Scope Demystified
http://attheo.do
Node.js meetup
Once and for all, hopefully
Scope in JS
A well-defined (?) set of rules for storing variables in some location, and for finding those variables at a later time.

Compiler Theory
Tokenizing / Lexing
Parsing
Code Generation
A little more Compiler Theory
Lefthand Side Lookup (LHS)
Righthand Side Lookup (RHS)
When a variable appears on the lefthand side of an assignment operation.
When a variable appears on the righthand side of an assignment operation.
Simply "Not lefthand side"
A little more Compiler Theory
Lefthand Side Lookup (LHS)
Righthand Side Lookup (RHS)
- "Who is the target of the assignment?"
- Failure (lookup fails, strict mode) = ReferenceError
- Failure (non-strict) = You get a new global! w00t!
- "Who is the source of the assignment?"
- Failure (lookup fails) = ReferenceError
- Failure (unorthodox utilisation) = TypeError
LHS/ RHS Errors
ReferenceError
TypeError
Scope resolution FAILED
- Scope resolution SUCCESSFUL.
- BUT, illegal/impossible action attempted against the result.
A little more Compiler Theory
function lala(a) {
console.log(a); // 2
}
lala(2);RHS
LHS
RHS
LHS/RHS
Understanding Scope
Engine
Compiler
Scope
Think like those guys!
}
Understating Scope
function lala(a) {
console.log(a); // 2
}
lala(2);Engine
"Hey Scope, ever heard of lala?"
Scope
"Yup, Compiler declared it. It's function. Take it"
Engine
"Hey Scope, I have an LHS for a, know it?"
Scope
"Compiler says it's a parameter to lala, here you go"
Engine
"Thanks Scope, please assign 2 to a"
Engine
"Hey Scope, me again. Need an RHS for console. Know it?"
"Yup, built-in shit. Take it."
Scope
Engine
"Yo Scope. Need RHS to a, remember anything?"
Understating (Nested) Scope
function lala(a) {
console.log(a+b);
}
var b = 2;
lala(2);Engine
"Hey Scope of lala, got an RHS for b"
Scope
"Fuck off Engine, know nuthin' "
Engine
"Hey outer scope, oh you're the global Scope! Need an RHS for b, know anything?"
Scope
"Sure thing dawg. Here ya go"
Nested Scope Resolution

Global Scope
Current Scope
Lexical Scope(s)
It's Lex time!

Lexical Scope
- Defined at "Lex-ing" time
- In other words... Variables and blocks of scope are mostly "scoped" at the moment you write your code.
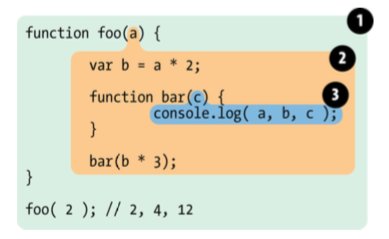
Global Scope
Foo Scope
Bar Scope
Lexical Scope

Scope "bubbles" are strictly nested.
Lexical Scope Lookups

Scope lookup stops once it finds the first match!
Cheating Lexical Scope
-
eval()
-
with

Function Scope VS Block Scope
"Can other structures in JS create bubbles of scope?"
Function Scope VS Block Scope
-
In general, JS has function-based scope.
-
No other structures create their own scope "bubbles".
not entirely true
Scope From Functions
function foo(a) {
var b = 2;
// some shit..
function bar() {
// some other shit...
}
// oh, look a turd!
var c = 3;
}
bar(); // Fails
console.log(a, b, c); // Fails"Hiding in Plain Scope"
function doSomething(a) {
b = a + doSomethingElse(a*2);
console.log(b*3);
}
function doSomethingElse(a) {
return a - 1;
}
var b;
doSomething(2); // 15"Hiding in Plain Scope"
function doSomething(a) {
var b;
function doSomethingElse(a) {
return a - 1;
}
b = a + doSomethingElse(a*2);
console.log(b*3);
}
doSomething(2); // 15Functions as Scopes
var a = 2;
function foo() { ///// <--- we add this...
var a = 3;
console.log(a); // 3
}
foo(); ////// <---- And this...
console.log(a); // 2Functions as Scopes (IIFE)
var a = 2;
(function IIFE(global) {
var = 3;
console.log(a); // 3
console.log(global.a); // 2
}) (window);
console.log(a); // 2Blocks as Scopes
Block-scoping: Declaring variables as close as possible, as local as possible, to where they will be used
Blocks as Scopes
Javascript has no facility for block scope.

Blocks as Scopes
... Or does it?
{
try {
throw undefined;
} catch(a) {
a = 2;
console.log(a);
}
}
console.log(a); // Fails{
let a = 2;
console.log(a); // 2
}
console.log(a); // ReferenceErrorHoisting

How declarations that appear in various locations in a scope, actually get attached to the scope
Hoisting
a = 2;
var a;
console.log(a);
/**** DIFFERENT CONTEXT ****/
console.log(a);
var a = 2;
WTF?!
Hoisting
All declarations (variables & functions) are processed first.
var a=2;{
var a;a = 2;Declaration!
Assignment
Hoisting
Only declarations are moved (hoisted)
Assignments are (obviously) left in place
Hoisting is applied to per scope
Hoisting
var a;
a = 2;
console.log(a);
/**** DIFFERENT CONTEXT ****/
var a;
console.log(a);
a = 2;
Function Hoisting
Function declarations are hoisted
Function expressions are NOT hoisted
Function declarations are hoisted FIRST , before variables
Function Hoisting
Function Declarations
foo();
function foo() {
console.log(a); // undefined
var a = 2;
}Function Hoisting
Function Expressions
foo(); // TypeError! (Not ReferenceError)
var foo = function bar() {
console.log(a); // undefined
var a = 2;
}Function Hoisting
Function hoisting takes place BEFORE variable
foo(); // 1
var foo;
function foo() {
console.log(1);
}
foo = function() {
console.log(2);
};function foo() {
console.log(1);
}
// var foo; was ignored
foo(); // 1
foo = function() {
console.log(2);
}Closures & Scope
Closure is when a function is able to remember and access its lexical scope, even when that function is executing outside its lexical scope.

Closures & Scope
function foo() {
var a = 2;
function bar() {
console.log(a);
}
return bar;
}
var lala = foo();
lala(); // 2.. Wow so much closure!
Closures & Scope
function foo() {
var a = 2;
function baz() {
console.log(a); // 2
}
bar(baz);
}
function bar(fn) {
fn();
}
Closures & Scope
for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
setTimeout( function timer() {
console.log(i);
}, i * 1000);
}for (var i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
(function() {
var j = i;
setTimeout(function timer() {
console.log(j);
}, j*1000);
})();
}Closures & Scope
The "module" pattern using closures
var foo = (function MyModule() {
var something = 'cool';
var somethingElse = [1, 2, 3];
function doSomething() {
console.log(something);
}
function doAnother() {
console.log( somethingElse.join(" ! "));
}
return {
doSomething: doSomething,
doAnother: doAnother
};
})();
foo.doSomething(); // cool
foo.doAnother(); // 1 ! 2 ! 3Thanks folks!
Questions?
Copy of scope & this
By ibraimsap
Copy of scope & this
- 362



