Angular 2: Unit Testing
Some Convincing...
- Unit tests guard against breaking existing code (“regressions”) when we make changes.
- clarify what the code does (use as documentation)
- They reveal mistakes in design and implementation. Tests force us to look at our code from many angles and also make your code more modular
https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/guide/testing.html
Agenda
- ng-cli overview and testing setup
- Testing Components
- Testing Http
- Testing Components with async actions
- Testing pipes
Jasmine
- A BDD framework for JS code
- standalone, no DOM required
- Clean syntax: describe, it, expect
- Others: Mocha, QUnit, Jest (Facebook)
- Often used with a mocking library like Sinon
Suites
- test suite begins with "describe"
- takes a string (spec suite title) and a function (block of code being tested)
- suites can be nested
describe('SuperAwesomeModule', function() {
describe('featureA', function() {
});
describe('featureB', function() {
});
});Specs
- call global Jasmine function:
-
it(<string>, <fn>)
-
- a spec contains one or more expectations
- expectation: an assertion that is either true or false.
- spec with all true expectations: pass
- spec with one or more false expectations: fail
describe('SuperAwesomeModule', function() {
describe('featureA', function() {
it('should calculate some super awesome calculation', function() {
...
});
it('should also do this correctly', function() {
...
});
});
});Expectations and Matchers
- call global Jasmine function:
-
expect(<actual>).<matcher(expectedValue)>
- a matcher implements boolean comparison between the actual value and the expected value
describe('SuperAwesomeModule', function() {
describe('featureA', function() {
it('should calculate some super awesome calculation', function() {
expect(SuperAwesomeModule.featureA([1, 2, 4]).toEqual(7);
});
it('should also do this correctly', function() {
expect(SuperAwesomeModule.featureB('...').toBe(true);
});
});
});Included Matchers
expect(foo).toBe(true); // uses JS strict equality
expect(foo).not.toBe(true);
expect(foo).toEqual(482); // uses deep equality, recursive search through objects
expect(foo).toBeDefined();
expect(foo).not.toBeDefined();
expect(foo).toBeUndefined();
expect(foo).toBeTruthy(); // boolean cast testing
expect(foo).toBeFalsy();
expect(foo).toContain('student'); // find item in array
expect(e).toBeLessThan(pi);
expect(pi).toBeGreaterThan(e);
expect(a).toBeCloseTo(b, 2); // a to be close to b by 2 decimal pointsIncluded Matchers: Exceptions
expect(function() {
foo(1, '2')
}).toThrowError();
expect(function() {
foo(1, '2')
}).toThrow(new Error('Invalid parameter type.')Setup and Teardown
describe("A spec using beforeEach and afterEach", function() {
var foo = 0;
beforeEach(function() {
foo += 1;
});
afterEach(function() {
foo = 0;
});
it("is just a function, so it can contain any code", function() {
expect(foo).toEqual(1);
});
it("can have more than one expectation", function() {
expect(foo).toEqual(1);
expect(true).toEqual(true);
});
});Setup and Teardown
describe("A spec using beforeAll and afterAll", function() {
var foo;
beforeAll(function() {
foo = 1;
});
afterAll(function() {
foo = 0;
});
it("sets the initial value of foo before specs run", function() {
expect(foo).toEqual(1);
foo += 1;
});
it("does not reset foo between specs", function() {
expect(foo).toEqual(2);
});
});Disabling suites/specs
describe('SuperAwesomeModule', function() {
xdescribe('featureA', function() {
it('should ...', function() {
});
it('should ...', function() {
});
});
describe('featureB', function() {
xit('should ...', function() {
});
it('should ...', function() {
});
});
});Spies
- test double functions called spies.
- can stub any function and tracks calls to it and all arguments.
- A spy only exists in the describe or it block in which it is defined, and will be removed after each spec.
