
Welcome to v1.0 of the meta::[[verse]]!
# Slide 0# Slide 1- C++ Software Engineer, OS Internals
- ISO C++ foundation and Boost foundation board member
- Member of the ISO C++ Committee
- Israeli National Body Chair
- Library Evolution Work Group Chair
Inbal Levi
https://slides.com/inballevi/welcome-to-v1-0-of-the-meta-verse-cppcon

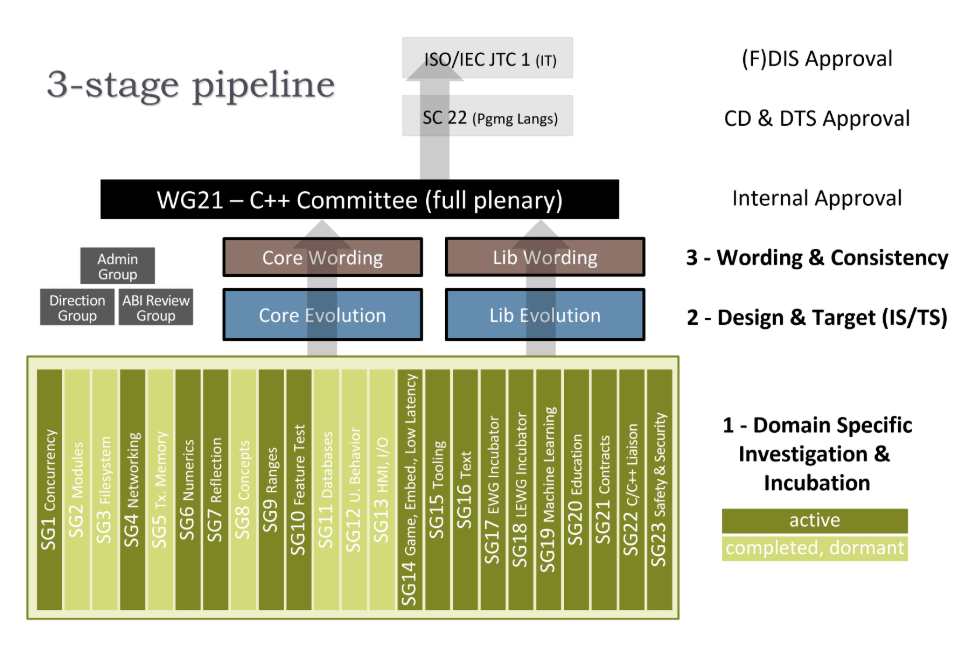
# Slide 2C++ Standards Committee




# Slide 3Reflection in C++

# Slide 4- The ability of software to expose its internal structure
-
Static reflection - compiler exposes structure at compile time
- Disclaimers:
- It's possible to "carry" the data into the runtime...
- But may introduce performance, security, or other issues
- This is out of scope for this talk (and for C++26, as of now)
This Talk
# Slide 5- Part I: Intro to reflection:
- A brief history of "Reflection" proposals in C++
- Latest proposal: "P2996: Reflection for C++26"
- Usage examples (reflection-based library) (*)
- Part II: Impact on our code bases
- Reflection as a Customization Point Mechanism
- Pipeline integration
- What's next?
(*) Examples from or derive from P2996, P3096, or EDG's implementation
# Slide 62015
Boost.Hana
(Louis Dionne)
Template metaprog. lib
A Brief History
Serialization
Delegates
Getters / Setters
Customization Points
# Slide 7A Brief History
Typefull
vs.
Monotype
Type based
vs.
Value based
meta objects
# Slide 9A Brief History
# Slide 9What do I mean by "Reflection"?
// Lib.hpp
class LibType : public BaseOne, public BaseTwo
{
int a;
double b;
};P2996
// main.cpp
#include <meta>
#include "Lib.hpp"
int main()
{
constexpr std::meta::info refexpr = ^^LibType;
constexpr auto res = std::meta::bases_of(refexpr)[0];
}https://godbolt.org/z/WxdvKdcMY
# Slide 10P2996: Reflection for C++26
-
Reflection Operator:
^^ -
Splicers: [
:…:] -
std::meta::info
-
Metafunctions
P2996
10. define_aggregate (inject)
-
Name & Location:
3. Template Queries:
10. define_class (inject)
-
identifier_of
-
display_string_of
-
source_location_of
-
template_of
-
template_arguments_of
11. Data Layout:
4. Member Queries:
-
offset_of -> member_offset
-
size_of
-
alignment_of
-
bit_size_of
2. Type Queries:
-
members_of, bases_of
-
(non)static_data_members_of
-
accessible_members_of (P3293R2)
-
enumerators_of
-
type_of
-
parent_of
-
dealias
-
Access modifiers: is_public, is_protected, is_private
-
Inheritance: is_virtual, is_pure_virtual, is_override, ...
-
Encapsulation: is_class_member, is_namespace_member, is_explicit, is_deleted, ...
-
Advanced Type Queries: is_complete_type, is_template, is_special_member, ...
