OAuth2 and Your Web Application
Donuts.js 8/8/2018
Bruce Campbell
What this talk is NOT:
- Deep dive into OAuth2 RFCs and Spec
- A Comprehensive Guide to OAuth
- Authorization Server Implementation Details
- The Gospel Truth about OAuth and OIDC
What this talk is:
- OAuth v2.0 at a high level
- What is it?
- How does it work?
- Demo of sample application
Introduction
What is Oauth2?
A standard way to secure and share a resource
Particularly good at access delegation... granting access from one app to another without giving out your password
example
👨🏼💼

🧡


Do you want to grant
the access to...
☑️ Friendlist
☑️ Birthday
☑️ Email Address
☑️ Post to your timeline
Yes
No


👨🏼💼


👨🏼💼


- Yelp never sees my fb password!
- The relationship can be revoked
👨🏼💼
App
Auth Provider
Key Terms
Authorization
What can be done
Authentication
Who the current user is and their presence in the application
vs
(AuthZ)
(AuthN)
OAuth 2.0
OpenID Connect
Resource Owner
The User
Resource Server
The API/Resource your application is trying to use
Authorization Server
The server the user interacts with to approve or deny requests to access their account, as well as the source of tokens
Client
The application attempting to access a resource on a User's behalf
client id
identifier (or username) that identifies a client to the authorization server
client secret
uh... the password
Grant Types or Flows
The process utilized to grant applications access to resources
Scopes
What am I allowing the application to do on my behalf?
Tokens
Strings that might be opaque, representing scopes and expiration/duration of access
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs)
A means of representing a relationship between 2 things
Resources Used
What is it?
Framework
with Extensions
Core RFC 6749 Endpoints
/authorize
/token
Extension Endpoints (Optional)
/revoke (RFC 7009)
/register (RFC 7591)
Access Token
The token given to the application to access the protected resource on the user or application's behalf
Refresh Token
The token given to the application to request a new access token on its expiration
*Contents of these tokens are not specified in OAuth 2.0 Core*
How Does it Work?
Grant Types / Flows
- Client Credential
- Implicit or Hybrid
- Authorization Code
Client Credential Flow
- Doesn't involve users
- Commonly known as "Service Accounts"
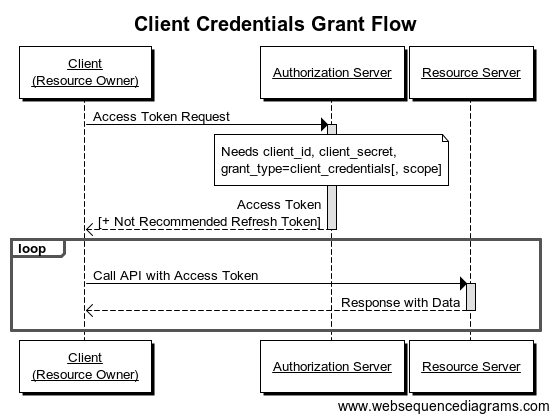
Client Credentials Flow
Images found from: http://www.bubblecode.net/en/2016/01/22/understanding-oauth2/
Implicit or Hybrid Flow
- Used when the user could possibly find out the client secret
- Therefore Doesn't utilize a client_secret
- Generally used in Mobile or Single Page Apps
- Access Token is included in URL directly
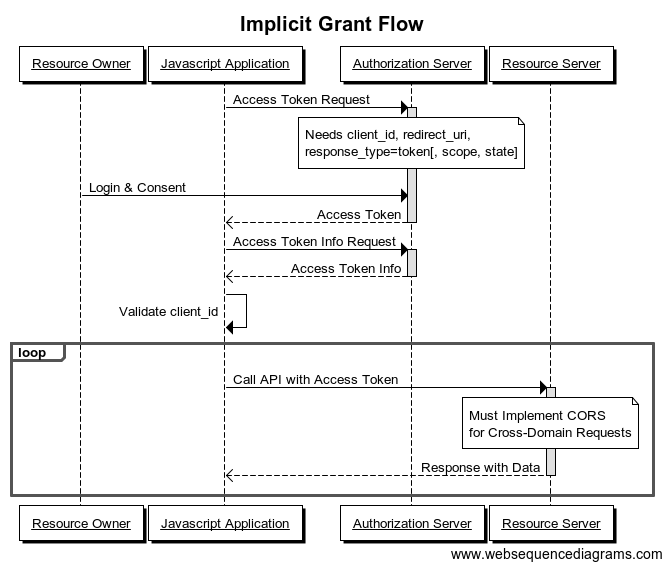
Implicit Flow Diagram
Authorization Code Flow
- Used when the client_secret can be kept secret
- Generally utilized with Server side code
