Adventures in Software Craftsmanship
Day 1 - September 14, 2015
- Intro and Philosophy
- Core Principles
- Clean Code Conventions
- Code Smells
Introduction
Daniel Yanos
July 2014
EDS - Retail
Silver Surfer - Big Data
Jason Riddle
Feb 2015
COS - Card Tech
Grayskull - CICD Engineer
What is "Software Craftsmanship?"
A craftsman or artisan is a skilled manual worker who makes items that may be functional or strictly decorative.
•How is software a craft?
•How is software different from typical crafts?
•What things make programmers artisans?
•Why is it important to improve in your craft?
•What are important qualities of a skilled craftsman?
•How can you improve your crafting skills?
The Art of Software
Writing code is similar to painting a picture. A programmer who writes clean code is an artist who can guide a blank screen through a series of transformations until it is an elegantly coded system.
- Easy to recognize a good painting
- Hard to paint a good picture
Programmers are authors – responsible for communicating well with their readers.
- You write for readers who will judge your effort and skill
- The ratio spent reading vs. writing code is usually at least 10:1
The Science of Software
What do these have in common?
- UI/UX Design
- Animating a Movie
- Engineering a Bridge
- Studying Quantum Entanglement
- Programming
Scientific Method
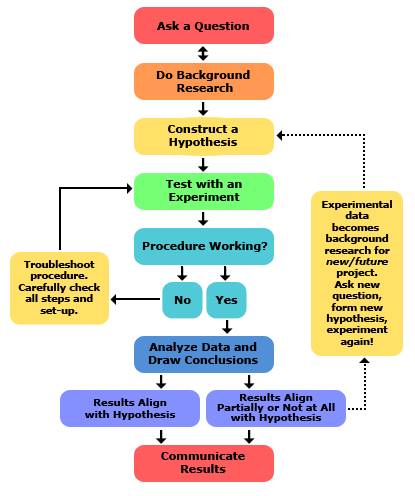
Science
UI/UX Design
Programming
Bridge Building
Ask a Question
Background Research
Construct Hypothesis
Test with Experiment
Analyze Data &
Draw Conclusions
Communicate Results
Identify a User Problem
User Research and Interviews
Construct
Prototype
User Testing and Feedback
Incorporate Feedback
Hand Off / Implement Design
Proposal Request
Survey Site
Design to Specifications
CAD and Physical Model
Improve Structure
Build Bridge
Identify Technical Problem
Gather Requirements
Plan Stories and Design System
PoC, User and Perf Testing
Improve Structure
QS Validation and Release
Thinking about software as a science will help break the bad habit of:
"I don't know what to do so I'll just write the code and see what happens."
The Science of Software
A civil engineer wouldn't say:
"I don't know what to do, so I'll just go ahead and start building this bridge and see what happens..."
Why is it helpful to think of software as a craft?
- Effective way to transition from the college mindset of software development to a professional mindset
- Aligns with Capital One's objective of becoming a leading technology company
- Important for improving your technical skills and succeeding in the workplace
From Journeyman to Master
As a student:
- Solve it
- Test it
- Fix it
- Turn it in
- Forget about it
As a professional:
- Solve it
- Make it easy to understand
- Make it easy to use
- Make it easy to change
- Test it
- Fix it
- Review it
- Commit it
- Test it
- Release it
- Support it
Mantras of a Software Craftsman
-
Broken windows
- One broken window, left un-repaired, instills in the community a sense of abandonment.
-
Boy Scout rule
- "Leave the campground cleaner than you found it."
-
Tests are your parachute
- Keep them free of holes and obstructions.
Your Knowledge Portfolio
Your knowledge and experience are your most important professional assets.
Unfortunately, they're expiring assets.
- Invest regularly
- Diversify
- Manage risk
- Buy low, sell high
- Review and rebalance
Expand your knowledge portfolio regularly; not only with technical expertise but also Capital One expertise.
