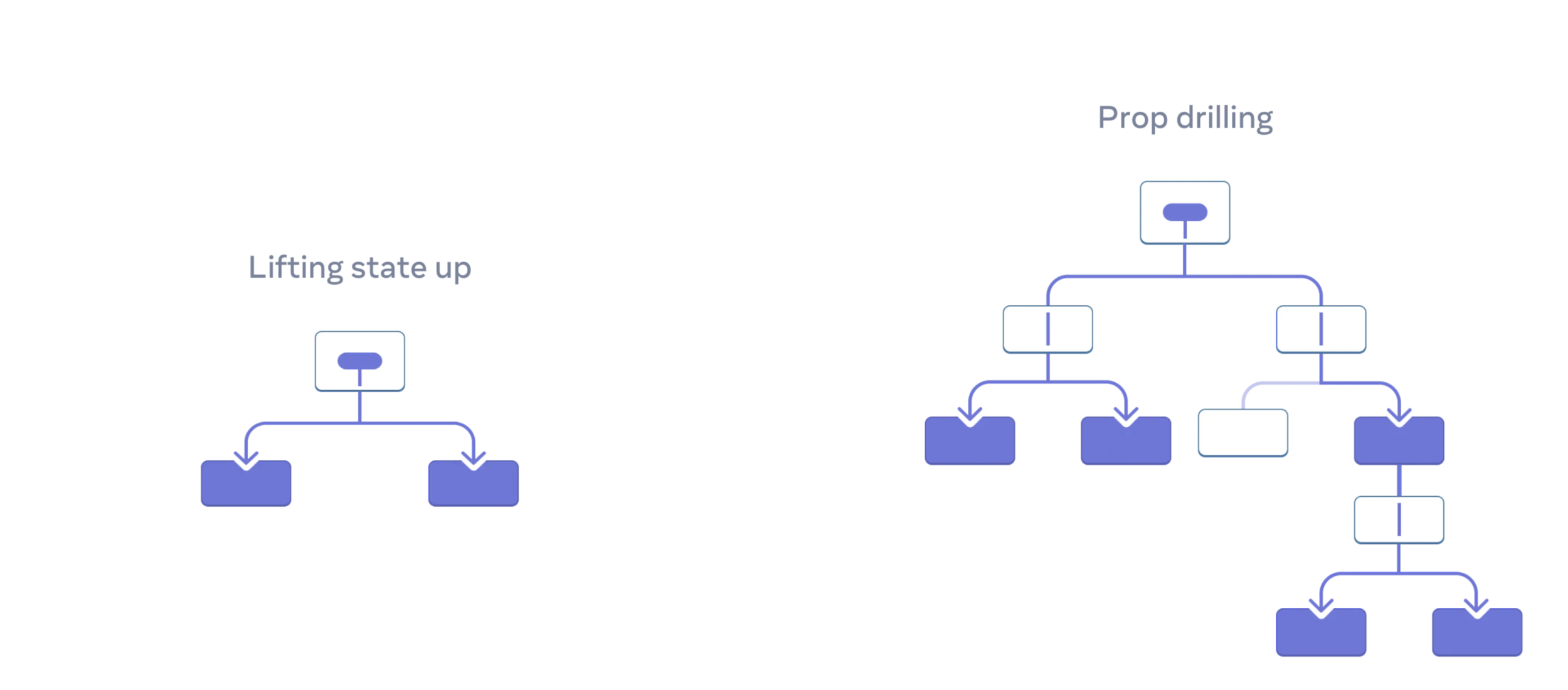
Sharing State Between Components
Sometimes, you want the state of two components to always change together.
To do it, remove state from both of them, move it to their closest common parent, and then pass it down to them via props.
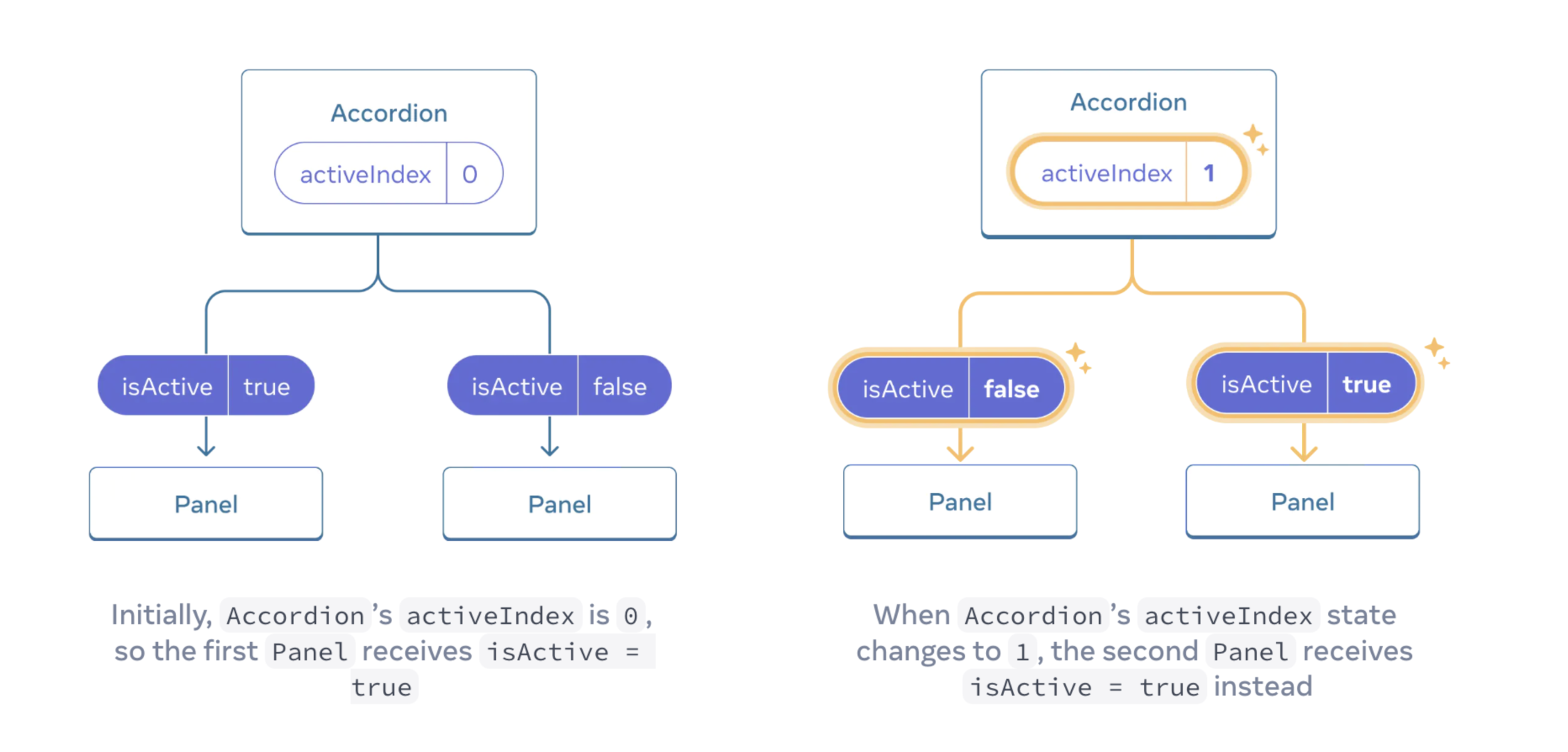
Lifting state up by example