- Authorization Code in URL and exchanged for token
Authorization Code Diagram
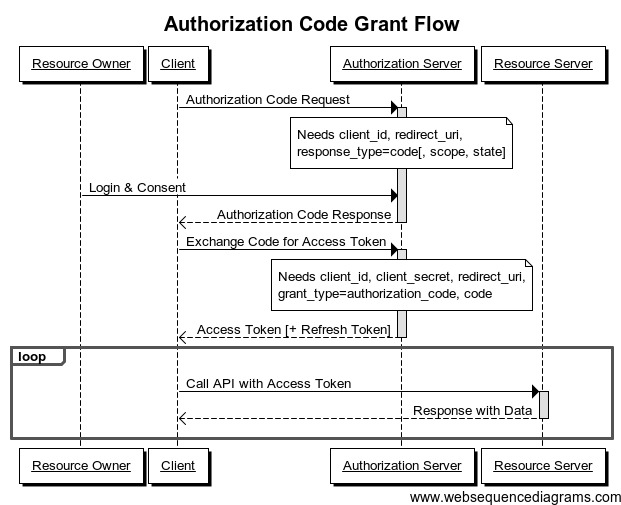
Redirect URIs
Utilized in Implicit and Authorization Code Flows as a whitelist of URIs that are allowed to use the client_id
State Parameter
Utilized with Redirect URIs by those who want to be more secure or as a way to persist data through the trip to the authorization server
Scopes
Depend on Implementation*
There isn't a standard list...
App Demo
Detailed Flow
Browser
node.js
app server
service a
service b
Architecture
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
Authorization Code Flow
- client already registered with the auth server - through the Oauth2 cloud foundry service
- single-page app with universal rendering using the architecture shown in the previous slide
- in this walk-through all request are successful
- the app server proxies all api requests
Browser
service a
service b
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
User navigates to https://myapp.lds.org/demo
node.js
app server
Browser
service a
service b
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
app server sends a redirect to the login screen
and the browser follows the redirect
node.js
app server
Browser
service a
service b
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
User authenticates...
submitting credentials to the auth server
node.js
app server

Browser
service a
service b
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
Auth Server responds with a redirect back to the app server... and includes an "authorization code"
node.js
app server
auth code
Browser
service a
service b
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
The app server exchanges the auth code for
a pair of tokens (access & refresh)
node.js
app server
auth code
tokens
Browser
service a
service b
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
app server needs data to render the page so...
makes an api call and includes the access token
node.js
app server
access token
Browser
service a
service b
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
"service a" verifies the access token using it's own client id and client secret
node.js
app server
access token
👍
Browser
service a
service b
Auth
Server
"client"
"user"
"service a" responds with the data, the app server renders the page and responds to the browser
node.js
app server

👞 👟 👠
👡 👢
Notes
- The app never knows the User's password
- The User never knows the client id / secret
- App server proxies api requests
...no CORS configuration required - Resource servers respond with 200's or 400's
...never a redirect!! - The tokens are stored in the browser via cookies
...so the app server can remain stateless! - We aren't using JWT's*
Getting Started
The End
Or is it just the beginning?
OAuth2 and Your Web Application
By Bruce Campbell
OAuth2 and Your Web Application
- 1,015



