CCPM
Critical Chain Project Management



OUTLINE
- Motivation & Overview
- Steps in CCPM
- An example
DEFINITION
Critical chain project management (CCPM) is a methodology for planning, executing and managing projects in single and multiproject environment.

HISTORY
MOTIVATION
Critical Chain Project Management was developed by Dr.Eli Goldratt and was first introduced to the market in his Theory of Constraints book "Critical Chain" in 1997
It was developed in response to many projects being dogged by poor performance manifested in:
- Longer than expected durations
- Frequently missed deadlines
- Increased cost in excess of budget
- Less deliverables than promised

PROBLEMS with Traditional Project Management
When planning for an upcoming project, estimates for task duration are required. In order for to be treated as realistic, much time is spent on ensuring that the estimates are accurate. Accurate estimates give us increased probability and high confidence on task completing on time.
- Localized Risk Management
- Student's Syndrome
- Parkinson's Law
- Multi-tasking

LOCALIZED RISK MANAGEMENT

"just in case!"
In order for the project to be completed on time, tasks need to be completed with certain degree of confidence...
This leads to resources giving a "safe" estimate rather than 50% confidence level.
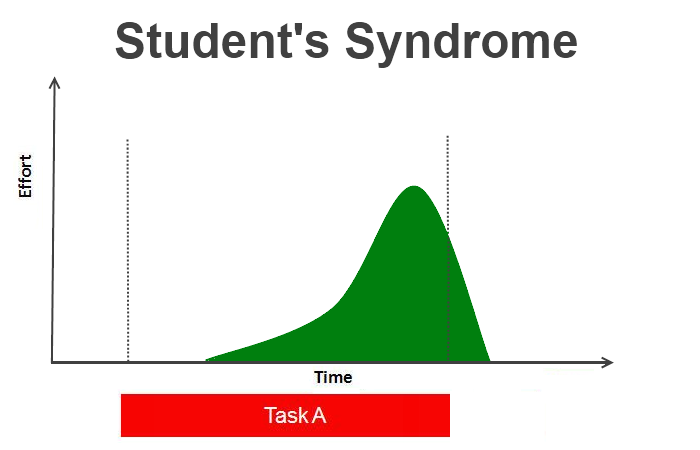
STUDENT'S SYNDROME
People do not start to work full fledge until the deadline is near.
Happens to students.
PARKINSON'S LAW
Delay or "pacing" the completion of the task.

MULTI-TASKING
Management forces people to work on more than one task at a time
T1
T2
T3
T1
T1
T2
T2
T3
T3
Non Multi-tasking approach
Multi-tasking approach
- Hidden Cost?
- Inefficiency?
MULTI-TASKING ACTIVITY
OTHER PROBLEMS
Resources do not report tasks if they are finished early.
Delays are being passed on to the entire project, however, benefits are rarely passed.
Traditional techniques such as Critical Path Management do not address issue of embedded safety.

THE CRITICAL CHAIN
- Longest chain of dependent tasks
Dependency refers to resources and resource contention across projects as well as dependencies of tasks themselves.
THE CRITICAL CHAIN
BENEFITS
To reduce the behaviors and time wasting associated with too much embedded safety.
CCPM recommends that task durations are cut half the length of a "normal" duration.
CCPM uses safety "buffers" to manage the impact of variation and uncertainty around the projects.
The safety at a task level is aggregated and moved to strategic points in the flow.
ESTIMATION
SAFETY

