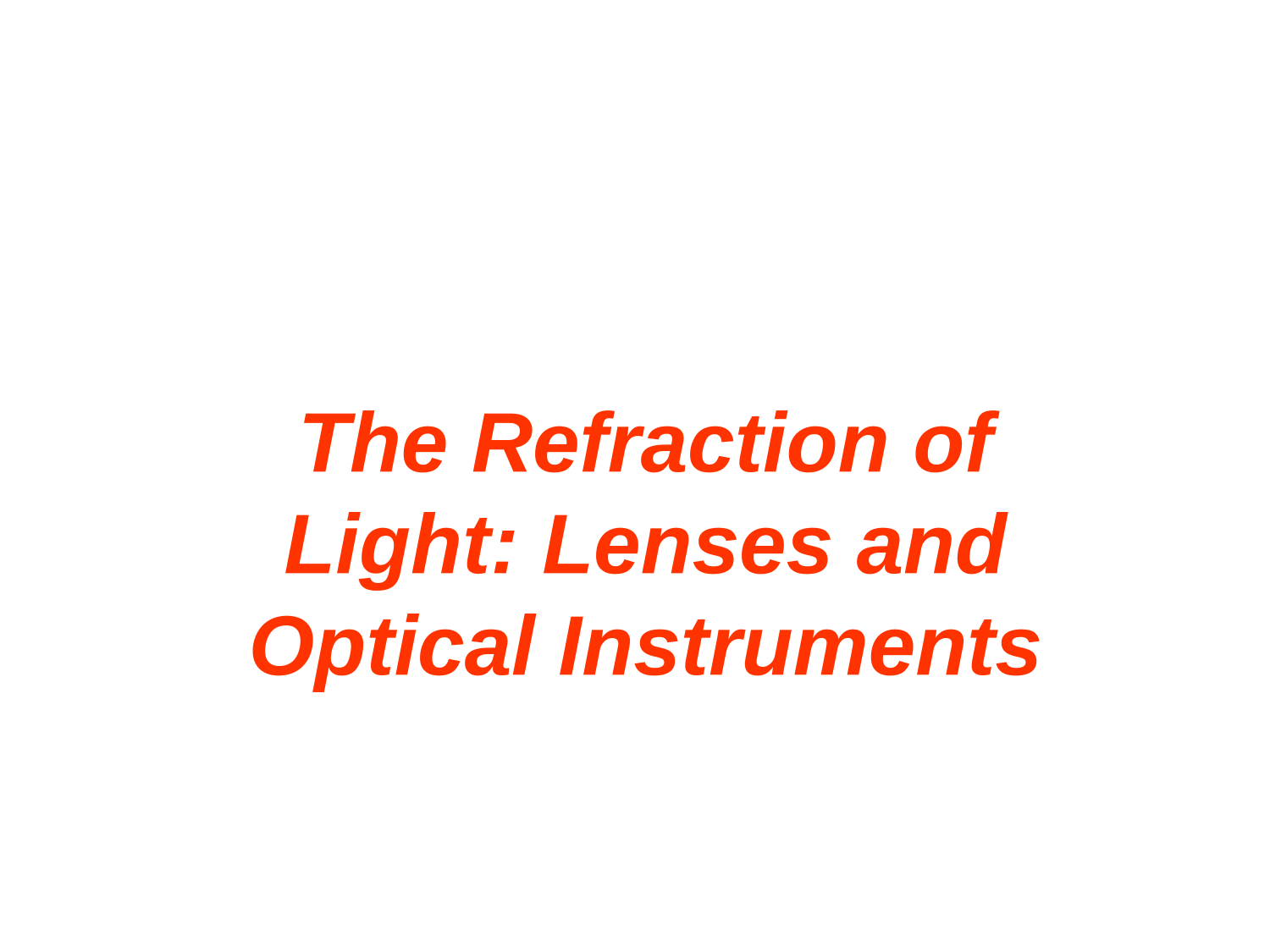
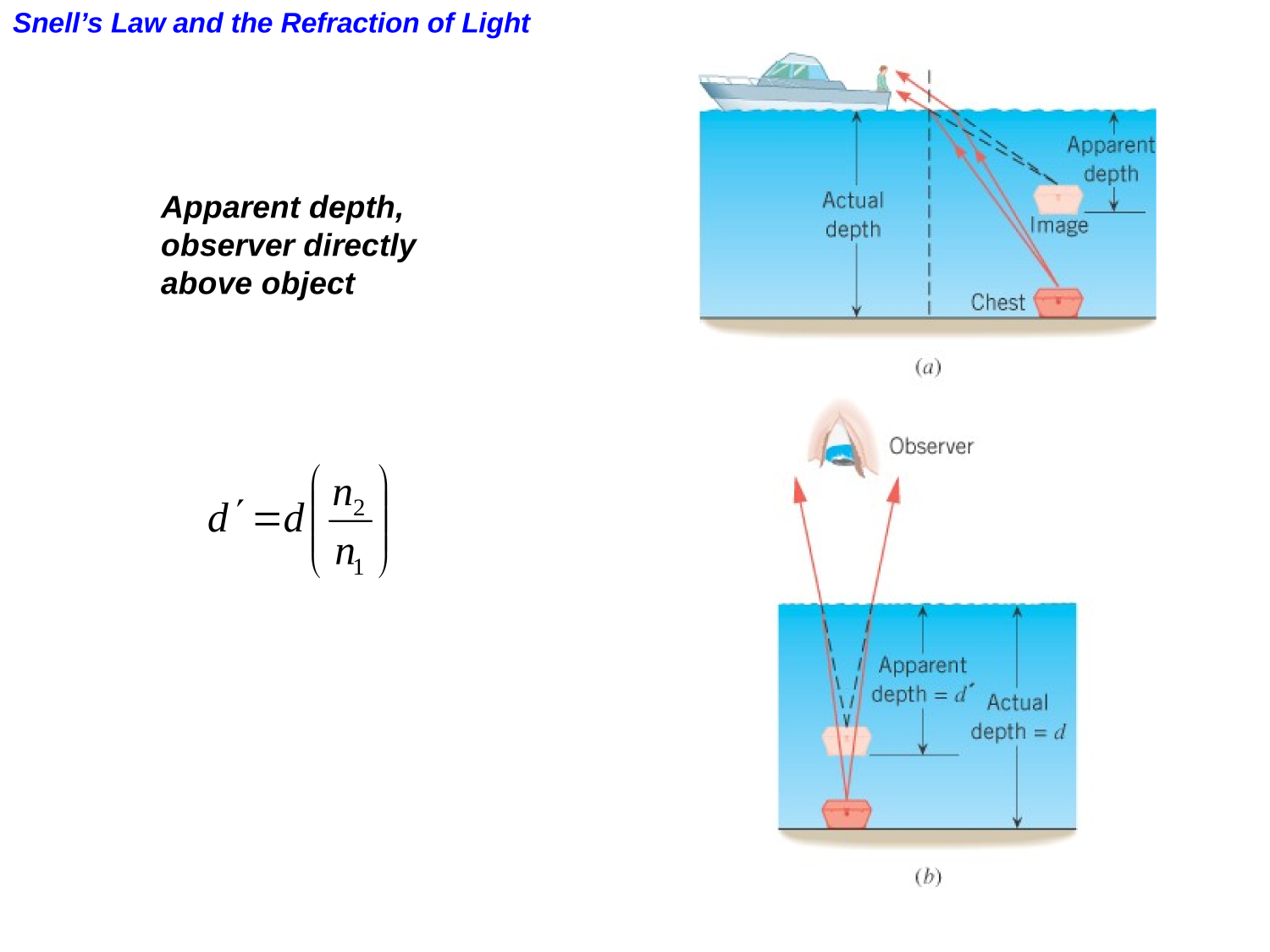
Index of refraction
Optics
Refraction

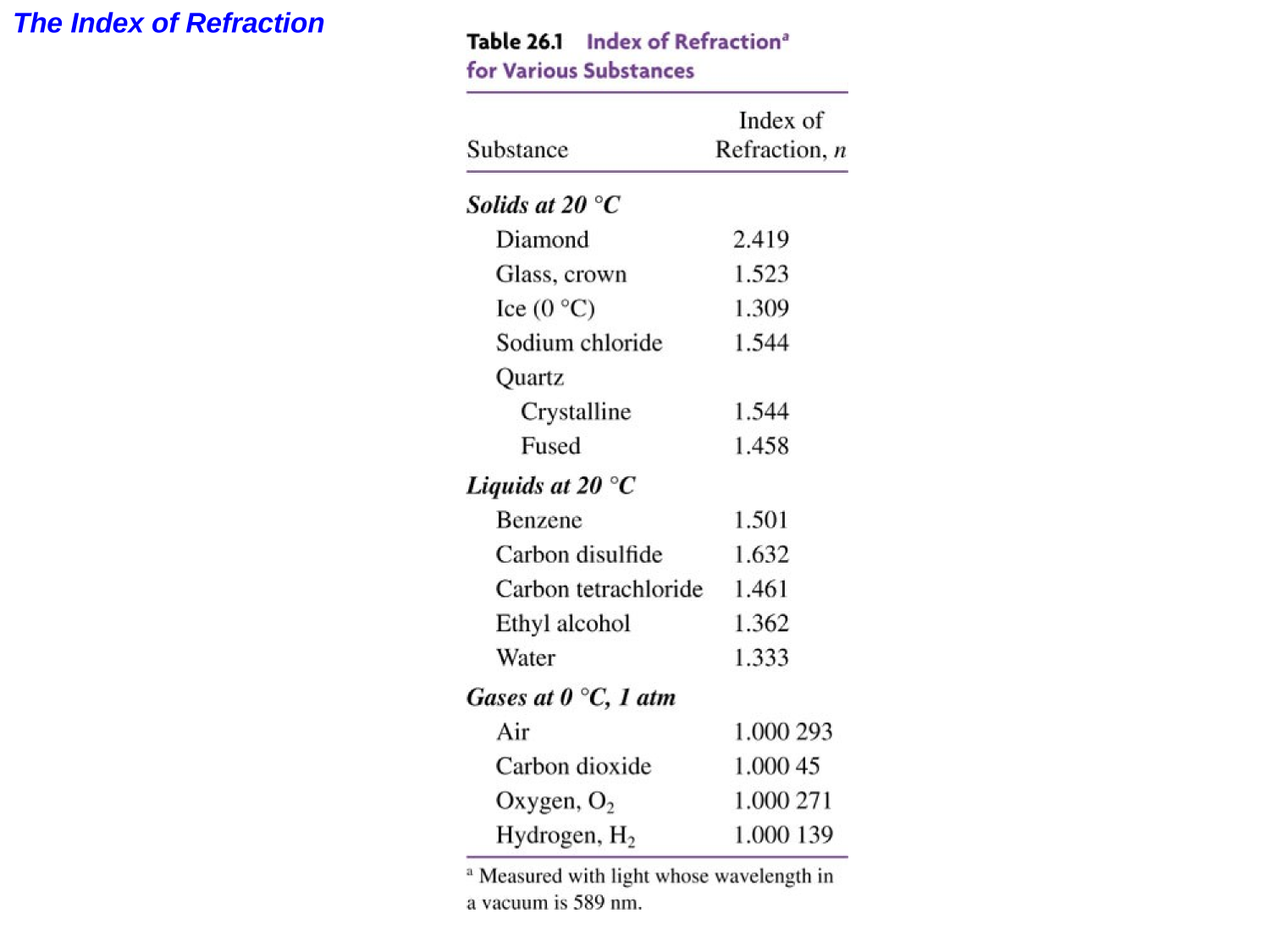
Snell's Law
Optics
Refraction
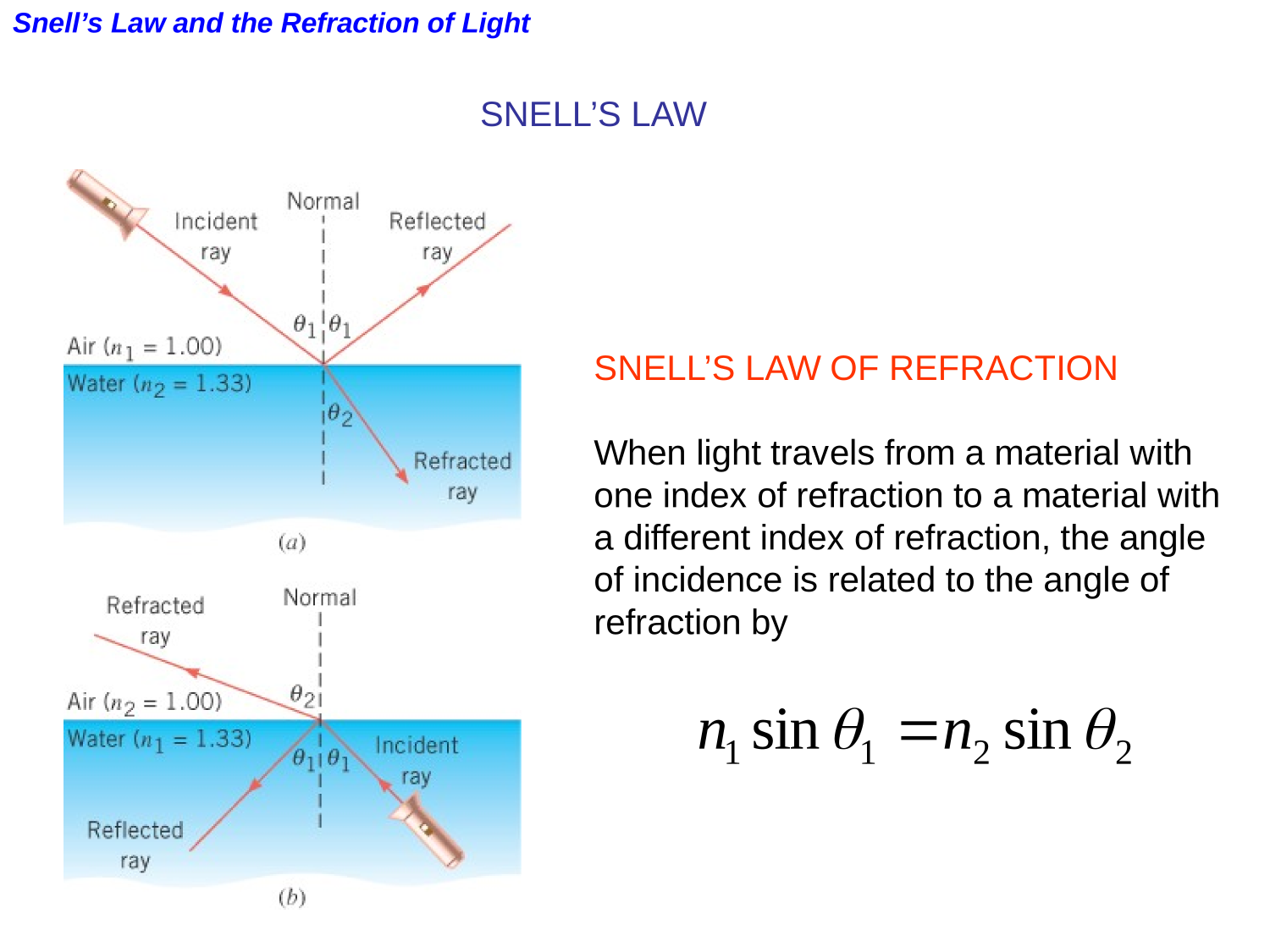


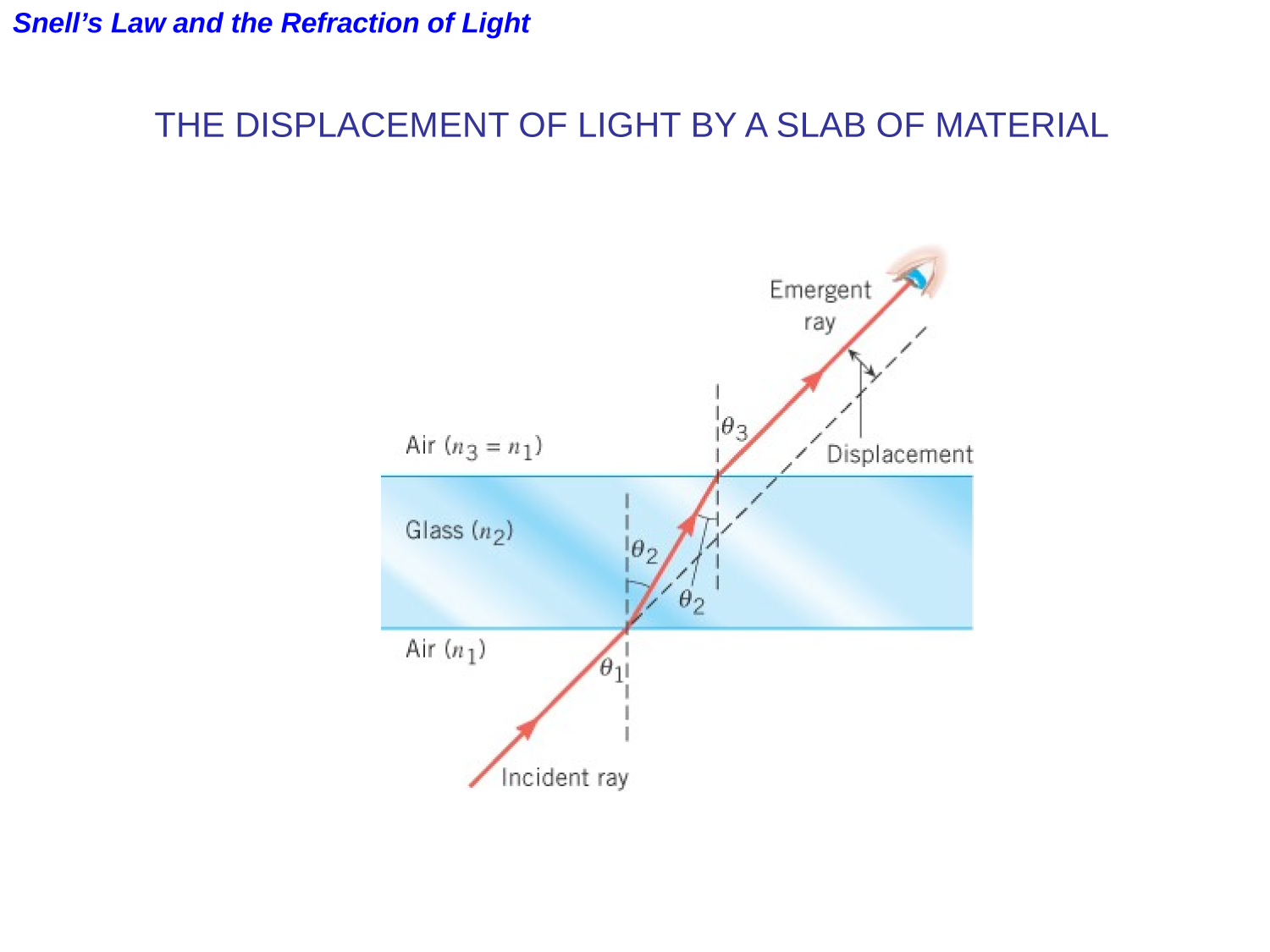
Find an expression for the displacement of a ray through a slab of material in terms of the slab's thickness, the material's refractive index and the angle of incidence.