12. (+) Type Traits
(+ Other Type Predicates)
5. substitute (template)
6. reflect Invoke (template)
7. extract<T>(info) (constexpr not required)
8. test_type(s) ("is_same")
9. reflect_x (extended)
-
reflect_constant
-
reflect_object
-
reflect_function
auto rexpr = ^ int;# Slide 11The Reflection Operator (^^) (Lift)
P2996
AKA Unibrow
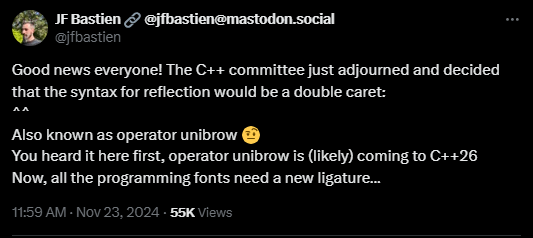
^auto rexpr = ^^int;# Slide 12The Reflection Operator (^^) (Lift)
- Shifts expressions into a "meta" - "reflection info" object
- Object can then to be used as input to reflection utilities
error: meta type variables must be constexpr
constexpr auto rexpr = ^^int;P2996
# Slide 13Splicers
- Splice extract the C++ expression back from "meta::info"...
- ...To be then used regularly to write the C++ program
constexpr auto rexpr = ^^int;
typename[:rexpr:] a = 42;What are you?
rexpr
meta::info obj, contains info on "int" type
typename[:rexpr:]
int
P2996
* More about the typename in P2996/[dcl.type.splice]
# Slide 14P2996: Reflection for C++26
P2996
-
Reflection Operator: ^^
-
Splicers: [
:…:] -
std::meta::info
-
Metafunctions
-
Name & Location:
3. Template Queries:
10. define_aggregate (inject)
-
identifier_of
-
display_string_of
-
source_location_of
-
template_of
-
template_arguments_of
11. Data Layout:
4. Member Queries:
-
offset_of -> member_offset
-
size_of
-
alignment_of
-
bit_size_of
2. Type Queries:
-
members_of, bases_of
-
(non)static_data_members_of
-
accessible_members_of(P3293R2) -
enumerators_of
-
type_of
-
parent_of
-
dealias
-
Access modifiers: is_public, is_protected, is_private
-
Inheritance: is_virtual, is_pure_virtual, is_override, ...
-
Encapsulation: is_class_member, is_namespace_member, is_explicit, is_deleted, ...
-
Advanced Type Queries: is_complete_type, is_template, is_special_member, ...
12. (+) Type Traits
(+ Other Type Predicates)
5. substitute (template)
6. reflect Invoke (template)
7. extract<T>(info) (constexpr not required)
8. test_type(s) ("is_same")
9. reflect_x (extended)
-
reflect_constant
-
reflect_object
-
reflect_function
+ consteval block (P3289R1), ...
# Slide 15std::meta::info
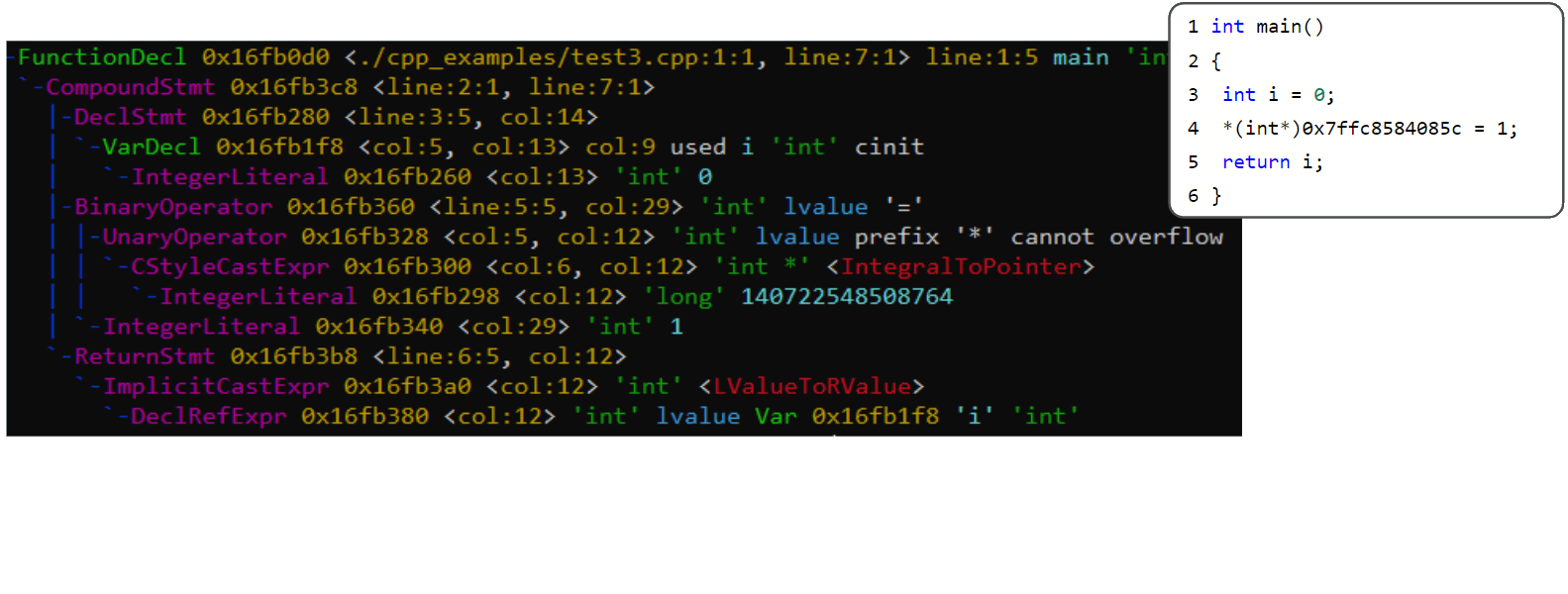
From: "Let's talk about abstraction layers"
P2996
# Slide 16std::meta::info
Represents:
- Type and type alias
- Function or member function
- Variable, static data member, or structured binding
- Non-static data member
- Enumerators
- Template
- Namespaces, namespace alias
- expression with that can only be evaluated at compile time
int arr[1];
auto a = std::meta::reflect_object(arr[1]);P2996
https://godbolt.org/z/o8sY1ePKe
int arr[1];
constexpr auto a = std::meta::reflect_object(arr[1]);# Slide 17std::meta::info
#include <iostream>
#include <experimental/meta>