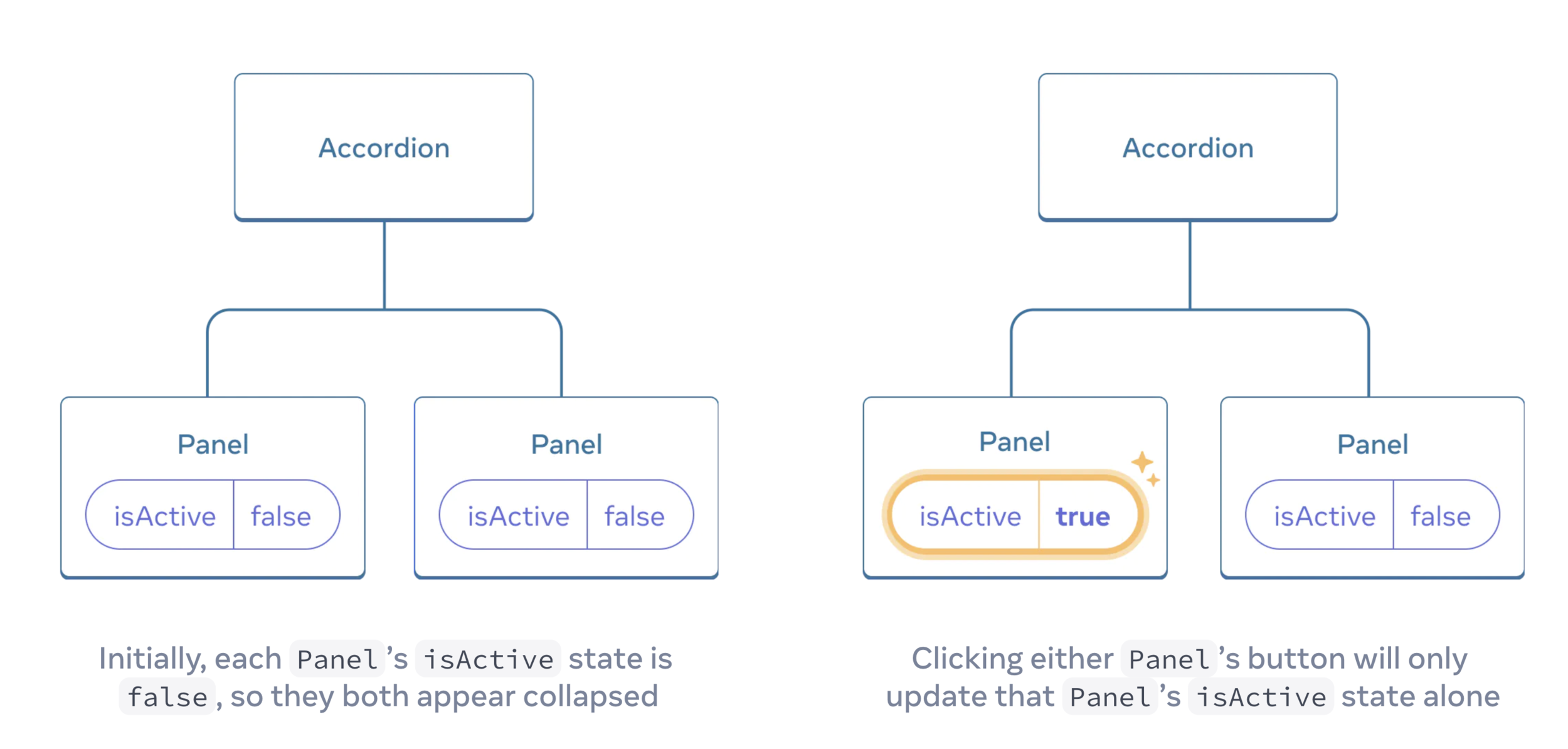
Notice how pressing one panel’s button does not affect the other panel—they are independent.
But now let’s say you want to change it so that only one panel is expanded at any given time.
Step 1: Remove state from the child components
Step 2: Add state to the common parent
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Lift State Up
Lift the state handleAddToCart up from the Card Component into the App Component.
Bonus: show on the Cart Icon how many Products are currently in the Bag.
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/galaxus-mini-state-solution-jj4jg3
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/galaxus-mini-state-up-solution-53vrq9
Context
Context lets the parent component make some information available to any component in the tree below it—no matter how deep—without passing it explicitly through props.
Step 1: Create the context
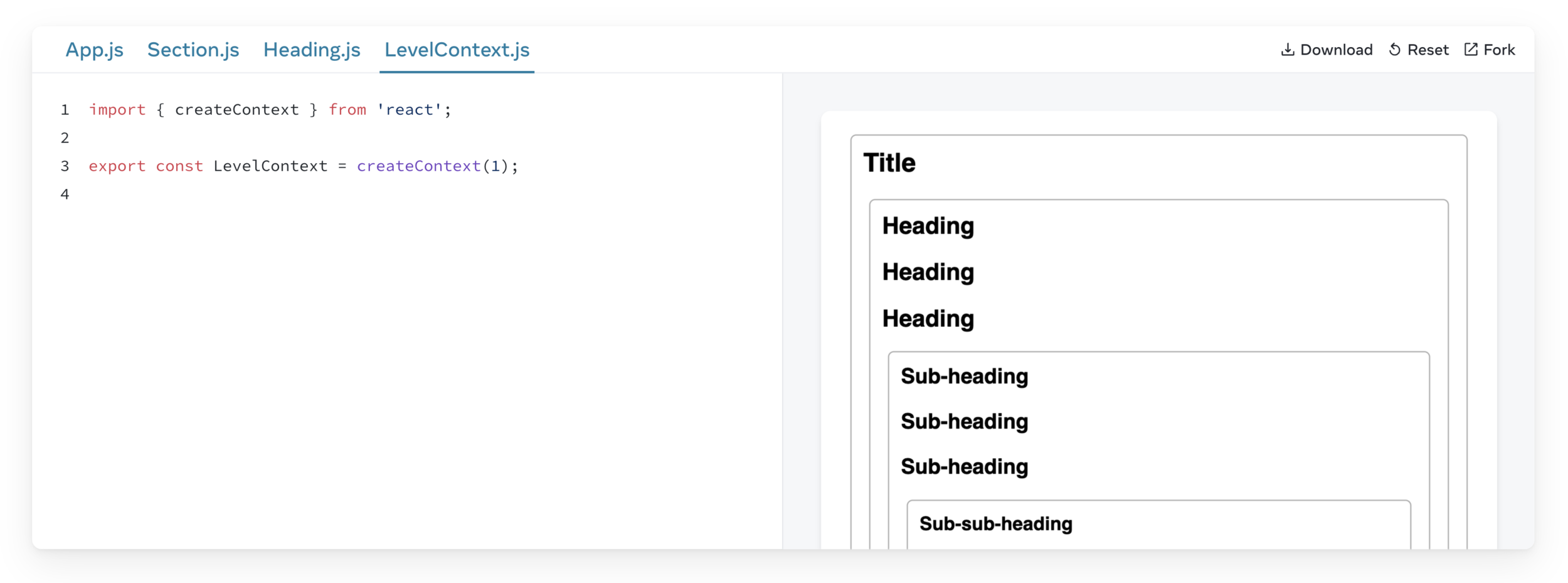
The only argument to createContext is the default value.
Step 2: Use the context
Import the useContext Hook from React and your context.
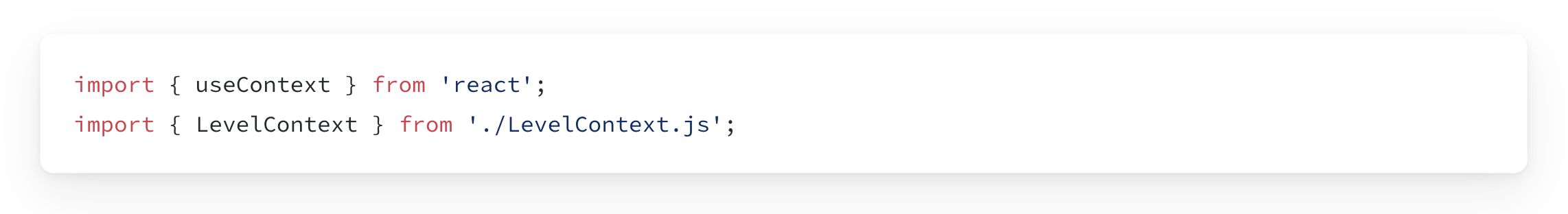
Read the value from the context you just imported.
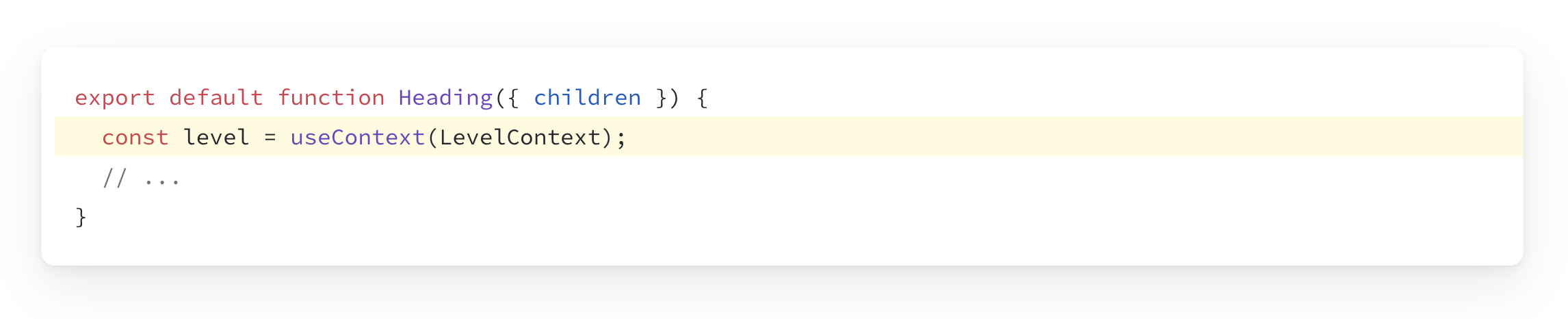
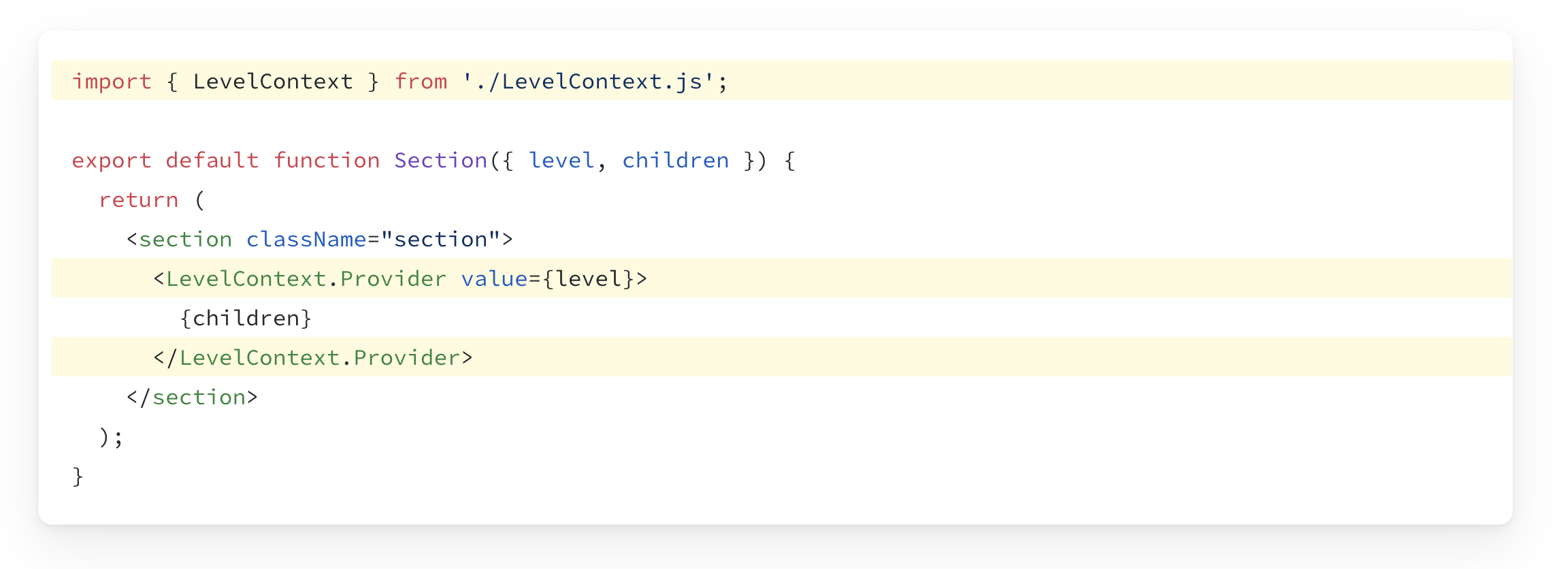
Step 3: Provide the context
Even though we’re using the context, we have not provided it yet. React just uses the default value we specified in the previous step.
Practice 👨💻🧑💻
Replace prop drilling with context
Toggling the checkbox changes the imageSize prop passed to each <PlaceImage>. The checkbox state is held in the top-level App component, but each <PlaceImage> needs to be aware of it.
Currently, App passes imageSize to List, which passes it to each Place, which passes it to the PlaceImage. Remove the imageSize prop, and instead pass it from the App component directly to PlaceImage. You can declare context in Context.js.
https://codesandbox.io/s/context-prop-drilling-2fl3yn
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/context-prop-drilling-solution-x62vmf
Use Cases for Context