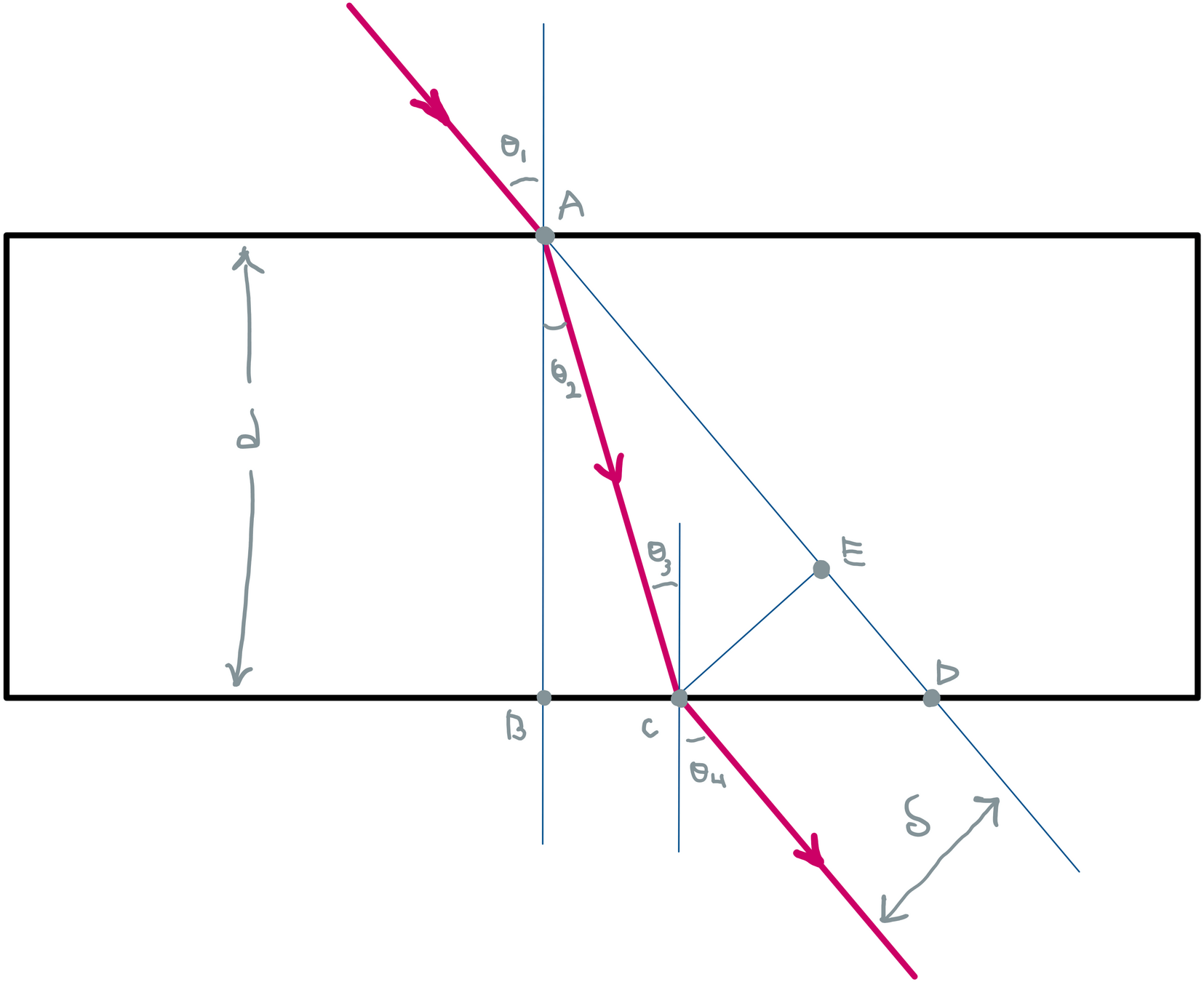
Applying Snell's Law at both interfaces, taking the refractive index of air to be 1.
\sin\theta_1=n\ \sin\theta_2
n\ \sin\theta_3= \sin\theta_4
Since the two interfaces are parallel, therefore so are the lines normal to those surfaces. Therefore, the alternate angles are equal:
\theta_2= \theta_3
\theta_1= \theta_4
Implying that all four terms in the equations above are equal, leading to:
