C6: Collections
C7: Overriding equals (and hashCode)
CPSC 210


https://bit.ly/cpsc210_24W1
CPSC 210 Mid course Feedback Form (Anonymous)!
C6: Implementing Collections and Maps
CPSC 210

Learning Goals
- Gain an overview over Java collections
- Use the Map<K, V> type in the Java library
- Select the appropriate collection type from the Java library

Java Collections
Collection
Map
Iterable
List
Queue
Set
HashMap
HashSet
ArrayList
LinkedList
...
has
Maps
-
Map<K, V> interface with two type parameters:
- K - represents the type for the key
- V - represents the type for the value
- In this course we will focus on HashMap<K, V>
- You have seen a collection of key-value pairs using a binary search tree in CPSC 110
HashMap Example
| "Firas" |
| "Felix" |
| "Taryn" |
Map<String, Instructor>Map<K, V>
values: instructor objects
keys: names
Map<String, Instructor> instructors;
instructors = new HashMap<String, Instructor>();
instructors.put("Firas", new Instructor());
instructors.put("Felix", new Instructor());
instructors.put("Taryn", new Instructor());Instructor firas = instructors.get("Firas");
Instructor felix = instructors.get("Felix");
Instructor taryn = instructors.get("Taryn");
Which Collection to Use?
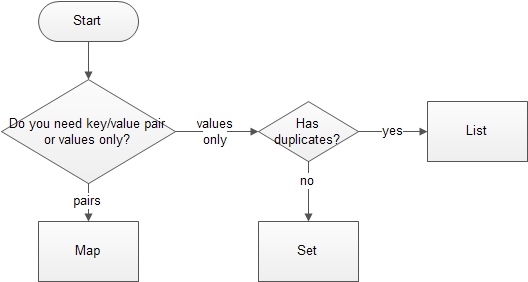


Which one to use? (2)
- Lists: for maintaining the order in which items were added
- Sets: if there are no duplicate items in the collection
- Maps: to represent collections of key-value pairs
HashSet
ArrayList
LinkedList
HashMap
Lecture Lab
(Practice outside class)

C6: Implementing Collections and Maps
The End - Thank You!
C7: Overriding equals (and hashCode)
CPSC 210

Learning Goals
- Understand why we sometimes need to override equals (and hashCode)
- Understand a given implementation of equals
- Learn how to override equals/hashCode (or use the IDE to help us)
- Understand the instanceof operator in Java

Handling Duplicate Objects
- At the top of every class hierarchy is the Object class
-
Among others, this class defines the following methods
- boolean equals(Object other)
- int hashCode()
- These are used, for example, by the contains methods in Java collections
List<Instructor> instructors = new ArrayList<>();
instructors.add(new Instructor("Felix"));
Instructor instructor = new Instructor("Felix");
instructors.contains(instructor);Handling Duplicate Objects (2)
-
What we need to know about in this course:
- Object class implements a.equals(b) as a == b
- Method can be overridden to change this behavior
-
We can let IntelliJ help us generate these methods:
- Code > Generate > equals() and hashCode()
Let's ask the docs!


Lecture Ticket Review
Live Coding!!!
public class RecipeBook {
private String name;
private Map<String, List<String>> recipes;
public RecipeBook(String name){
this.name = name;
this.recipes = new HashMap<>();
}
// REQUIRES: recipeName is not already in recipes
// MODIFIES: this
// EFFECTS: adds recipeName to recipes, and assigns an empty list of ingredients
public void addNewRecipe(String recipeName){
List<String> ingredients = new ArrayList<>();
//BLANK 1
}
// REQUIRES: recipeName is in recipes
// MODIFIES: this
// EFFECTS: adds ingredient to recipeName's list of ingredients
public void addToRecipe(String recipeName, String ingredient){
List<String> ingredients = recipes.get(recipeName);
//BLANK 2
}
public void printRecipes(){
System.out.println(this.recipes);
}
}Auto-generated equals method
- Let's assume we have a class Instructor with a field name and:
- we want to consider two instructor objects equal if they have the same name
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null )
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false
Instructor other = (Instructor) obj;
if (name != other.name )
return false
return true
}auto-generated equals
Java instanceof operator
- Example: a class Rectangle extends another class Shape
- If we have an object of type Shape named shape, then shape instanceof Shape will evaluate to true
- But: shape instanceof Rectangle will evaluate to false
- If we have an object of type Rectangle named rectangle, then rectangle instanceof Shape will evaluate to true
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
boolean equal = false;
if (o instanceof Instructor) {
Instructor that = (Instructor) o;
equal = this.name.equals(that.name);
}
return equal;
}instanceof: Checks whether the object on the left is the same type or a subtype of the object on the right
Lecture Lab

C7: Overriding equals and hashCode
The End - Thank You!
C7: Overriding equals and hashCode
By firas_moosvi
C7: Overriding equals and hashCode
- 297