Context is very tempting to use! However, this also means it’s too easy to overuse it. Just because you need to pass some props several levels deep doesn’t mean you should put that information into context.
Good Use Cases for context
- Theming: If your app lets the user change its appearance (e.g. dark mode).
- Current account: When components might need to know the currently logged in user.
- Routing: Most routing solutions use context internally to hold the current route. This is how every link “knows” whether it’s active or not.
- Managing state: As your app grows, you might end up with a lot of state closer to the top of your app. Many distant components below may want to change it. It is common to use a reducer together with context to manage complex state.
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Use Context for the Bag Count
Don't pass the count via Props to the MiniCart Component. Instead, use Context to provide it.
Bonus: Use Context to Provide a Dark Theme to every Component. The Theme is currently hardcoded to light in most Components.
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/galaxus-mini-state-up-solution-dng35k
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-context-solution-0tq066
UseEffect
The Effect Hook lets you perform side effects in function components.
A side effect can be data fetching, setting up a subscription or manually changing the DOM.
In other words: Effects let you run some code after rendering so that you can synchronize your component with some system outside of React.
Possible Use Cases
- Data Fetching: Load some data when the component is rendered for the first time.
- Focus an Inputfield: You want to set the Focus into an Inputfield when it renders.
-
Using a jQuery Plugin: Initalize a jQuery Plugin (i.e. Datepicker) when the React Component mounts and destroy it when the Component unmounts.
- ...
Basic Example
Resize Event Listener
https://codesandbox.io/s/use-effect-example-2n8ct9
Dependencies
Per default, the side effect inside useEffect runs on every Render.
We can provide a Dependency Array to run the effect only when one of the dependencies changes.