From triangle ABC, BC is
\bar{BC}=d\ \tan\theta_2
From triangle ABD, BD is
\bar{BD}=d\ \tan\theta_1
From triangle CED, CE is
\delta=\bar{CE}=\bar{CD}\ \cos\theta_4
=(d\ \tan\theta_1-d\ \tan\theta_2)\cos\theta_4
=d\left(\ \frac{\sin\theta_1}{\cos\theta_1}-\ \frac{\sin\theta_2}{\cos\theta_2}\right)\cos\theta_1
=d\left(\ \frac{\sin\theta_1}{\cos\theta_1}-\ \frac{\sin\theta_2}{\cos\theta_2}\right)\cos\theta_4
\delta=d\left(\ \frac{\sin\theta_1}{\cos\theta_1}-\ \frac{\sin\theta_1}{n\cos\theta_2}\right)\cos\theta_1
=d \sin\theta\left(\ 1-\ \frac{\cos\theta}{n\cos(\sin^{-1}(\tfrac{\sin \theta}{n}))}\right)
Substituting the relationships found from Snell's Law:
For small angles of incidence and refractive indexes, the cosines are almost equal, thus:
\delta \approx d \sin\theta\left(\ 1-\ \frac{1}{n}\right)
Solved numerical example:
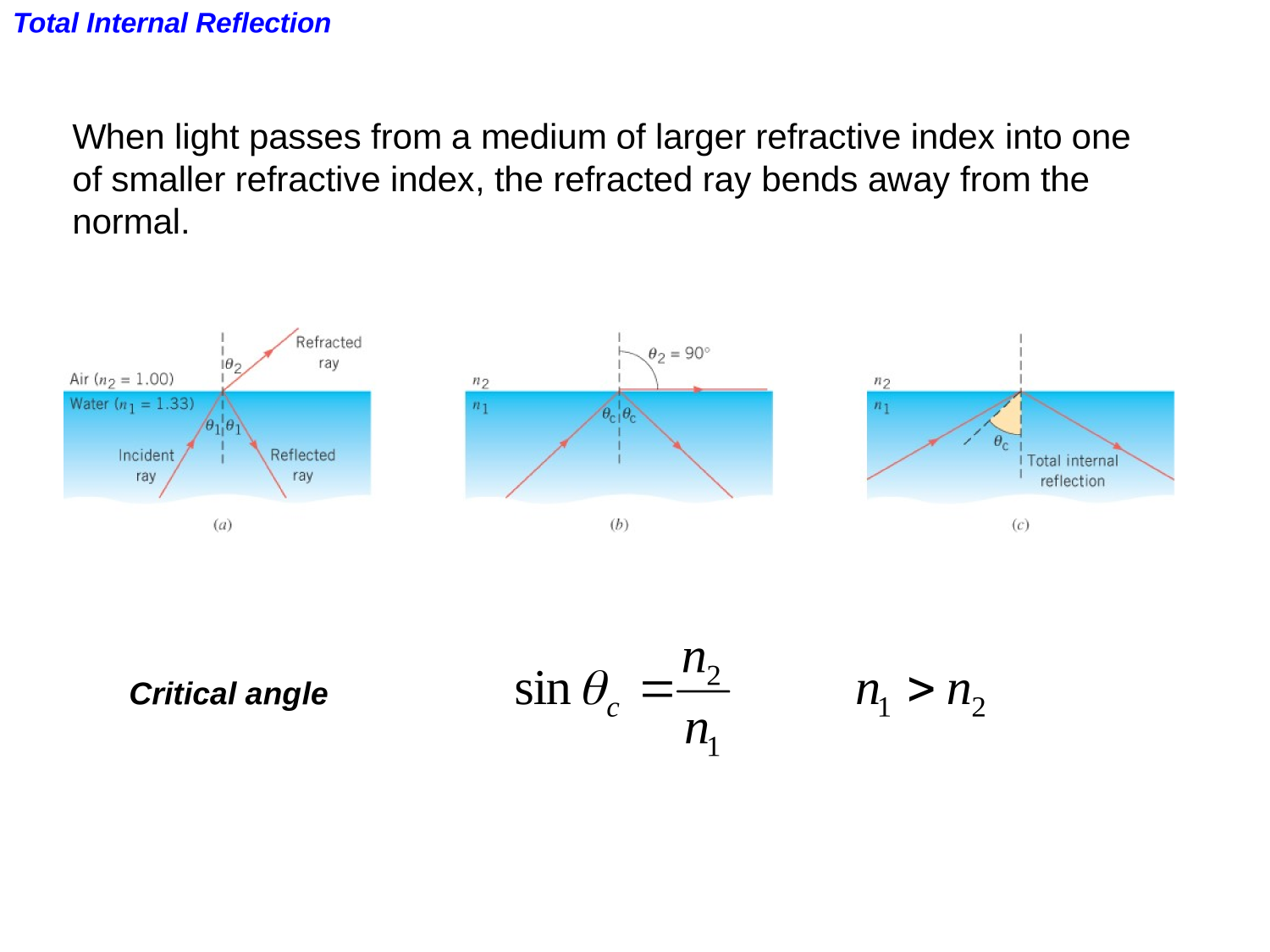
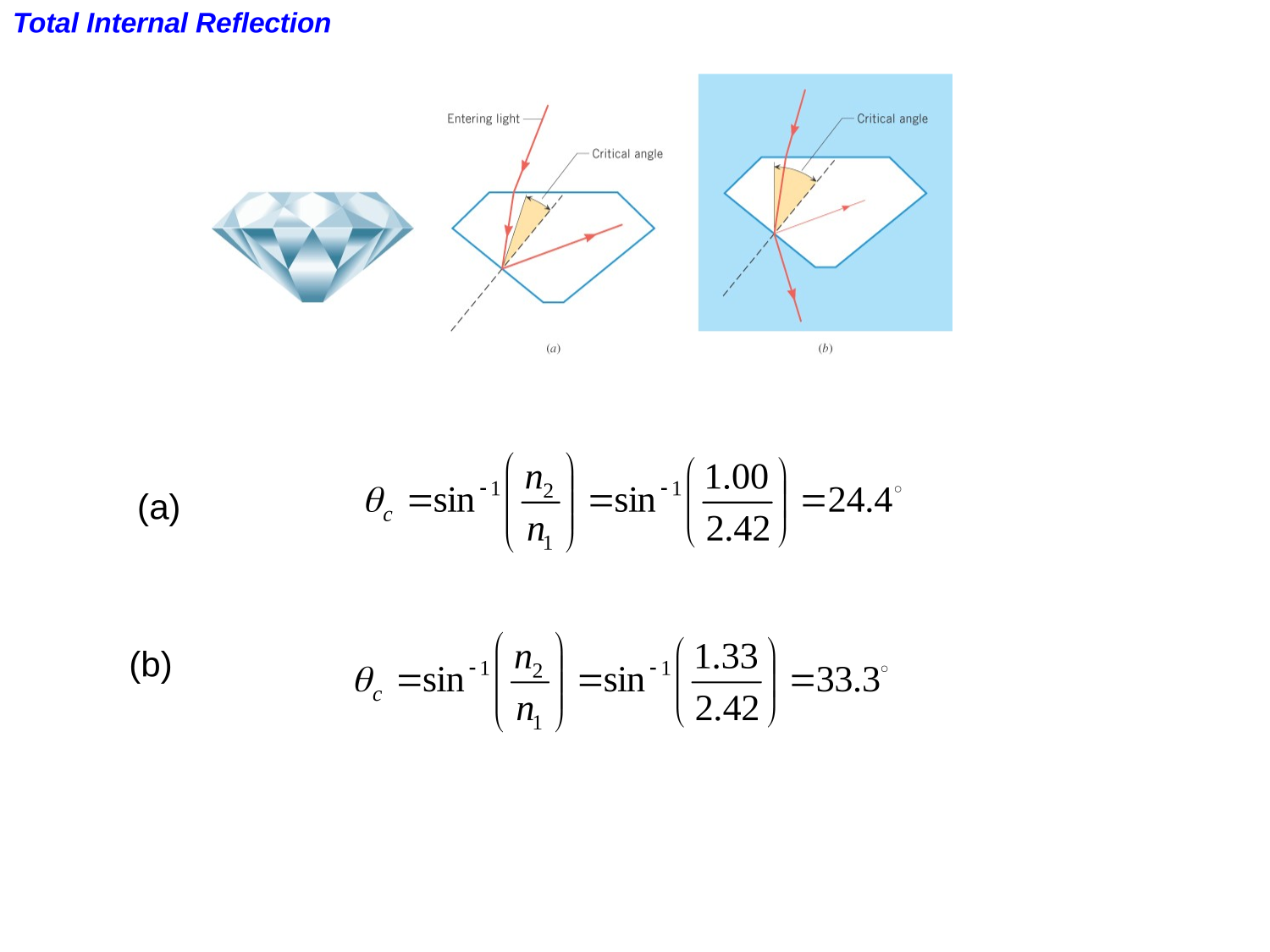
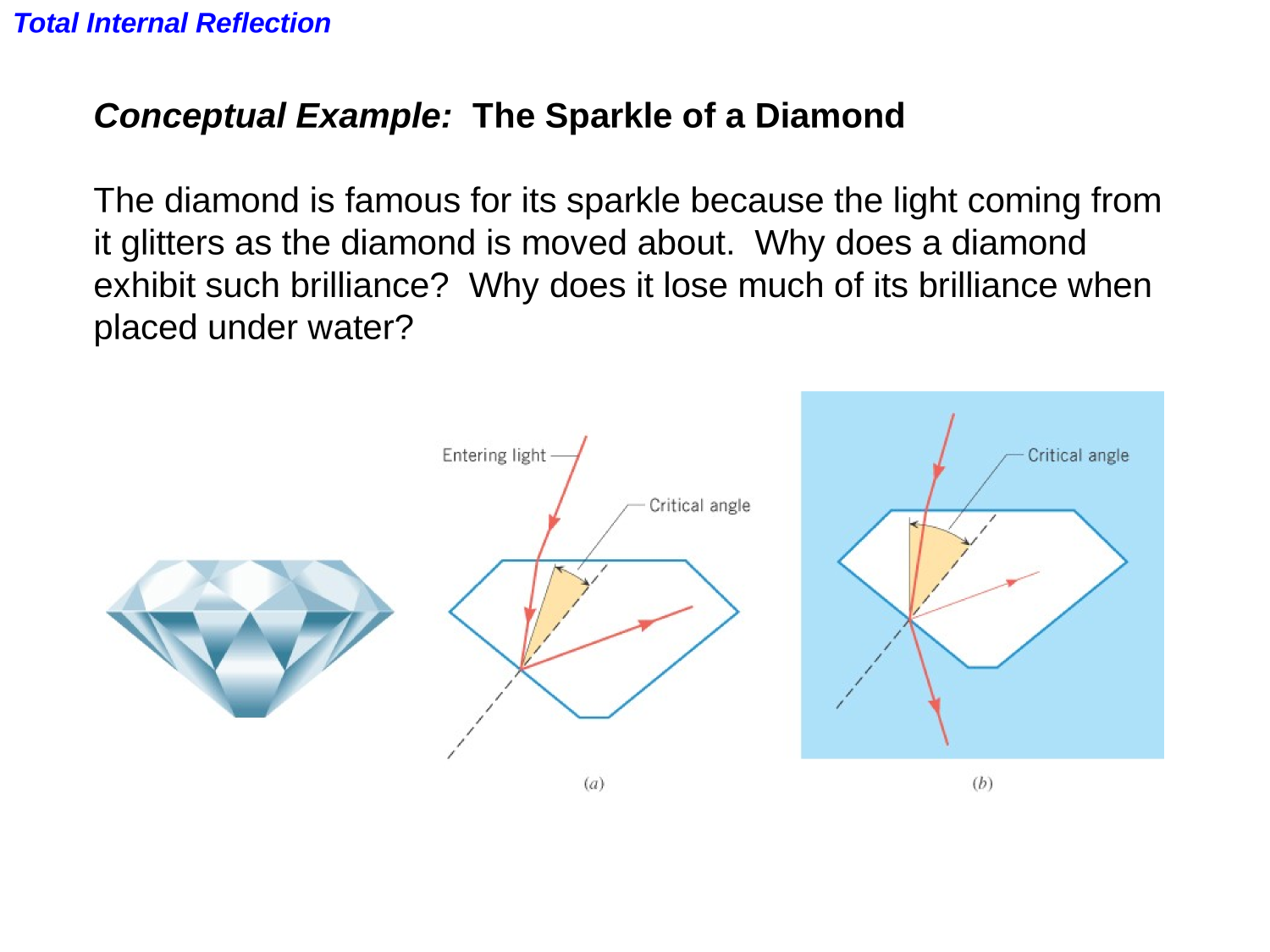
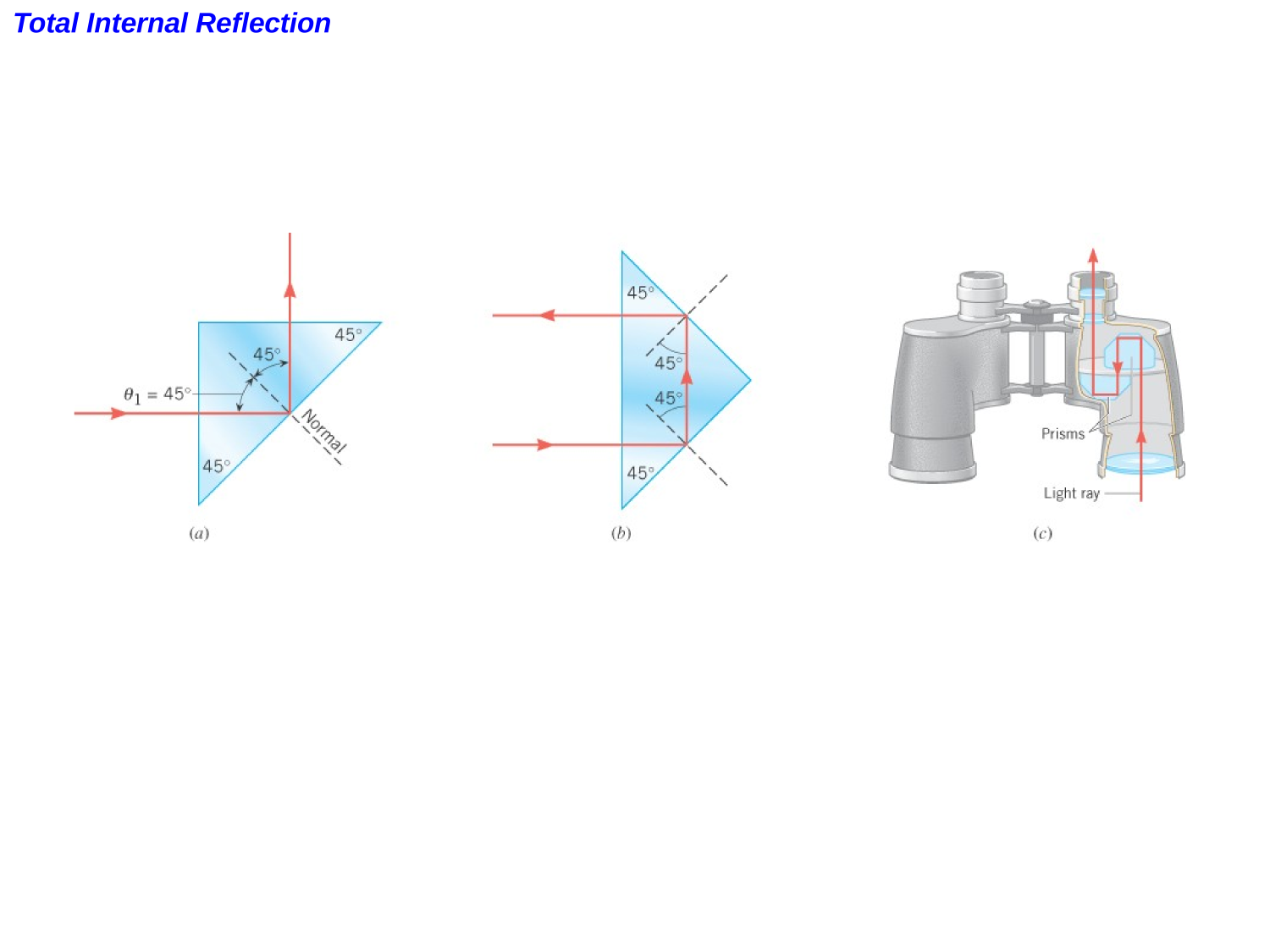
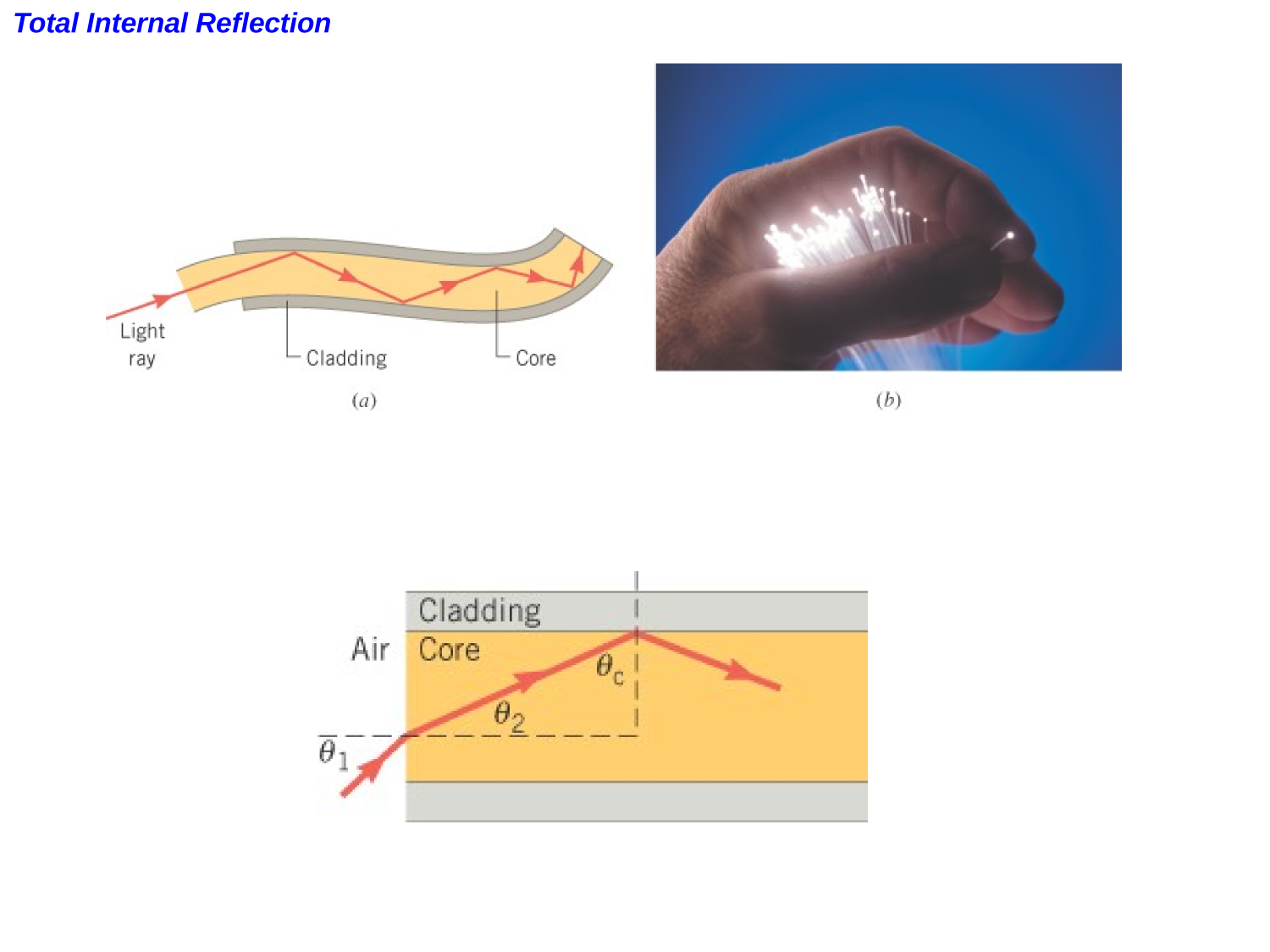
Total Internal Reflection
Optics
Refraction

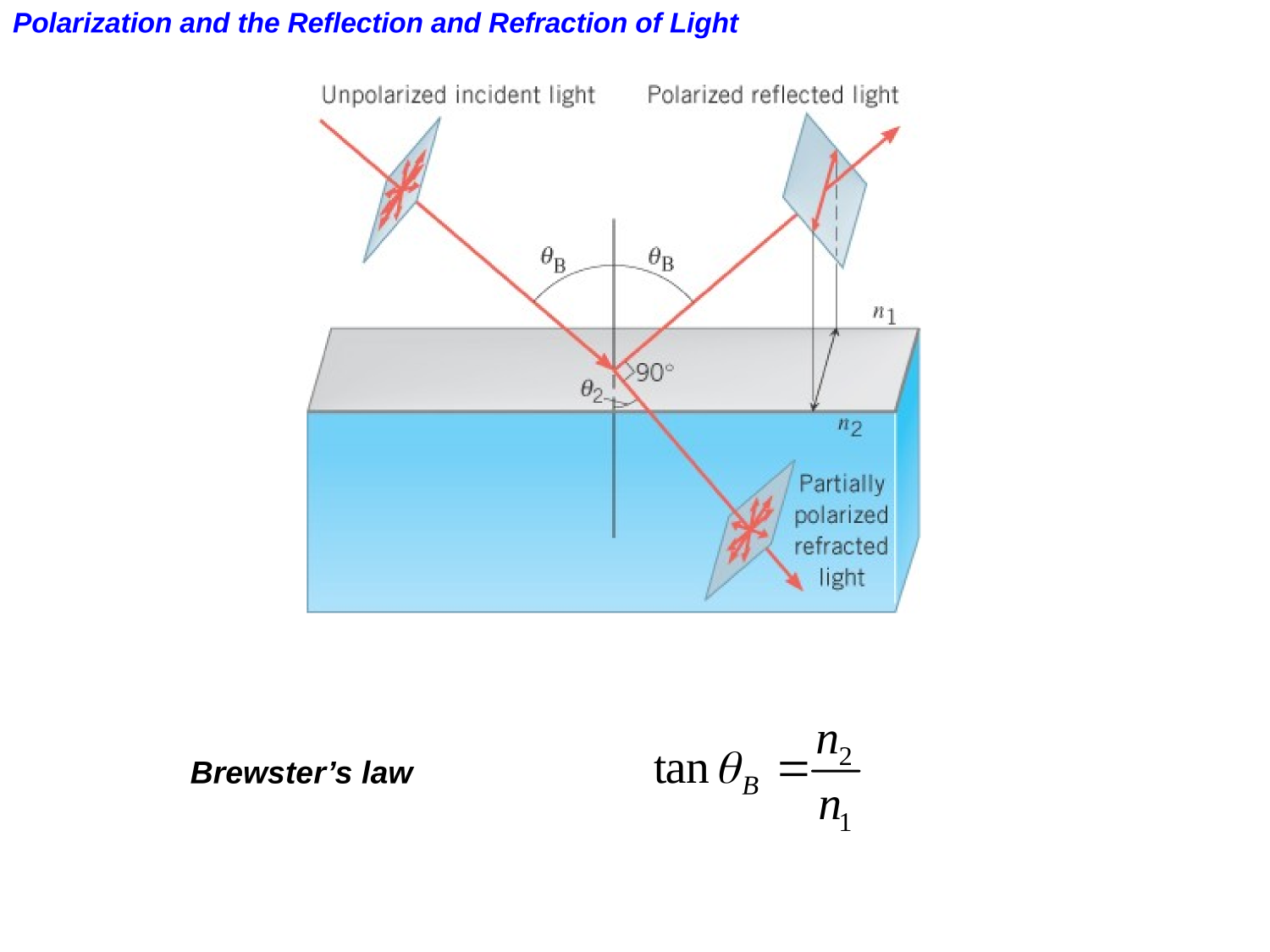
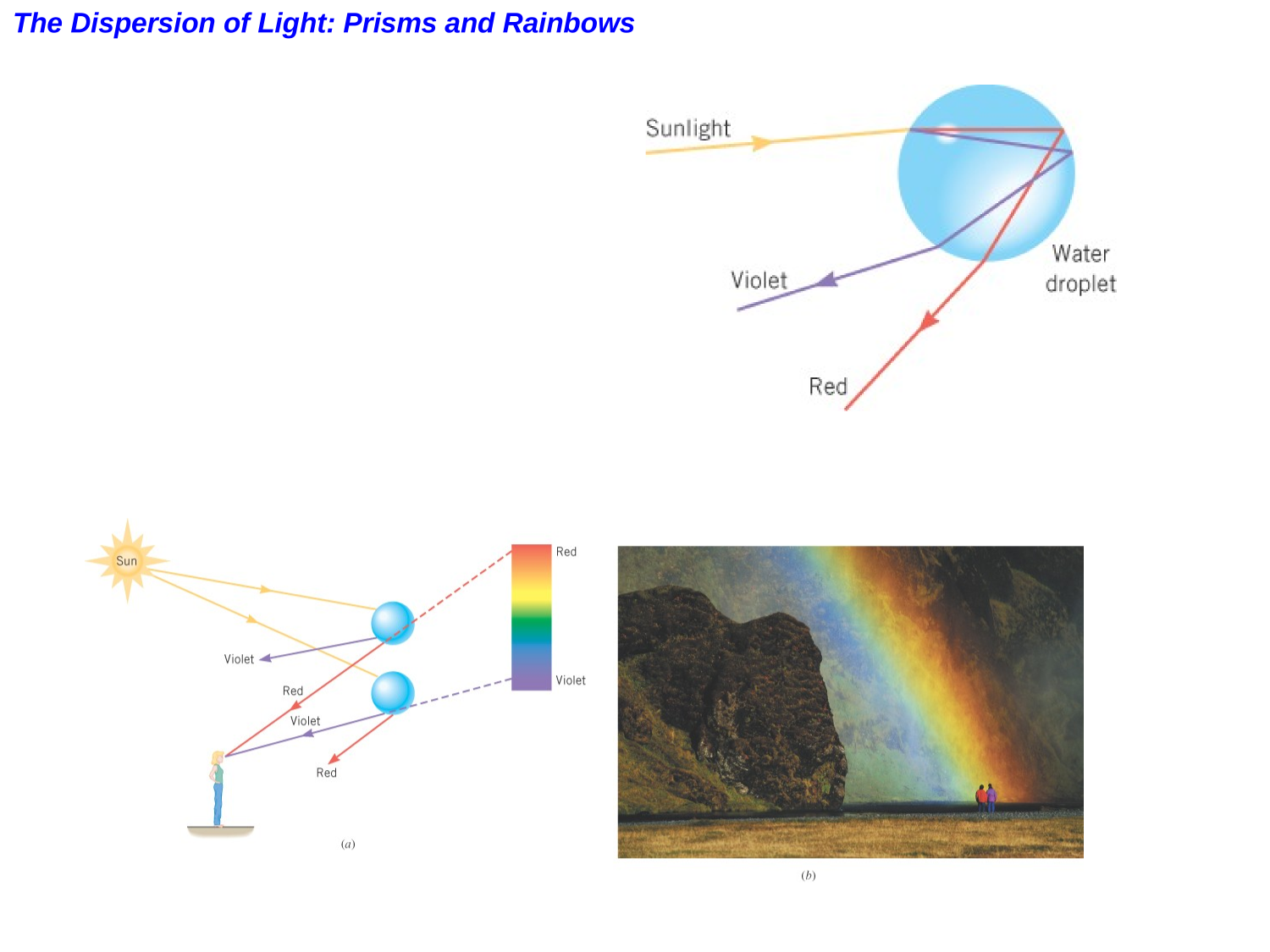
Dispersion
Optics
Refraction
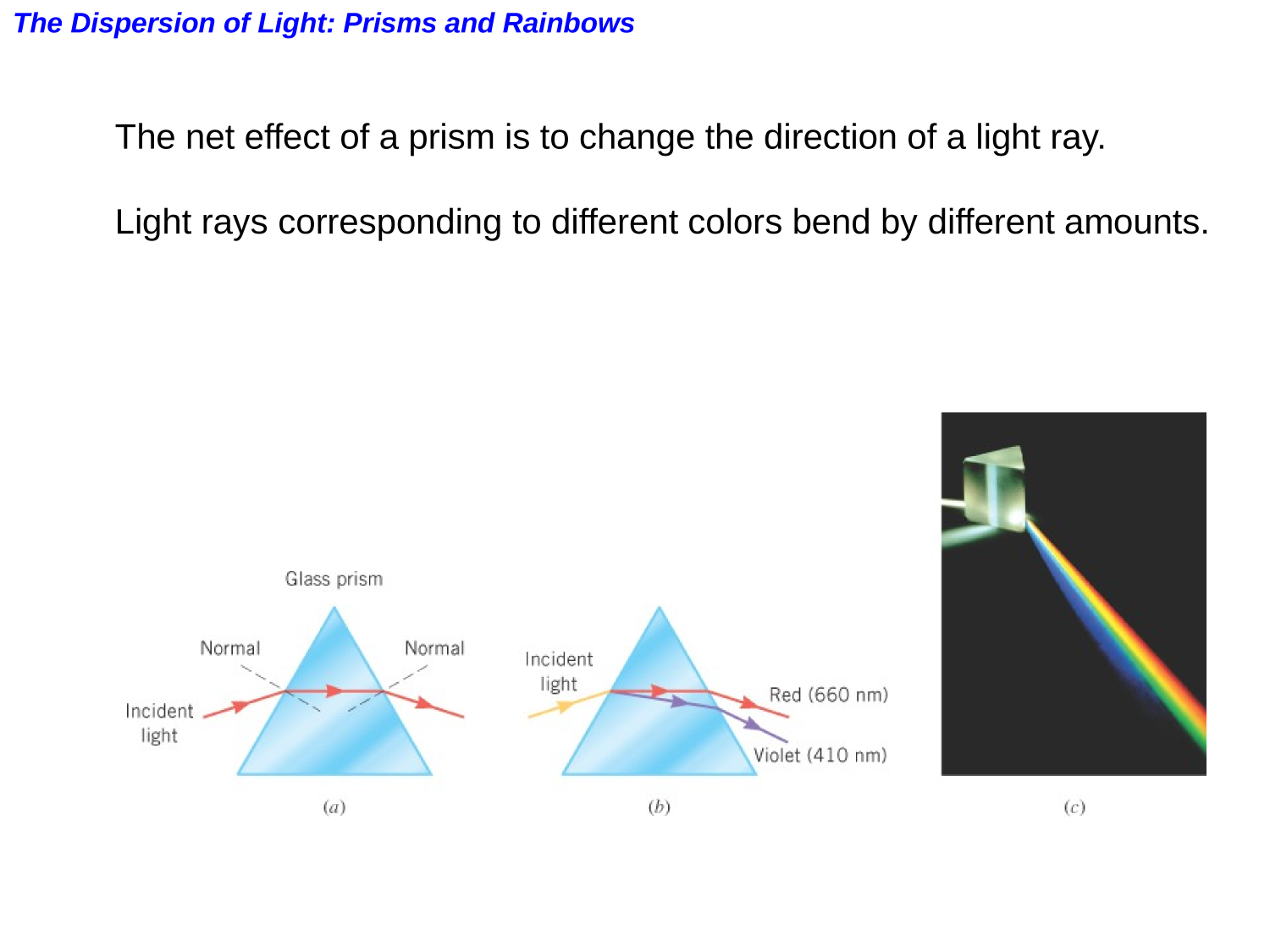