Care about your craft
Think about your work
Continuously make small improvements
Code Reading Competition
@implementation LoginVC
//###########################
#pragma Life Cycle
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
//Let the NavigationController know the rewind point
[(ApplicationNavigationController*)self.navigationController setLoginViewController:self];
//Set the current Error
self.currentError = nil;
//Prepare UI
self.titleLabel.font = [UIFont c1BoldHeader];
self.rememberMeCheckBoxLabel.font = [UIFont c1];
[self.usernameTextField setTextColor:[UIColor blackColor]];
[self.usernameTextField setFont:[UIFont c1ButtonTitle]];
[self.passwordTextField setTextColor:[UIColor blackColor]];
[self.passwordTextField setFont:[UIFont c1ButtonTitle]];
}
-(void)viewDidAppear:(BOOL)animated
{
[super viewDidAppear:YES];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self
selector:@selector(keyboardFrameDidChange:)
name:UIKeyboardWillChangeFrameNotification
object:nil];
//Configure controls based up login manager
LoginManager *loginManager = [LoginManager sharedInstance];
if (loginManager.rememberMe)
{
self.usernameTextField.text= [loginManager username];
self.usernameTextField.enabled = NO;
self.usernameTextField.text = [loginManager maskedUsername];
[self.passwordTextField becomeFirstResponder];
}
else
{
[self.usernameTextField becomeFirstResponder];
[self.BottomHalf updateConstraints];
[self.BottomHalf layoutSubviews];
}
if (loginManager.rememberMe) {
self.rememberMeCheckBoxSelected.hidden = false;
self.rememberMeCheckBoxUnselected.hidden = true;
self.rememberUserName = true;
}
else
{
self.rememberMeCheckBoxSelected.hidden = true;
self.rememberMeCheckBoxUnselected.hidden = false;
self.rememberUserName = false;
}
}
-(void)viewWillDisappear:(BOOL)animated
{
[super viewWillDisappear:animated];
[self clearTextFields];
}
//###########################
#pragma Keyboard
//Adjust the constraint for the login button taking into account the size of the keyboard
- (void)keyboardFrameDidChange:(NSNotification *)notification
{
CGRect keyboardBeginFrame = [[notification userInfo][UIKeyboardFrameBeginUserInfoKey] CGRectValue];
CGRect keyboardFrameBegin = [self.view convertRect:keyboardBeginFrame toView:nil];
CGRect keyboardEndFrame = [[notification userInfo][UIKeyboardFrameEndUserInfoKey] CGRectValue];
CGRect keyboardFrameEnd = [self.view convertRect:keyboardEndFrame toView:nil];
if (keyboardFrameBegin.origin.y > keyboardFrameEnd.origin.y)
{ //Keyboard opening
[self.ButtonDistanceFromBottomConstraint setConstant:keyboardFrameEnd.size.height + 8];
if (self.BottomHalf.bounds.size.height - keyboardFrameEnd.size.height - 16 > 32)
{
//Button can fit within the bottom half of the screen
[self.ButtonHeightConstraint setConstant:(self.BottomHalf.bounds.size.height - keyboardFrameEnd.size.height) - 16];
}
else
{
//Button does not fit so lock to a height of 32
[self.ButtonHeightConstraint setConstant:32];
}
}
else
{ //Keyboard closing
[self.ButtonDistanceFromBottomConstraint setConstant:8];
[self.ButtonHeightConstraint setConstant:32];
}
[UIView animateWithDuration:[[notification userInfo][UIKeyboardAnimationDurationUserInfoKey] doubleValue]
animations:^{
[self.loginButton layoutIfNeeded];
}];
[UIView commitAnimations];
}
- (BOOL)textFieldShouldReturn:(UITextField *)textField
{
if (textField == self.usernameTextField)
{
if ([textField.text length] > 0)
{
[self.passwordTextField becomeFirstResponder];
}
}
else if (textField == self.passwordTextField)
{
[self performLogin];
}
return NO;
}
- (void)clearTextFields
{
LoginManager *loginManager = [LoginManager sharedInstance];
self.passwordTextField.text = @"";
[loginManager setPassword:@""];
if (self.rememberMeCheckBoxSelected.hidden && !loginManager.rememberMeUsed)
{
self.usernameTextField.text = @"";
[self.usernameTextField becomeFirstResponder];
}
else if (!self.rememberMeCheckBoxSelected.hidden && !loginManager.rememberMeUsed)
{
loginManager.rememberMe = NO;
}
else if([loginManager maskedUsername] != nil)
{
self.usernameTextField.text = [loginManager maskedUsername];
[self.passwordTextField becomeFirstResponder];
}
}
//###########################
#pragma Login Events
- (IBAction)LoginAction:(id)sender
{
if ([self.usernameTextField.text length] > 0)
{
if ([self.passwordTextField.text length] > 0)
{
[self performLogin];
}
else
{
[self.passwordTextField becomeFirstResponder];
}
}
else
{
[self.usernameTextField becomeFirstResponder];
}
}
- (void)performLogin
{
LoginManager *loginManager = [LoginManager sharedInstance];
if (self.usernameTextField.enabled)
{
[loginManager setUsername:self.usernameTextField.text];
}
loginManager.password = self.passwordTextField.text;
loginManager.rememberMe = self.rememberUserName;
if (loginManager)
{
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] beginIgnoringInteractionEvents];