describe('SuperAwesomeModule', function() {
beforeEach(function() {
// track all calls to SuperAwesomeModule.coolHelperFunction()
// and also delegate to the actual implementation
spyOn(SuperAwesomeModule, 'coolHelperFunction').and.callThrough();
});
describe('featureA', function() {
it('should ...', function() {
expect(SuperAwesomeModule.featureA(2)).toBe(5);
// matchers for spies
expect(SuperAwesomeModule.coolHelperFunction).toHaveBeenCalled();
expect(SuperAwesomeModule.coolHelperFunction).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(1);
});
});
});Spies: and.returnValue
- Useful when you want to stub out return values
describe('SuperAwesomeModule', function() {
beforeEach(function() {
spyOn(SuperAwesomeModule, 'coolHelperFunction').and.returnValue('myValue');
});
});Karma.conf.js configuration
// list of files / patterns to load in the browser
files: [
'src/*.js',
'spec/*.js'
],
browsers: ['PhantomJS'], // run your tests in a headless browser!Make terminal reporting pretty
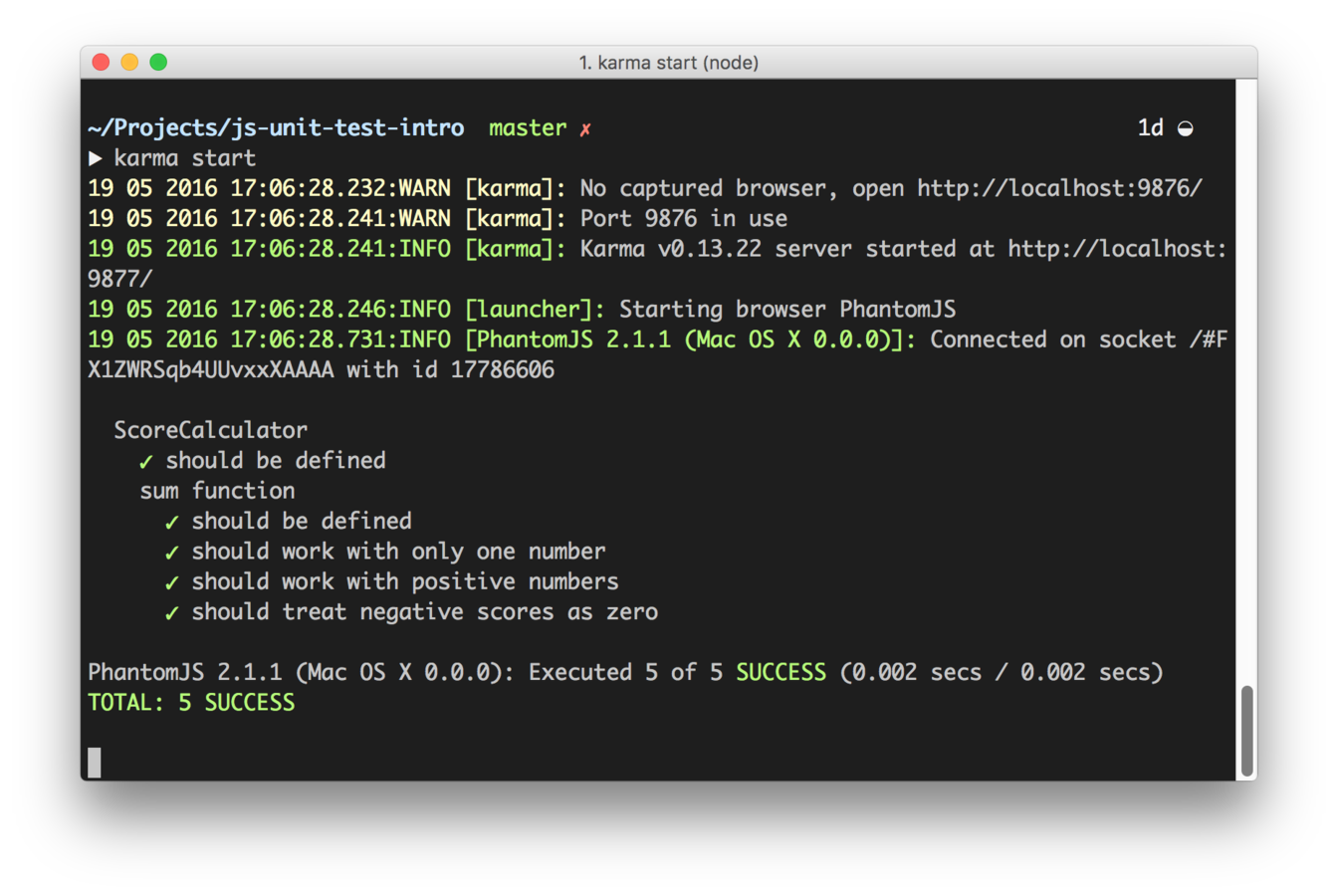
Make terminal reporting pretty
update karma.conf.js:
plugins: [
require("karma-jasmine"),
require("karma-phantomjs-launcher"),
require("karma-spec-reporter")
],
...
reporters: ['spec'],Build Integration
npm install husky --save-dev
// package.json
{
"scripts": {
"precommit": "npm test",
"prepush": "npm test",
"...": "..."