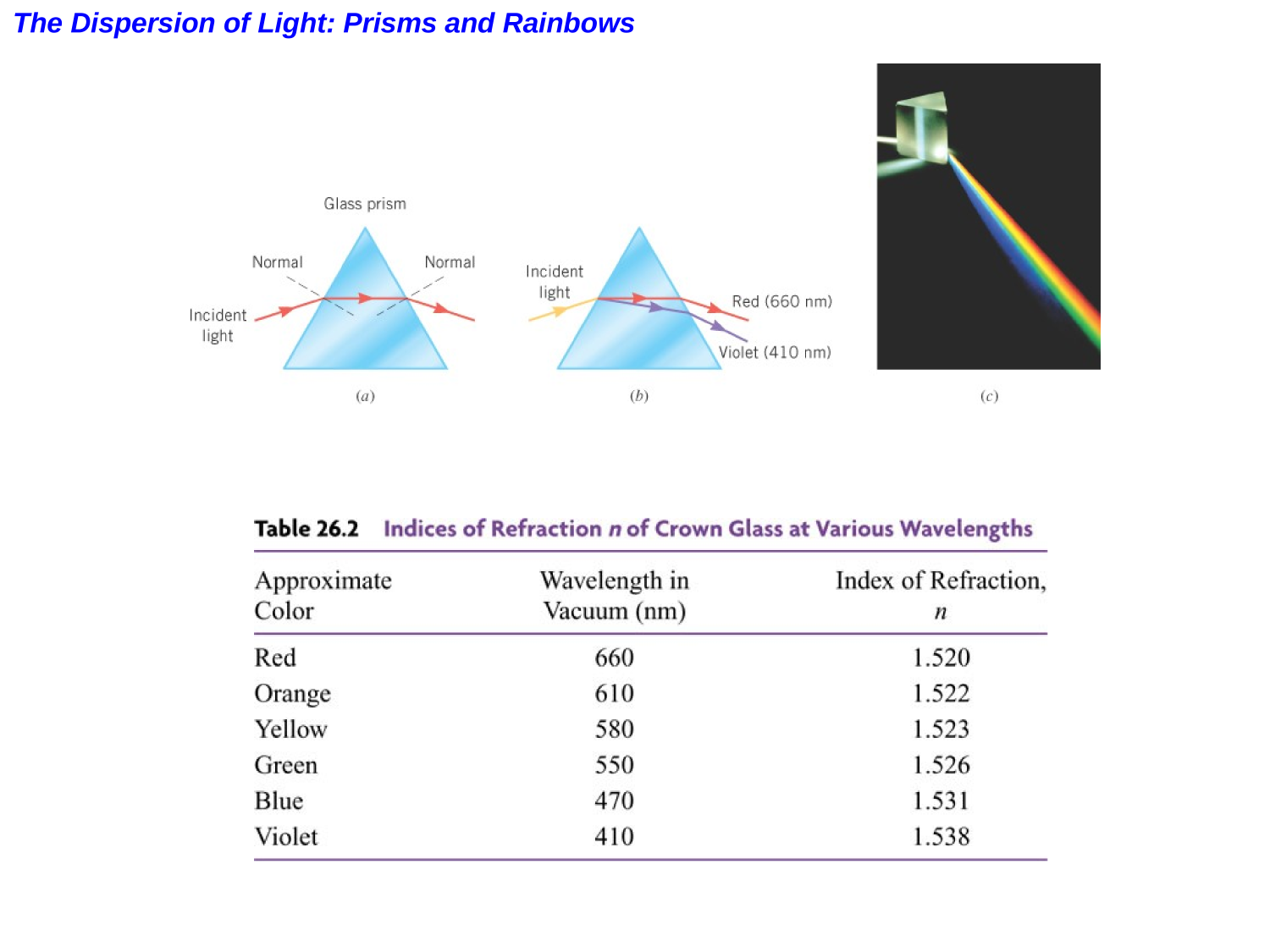
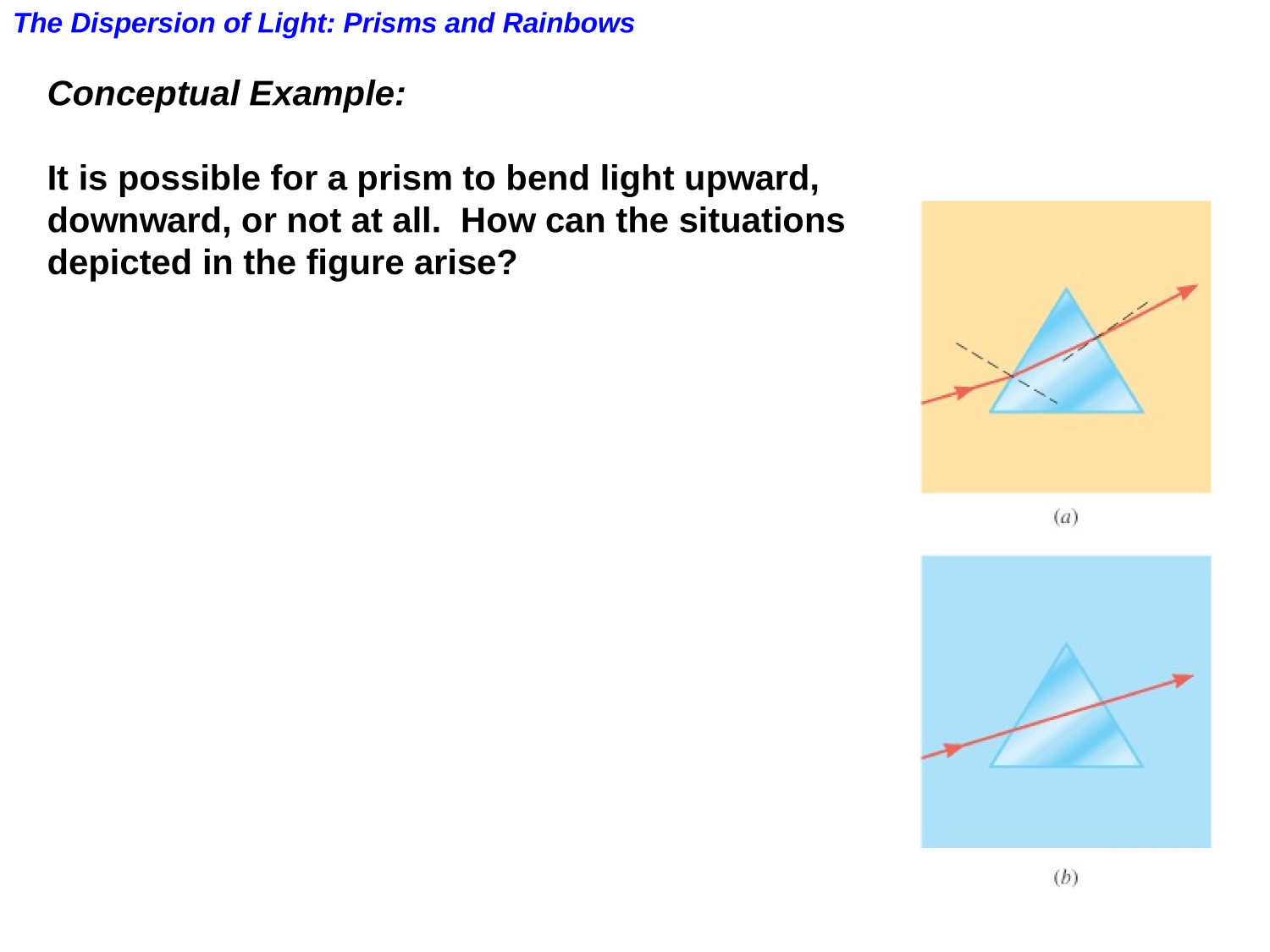
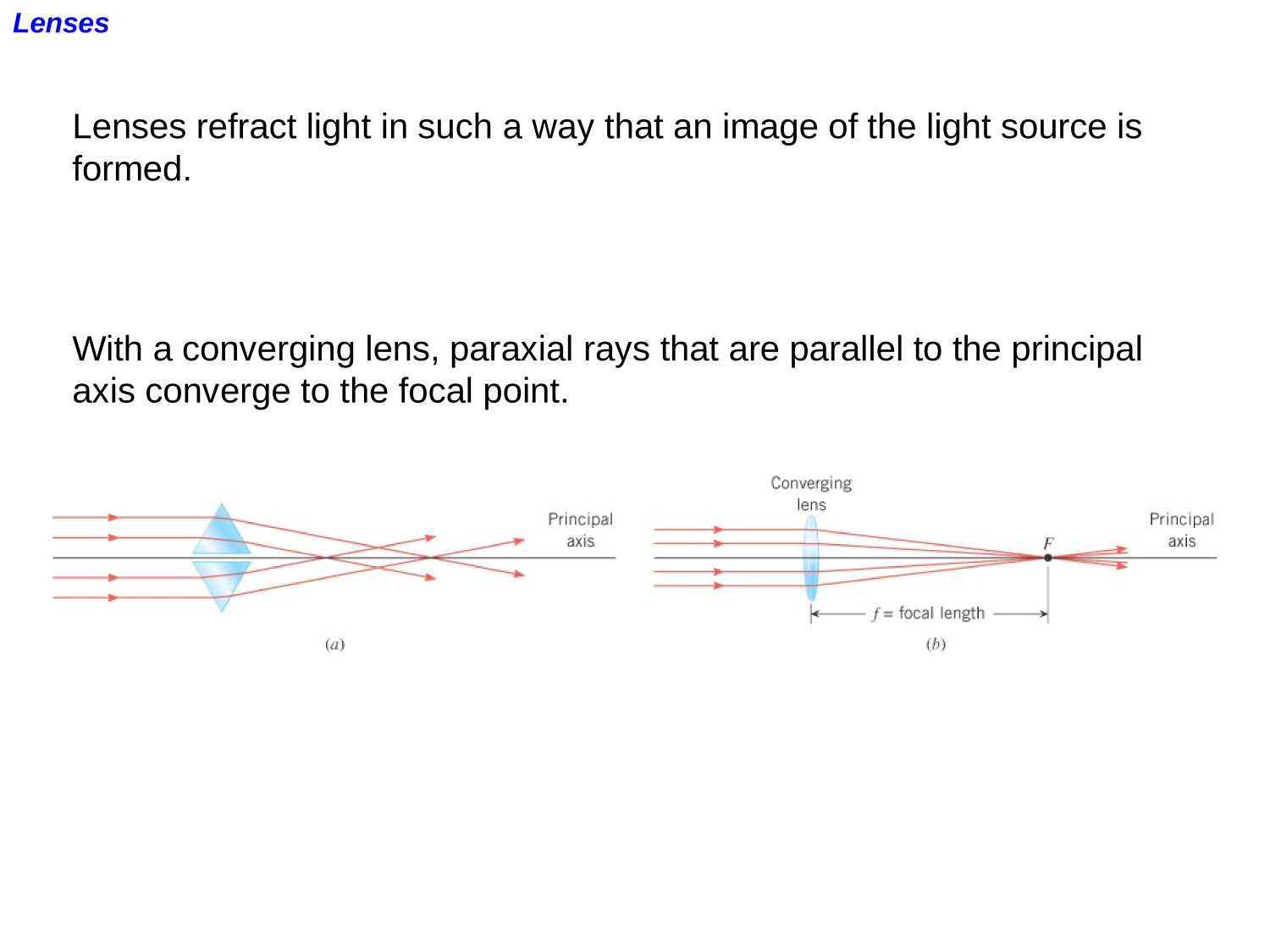
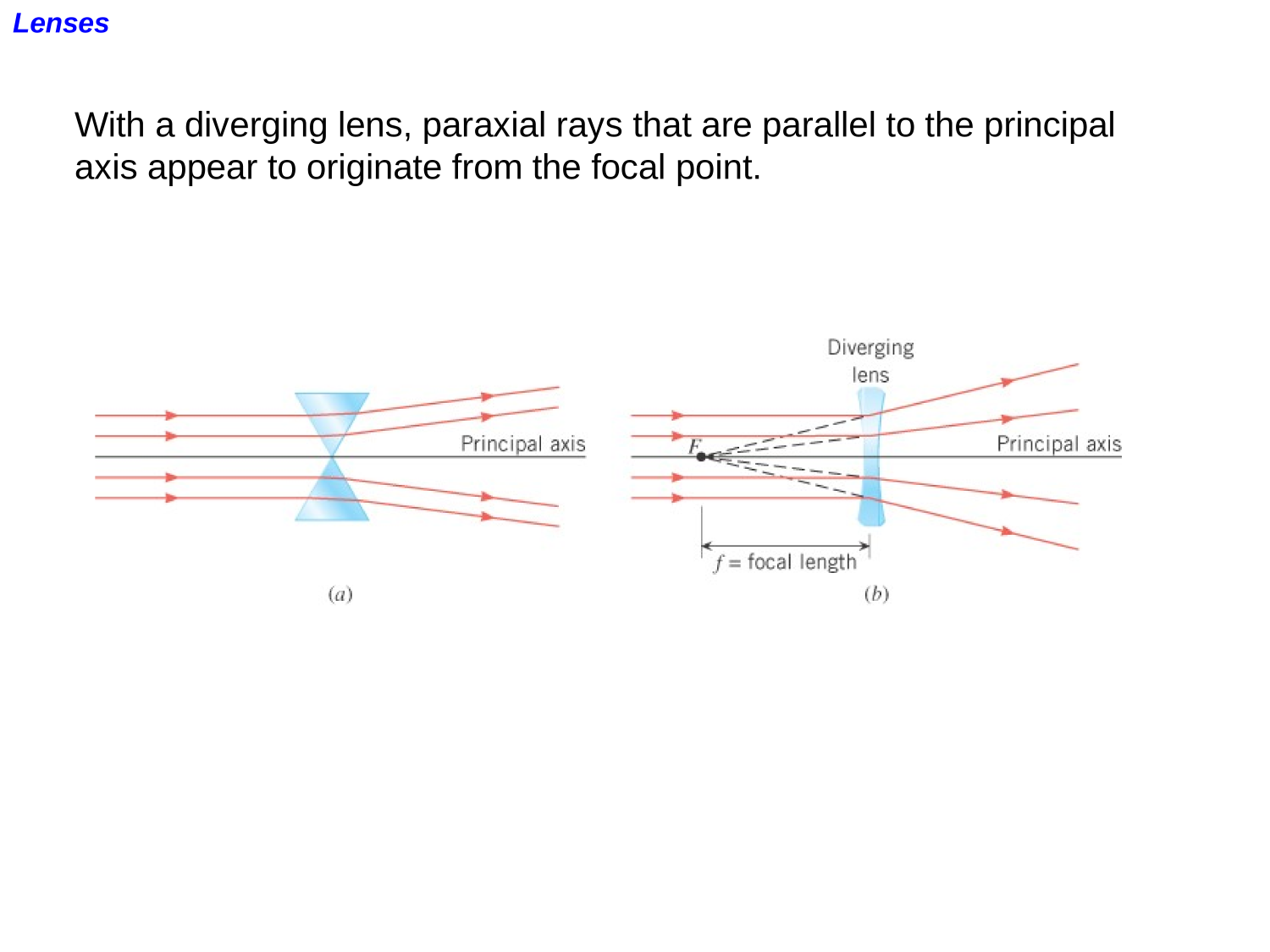
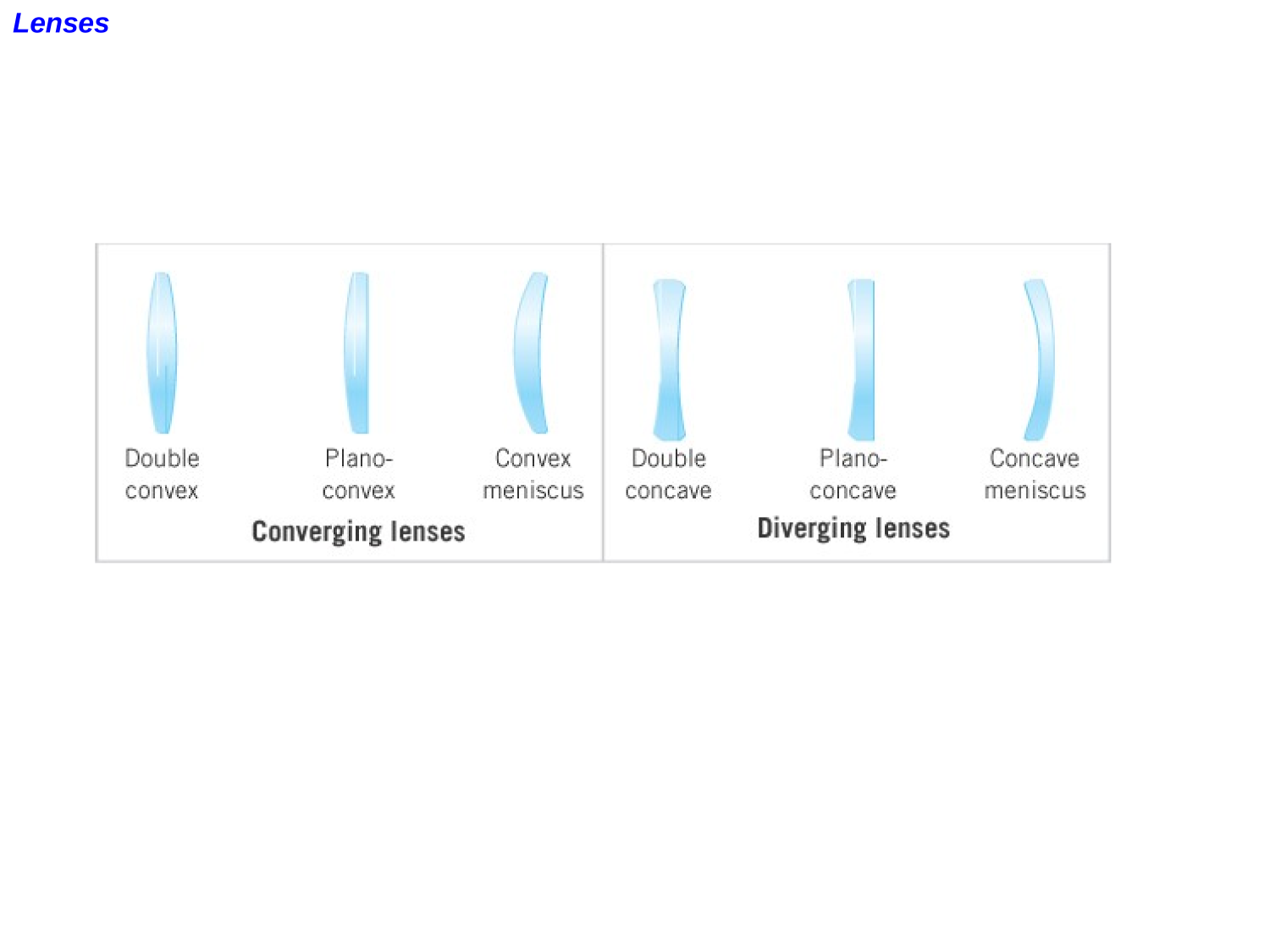
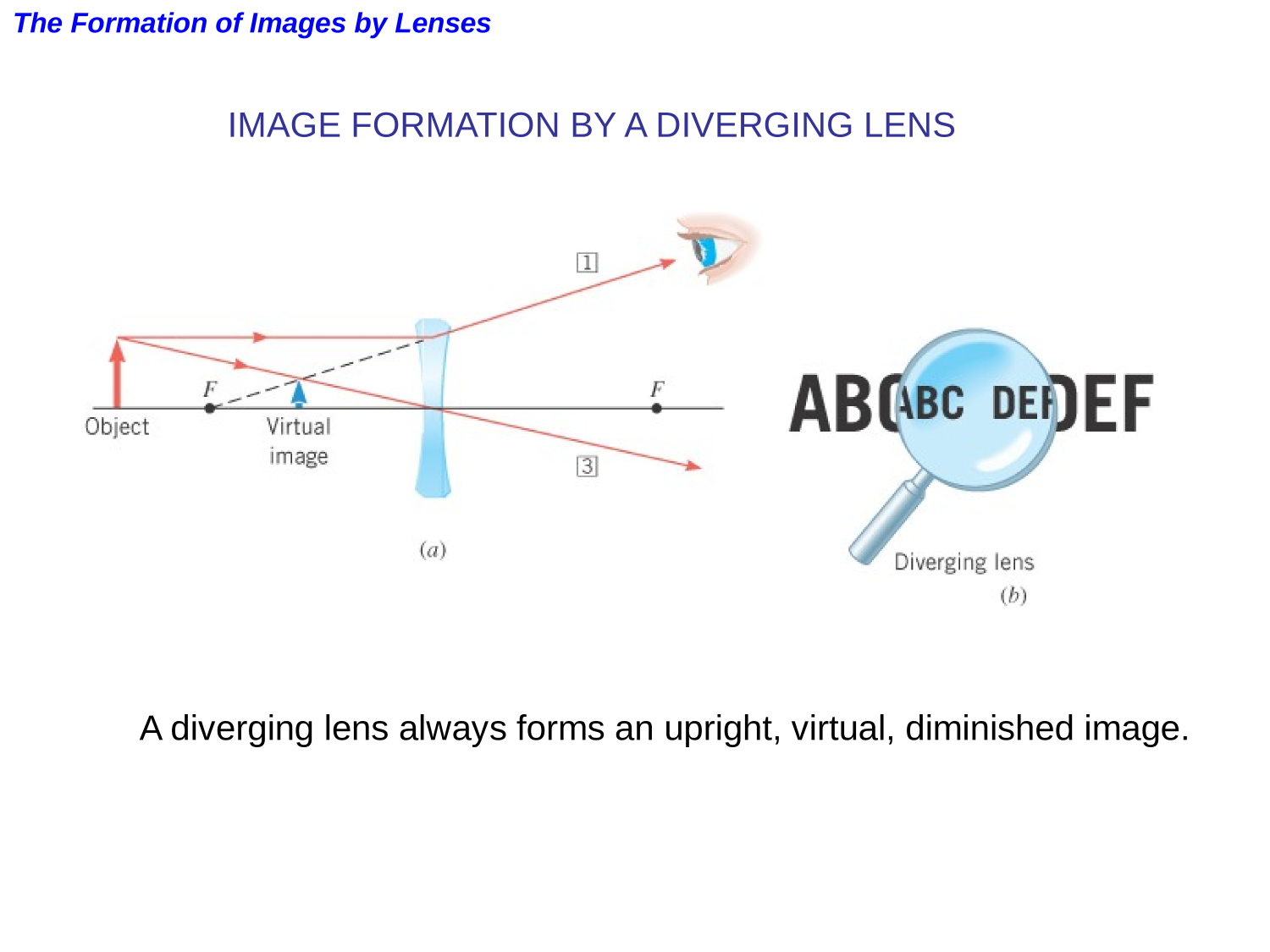
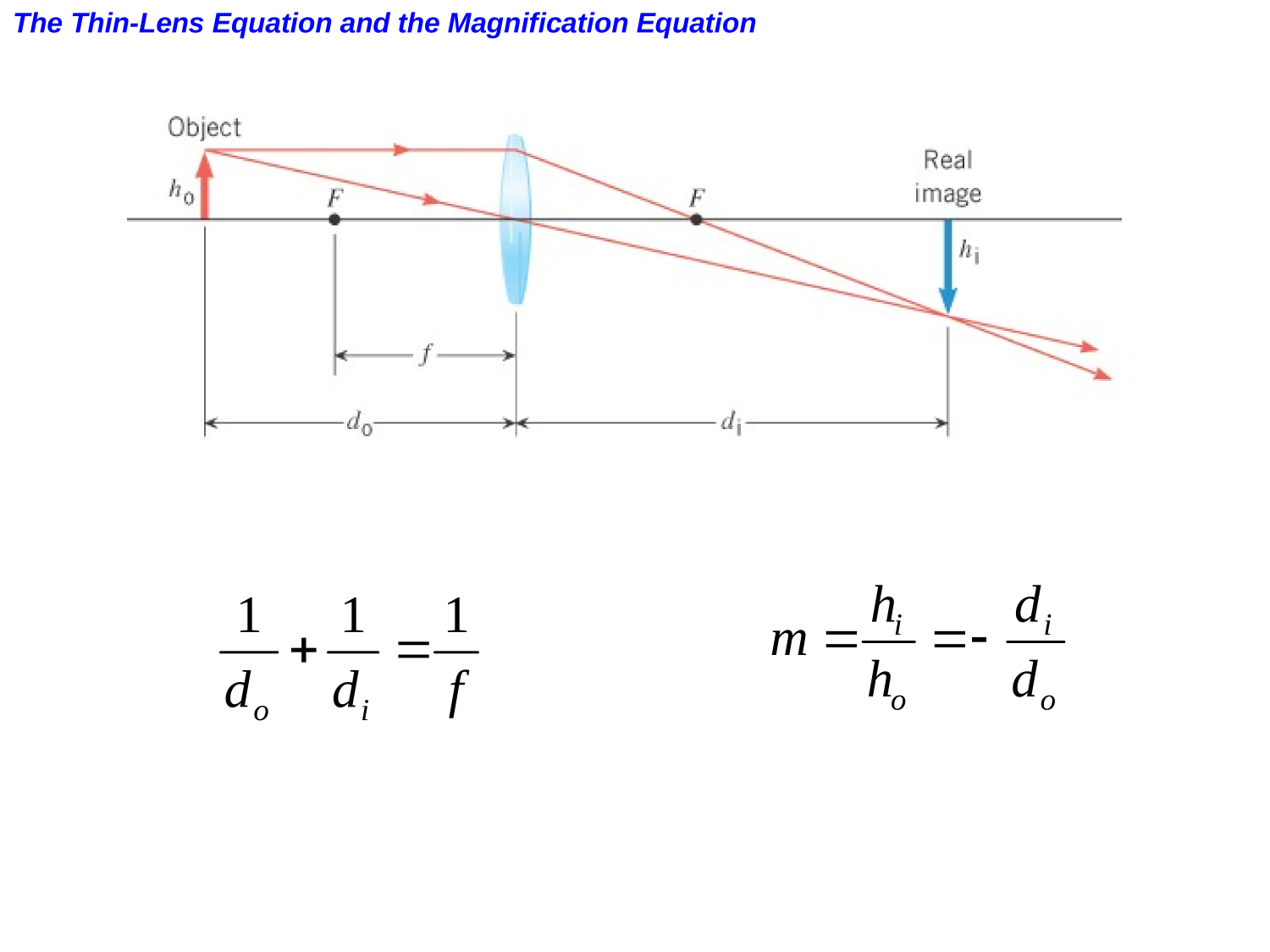
Lenses
Optics
Refraction
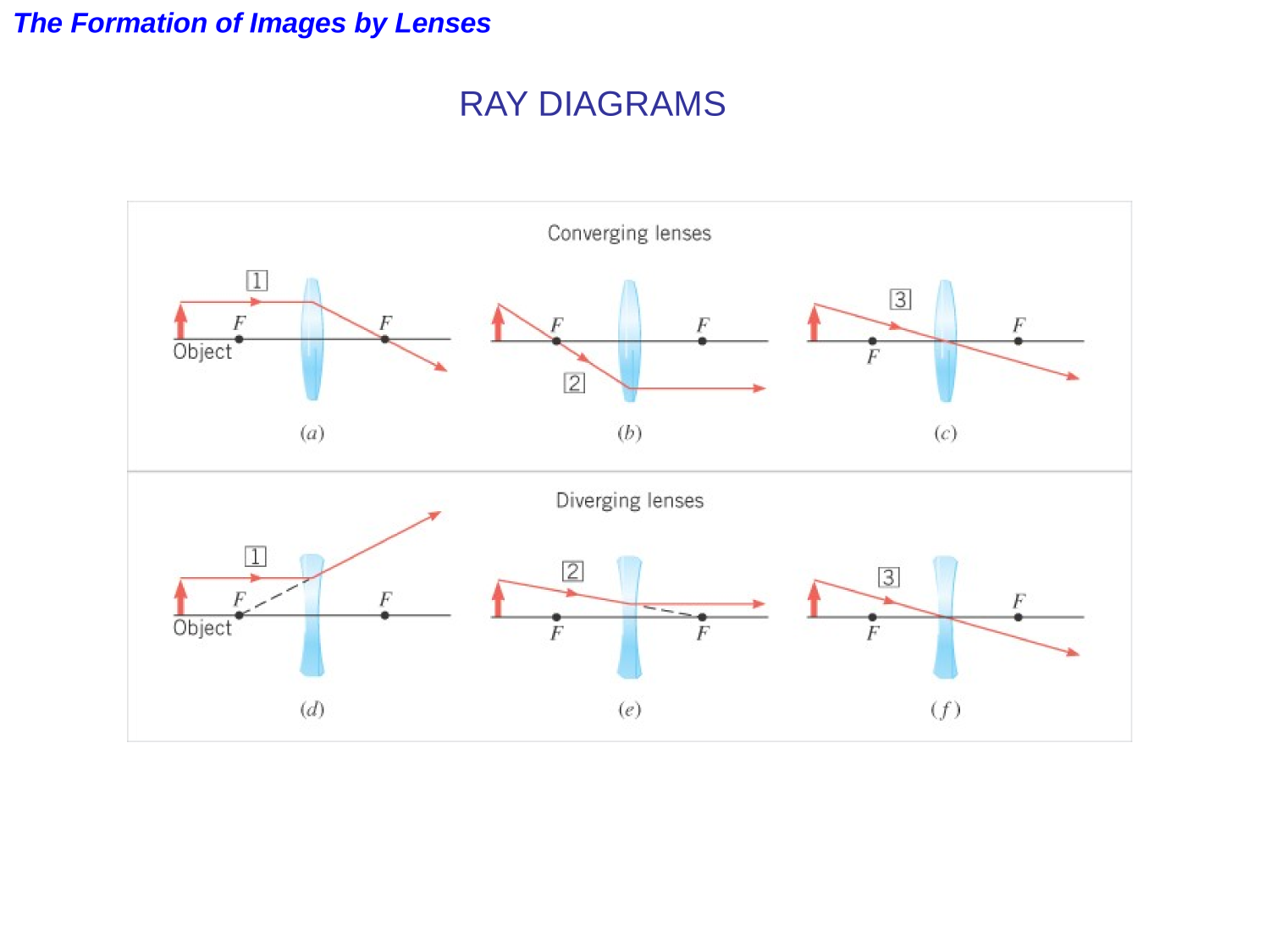
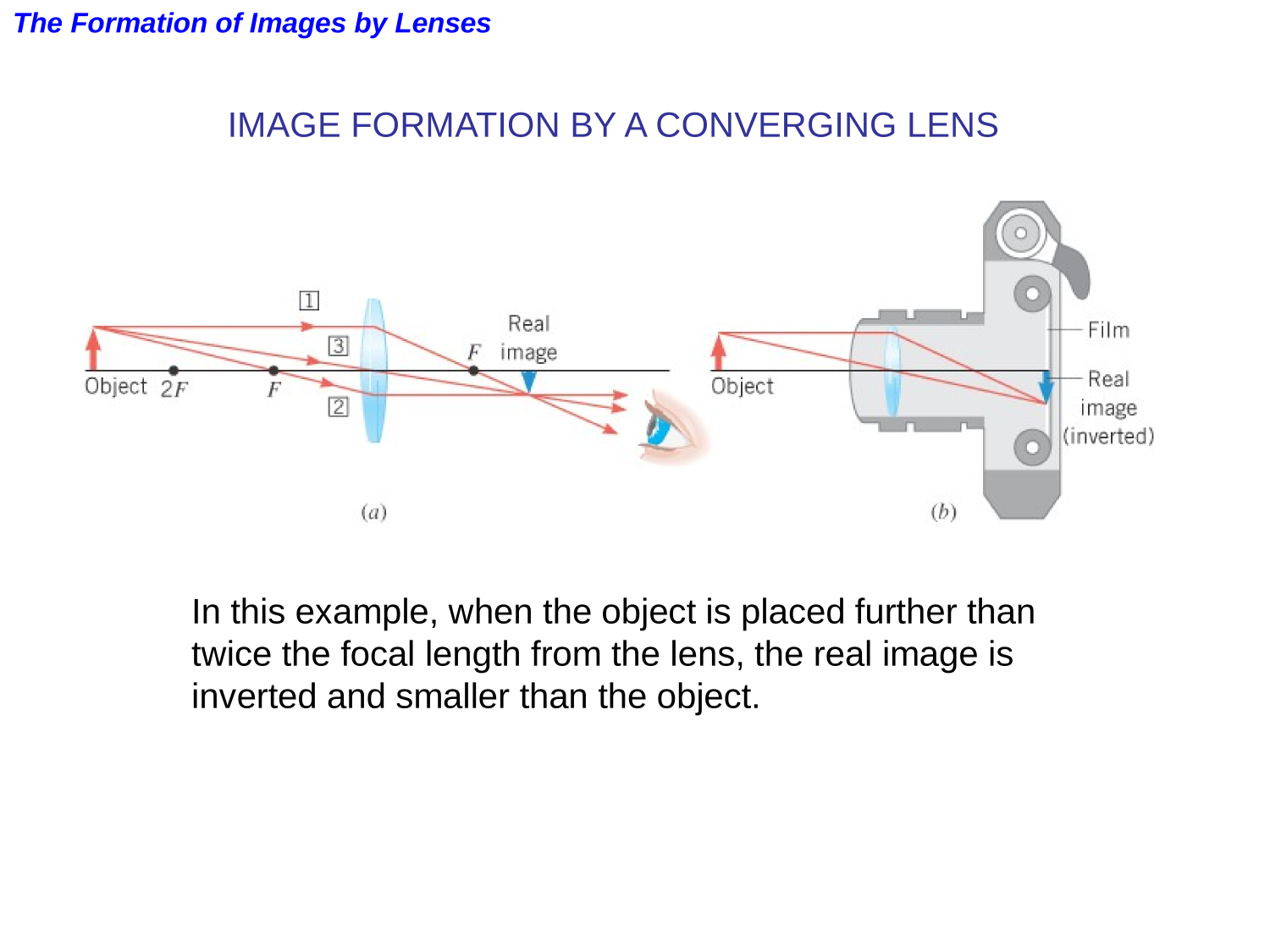