Dependencies
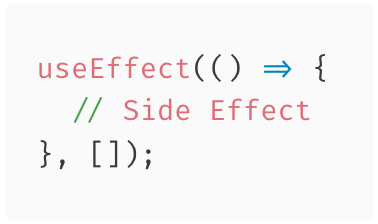
1. Side Effect Runs After Every Render
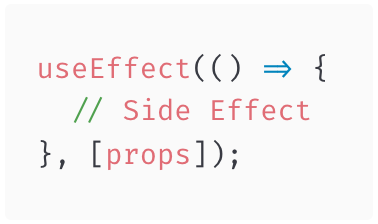
3. Side Effect Runs After State Value Changes

2. Side Effect Runs Only Once After Initial Render
4. Side Effect Runs After Props Value Change

Cleanup Function
Certain effects need cleanup when the React Component unmounts.
Whatever we return from an useEffect Hook will be run when the Component unmounts.
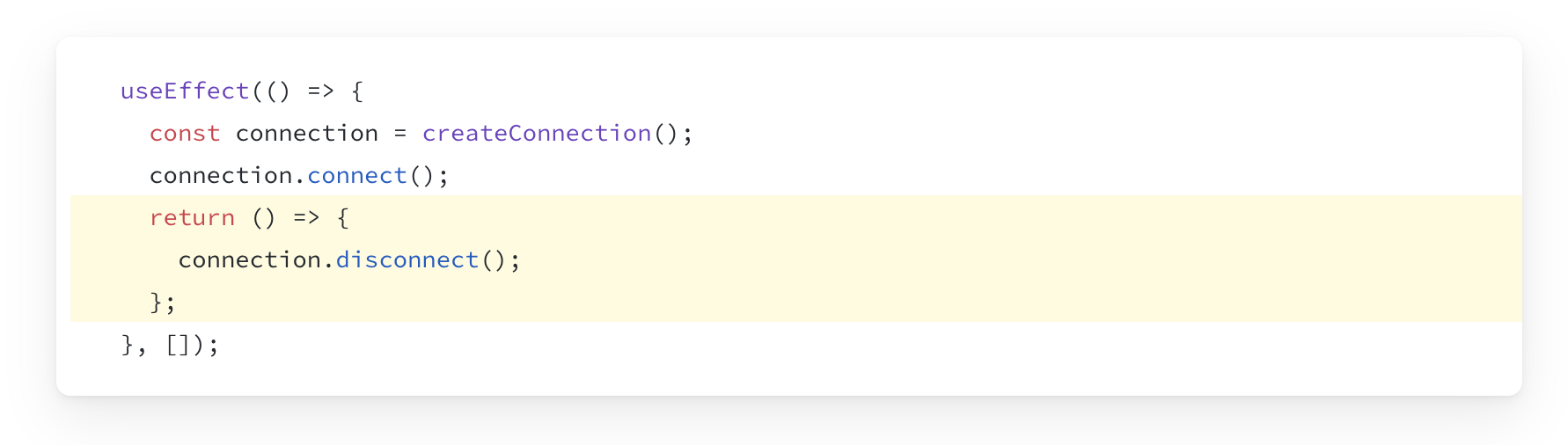
Cleanup Function
Some Examples
- Unmount
https://codesandbox.io/s/use-effect-unmount-kuzg7c
- Clear Interval
https://codesandbox.io/s/use-effect-interval-ulmsc4
- jQuery Plugin
https://codesandbox.io/s/use-effect-jquery-uvtpvb
Data Fetching

In simple application we can use the useEffect Hook for Data Fetching.
Custom Hook
Often times, a custom hook is created with useEffect for Data Loading.
Not an Effect
1. You don’t need Effects to transform data for rendering. Just do it in the render method.
2. You don’t need Effects to handle Events.
For example, let’s say you want to send an /api/buy POST request and show a notification when the user buys a product. Just do it in the Event Handler.
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Fetch the Products and the Cart
Fetch data by using two useEffect Hooks. Use getProducts() and getCartItems() to load data from the API.
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-use-effect-d2w0bw
→ neue Sandbox mit Loading Spinner, bitte diese verwenden.
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-use-effect-solution-br9yxq
Routing
We use React Router for our application.