}
}On npm install, that will install git commit hooks for you, and enable them by adding npm scripts
Testing Angular 2
Sample App
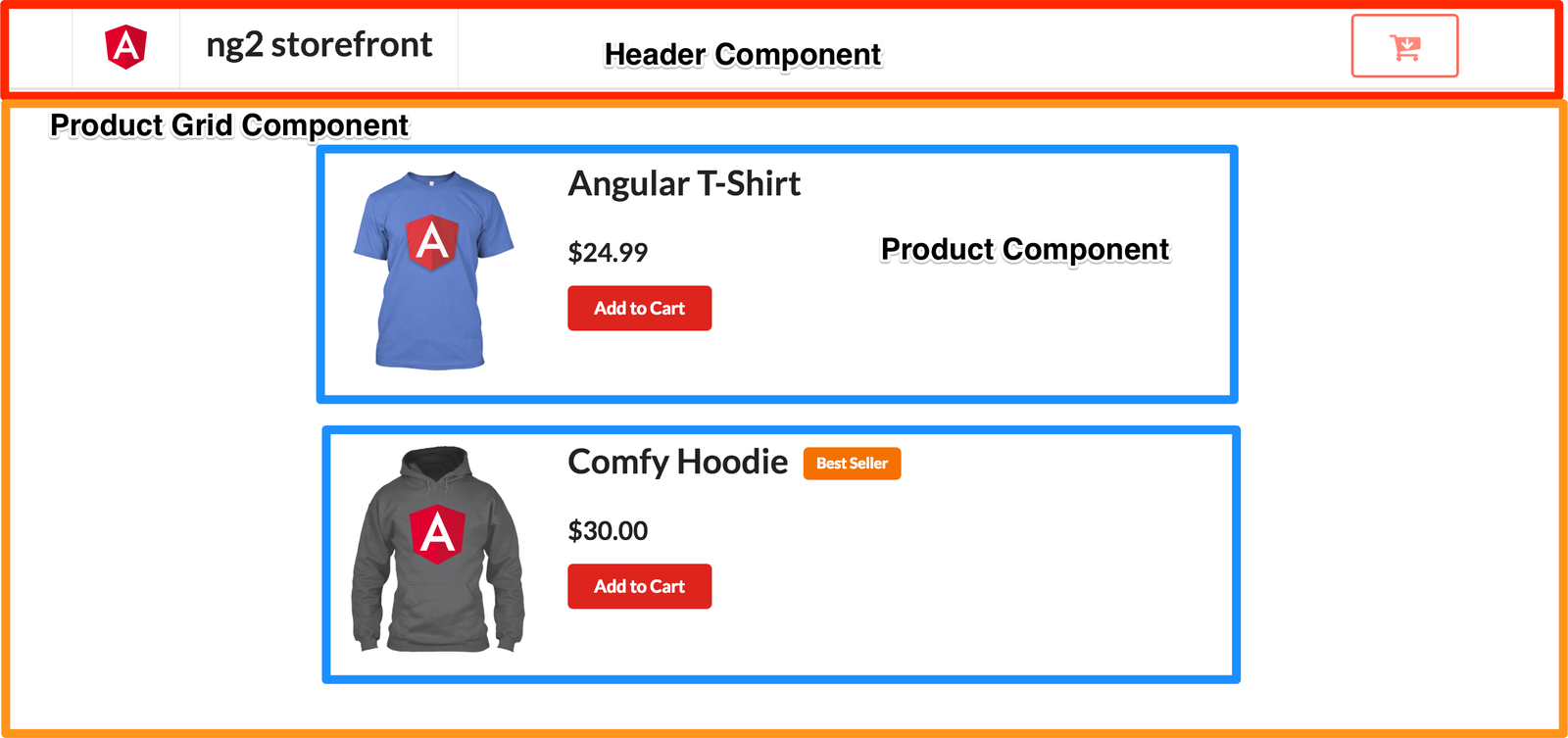
Testing Components
Components

Testing Components
import { TestBed } from '@angular/core/testing';
import { MyComponent } from './header.component';
describe('Component: MyComponent', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [MyComponent]
});
TestBed.compileComponents();
});
});Text
Set up each spec and configure the TestBed
Testing Components (fixtures)
let fixture = TestBed.createComponent(MyComponent);https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/api/core/testing/ComponentFixture-class.html
Returns a fixture for debugging and testing a component.
Testing Components (element)
let elem = fixture.debugElement.nativeElement;https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/api/core/testing/ComponentFixture-class.html
Returns the debug element associated with this component
Testing Components (component)
let component: HeaderComponent = fixture.debugElement.componentInstance;https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/api/core/testing/ComponentFixture-class.html
Returns the component instance.