class R;
constexpr std::meta::info res1 = ^^R;
constexpr auto print1 = std::meta::
is_complete_type(res1); // (1)
class R {
int a;
};
constexpr std::meta::info res2 = ^^R;
constexpr auto print2 = std::meta::
is_complete_type(res2); // (2)
constexpr auto print3 = std::meta::
is_complete_type(res1); // (3)
int main()
{
std::cout << "Res: " << print1 << "\n"; // (1)
std::cout << "Res: " << print2 << "\n"; // (2)
std::cout << "Res: " << print3 << "\n"; // (3)
}P2996
https://godbolt.org/z/cafxMPo4o

# Slide 18P2996: Reflection for C++26
P2996
-
Reflection Operator: ^^
-
Splicers: [
:…:] -
std::meta::info
-
Metafunctions
-
Name & Location:
3. Template Queries:
10. define_aggregate (inject)
-
identifier_of
-
display_string_of
-
source_location_of
-
template_of
-
template_arguments_of
11. Data Layout:
4. Member Queries:
-
offset_of -> member_offset
-
size_of
-
alignment_of
-
bit_size_of
2. Type Queries:
-
members_of, bases_of
-
(non)static_data_members_of
-
accessible_members_of(P3293R2) -
enumerators_of
-
type_of
-
parent_of
-
dealias
-
Access modifiers: is_public, is_protected, is_private
-
Inheritance: is_virtual, is_pure_virtual, is_override, ...
-
Encapsulation: is_class_member, is_namespace_member, is_explicit, is_deleted, ...
-
Advanced Type Queries: is_complete_type, is_template, is_special_member, ...
12. (+) Type Traits
(+ Other Type Predicates)
5. substitute (template)
6. reflect Invoke (template)
7. extract<T>(info) (constexpr not required)
8. test_type(s) ("is_same")
9. reflect_x (extended)
-
reflect_constant
-
reflect_object
-
reflect_function
+ consteval block (P3289R1), ...
# Slide 19Metafunctions
constexpr auto a = 42;
std::cout << meta::name_of(^^a) << "\n";All* the metafunctions accept "info" and return:
- string_view (e.g. identifier_of)
- std::meta::info (e.g. type_of)
- vector<std::meta::info> (e.g. bases_of)
- bool (e.g. is_concept)
- size_t (e.g. alignment_of)
- T (e.g. extract(info))
- source_location, member_offset (e.g. offset_of)
* Besides "reflect_value/object/function", which accepts type T
P2996
https://godbolt.org/z/9YW4bWGM7
constexpr auto a = 42;
std::cout << meta::identifier_of(^^a) << "\n";# Slide 20Substitute
- The equivalent "Reflection Relm" for instantiating a template
P2996
constexpr auto rexpr1 =
substitute(^^std::array, {^^int, reflect_value(3)});
typename[:rexpr1:] myArr1; // std::array<int, 3> myArr1
constexpr auto rexpr2 =
substitute(^^S, {^^int, 3});
typename[:rexpr2:] myArr2; // Fail# Slide 21Extract
- The equivalent "Reflection Relm" for extracting values
P2996
constexpr auto expr1 =
extract<int>(reflect_value(3)); // OK
constexpr auto expr2 =
extract<int>(reflect_value("3")); // Fail
# Slide 22Type Traits
- Two types of "Type Traits":