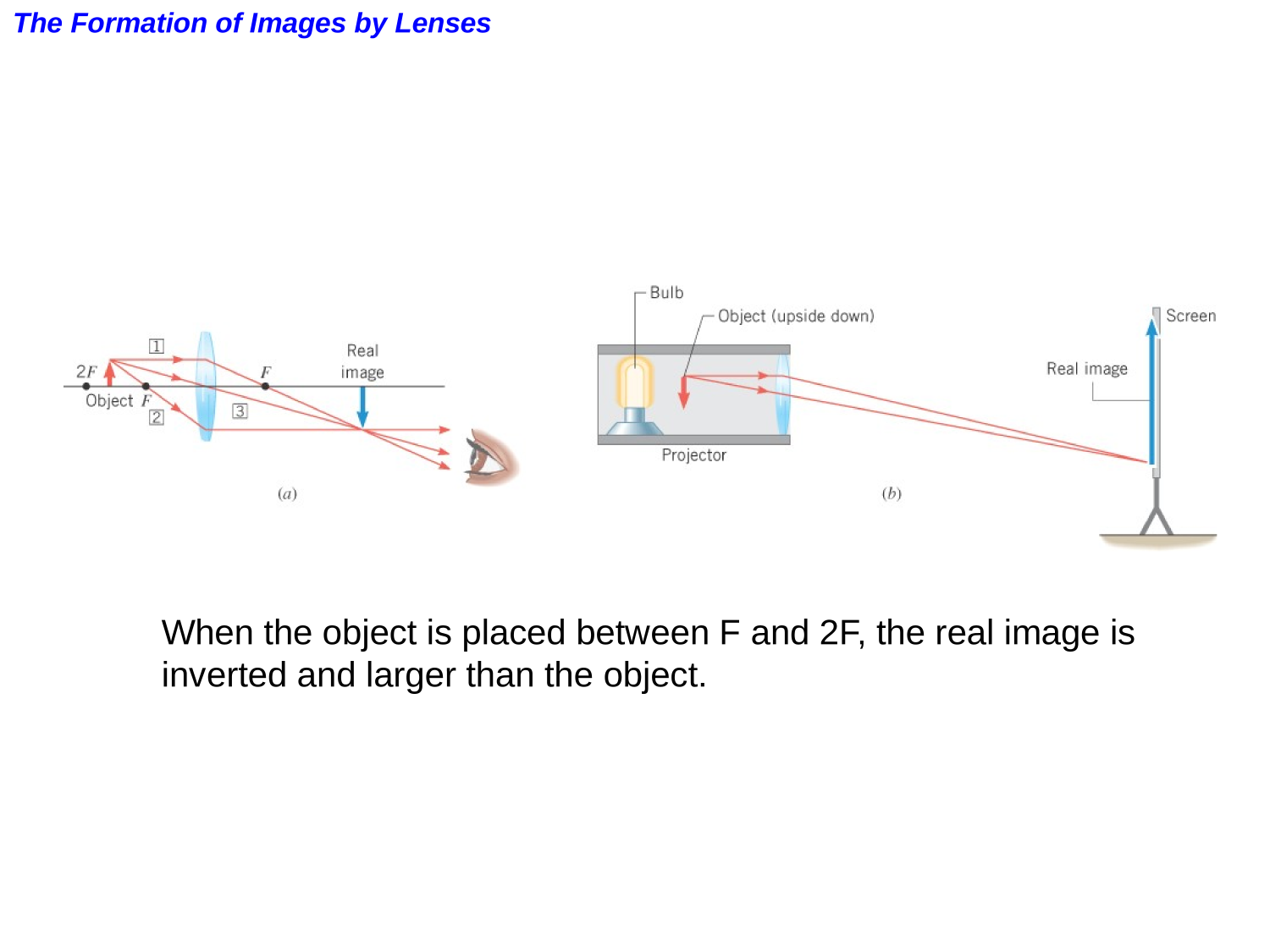
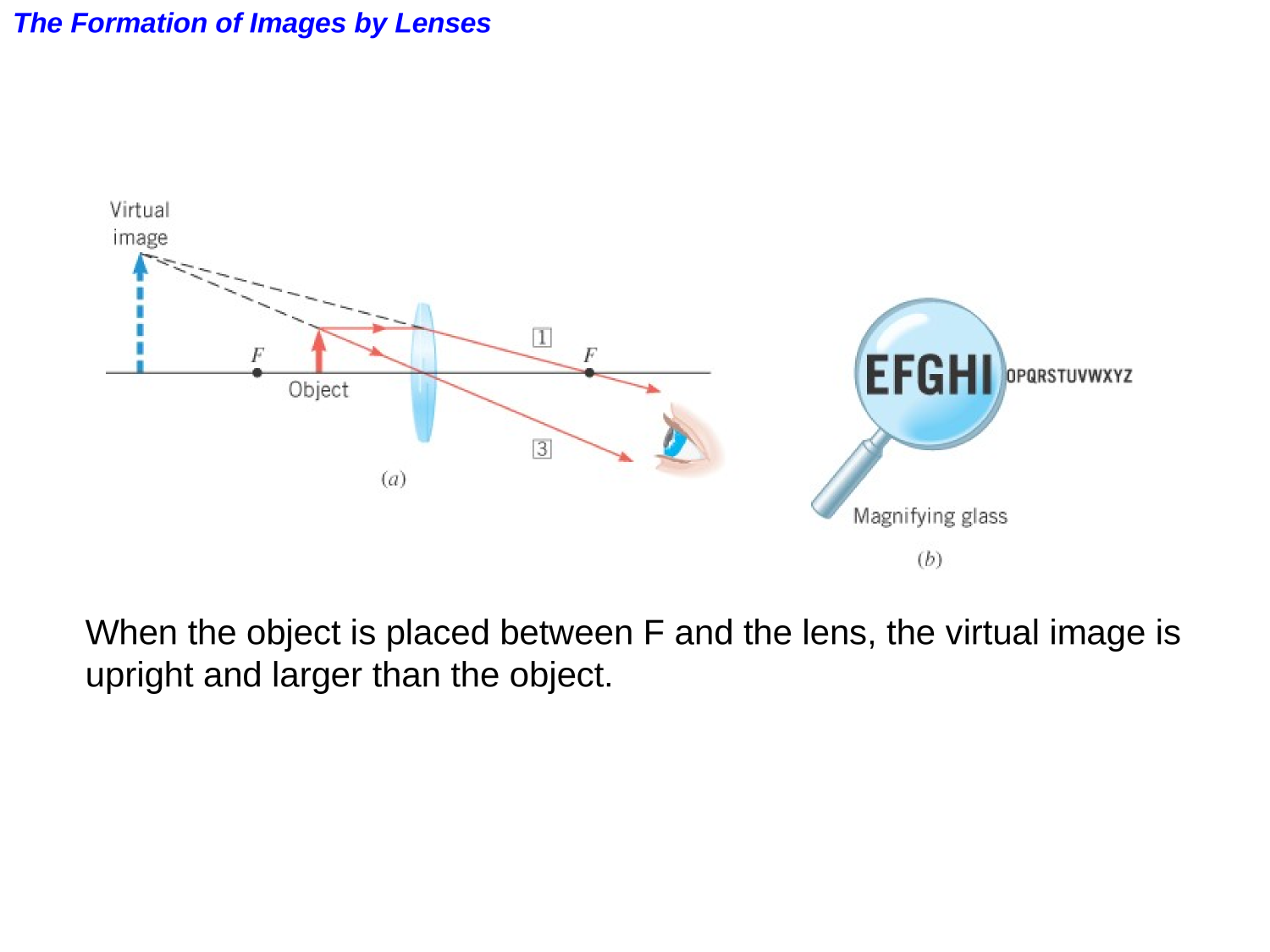



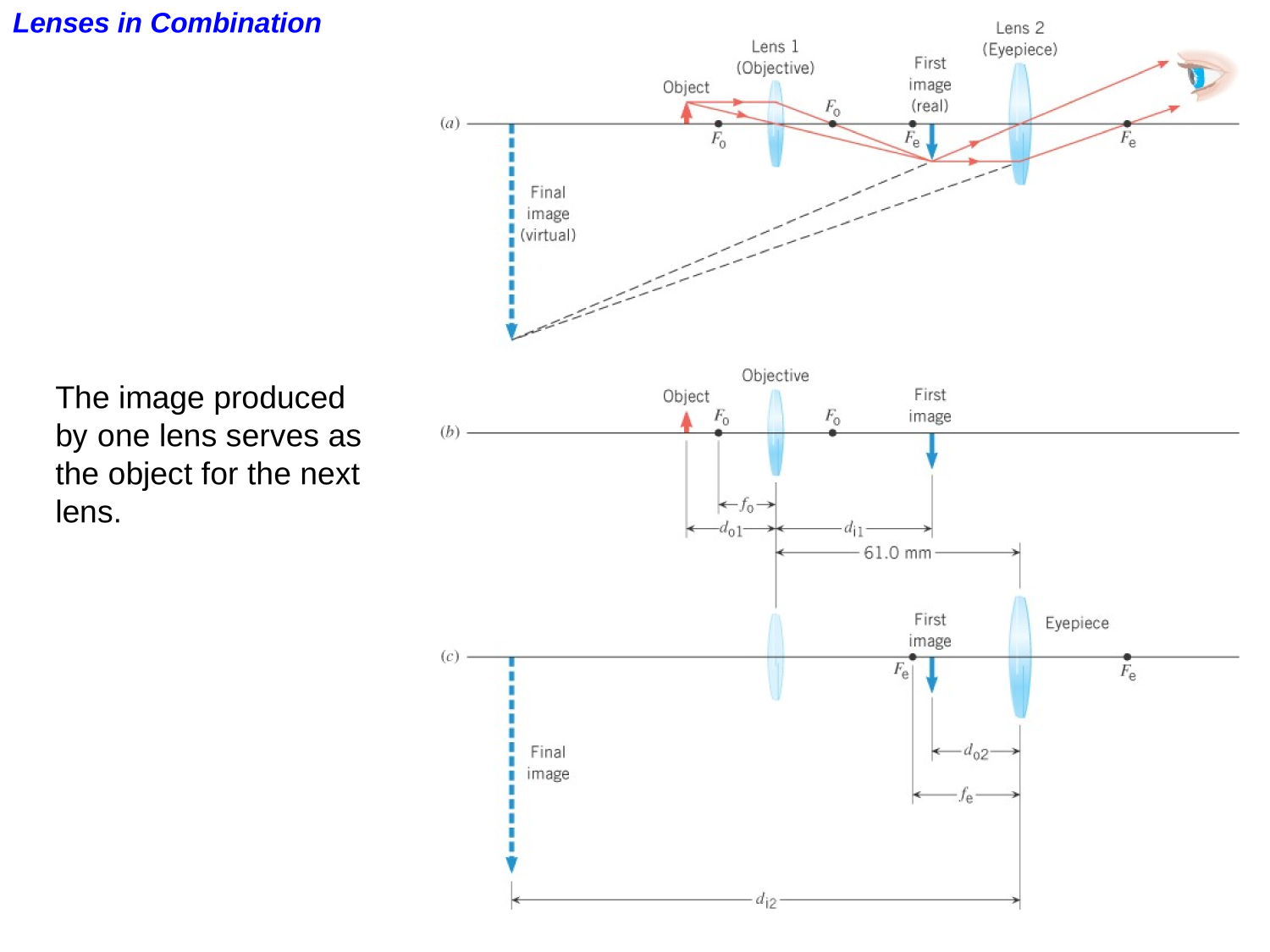
Lenses in combination
Optics
Refraction
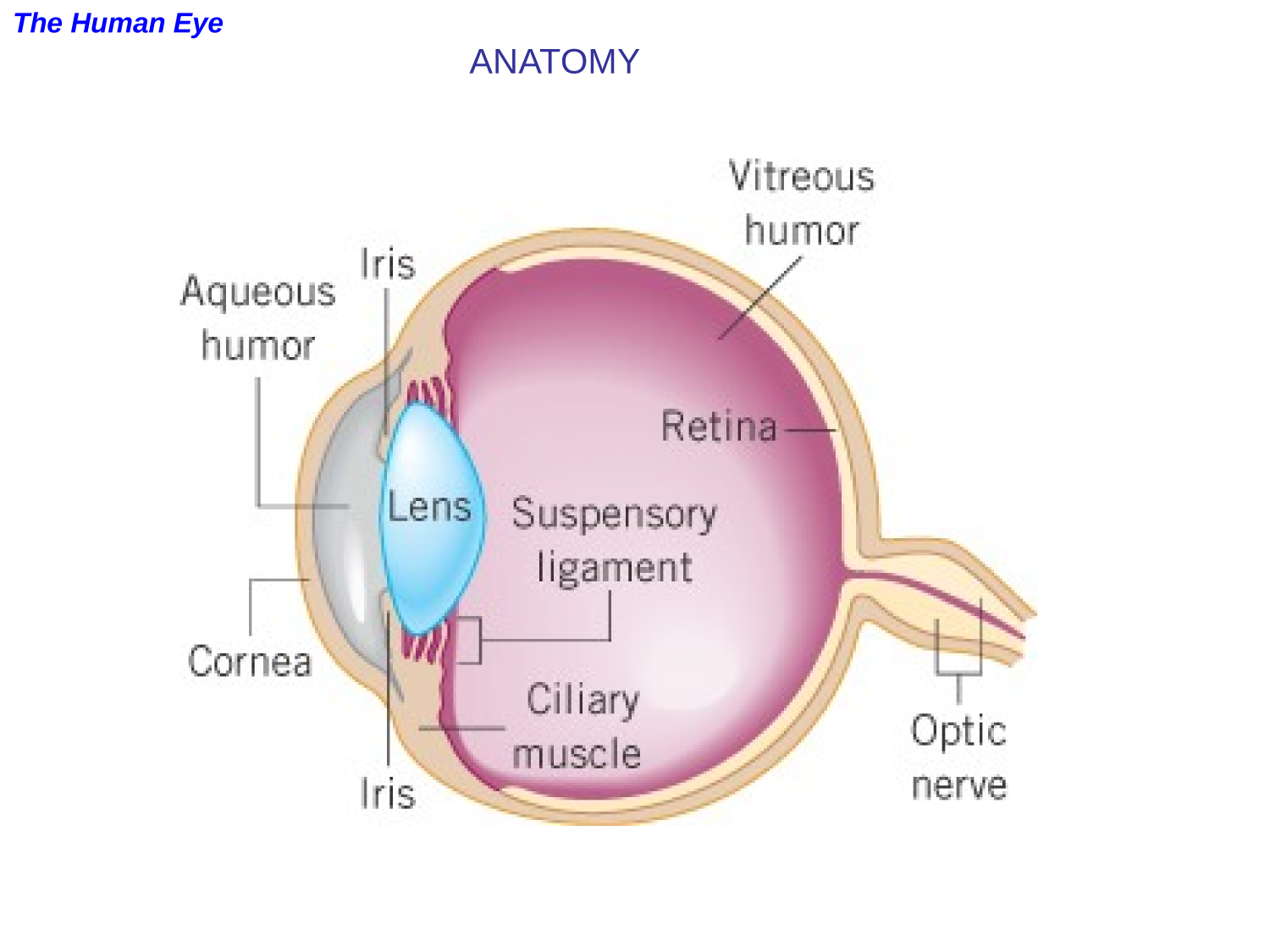
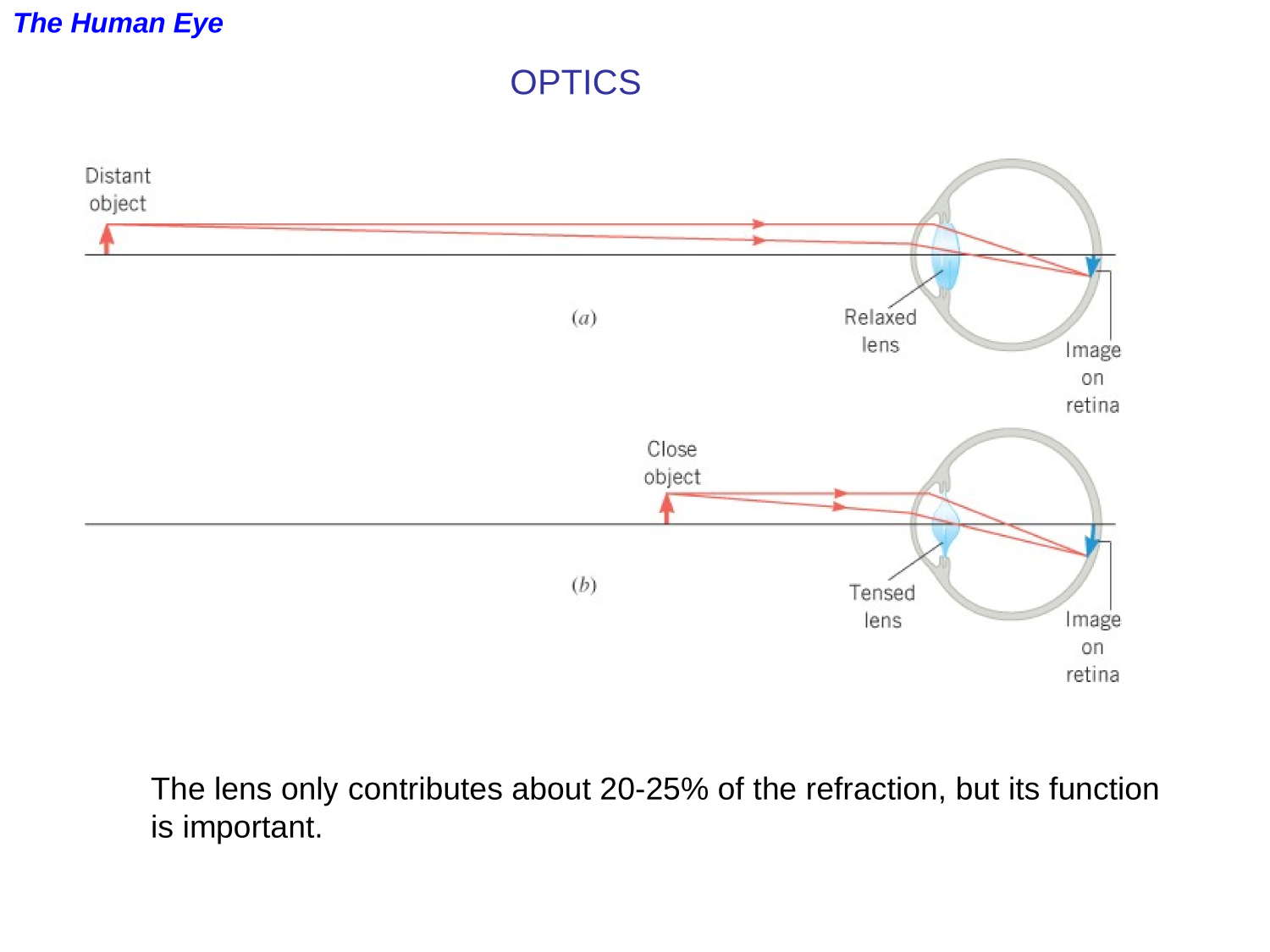
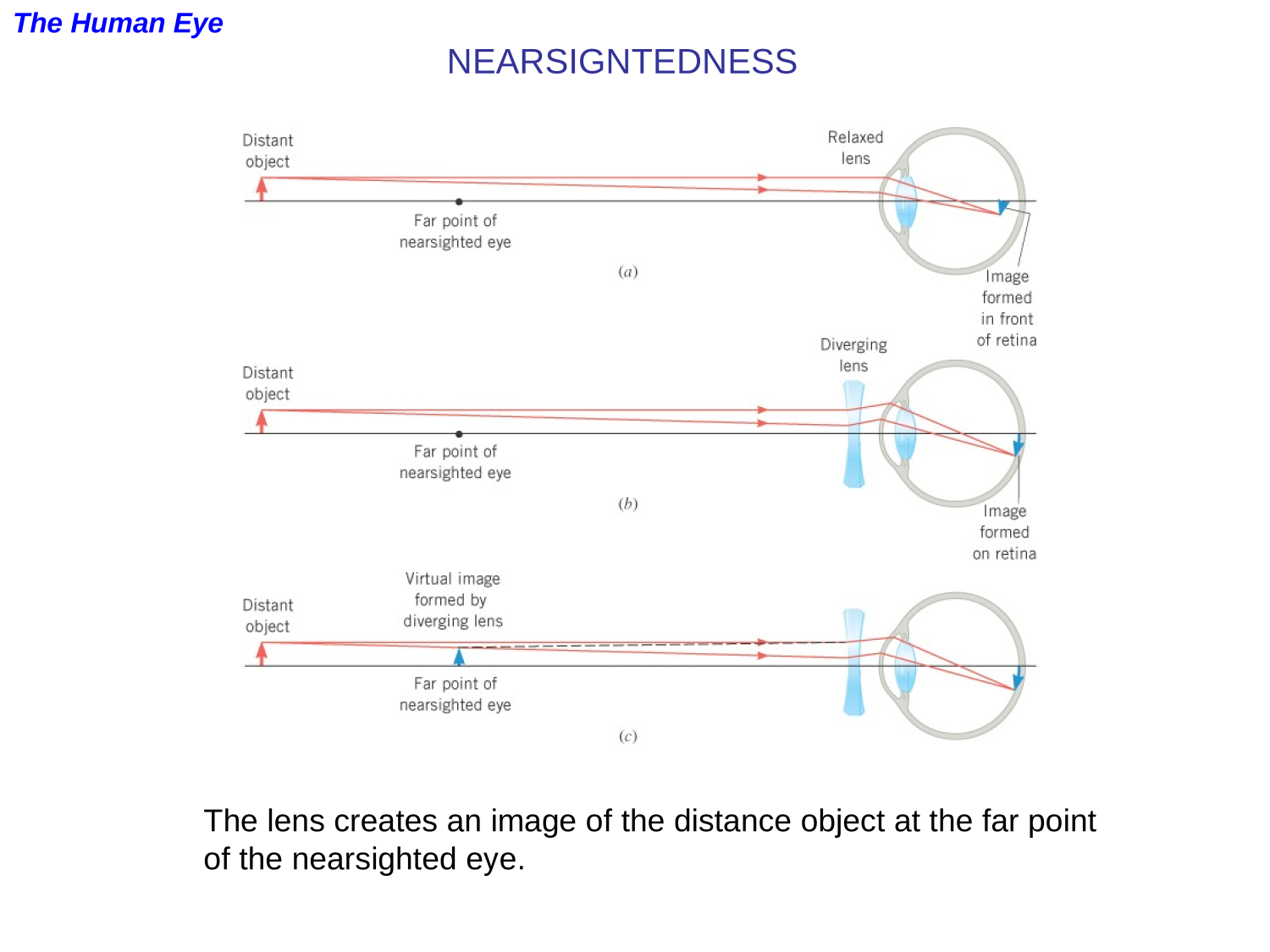
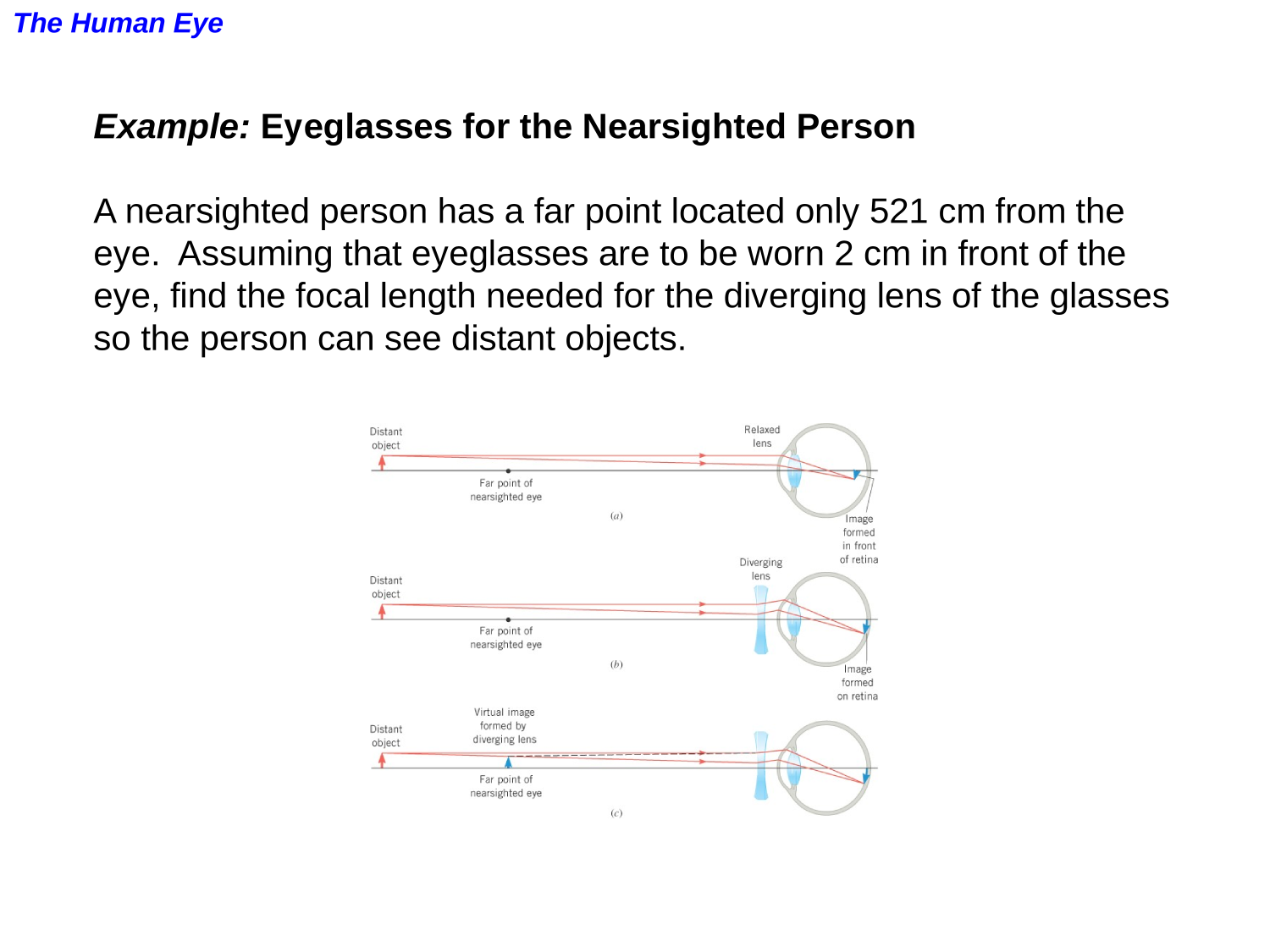
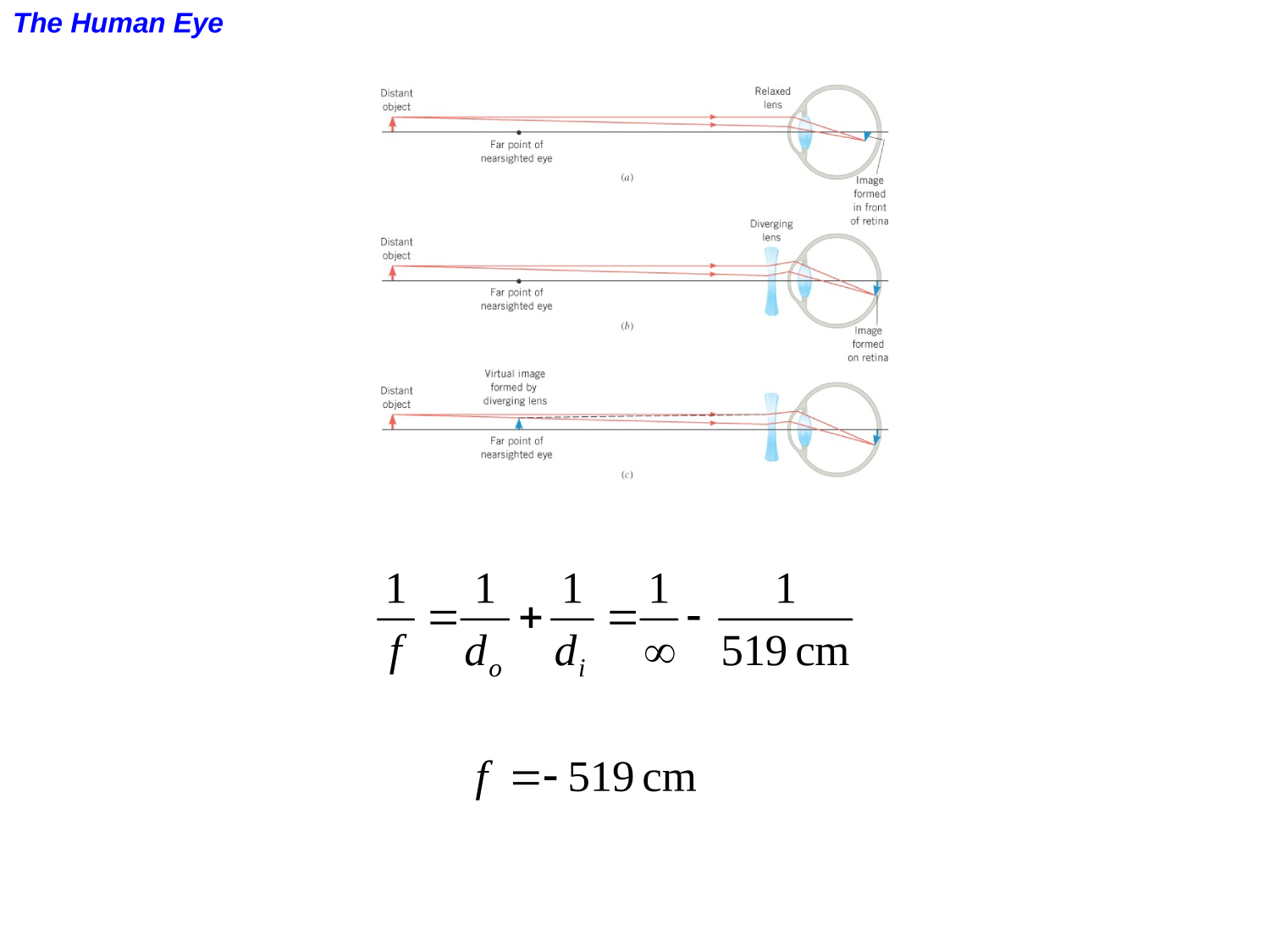
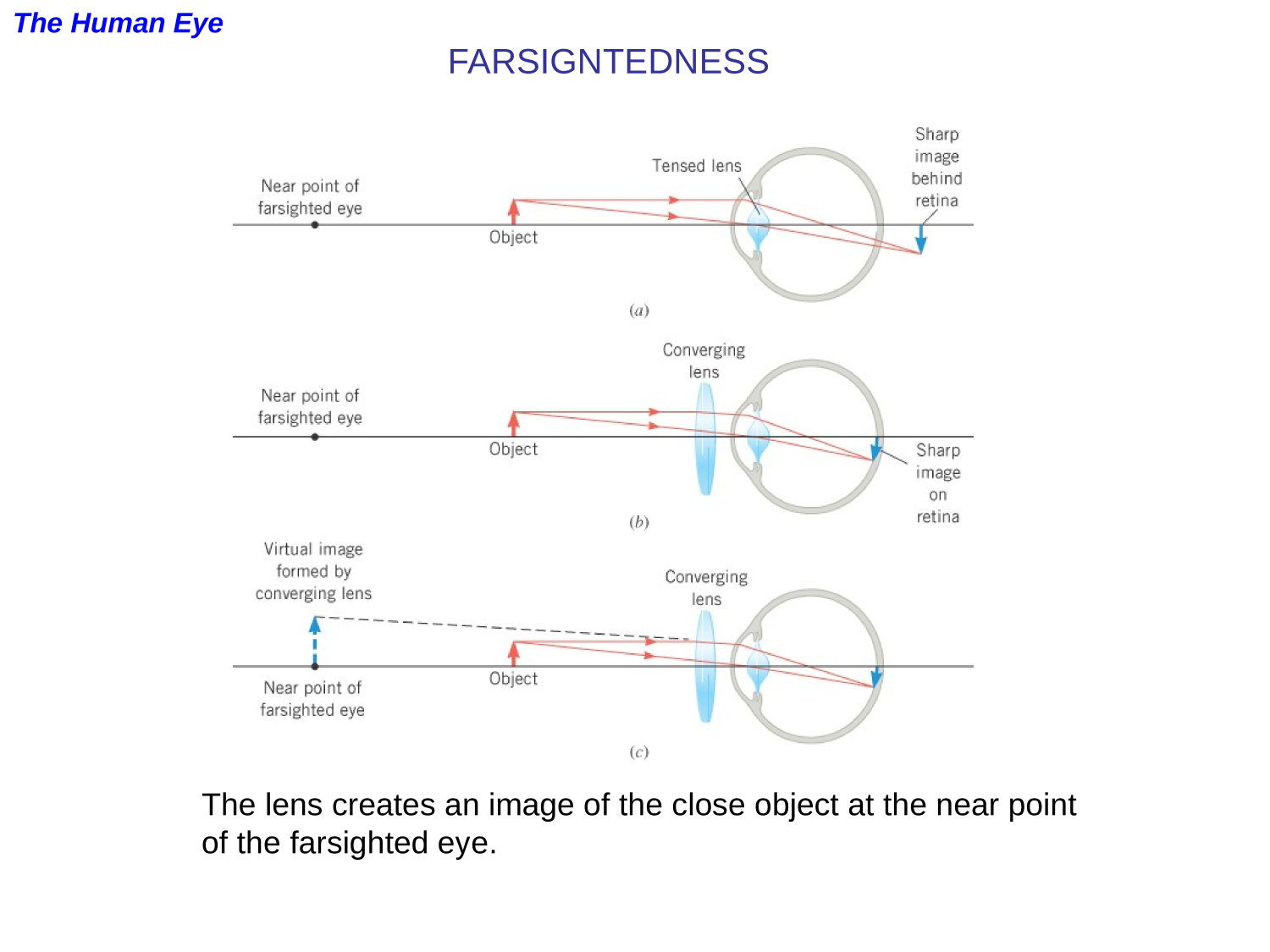