Testing Components
it('should render a title', () => {
let fixture = TestBed.createComponent(HeaderComponent);
let elem = fixture.debugElement.nativeElement;
let component: HeaderComponent = fixture.debugElement.componentInstance;
expect(elem.querySelector('h1.header').innerHTML).toBe('ng2 storefront');
});Testing Components
// Usage: <greeter name="Joe"></greeter>
// Renders: <h1>Hello Joe!</h1>
@Component({
selector: 'greeter',
template: `<h1>Hello {{name}}!</h1>`
})
export class Greeter {
@Input() name;
}Testing Components
describe('Component: Greeter', () => {
let fixture, greeter, element, de;
//setup
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [ Greeter ]
});
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(Greeter);
greeter = fixture.componentInstance; // to access properties and methods
element = fixture.nativeElement; // to access DOM element
de = fixture.debugElement; // test helper
});
//specs
it('should render `Hello World!`', async(() => {
greeter.name = 'World';
//trigger change detection
fixture.detectChanges();
fixture.whenStable().then(() => {
expect(element.querySelector('h1').innerText).toBe('Hello World!');
expect(de.query(By.css('h1')).nativeElement.innerText).toBe('Hello World!');
});
}));
}) Testing Compents with Dependencies
use the "providers" property when configuring the test bed
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [AppComponent],
providers: [
{
provide: ApiService,
useClass: MockApiService
}
]
});
TestBed.compileComponents();
});class MockApiService {
getProducts() {
return Promise.resolve(mockProductList);
}
}Testing Services
Testing Services: Http
- When testing services that make HTTP calls, we don't want to hit the server with real requests
- Time constraints, isolate from outside points of failure
- mock server requests
Testing Services: Http
Services often require dependencies that Angular injects through the constructor of the service's class
@Injectable()
export class StorefrontService {
constructor(public http: Http) { }
getProducts(): Observable<Response> {
return this.http.get('/mock/products.json')
.map(res => res.json());
}
}Testing Services: Http
Setup: configure TestBed with providers
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
providers: [
MockBackend,
BaseRequestOptions,
{
provide: Http,
useFactory: (mockbackend: ConnectionBackend, defaultOptions: BaseRequestOptions) => {
return new Http(mockbackend, defaultOptions);
},
deps: [MockBackend, BaseRequestOptions]
},
StorefrontService,
]
});
});Testing Services: Http
For each test, use the "async" and "inject" functions in @angular/core/testing
use the mock connection to test requests
it('should call api with correct url',
async(inject(
[ApiService, MockBackend],
(apiService: ApiService, mockBackend: MockBackend) => {
mockBackend.connections.subscribe( (connection: MockConnection) => {
expect(connection.request.method).toBe(RequestMethod.Get);
expect(connection.request.url).toBe('/mock/products.json');
});
apiService.getProducts();
}
)
)
);Testing Pipes
Format Price
- There is a "CurrencyPipe", but doesn't work in all browsers
- Let's create our own
@Pipe({
name: 'formatPrice'
})
export class FormatPricePipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: number): string {
return '$' + ( (value / 100).toFixed(2).replace(/\B(?=(\d{3})+(?!\d))/g, ",") );
}
}Testing Pipes
Nothing special, it's just a class!