- Query the type
- Modify the type
- P2996 proposes the first type (e.g. is_nothrow_swappable)
- Interesting functionality available by the second type
- ...But this is more challenging, as it interferes with the compiler's representation of the program
P2996
# Slide 23Function Param Names
#include <experimental/meta>
#include <iostream>
consteval auto PrintParamK(std::meta::info r, size_t k)
{
return name_of(parameters_of(r)[k]);
}
// Function Declaration
void func(int first, int last);
void PrintFuncParamAfterDeclaration()
{
std::cout << "Param names: "
<< PrintParamK(^func, 0) << ", "
<< PrintParamK(^func, 1) << "\n";
}
// Function Definition
void func(int n, int ln)
{}
void PrintFuncParamAfterDefinition()
{
std::cout << "Param names: "
<< PrintParamK(^func, 0) << ", "
<< PrintParamK(^func, 1) << "\n";
}
int main()
{
PrintFuncParamAfterDeclaration(); // Param names: first, last
PrintFuncParamAfterDefinition(); // Param names: n, ln
}
https://godbolt.org/z/M84Ea6P88
Based on example from P3096
P2996
# Slide 24
Function Param Names
- P3096 Introduces the following options:
- Compile, No Guarantees
(Different compilers' output may be inconsistent) - Enforce Consistent Naming
(Don't compile if more than one option exists) - Mark by attribute (e.g. [[canonical]])
(Explicitly mark, otherwise ill-formed)
- Compile, No Guarantees
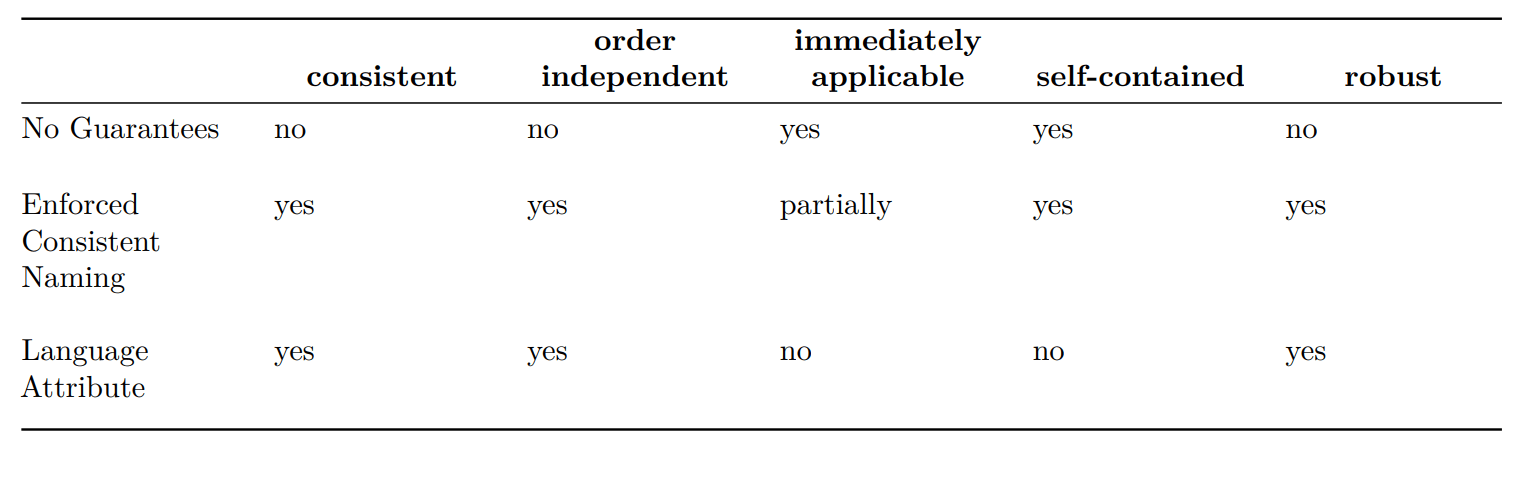
P2996
# Slide 25Reflection Logger
#include <string>
#include <experimental/meta>
consteval bool LogMembers(std::meta::info type)
{
// Verify type is a class/struct
// Ignore usecase of unnamed members (union/struct etc.)
std::__report_constexpr_value(identifier_of(type).data());
for (auto r : nonstatic_data_members_of(type))
{
std::__report_constexpr_value("\n\tmember:");
std::__report_constexpr_value(identifier_of(r).data());
}
return true;
}
// User code
static_assert(LogMembers(^^Student));https://godbolt.org/z/Yddfxdq8j
Reflection-Based Library
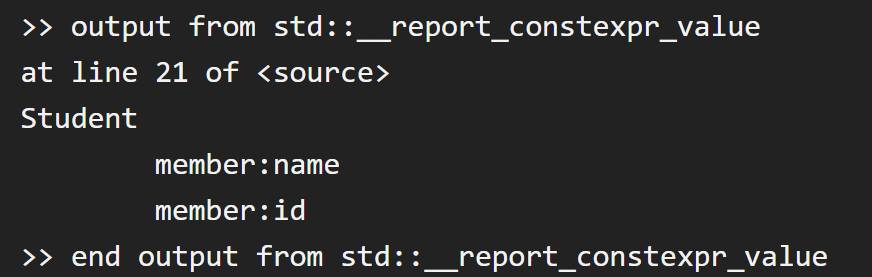
Based on example from EDG's CE implementation

#include <string>
struct Student
{
std::string name;
int id;
};https://drive.google.com/file/d/1SHDgRAqchwQXMopUecq0Ot5HCYYrKXta/view?usp=sharing

# Slide 26Detour: Customization Points
Reflection as CP
- Interaction between library code and user (*) code:
- Virtual functions:
- Library side: declaration of virtual functions
- User side: overriding virtual functions
- Template instantiation:
- Library side: declare a template
- User side: instantiate template for their types
- Provide functionality to be detected by ADL:
- Library side: allows/expects functions by name
- User side: declares a function within their type to be detected by ADL
- And now - Reflection?