Link
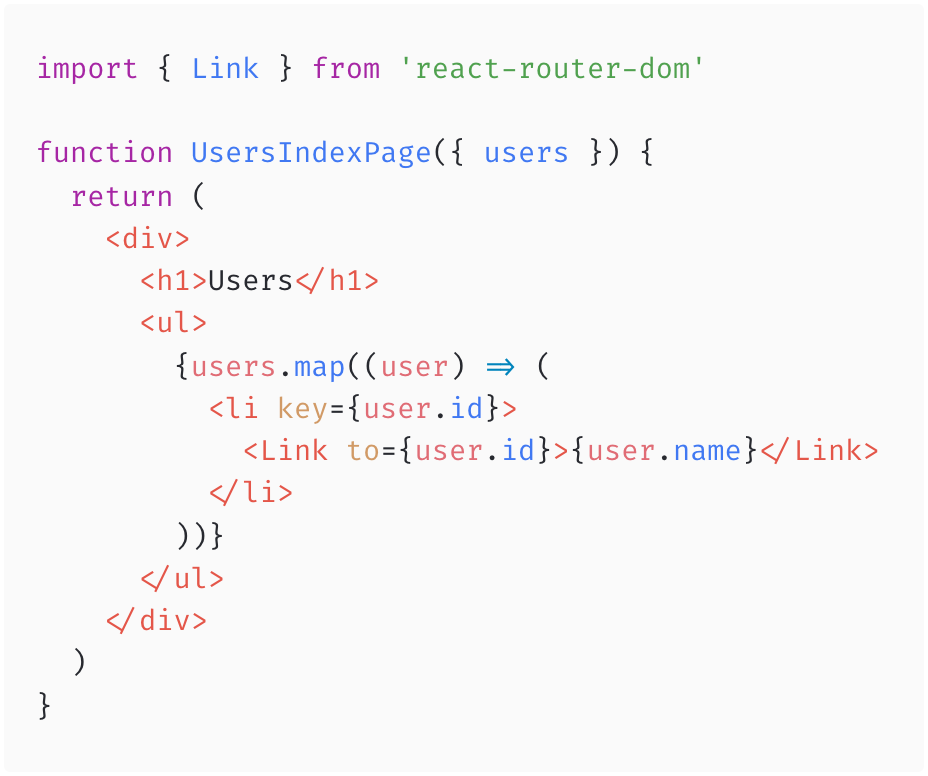
A relative <Link to> value (that does not begin with /) resolves relative to the parent route. It may contain .. to link to routes further up the hierarchy.
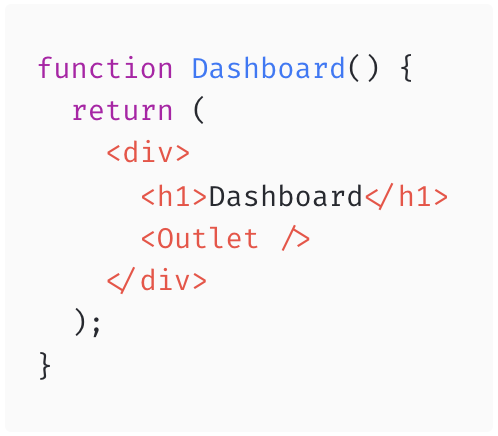
Nested Routes
Dashboard will render in the <Outlet>:
-
<DashboardMessages>when the URL is "/messages" -
<DashboardTasks>when the URL is "/tasks" -
nullwhen the URL is"/"

Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Route to the Cart Page
Use React Router to create a new Cart Page and navigate to it.
- When clicking on the MiniCart, navigate to the Cart Page.
- When clicking on the Galaxus Logo, navigate back to the Homepage.
-
When clicking on "Zurück zur Produktliste", navigate back to the Homepage.
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/galaxus-mini-router-4v5kqc
→ neue Sandbox mit Router, bitte diese verwenden.
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-router-solution-cp5w7d
TypeScript
In this chapter we will cover some common Use Cases for TypeScript with React.
A comprehensive overview can be found in the following Cheatsheet:
Components
Props and State
You can define your Props using a Type or using an Interface. Using a Type seems to be a more common these days for for typing React Props and State.

Components
Extending Props
Sometimes you want to take component props declared for one component and extend them to use them on another component. But you might want to modify one or two.
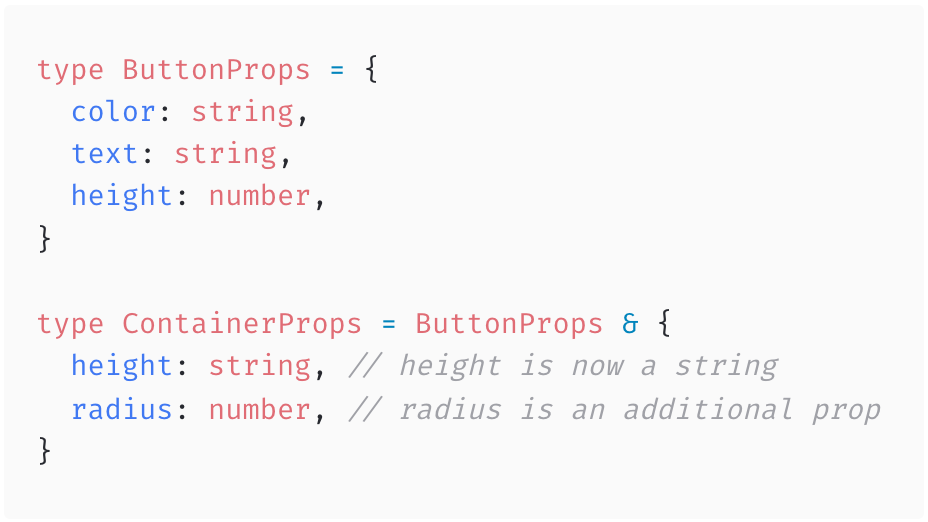
Components
Some Examples
Here are just some common examples for typing Props.