__weak LoginVC *weakself = self;
// this is the block to execute when login is completed
self.loginCompletion = ^()
{
[C1DataManager sharedManager].userLoggedInSuccessfully = TRUE;
//TODO - Remove, hard coded for testing
if ([weakself.usernameTextField.text isEqualToString:@"2xTablet144"])
{
[weakself segueToMFA];
}
else
{
[weakself segueViaNavigationController];
}
};
loginManager.loginSuccessBlock = ^(LoginManager *mgr)
{
mgr.loginSession.userName = [mgr username];
weakself.loginCompletion();
};
loginManager.loginFailureBlock = ^(LoginManager *mgr, NSError *error)
{
[self generatePopupFromError:error];
};
loginManager.loginMFABlock = ^(LoginManager *mgr)
{
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] endIgnoringInteractionEvents];
};
loginManager.loginMFACollectBlock = ^(LoginManager *mgr)
{
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] endIgnoringInteractionEvents];
};
[loginManager performLogin];
}
}
- (void)generatePopupFromError:(NSError*)error
{
self.currentError = error;
UIAlertView *alert;
//Error generating from from successfully connecting to the login server
if ([error.domain isEqual:@"com.capitalone.core.eapi"])
{
//[2] (null) @"C1SSErrorButtonTypes" : @"2 objects" C1SSErrorButtonType
NSArray *button = error.userInfo[C1SSErrorUserInfoKeyButtonTextLocalizationKey];
//We need to handle the recovery option
if (button.count == 2)
{
alert = [[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:error.localizedDescription
message:error.localizedRecoverySuggestion
delegate:self
cancelButtonTitle:button[0]
otherButtonTitles:button[1], nil];
}
else if (button.count == 0)
{
alert = [[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:error.localizedDescription
message:error.localizedRecoverySuggestion
delegate:self
cancelButtonTitle:@"OK"
otherButtonTitles:nil];
}
else
{
alert = [[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:error.localizedDescription
message:error.localizedRecoverySuggestion
delegate:self
cancelButtonTitle:button[0]
otherButtonTitles:nil];
}
}
//Error from not being able to hit the login server
else
{
alert = [[UIAlertView alloc]initWithTitle:@"Network Error"
message:@"Unable to connect to COF"
delegate:self
cancelButtonTitle:@"Ok"
otherButtonTitles:nil];
}
[alert show];
[self clearTextFields];
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] endIgnoringInteractionEvents];
}
- (void)alertView:(UIAlertView *)alertView clickedButtonAtIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex
{
assert(self.currentError != nil);
if (buttonIndex != 1) { return; }
NSDictionary* errorAttributes = (NSDictionary*)(self.currentError.userInfo[C1SSErrorUserInfoKeyAttributes][0]);
NSNumber* button = (NSNumber*)(self.currentError.userInfo[C1SSErrorUserInfoKeyButtonTypes][1]);
switch ([button unsignedIntegerValue])
{
case C1SSErrorButtonTypeNone:
break;
case C1SSErrorButtonTypeOK:
break;
case C1SSErrorButtonTypeDismiss:
break;
case C1SSErrorButtonTypeCall:
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:
[NSURL URLWithString:[self buildPhoneNumberString:errorAttributes[C1SSErrorAttributesKeyPhone]]]];
break;
case C1SSErrorButtonTypeGo:
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:
[NSURL URLWithString:errorAttributes[C1SSErrorAttributesKeyURL]]];
break;
default:
break;
}
self.currentError = nil;
}
- (NSString*)buildPhoneNumberString:(NSString*)phoneNumber
{
phoneNumber = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"tel:%@", phoneNumber];
phoneNumber = [phoneNumber stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"(" withString:@""];
phoneNumber = [phoneNumber stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@")" withString:@""];
phoneNumber = [phoneNumber stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"-" withString:@""];
phoneNumber = [phoneNumber stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@" " withString:@""];
return phoneNumber;
}
//###########################
#pragma Navigation
- (void)prepareForSegue:(UIStoryboardSegue *)segue sender:(id)sender
{
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] endIgnoringInteractionEvents];
}
- (void)segueViaNavigationController
{
[(ApplicationNavigationController*)self.navigationController segueFromLoginToLegalOrAccountDetails:self];
}
- (void)segueToMFA
{
[self performSegueWithIdentifier:@"toMFA" sender:self];
}
//###########################
#pragma Actions
- (IBAction)RememberUsernameToggle:(id)sender
{
self.rememberUserName = !(self.rememberUserName);
LoginManager *loginManager = [LoginManager sharedInstance];
loginManager.rememberMe = self.rememberUserName;
if (self.rememberUserName)
{
self.rememberMeCheckBoxSelected.hidden = false;
self.rememberMeCheckBoxUnselected.hidden = true;
}
else
{
self.rememberMeCheckBoxSelected.hidden = true;
self.rememberMeCheckBoxUnselected.hidden = false;
if(!self.usernameTextField.enabled){
