CPSC 210
B3: Classes & Objects
Learning Goals
- Identify fields, methods and constructors of a class
- Distinguish between primitive and reference variables
- Use an ArrayList to store data
- Identify "active" (or: instantiated) objects at a point of execution in code
- Use the debugger 🐞 to step through code and inspect variables

OO Terminology (1)
| Class | Cat |
| Attribute / Field | name, age, weight |
| Method | meow(3), sleep(), eat() |
| Constructor (just a special method) | Create a new cat objects (e.g. Luna) |
| Object / Instance | Luna (created by constructor) |

OO Terminology (2)
| Class | Dog |
| Attribute / Field | name, age, weight |
| Method | bark(2), sleep(), eat() |
| Constructor (just a special method) | Create new dog objects (e.g. Charlie) |
| Object / Instance | Charlie (created by constructor) |

Class Example: Tank
Methods
From: Space Invaders
Class
"final" Attributes/Fields
Constructor
1
5
4
2
3
Attributes/Fields
Tank myTank;myTank = new Tank(400);Tank object
direction 1
x 400
myTank
myTank
This does not create an object/instance yet, but only a (potential) reference to a tank
We first need to create an object
Objects vs. References (1)
Objects vs. References (2)
myTank.faceLeft();myTank
Tank object
direction -1
x 400
Objects vs. References (3)
myTank.move();myTank
Tank object
direction -1
x 399
Pod Activity (Do in Groups of 3-5)

- Each student open the SpaceInvadersBase project in VisualStudio code from last class, open Tank.java
- (do not use the downloaded zip file from edX)
- (do not use the downloaded zip file from edX)
- Answer the following questions as a group:
- What do you think the final keyword does and why is it needed?
- What happens when you set x=x on Line 22 ? Why ?
- What do you think the this keyword is , and why is it needed?
Types in Java
-
Java primitive (built-in) types
-
byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean, char
-
byte, short, int, long, float, double, boolean, char
-
All other types are reference types
-
They are used to reference an object
-
-
They are used to reference an object
Person
object
Person p = new Person();p
int count = 4;count 4
Pod Activity (Do in Groups of 3-5)

- Each student should clone the ArrayListDemo repository
- Follow the class demo on the VS Code debugger (this is VERY important!!) -- Add a breakpoint at Line 9
- Then, answer the following questions as a group:
- The instructor told you about "Step Into", "Step Over", and "Step Out". What do each of these mean?
- Slowly step through the Main.java file, Pause at each step and make sure you understand how assignment and objects work!
ArrayList in Java
- Used to store data of arbitrary size
- In Racket, you treated (listof X) as built-in, where X is a type parameter
-
Similarly, ArrayList<E> is part of the Java library:
- E is a type parameter that represents the type of data to be stored in the list
1
2
3
4
0
...
Lecture Ticket Review
Which of the following are valid Java code segments?
int y = 3;A a;
a = new A();B b = make B();int x = 3;
x.add(1);Q1
public class Person {
private String name;
public Person () {
this.name = "Unnamed Person";
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("Now my name is " +
this.name);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person harry = new Person();
Person hermione = new Person();
harry.setName("Harry");
hermione.setName("Hermione");
ArrayList<Person> people =
new ArrayList<>();
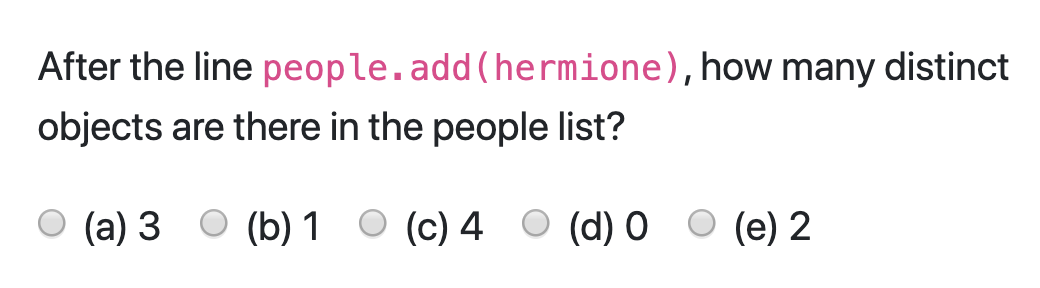
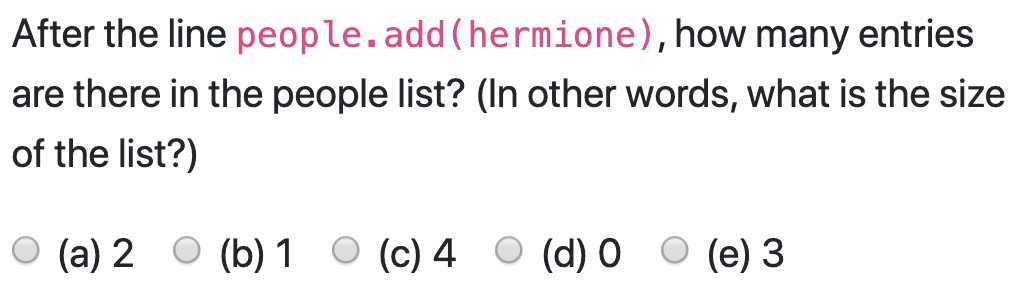
people.add(harry);
people.add(harry);
people.add(hermione);
Person someone = people.get(1);
someone.setName("Ron");
}
}

Q2
Lecture Lab: Buggy Pizza

Hypothesis driven debugging: making careful educated guesses, with plans for how to validate or invalidate them.

Extra: Git Branching
Branch: main
Branch: myfavoriteanimal
Create
Branch
Merge
Branch

Commits
B3: Classes & Objects
The End - Thank You!
B3 Classes and Objects
By firas_moosvi
B3 Classes and Objects
- 227