BUFFERS
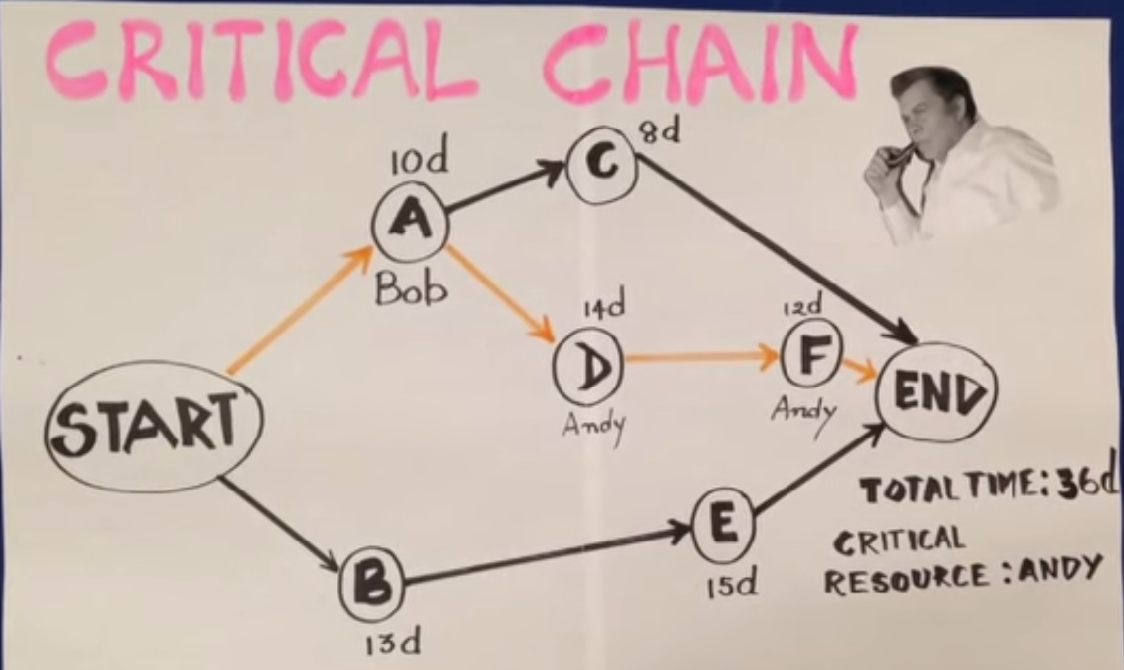
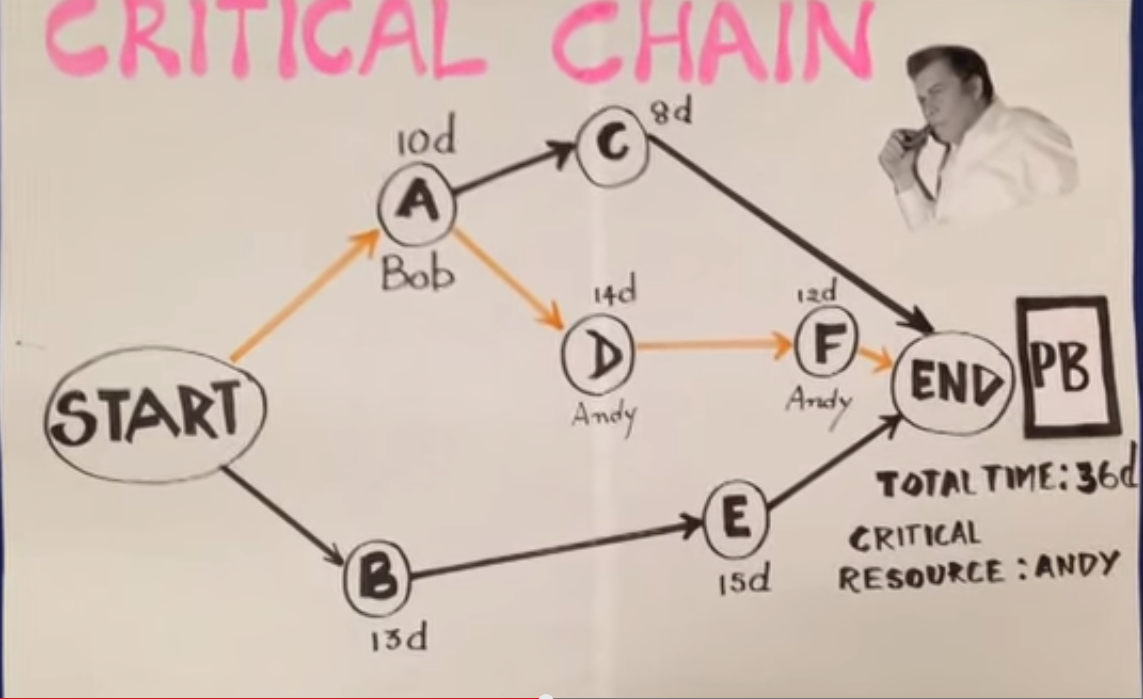
PROJECT BUFFER
A project buffer is inserted at the end of the project network between the last task and completion date.
Any delays on the critical chain will consume the buffer.
BUFFERS
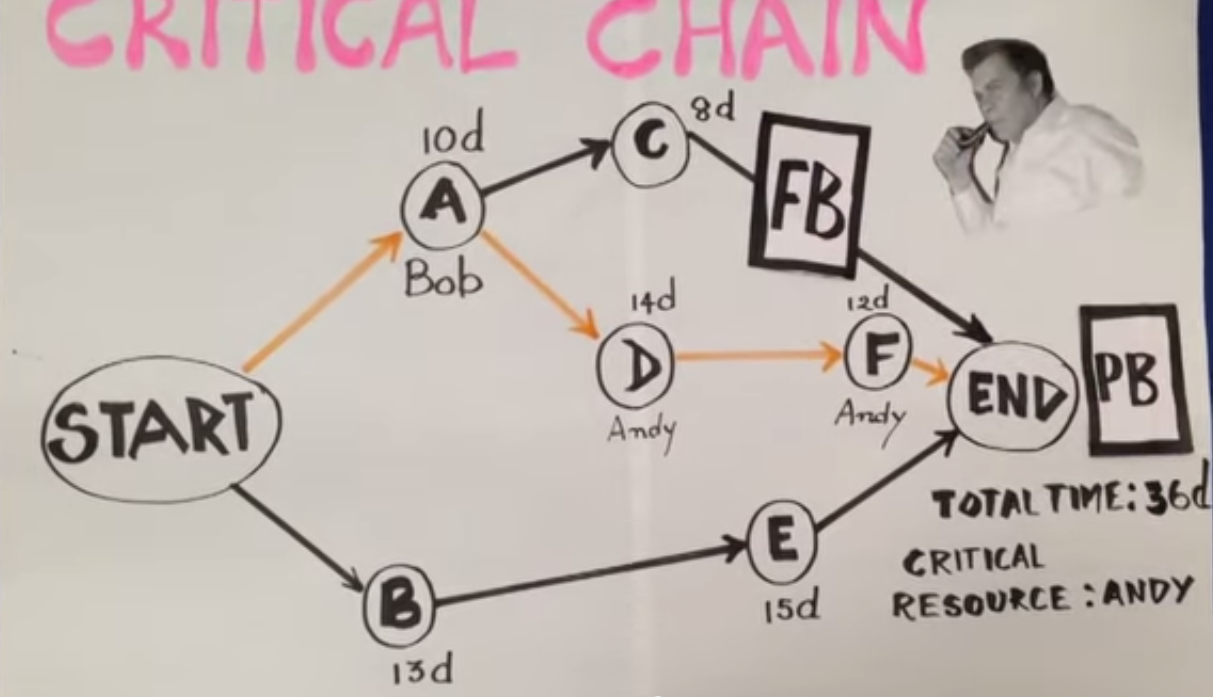
FEEDING BUFFER
Delays on paths of tasks feeding into longest path can impact the project by delaying a subsequent task on the critical chain.
To protect this, feeding buffers are inserted between the last task on a feeding chain and the critical chain.
BUFFERS
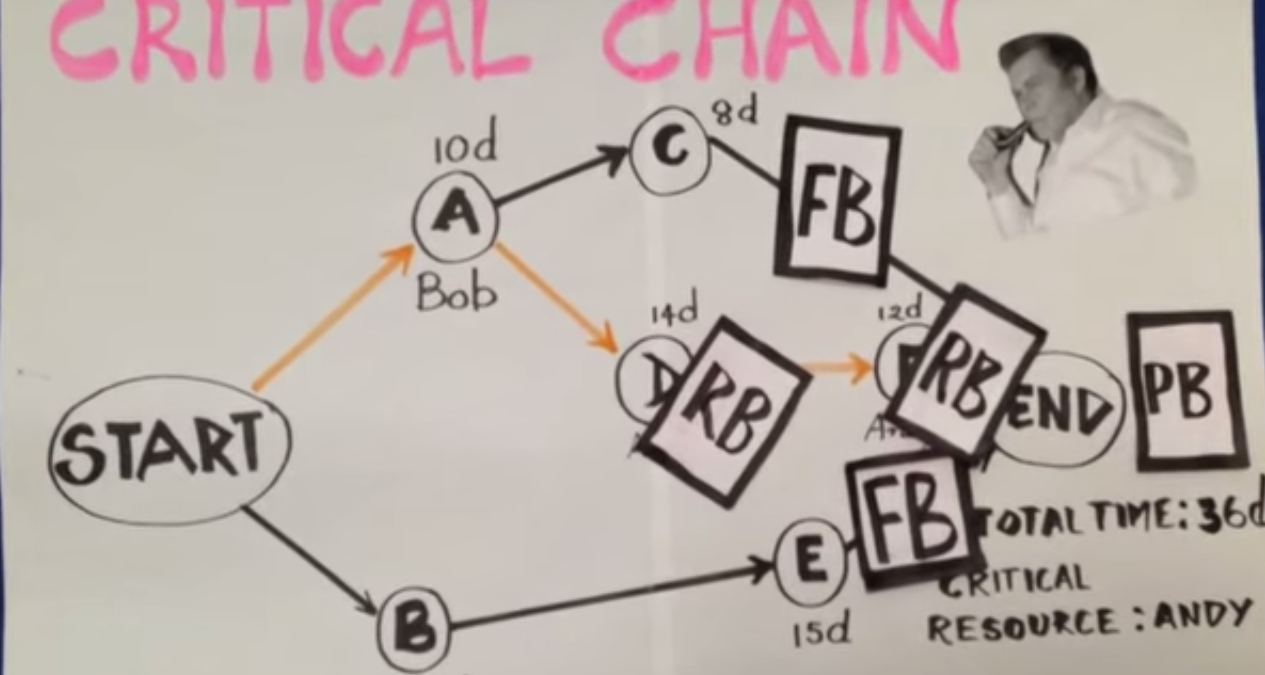
RESOURCE BUFFER