self.usernameTextField.enabled = YES;
self.usernameTextField.text = @"";
self.passwordTextField.text = @"";
[self.usernameTextField becomeFirstResponder];
}
}
}
@end
throw new EPFSystemException("Structure exceeds two levels " + objEntry + " " + json);if (l2Temp != null && l2Temp.isValueNode()) {
logger.debug("Is nested value node {} stack id {}", objEntry, stackId);
buildAndAddEvtDetail(event, objEntry, l2Temp.asText(), stackId);
}
else {
throw new EPFSystemException("Structure exceeds two levels " + objEntry + " " + json);
}for (int x = 0; x < anode.size(); x++) {
Iterator<String> level2 = anode.get(x).fieldNames();
while (level2.hasNext()) {
String objEntry = level2.next();
logger.debug("Processing nested object {} stack id {}", objEntry, stackId);
JsonNode l2Temp = anode.get(objEntry);
if (l2Temp != null && l2Temp.isValueNode()) {
logger.debug("Is nested value node {} stack id {}", objEntry, stackId);
buildAndAddEvtDetail(event, objEntry, l2Temp.asText(), stackId);
}
else {
throw new EPFSystemException("Structure exceeds two levels " + objEntry + " " + json);
}
}
stackId++;
}if (temp.isValueNode()) {
logger.debug("Found value node, building detail {}", fname);
buildAndAddEvtDetail(event, fname, temp.asText(), 0);
}
else if (temp.isArray()) {
logger.debug("Found array, building detail {}", fname);
ArrayNode anode = (ArrayNode) temp;
if (anode.size() > 0) {
JsonNode obj = findNonNullObject(anode);
if (obj == null || obj.isValueNode()) {
logger.debug("Found Array of value nodes {} size {}", fname, anode.size());
int stackId = 1;
for (int x = 0; x < anode.size(); x++) {
if (anode.get(x) != null) {
buildAndAddEvtDetail(event, fname, anode.get(x).asText(), stackId);
}
stackId++;
}
}
else if (obj.isObject()) {
logger.debug("Found Array of objects {} size {}", fname, anode.size());
int stackId = 1;
for (int x = 0; x < anode.size(); x++) {
Iterator<String> level2 = anode.get(x).fieldNames();
while (level2.hasNext()) {
String objEntry = level2.next();
logger.debug("Processing nested object {} stack id {}", objEntry, stackId);
JsonNode l2Temp = anode.get(objEntry);
if (l2Temp != null && l2Temp.isValueNode()) {
logger.debug("Is nested value node {} stack id {}", objEntry, stackId);
buildAndAddEvtDetail(event, objEntry, l2Temp.asText(), stackId);
}
else {
throw new EPFSystemException("Structure exceeds two levels " + objEntry + " " + json);
}
}
stackId++;
}
}
else {
throw new EPFSystemException("error - found unexpected object type found " + fname + " " + json);
}
}
}
else if (temp.isObject()) {
logger.debug("Found object, building detail {}", fname);
Iterator<String> level1 = temp.fieldNames();
while (level1.hasNext()) {
String objEntry = level1.next();
logger.debug("Processing object {}", objEntry);
JsonNode l2Temp = temp.get(objEntry);
if (l2Temp != null && l2Temp.isValueNode()) {
logger.debug("Is a value node {}", objEntry);
buildAndAddEvtDetail(event, objEntry, l2Temp.asText(), 0);
}
else {
throw new EPFSystemException("error - found unexpected object type found " + objEntry + " " + json);
}
}
}public void fireLoadSummaryEventAction(ActionRequest request, ActionResponse response) {
ApplicationObject appObject = null;
String token = null;
EPFContext context = EPFContextContainer.getcurrentContext().get();
String correlationID = context.getCorrelationId();
try {
try {
//retrieve token
HttpServletRequest httpServletReq = (HttpServletRequest) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.request");
HttpSession session = httpServletReq.getSession();
token = (String)session.getAttribute("eosToken");
//retrieve composite object and store in cache
appObject = creditcardappdataserviceclient.retrieveApplicationData(token);
//store composite object in cache
UserContext userContext = cache.getCachedUserContext(correlationID, appObject);
} catch (JaxWsSoapFaultException sfe) {
logger.error("SOAP Fault on composite object retreival");
appObject = new ApplicationObject();
//set statCd to soap fault, for data retrieval audit logging
setStatCd(appObject,STATUS_CODE_RTM_SOAP_FAULT);
//audit data retrieval status
auditLogUtil.auditEOSEvent(token, auditLogUtil.AUDIT_EVENT_APP_DATA_RETRIEVAL_NAME, appObject, auditLogUtil.AUDIT_EVENT_STATUS_SOAP_FAULT);
//set statCd to "data not retrieved", for soft decline audit logging
setStatCd(appObject,STATUS_CODE_DATA_RETRIEVAL_FAILED);
throw new EPFSystemException("SOAP Fault", sfe);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error retrieving or caching composite object. " + e.getMessage());
if (appObject == null ) {
appObject = new ApplicationObject();
}
//set statCd to general error, for data retrieval audit logging
setStatCd(appObject,STATUS_CODE_GENERAL_DATA_RETRIEVAL_ERROR);
//audit data retrieval status
auditLogUtil.auditEOSEvent(token, auditLogUtil.AUDIT_EVENT_APP_DATA_RETRIEVAL_NAME, appObject, auditLogUtil.AUDIT_EVENT_STATUS_ERROR);