Forms & Events
React uses its own event system. That’s why you can’t use typical MouseEvent or similar on your elements. You need to use the specific React version
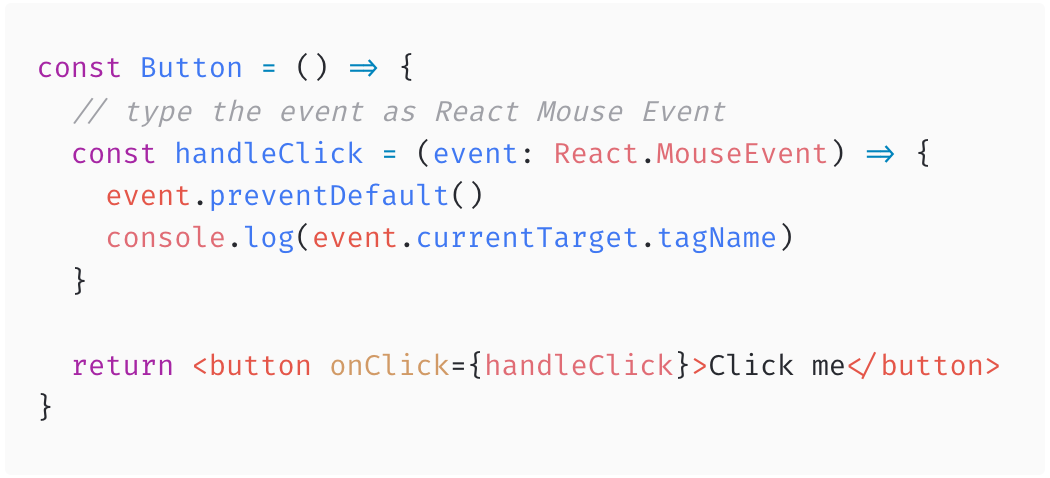
Type the Event
Restric Event to an Element

Forms & Events
One of the most common cases is correctly typing the onChange event used on an input field in a form.
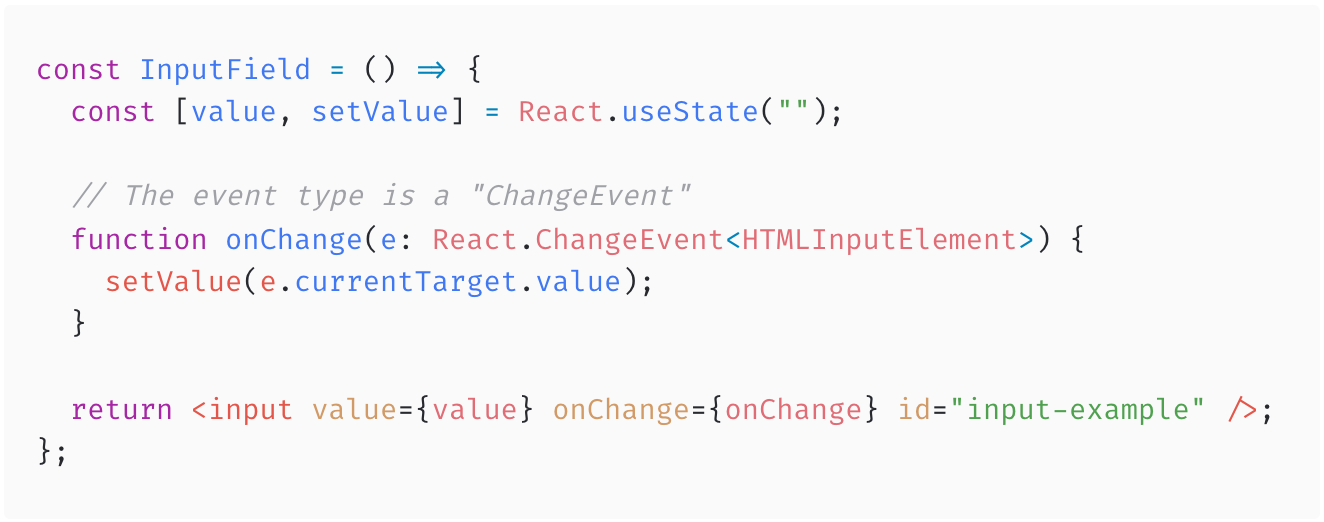
useState
TypeScript can infer the values of the useState hook:
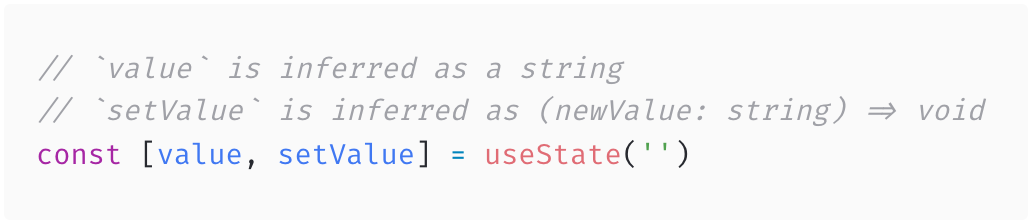
When you need to initialize a hook with a null-ish value, you can make use of a generic and pass a union to correctly type your hook:

useEffect
You don’t need to provide any extra typings. TypeScript will check that the method signature of the function you provide is correct — and makes sure you return a function for the cleanup.

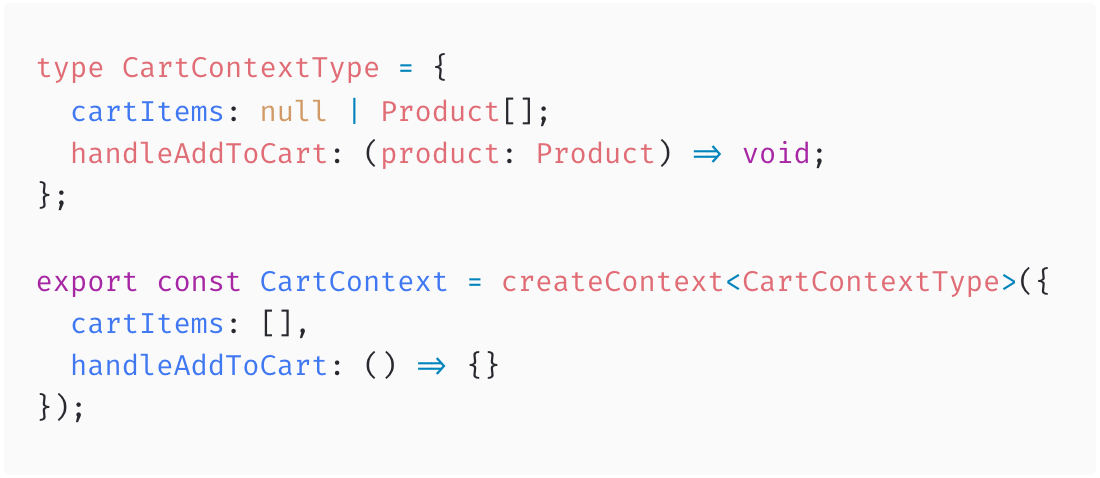
Context
You can type the Context by using a Generic in the createContext Function.
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Add Typings to the Application
Add Typings for cartProducts State in the App Component.
Add Typings for CardProps and CardState in the Card Component.
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-typescript-ud8775
→ neue Sandbox mit TSX, bitte diese verwenden.
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-typescript-solution-37fsmu
State Management
Global State Management helps with Prop Drilling, accessing Data without duplicating it, Data Fetching...