describe('Pipe: FormatPrice', () => {
let pipe: FormatPricePipe;
beforeEach(() => {
pipe = new FormatPricePipe();
});
it('should format price correclty', () => {
expect(pipe.transform(2499)).toBe('$24.99');
});
});Testing Pipes
import {Pipe, PipeTransform} from '@angular/core';
@Pipe({
name: 'capitalise'
})
export class CapitalisePipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(value: string): string {
if (typeof value !== 'string') {
throw new Error('Requires a String as input');
}
return value.toUpperCase();
}Testing Pipes
describe('Pipe: CapitalisePipe', () => {
let pipe;
//setup
beforeEach(() => TestBed.configureTestingModule({
providers: [ CapitalisePipe ]
}));
beforeEach(inject([CapitalisePipe], p => {
pipe = p;
}));
//specs
it('should work with empty string', () => {
expect(pipe.transform('')).toEqual('');
});
it('should capitalise', () => {
expect(pipe.transform('wow')).toEqual('WOW');
});
it('should throw with invalid values', () => {
//must use arrow function for expect to capture exception
expect(()=>pipe.transform(undefined)).toThrow();
expect(()=>pipe.transform()).toThrow();
expect(()=>pipe.transform()).toThrowError('Requires a String as input');
});
}) Testing Directive
Directive
// Example: <div log-clicks></div>
@Directive({
selector: "[log-clicks]"
})
export class logClicks {
counter = 0;
@Output() changes = new EventEmitter();
@HostListener('click', ['$event.target'])
clicked(target) {
console.log(`Click on [${target}]: ${++this.counter}`);
//we use emit as next is marked as deprecated
this.changes.emit(this.counter);
}
}Directive
@Component({
selector: 'container',
template: `<div log-clicks (changes)="changed($event)"></div>`,
directives: [logClicks]
})
export class Container {
@Output() changes = new EventEmitter();
changed(value){
this.changes.emit(value);
}
}
Directive
describe('Directive: logClicks', () => {
let fixture;
let container;
let element;
//setup
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [ Container, logClicks ]
});
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(Container);
container = fixture.componentInstance; // to access properties and methods
element = fixture.nativeElement; // to access DOM element
});
//specs
it('should increment counter', fakeAsync(() => {
let div = element.querySelector('div');
//set up subscriber
container.changes.subscribe(x => {
expect(x).toBe(1);
});
//trigger click on container
div.click();
//execute all pending asynchronous calls
tick();
}));
}) Testing Routes
Routes
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `<router-outlet></router-outlet>`
})
class TestComponent { }
@Component({
selector: 'home',
template: `<h1>Home</h1>`
})
export class Home { }
export const routes: Routes = [
{ path: '', redirectTo: 'home', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: 'home', component: Home },
{ path: '**', redirectTo: 'home' }
];
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule, RouterModule.forRoot(routes),
],
declarations: [TestComponent, Home],
bootstrap: [TestComponent],
exports: [TestComponent]
})
export class AppModule {}Routes
describe('Router tests', () => {
//setup
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [
RouterTestingModule.withRoutes(routes),
AppModule
]
});
});
//specs
it('can navigate to home (async)', async(() => {
let fixture = TestBed.createComponent(TestComponent);
TestBed.get(Router)
.navigate(['/home'])
.then(() => {
expect(location.pathname.endsWith('/home')).toBe(true);
}).catch(e => console.log(e));
}));
it('can navigate to home (fakeAsync/tick)', fakeAsync(() => {
let fixture = TestBed.createComponent(TestComponent);
TestBed.get(Router).navigate(['/home']);
fixture.detectChanges();
//execute all pending asynchronous calls
tick();
expect(location.pathname.endsWith('/home')).toBe(true);
}));
it('can navigate to home (done)', done => {
let fixture = TestBed.createComponent(TestComponent);
TestBed.get(Router)
.navigate(['/home'])
.then(() => {
expect(location.pathname.endsWith('/home')).toBe(true);
done();
}).catch(e => console.log(e));
});
});Testing Observables
Observables
describe('Observable: basic observable', () => {
var basic$;
//setup
beforeEach(() => {
basic$ = new Observable(observer => {
//pushing values
observer.next(1);
observer.next(2);
observer.next(3);
//complete stream
observer.complete();
});
})
//specs
it('should create the expected sequence (async)', async(() => {
let expected = [1,2,3],
index = 0;
basic$
.subscribe({
next: x => expect(x).toEqual(expected[index++]),
error: e => console.log(e)
});
}));
});Testing EventEmitters
EventEmitters
@Component({
selector: 'counter',
template: `
<div>
<h1>{{counter}}</h1>
<button (click)="change(1)">+1</button>
<button (click)="change(-1)">-1</button>
</div>`
})
export class Counter {
@Output() changes = new EventEmitter();
constructor(){
this.counter = 0;
}
change(increment) {
this.counter += increment;
//we use emit as next is marked as deprecated
this.changes.emit(this.counter);
}
}EventEmitters
describe('EventEmitter: Counter', () => {
let counter;
//setup
beforeEach(() => TestBed.configureTestingModule({
providers: [ Counter ]
}));
beforeEach(inject([Counter], c => {
counter = c;
}))
//specs
it('should increment +1 (async)', async(() => {
counter.changes.subscribe(x => {
expect(x).toBe(1);
});
counter.change(1);
}));
it('should decrement -1 (async)', async(() => {
counter.changes.subscribe(x => {
expect(x).toBe(-1);
});
counter.change(-1);
}));
}) Q&A
Sync or Async?
Does your test makes asynchronous calls? Uses XHR, Promises, Observables, etc. Is the Component using TemplateUrl or styleUrls or inline? Make sure you are using the corresponding APIs.
Demo
Links
Thanks!
Angular 2: Unit Testing
By Pavel Nasovich
Angular 2: Unit Testing
Angular 2: Unit Testing
- 2,768