//set statCd to "data not retrieved", for soft decline audit logging
setStatCd(appObject,STATUS_CODE_DATA_RETRIEVAL_FAILED);
throw new EPFBusinessException(new EPFMessage(e.getMessage()));
}
//audit data retrieval status
auditLogUtil.auditEOSEvent(token, auditLogUtil.AUDIT_EVENT_APP_DATA_RETRIEVAL_NAME, appObject, null);
//check for an error/warning in stat code
if (findStatusError(appObject)) {
String errorCode = getStatCode(appObject);
String errorMsg = "A status of error or warning was returned by RTM. RTM Status code:" + errorCode;
logger.warn(errorMsg);
//set statCd to "data not retrieved", for soft decline audit logging
setStatCd(appObject,STATUS_CODE_DATA_RETRIEVAL_FAILED);
throw new EPFBusinessException(new EPFMessage(errorCode));
}
//check if token expired
verifyTokenNotExpired(appObject);
//verify the disclosure can be built
buildDisclosure(appObject);
//update disclosure flag
invokeDisclosureFlagUpdate(appObject, token);
//fetch values required by DSD portlets
EnrollmentEvent sspEvent = getUserInfo(appObject);
//fire JSR event to invoke DSD portlet to receive required info
QName qname2 = new QName("http://www.capitalone.com/sspEvent","sspEvent");
response.setEvent(qname2, sspEvent);
//fire JSR event to invoke summary portlet controller
QName qname = new QName("http://eos.capitalone.com","loadResultsCustomEvent");
response.setEvent(qname, null);
//fire WLP event for portal page change
QName qname1 = new QName("http://eos.capitalone.com","pageChangeEvent");
response.setEvent(qname1, null);
response.setRenderParameter("myaction", "done");
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error preparing to display results", e);
//audit soft approval (display of error page)
auditLogUtil.auditEOSEvent(token, auditLogUtil.AUDIT_EVENT_APP_SOFT_DECLINE_NAME, appObject, auditLogUtil.AUDIT_EVENT_STATUS_NOT_PROVIDED);
//set render param to invoke error page
response.setRenderParameter("myaction", "errorRenderMapping");
}
} The Perils of Messy Code

Mess builds, productivity of team decreases
Under pressure, the team makes more messes
Entropy - The amount of disorder in a system. When disorder increases in software, it is called "code rot".
The only way to develop quickly and meet deadlines is to keep the code as clean as possible at all times.
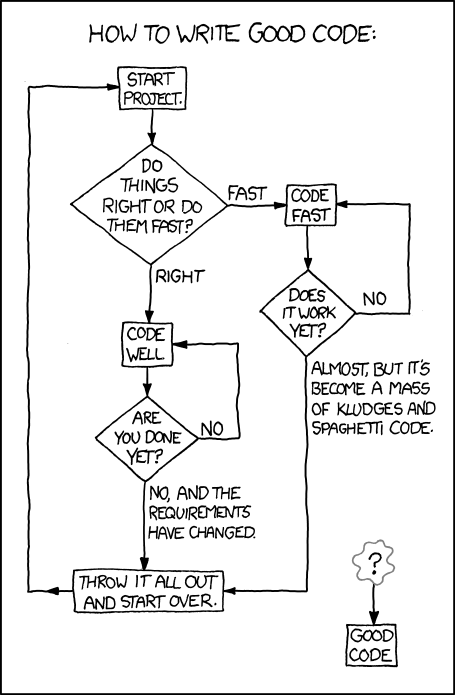
http://xkcd.com/844/
What is messy code?
- Smells bad
- Follows anti-patterns
- Includes spaghetti code
- Contains duplication
- Comprises complexity
- Obscures intent
- Complicates logical flow
- Perpetuates inconsistencies
- Becomes unmaintained
Messy code is a symptom of an underlying poor design or other problem.
What is clean code?
- Reads like well-written prose
- Clarifies the designer's intent
- Sustains simple and direct modules
- Preserves straightforward logical flow
- Employs efficient abstractions
- Fosters maintenance and enhancement
- Provides one way to do one thing
- Presents a clear and minimal API
- Includes unit and acceptance tests
- Requires minimal dependencies
Clean code is the reward for elegant design, planning, and execution.
if (appObject.isDsclsrOnlineRequiredInd() || appObject.isDsclsrCreditScoreRequiredInd()) {
if (appObject.isDsclsrOnlineRequiredInd()) {
// Pull account disclosure
setDisclosureVariableFromContent(AOD, aodVariableReplacer,
appObject.getDecisionedOfferID(), model, evalContext);
}
if (appObject.isDsclsrCreditScoreRequiredInd() && appObject.getMinCreditScore() != null
&& appObject.getMinCreditScore().getBureauCode()!=null) {
// Pull credit disclosure
if(appObject.getMinCreditScore().getBureauCode().equals("")){
setDisclosureVariableFromContent(CSD, csdVariableReplacer,
NO_HIT_KEY , model, evalContext);
}else{
setDisclosureVariableFromContent(CSD, csdVariableReplacer,
appObject.getMinCreditScore().getBureauCode() , model, evalContext);
}
}
}
if (appObject.getApplicant() != null && appObject.getApplicant().get(0) != null ) {
userInfo.setFirstName(appObject.getApplicant().get(0).getFirstName());
userInfo.setLastName(appObject.getApplicant().get(0).getLastName());
userInfo.setLangCode(appObject.getApplicant().get(0).getLangCode());
userInfo.setSsoId(null);
userInfo.setUserId(appObject.getApplicant().get(0).getCustomerID());
if (appObject.getApplicant().get(0).getEmailAddresses() != null &&
appObject.getApplicant().get(0).getEmailAddresses().size() > 0) {
userInfo.setEmailAddress(appObject.getApplicant().get(0).getEmailAddresses().get(0));
}
}Coupling and Cohesion
With tightly coupled systems:
- A change in one module forces changes in others
- Modules are harder to reuse
- Modules are harder to test
With low cohesion systems:
- Modules are complex with more operations
- Modules are less maintainable and harder to work with
Coupling is a measure of how closely connected two routines or modules are.