Resource buffers can be set to ensure that the appropriate people and skills are available to work on the critical chain tasks as soon as possible.
KEY CONCEPTS
- Priorities
- Completion
- Buffer management
- Remaining duration
KEY CONCEPTS
- Priorities
All resources on a project are given clear and aligned priorities relating to the "health" of the Critical Chain relative to its associated buffer and hence the project as a whole.
A resource with more than one task open should normally be assigned to complete task that will jeopardize the Critical Chain.
KEY CONCEPTS
- Completion
When there is work available it should be progressed at the fastest possible speed.
Tasks are not left partially complete to remove the temptation to multi-task.
KEY CONCEPTS
- Buffer Management
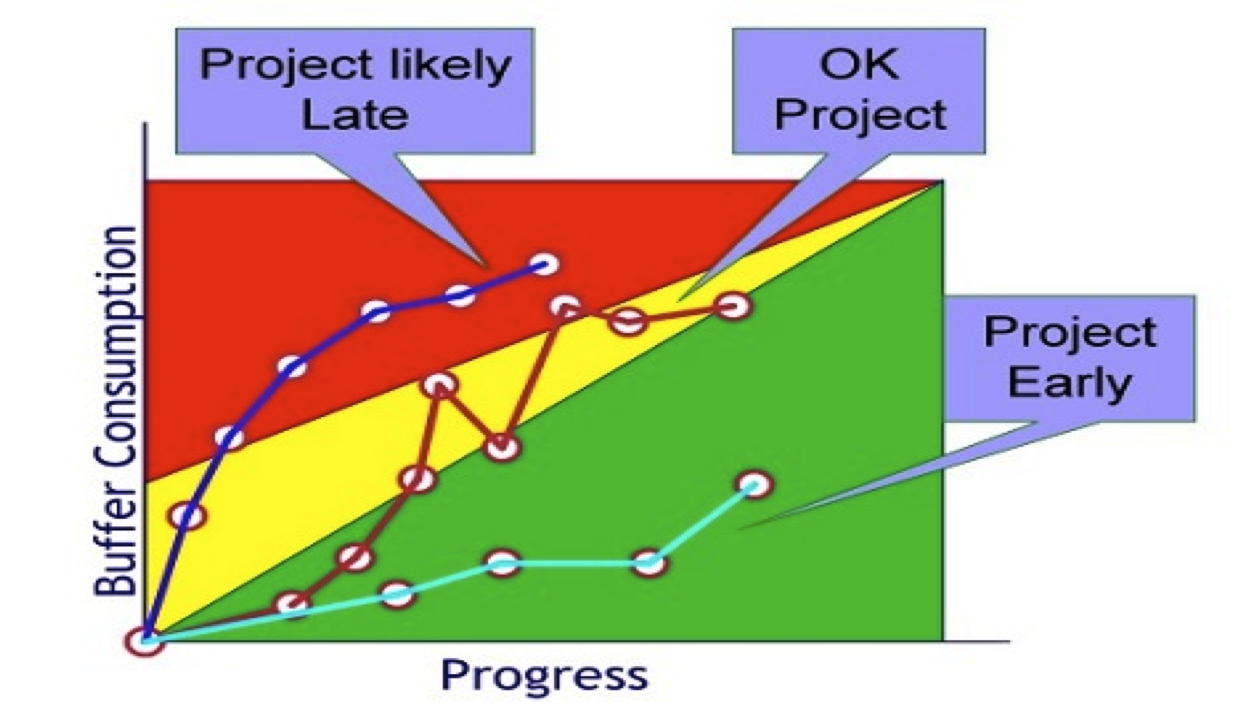
The amount each buffer is consumed relative to the project progress tells us how badly the delays are effecting our committed delivery date.
If the variation throughout the project is uniform then the project should consume its project buffer at the rate tasks are completed.
KEY CONCEPTS
- Remaining Duration
Tasks are monitored on their remaining duration, not their percentage complete.
Resources report upon tasks in progress based on the number of days they estimate until the task will be complete.
PATH VS CHAIN
CRITICAL PATH
CRITICAL CHAIN
- Goes from start to end
- More subjective towards dates and milestones
- Goes from start to project buffer
- Takes resource contentions into account
- Problems: Student's Syndrome, Parkinson's Law etc..
Critical Chain Project Management Steps
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
Standard Conventional Project Schedule
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
Safety Buffers
Sequence Dependency
Resource Dependency
Safety Exclusion
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11