- Virtual functions:
C++Now 2022, Cpp India 2022, CoreC++ 2022, CppCon 2023
"Customization Methods: Connecting User and C++ Library Code"

# Slide 27Guarantees and requirements provided by the library
can be expressed as "Customization Points"
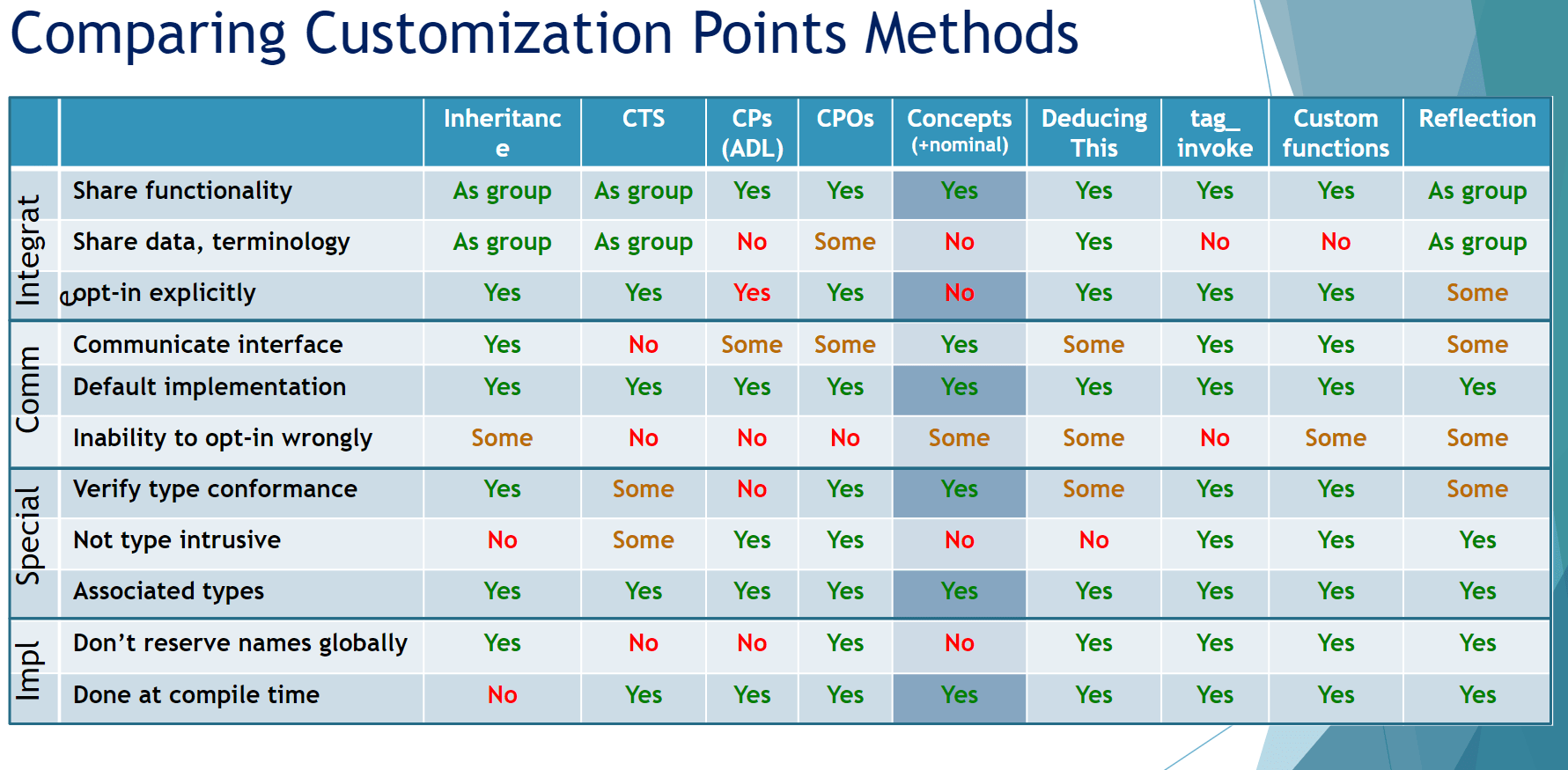
Reflection as CP
Detour: Customization Points
C++Now 2022, Cpp India 2022, CoreC++ 2022, CppCon 2023
"Customization Methods: Connecting User and C++ Library Code"

# Slide 28Reflection as Customization
template<class_type T, structural_subtype_of<T> U>
void LibFunc(const T& src, U& dst)
{
constexpr auto members = meta::data_members_of(reflexpr(src));
template for (constexpr meta::info a : members)
{
constexpr meta::info b = meta::lookup(dst, meta::name_of(a));
dst.|b| = src.|a|;
}
} // `structural_copy`Example from "P2237: Metaprogramming" (Andrew Sutton)
C++Now 2022, Cpp India 2022, CoreC++ 2022, CppCon 2023
"Customization Methods: Connecting User and C++ Library Code"

Reflection as CP
# Slide 29- Interaction between library code and user(*) code
int main()
{
type.[:get_member_i(0):] = 1;
type.[:get_member_i(1):] = 1;
type.[:member_named("pub"):] = 2;
type.[:member_named("prv"):] = 2;
}Library Code
User(*) Code
Reflection as Customization
class LibType {
public:
int pub;
private:
int prv;
public:
void Print();
};Reflection as CP
# Slide 30Function Param Names
- Forward competability
void PrintFuncParams()
{
std::cout << "Param names: "
<< PrintParamK(^^func, 0) << ", "
<< PrintParamK(^^func, 1) << "\n";
}
void func(int first, int last);
// PrintParamsLocation1() { ... }
void func(int first, int last)
{ ... }
// PrintParamsLocation2() { ... }
int main()
{
PrintFuncParamsLocation1();
PrintFuncParamsLocation2();
}Library Code
New User Code
void func(int first, int last);
// PrintParamsLocation1() { ... }
void func(int a, int b)
{ ... }
// PrintParamsLocation2() { ... }
int main()
{
PrintFuncParamsLocation1();
PrintFuncParamsLocation2();
}"P3096: Function Parameter Reflection in Reflection for C++26"
(Adam Lach, Walter Genovese)
Reflection-Based Library
# Slide 31Pipeline Integration
Pipeline Integration
AppCode
LoggerLib
Compiler
LoggerLib.o
AppCode.o
Linker
version / macros
- The compiler provides:
- Standard version flag and implementation macros
- The library can then "ifdef" based on it to figure out
- Standard version
- Avaliable features
main.out
# Slide 32
Pipeline Integration
Pipeline Integration
main.out
Linker
main.o
AppCode
LoggerLib
Compiler
version / macros
Linker
OldAppCode
LoggerLib
Compiler
version / macros
Backward Compatibility
# Slide 33Detour: But what about AI?
Summary
Generate "MyTypeSerializer" class in a header (you can add .cpp file if needed), based on "MyType.h" which provide "serialize" and "deserialize" methods for "MyType", turning it into bytes buffer and back into a "MyType" class.