Cohesion is a measure of how strongly related each piece of functionality is.
Coupling and Cohesion have an inverse relationship
Law of Demeter
- Object A can call a method of object B but should not "reach through" B to acquire a reference to object C.
- A method m of class A may only invoke methods on:
- A itself
- m's parameters
- Objects instantiated within m
- A's direct instance objects
- A global variable, accessible by A, in the scope of m
Since objects are less dependent on the internal structure of other objects, classes can be changed without reworking their callers.
Orthogonality
-
When components are highly interdependent, there is no such thing as a quick, local fix.
-
Orthogonal software provides increased productivity and decreased risk because developers never have to worry about side-effects of making changes.
-
Orthogonal components are easier to swap meaning less dependence on a specific library or vendor.
Two or more modules are orthogonal if
changes in one do not affect the other.
The Evils of Duplication
-
Requirements, understanding, and environments change. Your code will need to change with it.
-
It's not a matter of if you'll remember, but when you'll forget.
DRY - Don't Repeat Yourself
- Imposed duplication
- Inadvertent duplication
- Impatient duplication
- Inter-developer duplication
SOLID Design Principles
-
Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
-
Open/Closed Principle (OCP)
-
Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)
-
Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
-
Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
public Map<String, AppFeature> getAllFeature(DomainProfile domainInfo) {
Map<String, AppFeature> appFeatureMap = new Hashtable<String, AppFeature>();
if (domainInfo.getSystemOfRecord().equalsIgnoreCase(FeatureToggleConstants.DB_SYSTEM_STORAGE)) {
try {
readItFromDB(domainInfo, upfAppFeatureMap);
}
catch (RuntimeException dbError) {
logger.error("Error reading from Database, the provided details were: App Name: " + domainInfo.getAppName()
+ " Domain Name:" + domainInfo.getDomainIndentifier()
+ ". Will try reading it from backup source (file system)", dbError);
readItFromFileSystem(domainInfo, upfAppFeatureMap);
}
}
else if (domainInfo.getSystemOfRecord().equalsIgnoreCase(FeatureToggleConstants.FILE_SYSTEM_STORAGE)) {
readItFromFileSystem(domainInfo, upfAppFeatureMap);
}
else {
logger.error("ERROR fetching features from system of record, no matching system of record found: ",
domainInfo.getSystemOfRecord());
return null;
}
return appFeatureMap;
}private void readItFromDB(DomainProfile domainInfo, Map<String, AppFeature> appFeatureMap) {
logger.debug("Fetching features data from DB system, the system of record value is: "
+ domainInfo.getSystemOfRecord() + "App Name: " + domainInfo.getAppName() + " Domain Name:"
+ domainInfo.getDomainIndentifier());
Map<String, Feature> featureFromDB;
if (isMongoDBImpl()) {
featureFromDB = mongoDBFeatureStore.readAll(domainInfo.getAppName(), domainInfo.getDomainIndentifier());
}
else {
featureFromDB = jdbcFeatureStore.readAll(domainInfo.getAppName(), domainInfo.getDomainIndentifier());
}
loadUPFFeaturesMap(featureFromDB, appFeatureMap);
// write it to the file system for backup activities:
try {
writeFeaturesOnFilesystemForBackup(featureFromDB);
}
catch (Exception excpetion) {
logger.error("Could not write to file system path: " + domainInfo.getFeaturesFilePath(), excpetion);
}
}public void toggleFeature(DomainProfile domainProfile, String regionIdentifier, String toggle, String featureName, String featureGroup) {
if (domainProfile.getSystemOfRecord().equalsIgnoreCase(FeatureToggleConstants.DB_SOR)) {
if (toggle.equalsIgnoreCase("enable")) {
if (isMongoDBImpl()) {
mongoDBFeatureStore.enable(featureName, featureGroup, regionIdentifier);
}
else {
jdbcFeatureStore.enable(featureName, featureGroup, regionIdentifier);
}
}
else if (toggle.equalsIgnoreCase("disable")) {
if (isMongoDBImpl()) {
mongoDBFeatureStore.disable(featureName, featureGroup, regionIdentifier);
}
else {
jdbcFeatureStore.disable(featureName, featureGroup, regionIdentifier);
}
}
else {
Message error = new Message(appConfiguration.getString(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_ERROR_CODE));
error.setInputParams(appConfiguration.getString(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_MESSAGE));
throw new RuntimeException(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_MESSAGE);
}
}
else if (domainProfile.getSystemOfRecord().equalsIgnoreCase(FeatureToggleConstants.FS_SOR)) {
if (toggle.equalsIgnoreCase("enable")) {
fileSystemStore.enable(featureName);
}
else if (toggle.equalsIgnoreCase("disable")) {
fileSystemStore.disable(featureName);
}
else {
Message error = new Message(appConfiguration.getString(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_ERROR_CODE));
error.setInputParams(appConfiguration.getString(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_MESSAGE));
throw new RuntimeException(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_MESSAGE);
}
}
else {
throw new EPFSystemException(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_SYSTEM_OF_RECORD_OPT);
}
}Single Responsibility Principle
-
The single responsibility should be entirely encapsulated by its context
-
A unit of code should have only one reason to change
-
Keeps a class focused (high cohesion)
-
Lowers coupling
A class or module should be defined by one, and only one, responsibility.