Safety Buffer Exclusion
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours

Resource Leveling
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
A7
A8
A9
A10
Critical chain is the sequence of dependent activities that determines the minimum time it will take a project to complete, taking into account both activity dependencies and resource constraints.
Critical Chain
Buffer Creation
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A9
A10
A11
5 hours
5 hours
5 hours
A7
A8
Critical Chain
FB
PB
FB
FB: Feeding Buffer
PB: Project Buffer
Feeding Chain
Project Buffer Incursion Chart
Advantages
Safety Buffer Exclusion
Resource Leveling
Buffer Creation
Overall benefits:
- Cultivate team culture and motivate workforce
- Low overall protection required
- Higher coverage from exceptional scenarios on selective tasks
- High success rate
- Eliminates student's syndrome
- Takes care of Parkinson's law
- Avoids multi-tasking
- Resolves resource and sequence dependencies
- Feeder buffer protects critical chain
- Project buffer protects whole project
The MMOR Barbecue Party



MMOR15
I'll ask Haider
& Tony for help!
Success...
Not a MESS!

...RBS?
...WBS?

TIMELINE?

Budget?
What kind of meat are we talking about?
Intense Project Scoping & Planning Meeting...

1. Send & Confirm Invitation
2. Buy Food & Drinks


3. Prepare Food
4. Mow Lawn

5. Take Tables Outside

6. Setup Tables
7. Heat Up Grill


Ravi
Haider
Tony
Tony
Haider
60Min
120Min
120Min
60Min
60Min
75Min
30Min
+15Min
+15Min
+15Min
+30Min
+30Min
Ravi
Haider
Tony
Ravi
+15Min
Haider
Ravi
Ravi
+30Min
#1
#2,5
-
-
#4
#3
#6








10AM
12PM
2PM
4PM
6PM
60+15Min
120+30Min
120+30Min
75+30Min
30+15
60+15Min
60+15Min
- Start By 10AM
- Guest Arrive By 6PM
- Everything Ready By 6:45PM
- "Safety time" - 150 Minutes
Execution
10:00AM


BBQ
PARTY!!!!
LOL



11:00AM
10:30AM
Execution
11:05AM

11:30AM


Oh boy..

Good thing
we planned ahead



Execution





Just need to
get it done
by 1PM..
11:30AM
Execution




11:50AM
Execution

12:10PM





Am I in heaven?
Execution

12:30PM
What am I
buying again?
Execution
1:05PM
1:15PM
Can't find the keys to garage...
1:30PM
Found it!
Execution
2:05PM
Where are the rest of the tables?


Execution
2:10PM



Execution

2:10PM
2:15PM


I can't work like this...
Execution
5:10PM



5:40PM

Execution



6:00PM



Execution



7:10PM




- Process was messy
- Barbeque delayed to 7:10PM (instead of 6:45PM)
What went Wrong?







10AM
12PM
2PM
4PM
6PM
60+15Min
120+30Min
120+30Min
75+30Min
30+15
60+15Min
60+15Min
As Plan
Supermarket busy, Distraction
Late start
Key search
Crowded Kitchen
Had to split up
Guest interference
What went Wrong?
MURPHY'S LAW
- Bad Multitasking: Multitasking in supermarket
- Student's Syndrome: Start task late thinking there is more then enough time
Safety buffers will be consumed no matter what. Only way to get around this is to make tasks important and urgent.
- "Anything that can go wrong will go wrong."
- Supermarket was crowded
- Garage key was lost
- Kitchen was too small
- Guests arrived early
PARKINSON'S LAW
Only way to get around this is to add resources and buffers.
dilemma?
CCPM
- Allocate minimum amount of time to a task so the task stays urgent
- Keep a critical chain by making sure that resources will be available at the end of the previous task(s)
- Use buffer to variances in task duration




CCPM







10AM
12PM
2PM
4PM
6PM
60Min
120Min
120Min
75Min
30Min
60Min
60Min
CCPM







10AM
12PM
2PM
4PM
6PM
60Min
120Min
120Min
75Min
30
60Min
60Min
FB:75Min
PB:105Min
- Earliest due date: 5PM
- Latest due date: 6:45PM
Copy of Critical Chain Project Management
By Haider Shah
Copy of Critical Chain Project Management
- 1,407