# Slide 34Detour: But what about AI?
Summary
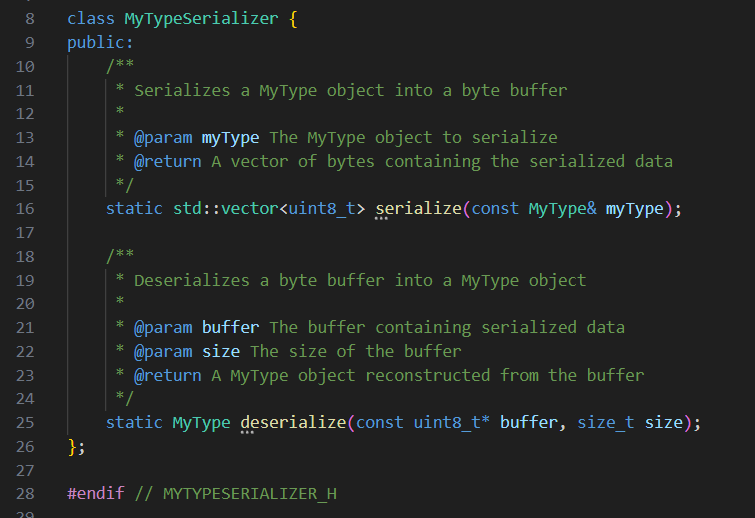
# Slide 35Detour: But what about AI?
Summary
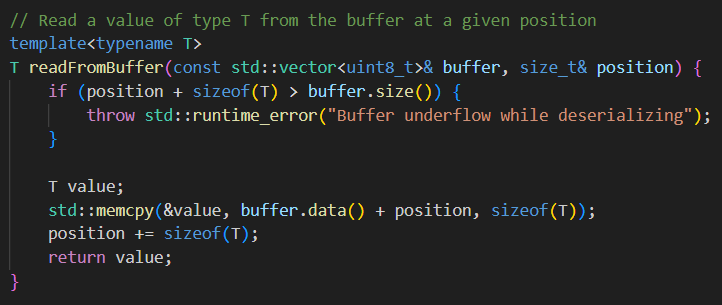
# Slide 36Detour: But what about AI?
Summary
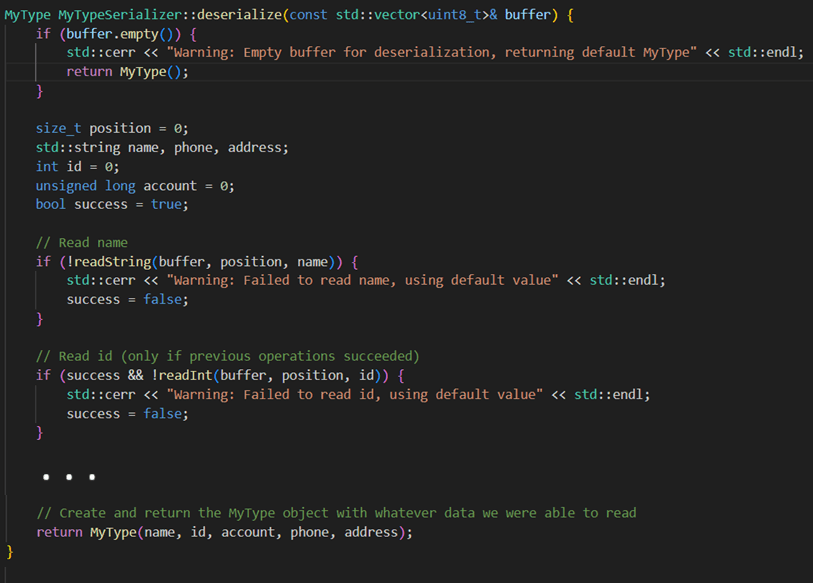
# Slide 37Detour: But what about AI?
Summary
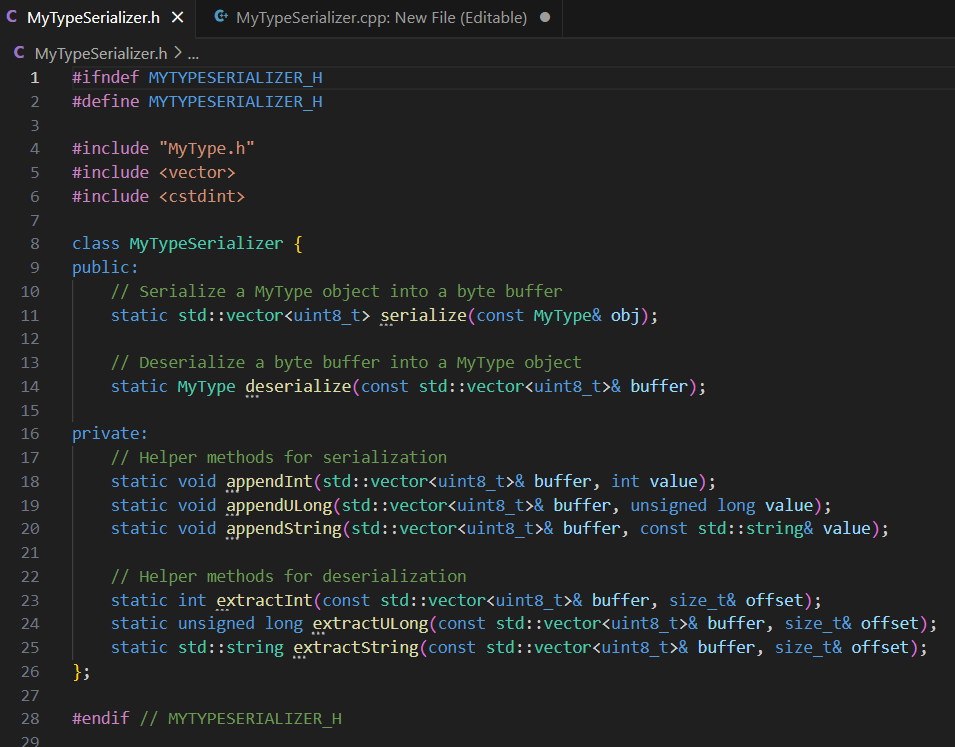
# Slide 38Detour: But what about AI?
- The process of LLMs is non-deterministic
- There is wide veriaty in outputs
- Giving examples or defining the template works better
- There are no guarantees between executions
Summary
Disclaimer: as of now...
# Slide 39Detour: But what about "Rust"?
Rust's toolkit:
Summary
- "procedural macros" - extend to inject code, pre-compiler
- "syn" - library for injecting tokens into the AST
| C++ | Rust | |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Functions & traits | Expend code / Token manipulation |
| Failure Outcome | Ill-formed / Compile | Compile |
| Error indication | constexpr exception | CT /RT / Tests |
- Apr 2023: a-plan-for-generic-compile-time-introspection-in-rust
- Jul 2024: First-class CT type manipulation: rfcs#3669
- March 2025: Reflect lib (source, crate, discussion)
# Slide 40What should we expect from "reflection libraries"?
Which guarantees we provide:
- No compatibility between standard versions
- No guarantees for existing code
Possible outcomes of "breaking the contract"
- Program is ill-formed (fails to compile)
- Program contains UB (undefined behavior)
Summary
Errors at compile time:
- Should indicate to "reflection" stage (NOT "old" compilation)
- Throw constexpr exceptions (Thanks to Hana Dusíková!)
- Warnings?
# Slide 41Reflection Libraries
Which "reflection libs" should go into the standard library?
Would love your input!
-
P3157R0: Generative Extensions for Reflection
(Andrei Alexandrescu, Bryce Lelbach, Michael Garland) - P3095R0: ABI comparison with reflection (Saksham Sharma)
- P2996's Implementation (Bloomberg)
- Comparing AI models (suggested uses)
- ACCU 2025: Crafting the code you dont write: sculpting software in an AI world (Daisy Hollman)
More info:
What's Next?