Client & Server State
Global State Management can be divided in Client State and Server State.
Until now we just used setState and Context for Client State. And we used useEffect for Server State.

Client State
Server State
Client State
This kind of state lives only on the Client and is not persited on the Server. It is synchronous, not async.
Use Cases:
- Global Layout States (is the Sidebar Open..)
- Theming (dark, light..)
- ...
Client State
Out of the Box
For simple State that lives inside of a component we can use setState. We can lift state up and provide it to some Child Components. With Context we can provide it to all components.
Most applications do not have complex Client state. With Context (and possibly useReducer) we can build our own a simple State Management.
Client State
useReducer
tbd
Client State
Libraries
Redux is the de-facto standard. It can also handle Server State and has awesome DevTools. People complain about too much boilerplate to accomplish simple things. Redux Toolkit solves a lot of those issues.
MobX provides simple, scalable state management by using Observables.
Zustand is a newer Library that is currently hyped.
Client State
Redux
tbd
Server State
Managing Server State is a lot harder than Client State.
Things we need: Fetching, Caching, Invalidating and Updating Server Data. And Loading States.
Bonus Features: Polling, Optimistic Updates, Pagination, Prefetching server data.
Server State
Out of the Box
In a useEffect Hook we can fetch data from a Server and use useState to save and re-render the Component.
...but it has a few downsides and lacks a lot of useful features.
Server State
Why not just useEffect?
Fetching directly in Effects makes it easy to create “network waterfalls”. You render the parent component, it fetches some data, renders the child components, and then they start fetching their data.
Fetching directly in Effects usually means you don’t preload or cache data. For example, if the component unmounts and then mounts again, it would have to fetch the data again.
Fetching all data of your application in the <App> component loads unnecessary data and does not scale well.
Server State
Libraries
React Query and SWR a popular Libraries for managing Server State.
When using GraphQL, Apollo is a popular and comprehensive Library.
Libraries for Client & Server
Many Libraries tried to solve Client and Server State in one Library i.e. Redux Toolkit Query.
Modern State Management Libraries focus on solving just one of those, because the challenges are completely different.
Let's have a look at a modern Server State Library, React Query.
React Query
React Query in 100 Seconds
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=novnyCaa7To
Example
https://codesandbox.io/s/react-query-intro-dq5jcj
- Cached Data
- Loading States
- Background Refetching
React Query
Queries
A query is a declarative dependency on an asynchronous source of data that is tied to a unique key.
The unique key you provide is used internally for refetching, caching, and sharing your queries throughout your application.

React Query
Queries
The query result contains all of the information about the query that is needed for templating and any other usage of the data.

React Query
Stale Queries
Per default, every cache Query is considered as stale data.
Stale queries are refetched automatically in the background when:
- New instances of the query mount
- The window is refocused
- The network is reconnected.
React Query
Named Queries aka Custom Hooks
Each query can be refactored to be it's own custom hook. This design is the suggested way to use React Query, as it makes it much easier to manage query keys and shared query logic.

React Query
Invalidating Queries
Waiting for queries to become stale before they are fetched again doesn't always work, especially when you know for a fact that a query's data is out of date because of something the user has done.

React Query
Mutations
Mutations are used to create/update/delete data. For this purpose, React Query exports a useMutation hook.

React Query
Optimistic Updates

Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Use React Query for Server State
- In MiniCart.tsx refactor the
useQueryto use a custom Query useCartProducts.ts
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-state-management-uykx2s
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-state-management-solution-ttp2id
Testing
Test Runner & Tools
-
Jest is a JavaScript test runner that lets you access the DOM via
jsdom. Alternatives: Mocha, ava.
-
React Testing Library is a set of helpers that let you test React components without relying on their implementation details. Alternative: Enzyme.
- Cypress for End-to-End Testing. Alternatives: Playwright, Puppeteer.
Jest
Snapshot Testing
Snapshot tests are a very useful tool whenever you want to make sure your UI does not change unexpectedly.

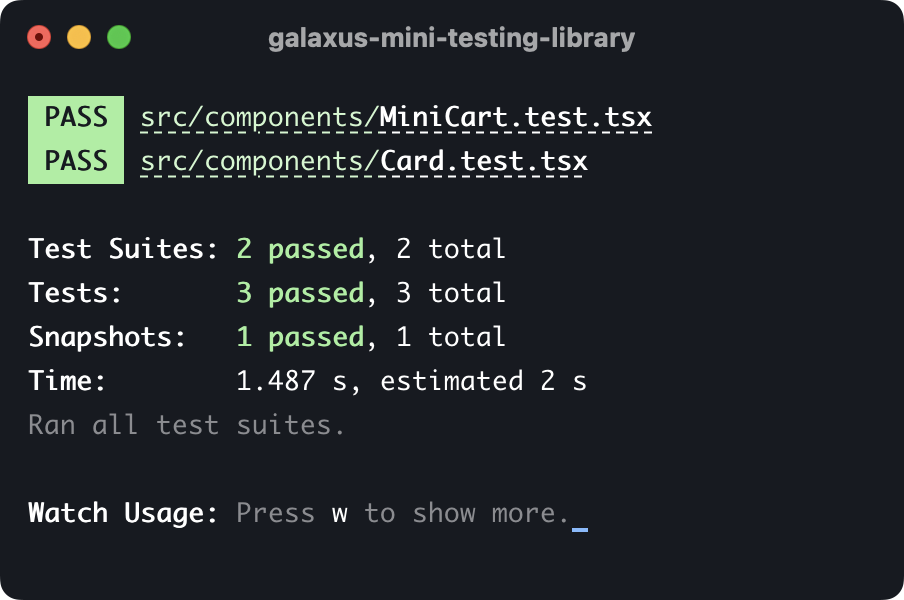
React Testing Library
Unit Testing
The React Testing Library is a light-weight solution for testing React components. It provides utility functions in a way that encourages better testing practices.
The goal is not to test implementation details but real user interactions.
Testing Library runs on top of Jest and is a replacement for Enzyme.
React Testing Library
Finding DOM Nodes
The utilities facilitate querying the DOM in the same way the user would i.e. finding elements by their label text, finding links from their text etc. like a user would.