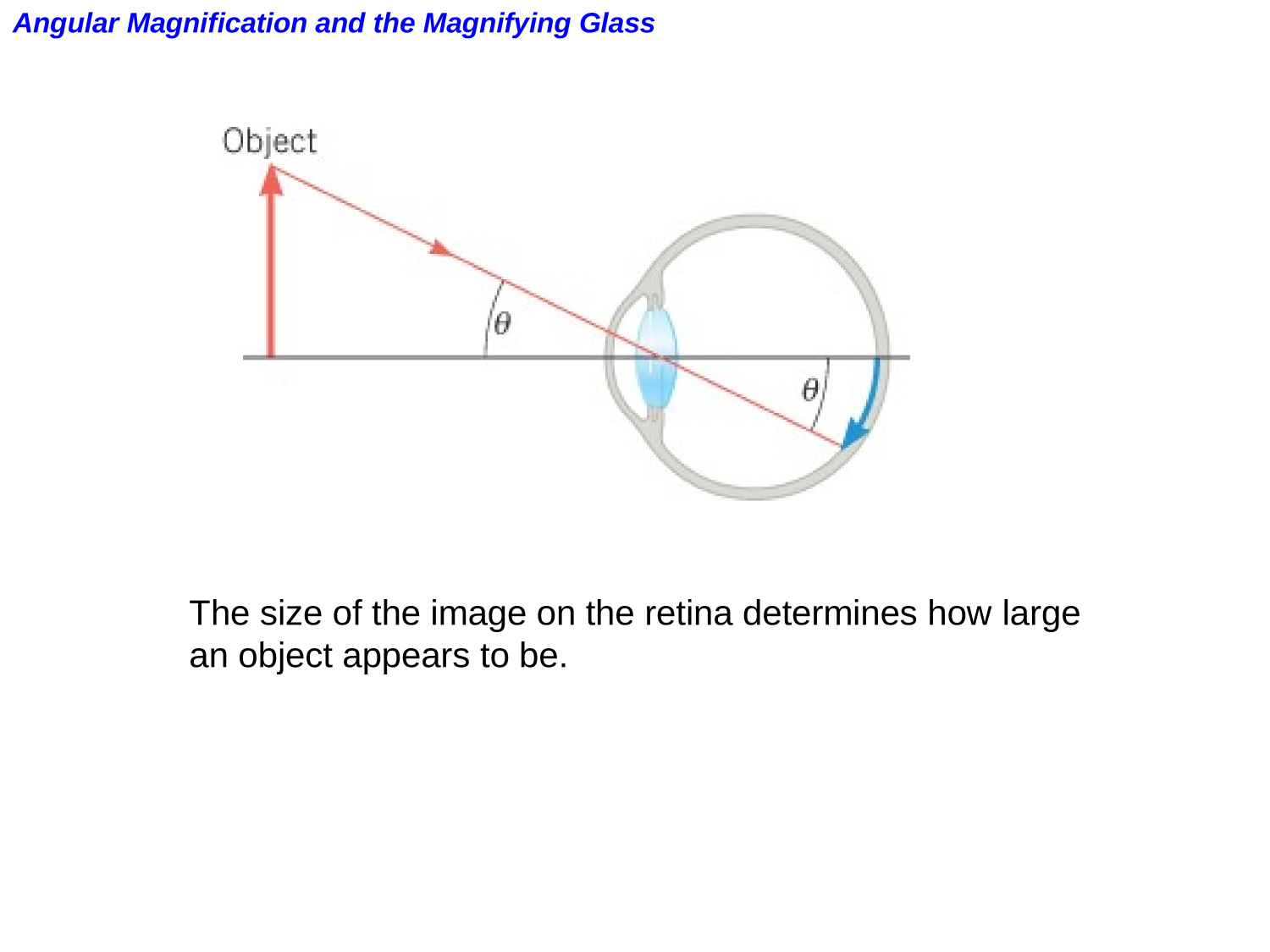
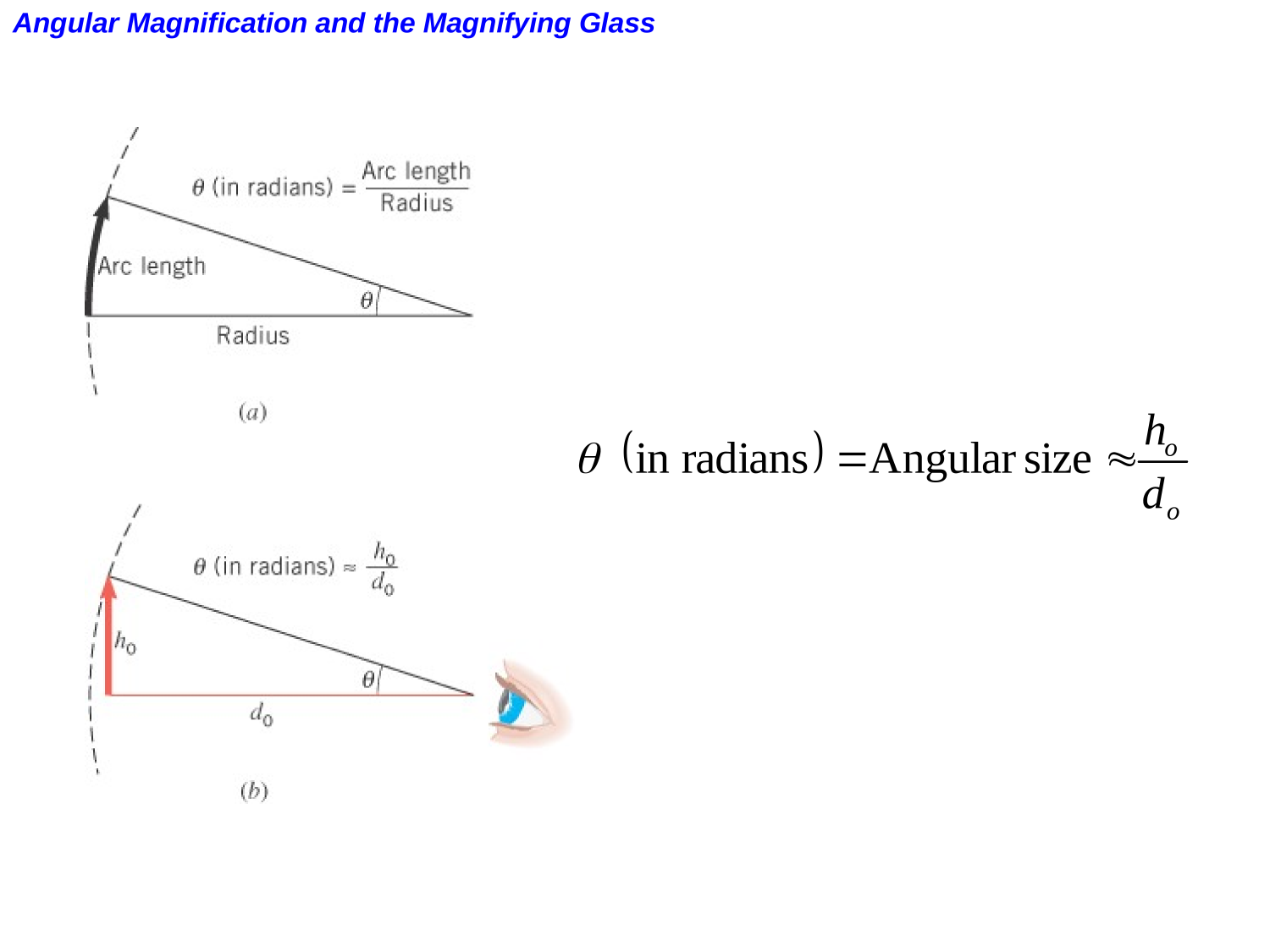
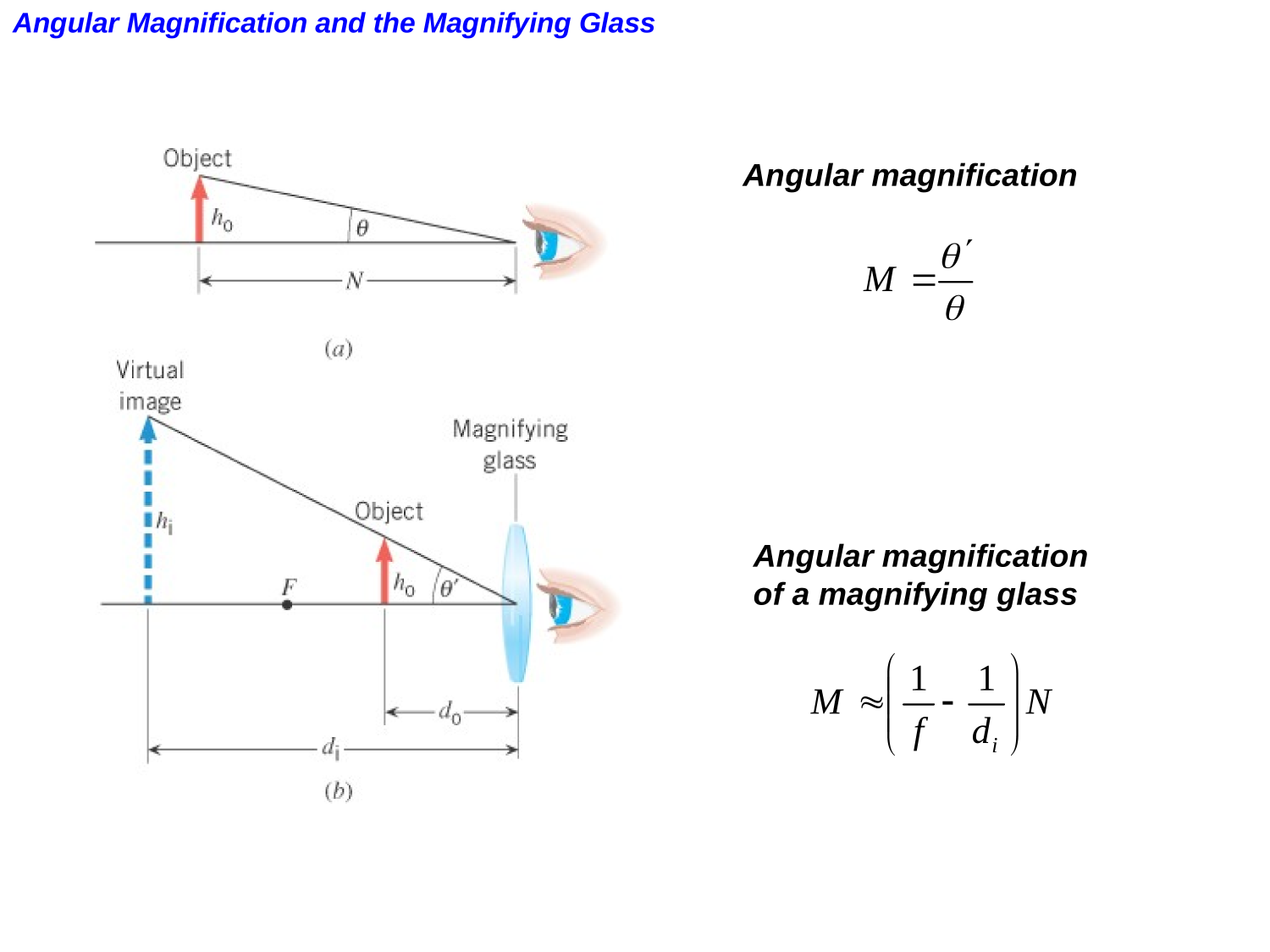
The Human Eye
Optics
Refraction


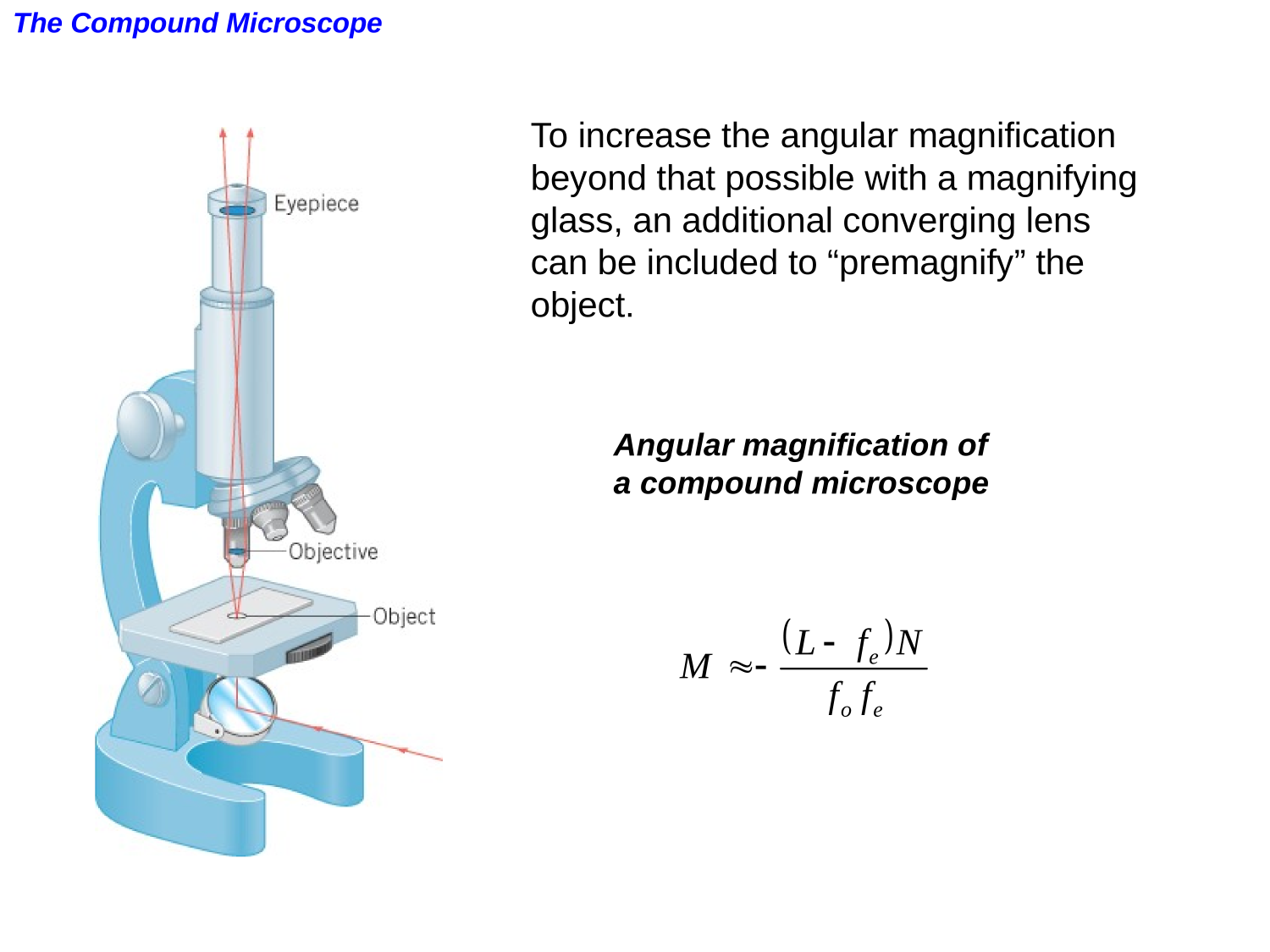
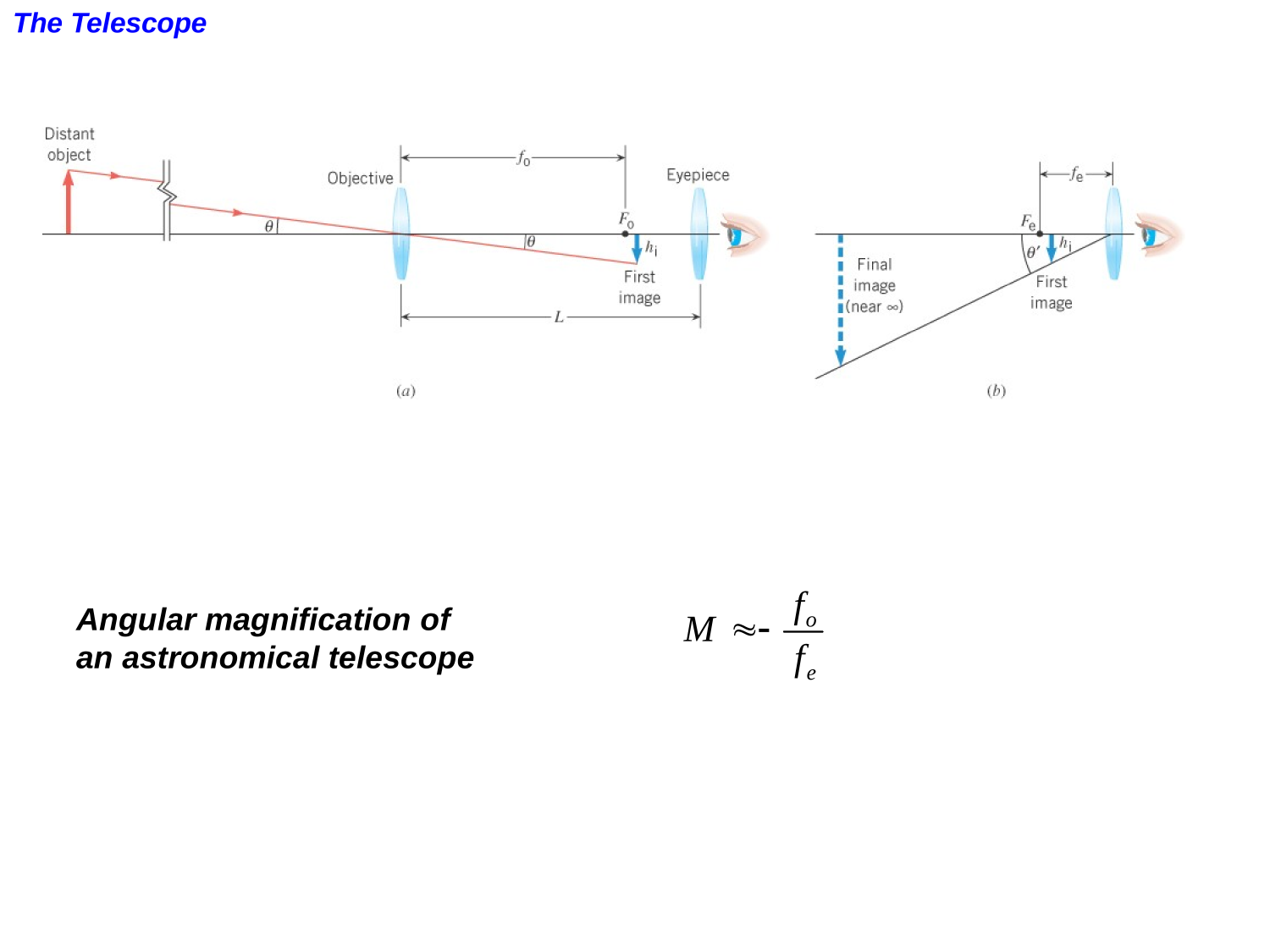
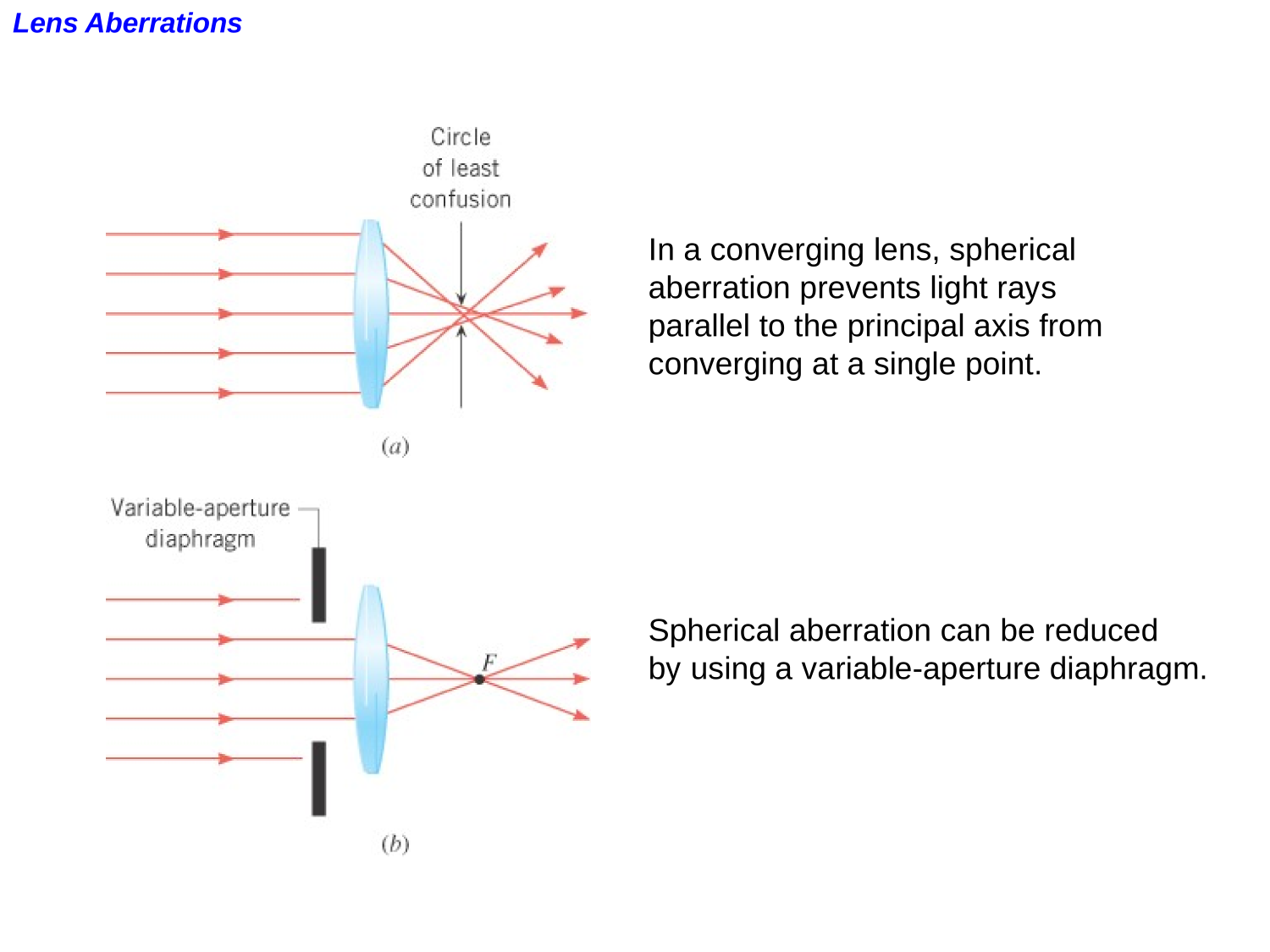
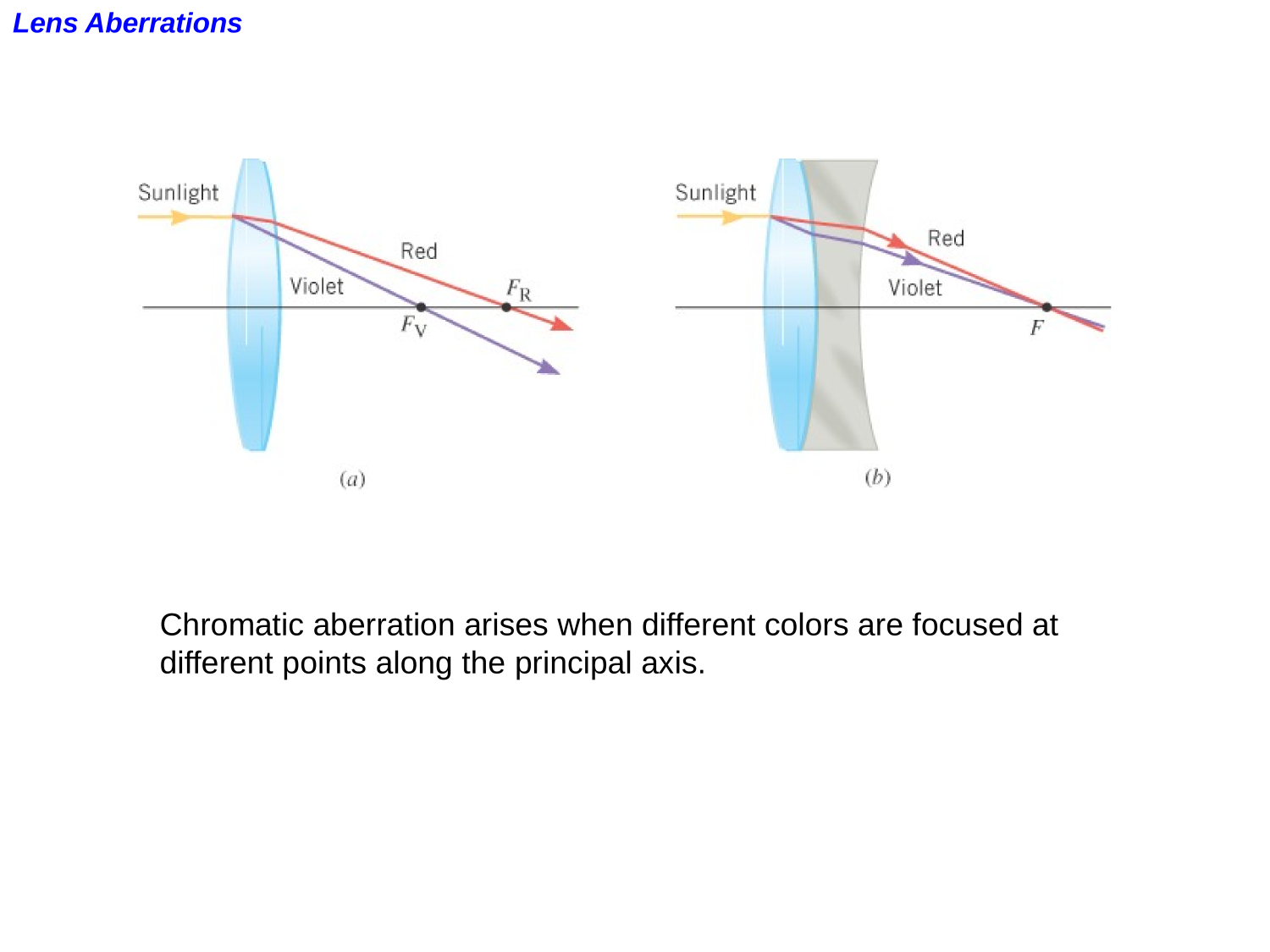
Lens Abberations
Optics
Refraction
Optics - Refraction
By drmoussaphysics
Optics - Refraction
- 252