public class AreaCalculator {
public double pi = Math.PI;
public double calculateArea(Shape[] shapes) {
double area = 0;
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
if (shape instanceof Rectangle) {
Rectangle rectangle = (Rectangle) shape;
area += rectangle.getWidth() * rectangle.getHeight();
} else {
if (shape instanceof Circle) {
Circle circle = (Circle) shape;
area += circle.getRadius() * circle.getRadius() * pi;
}
}
}
return area;
}
}Open/Closed Principle
-
Allows its behavior to be extended without modifying its source code
-
Utilizes inheritance and polymorphism
-
Promotes code reusability
-
Prevents unnecessary code reviews and testing
Software entities should be open for extension, but closed for modification.
public class Blah {
private HashMap<String, String> map;
public ArrayList<String> getUniqueValues(TreeMap<Integer, String> map) {
. . .
}
}
public class Square extends Rectangle {
public void setHeight(int height) { . . . }
public void setWidth(int width) { . . . }
}Liskov Substitution Principle
Objects in a program should be replaceable with instances of their subtypes without altering the correctness of that program.
Always reference the most abstract type that provides all the required methods.
Subclass implementations can be swapped out later.
Multiple implementations can be accommodated by a library.
private Map<String, Integer> blah;
private Map<String, Integer> gah;
public BlahGah() {
blah = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
gah = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
}public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) { . . . }public interface Bank {
public void addAccount(Account account);
public Account getAccount(String accountNumber);
public void deposit(String accountNumber, double amount);
public void withdraw(String accountNumber, double amount);
public void applyInterest(String accountNumber);
public void applyFee(String accountNumber, double fee);
}
Interface Segregation Principle
Interface-based design:
- The foundation of APIs
- Design from the outside in
- Write the interfaces first
- Practice TDD
Keep interfaces focused and segregated by purpose. Many client-specific interfaces are better than one general purpose interface.
DIP violation examples
class GameBoard {
private List<MonopolyPlayer> players;
private Dice dice;
}
class MonopolyPlayer implements Player {
void playTurn() {
Dice di = GameBoard.getdice(); // or GameBoard.DICE [Test dependency]
int numMoves = di.roll();
. . .
}
}
interface Dice {
public int roll();
}
Dependency Inversion Principle
-
Separate high-level and low-level components into separate packages
-
Interfaces belong in high-level package, implementations in low-level
-
Keep consistent and developer friendly
-
Allows for swapping implementations
-
Promotes code encapsulation with flexibility
- High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules.
- Abstractions should not depend on details.
class Player {
void playTurn(Dice di) {
int numMoves = di.roll(); // or 'inject' numMoves if 'di' (analogy) is not needed further
. . .
}
}@Repository
public class UserDao extends JdbcDaoSupport {
@InjectLogger
private Logger logger;
@Inject
public UserDao(final DataSource dataSource) {
setDataSource(dataSource);
}
}
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydb");
dataSource.setUsername("username");
dataSource.setPassword("password");
return dataSource;
}
} public String generateMessage(StreamMessageContext ctx, Object... data) {
int size = ((data == null) ? 1 : data.length + 1);
// serialize each object
int i = 1;
String[] jsonEntries = new String[size];
jsonEntries[0] = DataConversionSupport.serializeToJsonString(ctx);
for (Object datum : data) {
jsonEntries[i] = DataConversionSupport.serializeToJsonString(datum);
++i;
}
// then aggregate all the serializations together
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('{').append('\"').append(ctx.getClass().getSimpleName()).append("\":").append(jsonEntries[0]); // the key
for (int j = 0; j < i - 1; ++j) {
sb.append(',\"').append(data[j].getClass().getSimpleName()).append("\":"); // item name
sb.append(jsonEntries[j + 1]); // item json
}
sb.append('}');
return sb.toString();
}
public String generateMessage(StreamMessageContext ctx, String[] dataKeys, Object... data) {
int size = ((data == null) ? 1 : data.length + 1);
// serialize each object
int i = 1;
String[] jsonEntries = new String[size];
jsonEntries[0] = DataConversionSupport.serializeToJsonString(ctx);
for (Object datum : data) {
jsonEntries[i] = DataConversionSupport.serializeToJsonString(datum);
++i;
}
// build up keys
String[] keys = processDataKeys(dataKeys, data);
// then aggregate all the serializations together
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('{').append('\"').append(ctx.getClass().getSimpleName()).append("\":").append(jsonEntries[0]); // the key
for (int j = 0; j < i - 1; ++j) {
sb.append(',\"').append(keys[j]).append("\":"); // item name
sb.append(jsonEntries[j + 1]); // item json
}
sb.append('}');
return sb.toString();
}Interface Design
Capital One is doing pretty well in the banking industry, but Uncle Rich has decided we need to diversify our product offerings, and he's made the decision to go into the lucrative business of opening PB&J sandwich shops (that's right, we're only selling peanut butter and jelly sandwiches). He's put you in charge of designing the backend system that allow users to place orders for custom sandwiches. Being the software craftsman that you are, you know we need to design this system from the outside in - that means creating interfaces for our sandwich shop before we come up with concrete implmentations.