HTML
Testing Library Query
React Testing Library
Finding DOM Nodes
It also exposes a recommended way to find elements by a data-testid as an "escape hatch" for elements where the text content and label do not make sense or is not practical.
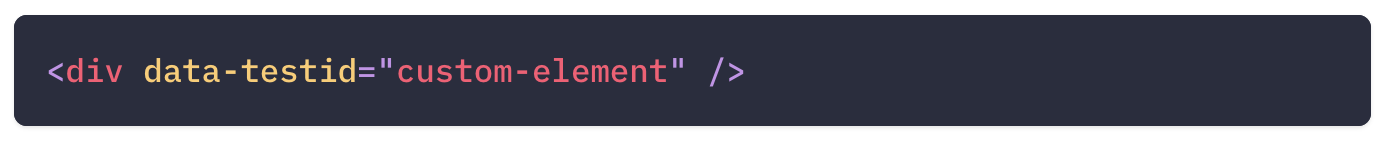

HTML
Testing Library Query
React Testing Library
Debugging
For convenience screen also exposes a debug method in addition to the queries. It supports debugging the document, a single element, or an array of elements.
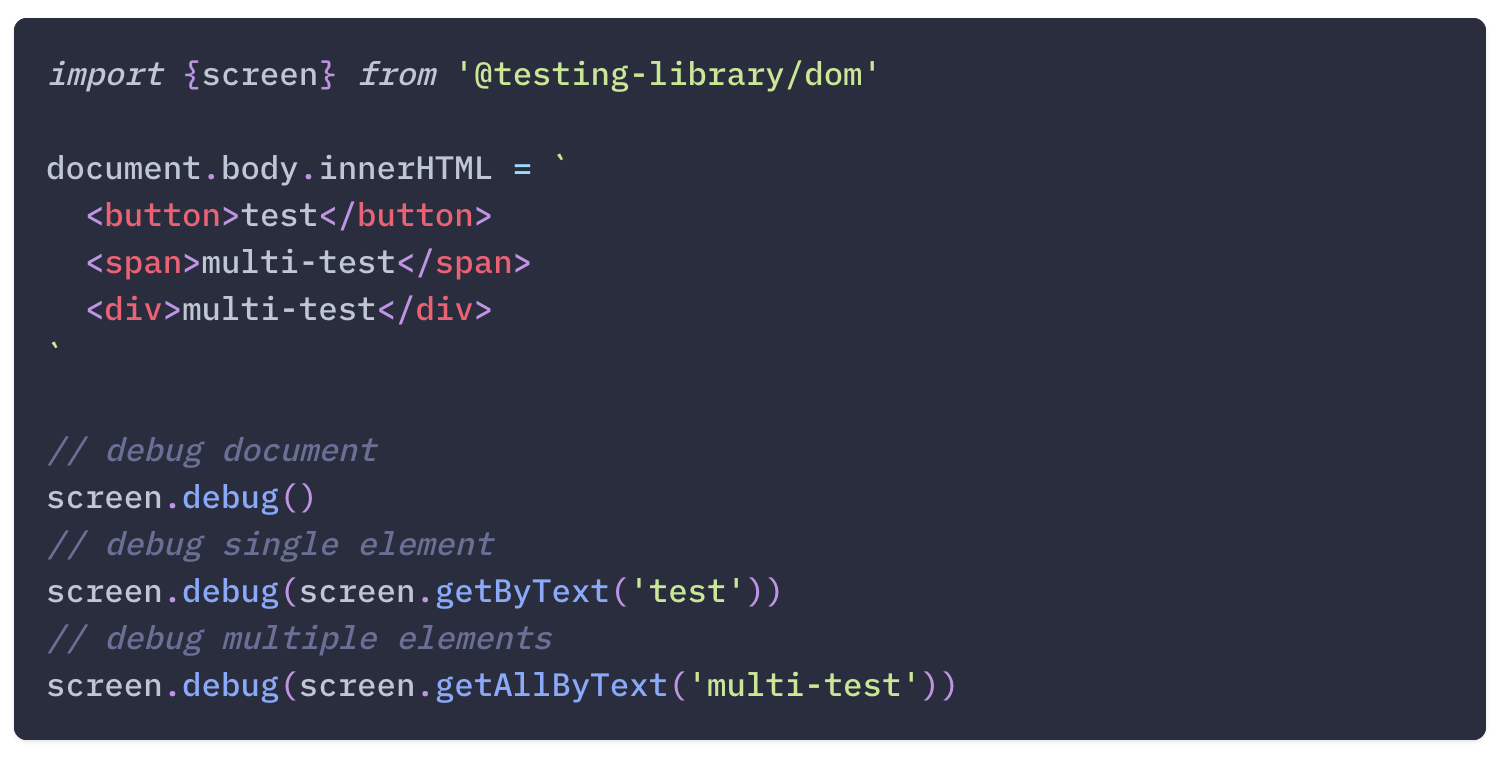
React Testing Library
User Actions

React Testing Library
Examples
https://codesandbox.io/s/testing-library-examples-gk2htq
Siehe Files im src/__tests__ folder.
Galaxus mini 👨💻🧑💻
Write some Tests
Download the Sandbox as ZIP and add a Snapshot Test.
Write a new Test to check if a Product was marked as Favorite.
https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-testing-library-46ey1n
Solution 💡 https://codesandbox.io/s/galaxus-mini-testing-library-solution-ji8ckv
Forms
Controlled vs. uncontrolled Forms
HTML form elements work a bit differently from other DOM elements in React, because form elements naturally keep some internal state.
There are two approaches: controlled and uncontrolled Forms.
https://codesandbox.io/s/forms-uncontrolled-controlled-1l0nfe
Forms
Controlled vs. uncontrolled Forms
With Controlled forms, we have access to all values all the time. This can be useful for i.e. validation checks.
The recommendation is to use controlled Forms.

Forms
Library
Formik is a great Library for Forms.
React JS
By Dominic Modalek
React JS
- 888