# Slide 42C++ 26 Reflection
How will Reflection impact our code bases?
Summary
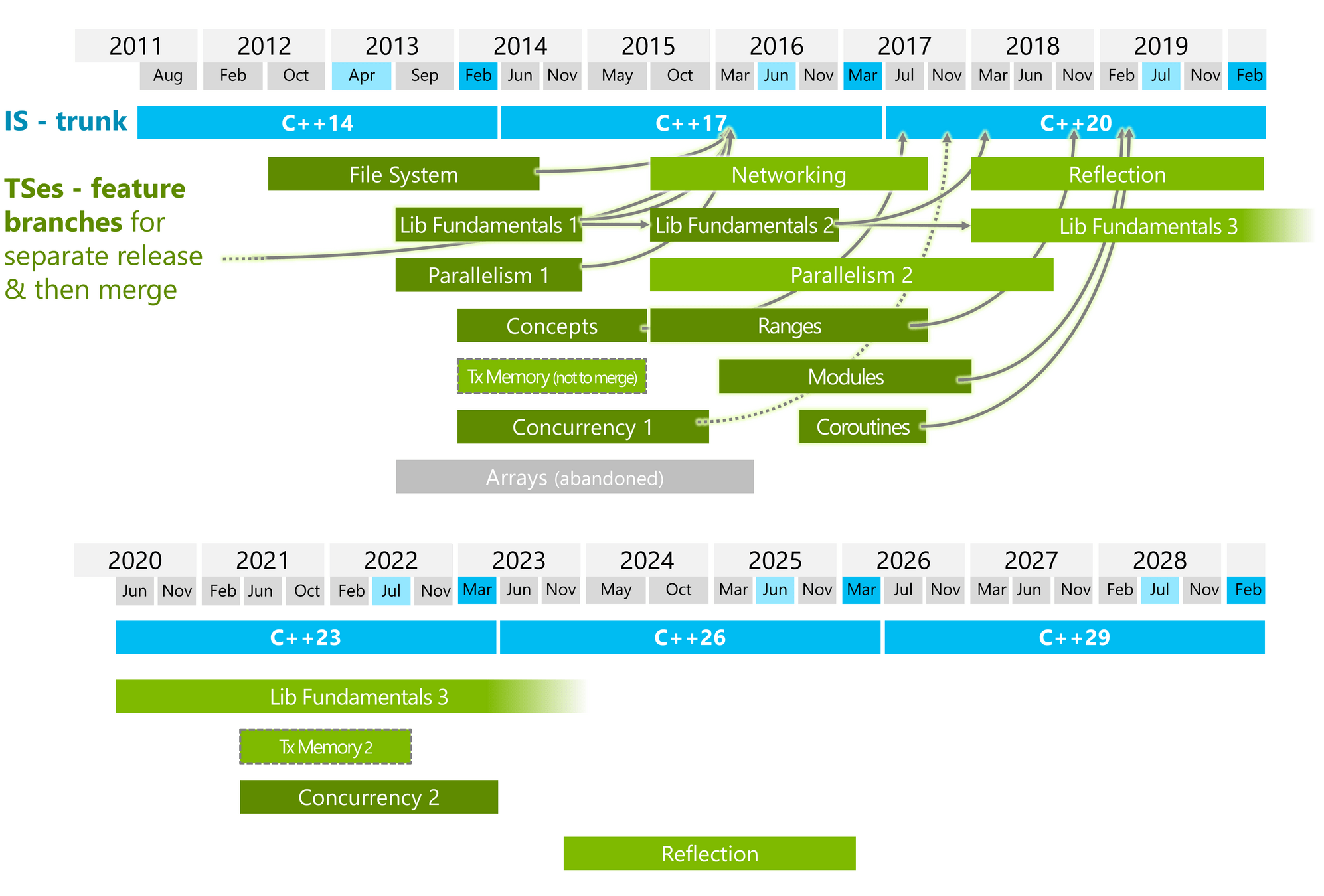

From: https://isocpp.org/std/status (by Herb Sutter)
# Slide 43Thank you!
Inbal Levi
sinbal2lextra@gmail.com
linkedin.com/in/inballevi/
Thank you!
Stay in touch!
Thanks to:
- CoreC++ user group
- Hana Dusíková (SG7 chair)
- Matus Chochlik
- David Sankel
- Corentin Jabot
- Lewis Baker
- Adi Shavit
Thank you for being passionate about C++!
-
Reflection Papers' authors!
Wyatt Childers, Peter Dimov, Dan Katz, Barry Revzin, Andrew Sutton, Faisal Vali, Daveed Vandevoorde, Matus Chochlik, Herb Sutter, Bjarne Stroustrup, David Sankel, Axel Naumann, Andrei Alexandrescu, Bryce Lelbach, Michael Garland, Louis Dionne, Adam Lach, Jagrut Dave, Walter Genovese, Saksham Sharma

Welcome to v1.0 of the meta::[[verse]] - CppCon
By Inbal Levi
Welcome to v1.0 of the meta::[[verse]] - CppCon
- 167