Code Conventions
Follow the Rules
Actually, follow the Principles
Rules are attempts to standardize agreement of how we follow Principles.
Rules change over time, teams, and environments.
The underlying Principles stay the same.
Breaking rules can be fine but breaking principles will cost down the line.
Rule: Don't tell lies
Principle: Honesty and Kindness
Naming Conventions
Intention revealing
int d; // elapsed time in days
int daysSinceCreation;Avoid disinformation
Account[] accountList;
boolean notActive;
Make meaningful distinctions
void arrayCopy(char[] a1, char[] a2);
void arrayCopy(char[] source, char[] destination);Pronounceable
String evtStCd, evtAudtg;Searchable
Date date, transactionDate;
public class RequestBuilder { ...Solution/Problem relevant
int tableUsage, loadFactor;
Node tortoise, hare;Function Conventions
- Small
- Do only one thing
- One level of abstraction per function
- Descriptive names
int getStatus();
int getResponseStatusCode();- Minimal parameters
- Don't pass codes
- Don't return null
- Verbs not nouns
int cardCount();
int getCardCount();
void newCard();
void addNewCard();Commenting Conventions
"Programs must be written for people to read and only incidentally for machines to execute" - Hal Abelson
- The only "comment" guaranteed to be accurate is the code its self
- Comments have to be maintained and updated same as the code
- The more complex the comments are, the more likely they are to be wrong or out of date
The best solution is to write easily comprehensible code.
Good Comments
Code can't explain why the program is being written, and the rationale for choosing this or that method. Code cannot discuss reasons certain alternative approaches were taken.
Comments are best used to provide contextual information that makes it easier to understand the code.
- How the code fits into the big picture
- Why this methodology was chosen and why others were rejected
- Code is written to solve a problem. Describe how your code solves the problem and why it is better than the alternatives
- Warning of consequences
Bad Comments
Single line comments are usually unnecessary and should only be used if the operation is complex.
j = j + 1; //Increment j
int a = c * 100; //convert to cents
double avg = a / n; //average cents per customer
int totalCents = totalDollars * 100;
double averageCentsPerCustomer = totalCents / customerCount;Instead of writing comments that are designed to make code more readable, rewrite the code.
BAD
GOOD
Do not release with TODOs or commented-out code
/*
* Purpose: Check the status of the composite object for errors or warnings.
*/
private boolean findStatusError(ApplicationObject appObject) {
if (appObject == null ||
appObject.getStatusListAppDataInq() == null ||
appObject.getStatusListAppDataInq().size() == 0 ||
appObject.getStatusListAppDataInq().get(0) == null ||
appObject.getStatusListAppDataInq().get(0).getSeverity() == null ||
(appObject.getStatusListAppDataInq().get(0).getSeverity().name()).equals(Severity.ERROR.toString()) ||
(appObject.getStatusListAppDataInq().get(0).getSeverity().name()).equals(Severity.WARNING.toString()) ||
(appObject.getStatusListAppDataInq().get(0).getSeverity().name()).equals(Severity.FAULT.toString()))
return true;
else
return false;
}
}Code Formatting Conventions
- Density
- Distance
- Order
Horizontal formatting
- Density
- Alignment
- Indentation
Vertical formatting
Code Formatting Conventions
https://google-styleguide.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/javaguide.html
http://lars-lab.jpl.nasa.gov/JPL_Coding_Standard_Java.pdf
Common rules:
- Documentation (JavaDoc) conventions
- Upper-case class names; camel-case variable names
- New line after conditionals; always using braces
- One variable per declaration
- No chained method calls
- Store common references for reuse
- Encapsulate and use positive conditionals
- Declare abstract type, instantantiate implementation
Follow team and company rules
Exception Conventions
- Fail fast
- Catch specific exceptions
- Catch only when it can be handled in a meaningful way
- Use exceptions rather than return codes
- Do not use exceptions for control flow
- Provide context with exceptions
- Informative error messages
- Failed operation and values
Adventures in Software Craftsmanship
By dyanos91
Adventures in Software Craftsmanship
Fall 2015 - Day 1
- 509



