JavaEE workshop #7
Viktor Martiš
(spring-mvc, E2E testy)

Previous workshop
- IDEA shortcut: Alt + insert, Ctrl +J
- Adapter pattern
- Proxing in spring framework
- AOP
- Transactions in detail
- Mockito
Contents
- IDEA shortcut: Ctrl + D, Ctrl + Y
- Facade pattern
- Spring MVC
- E2E testing
IDEA shortcut
-
IDEA shortcut: Ctrl + D, Ctrl + Y
- duplicate, delete
- provides a simplified interface
Web applications
- Server side rendering
- client-server
- server is responsible for render HTML pages
- Simple page application
- used in our courses
- server exposes REST API
- client side is javascript application
- client is responsible for view rendering and view routing
Spring MVC - Introduction
- designed around a DispatcherServlet that dispatches requests to handlers, with configurable handler mappings, view resolution, locale, time zone and theme resolution as well as support for uploading files
- handler is based on the @Controller and @RequestMapping
- @Controller mechanism also allows you to create RESTful Web sites and applications, through the @PathVariable
Spring MVC
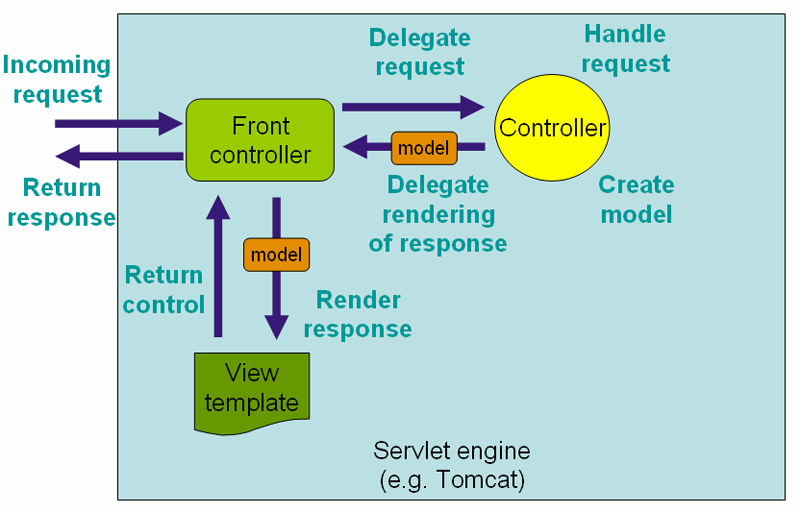
DispatcherServlet registration
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/example/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>DispatcherServlet registration
- In a Servlet 3.0+ environment
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration =
container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet());
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/example/*");
}
}Spring MVC
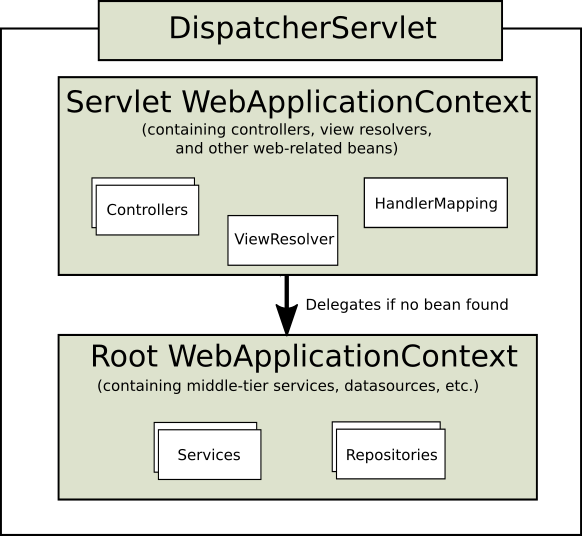
- each DispatcherServlet has its own WebApplicationContext, which inherits all the beans already defined in the root WebApplicationContext
Spring MVC configuration
- AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer or AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer (initialized by SpringServletContainerInitializer)
- @EnableWebMvc
- WebMvcConfigurerAdapter
- Separated context configuration
- controllers and some other MVC required beans
Special Bean Types
| HandlerMapping | Maps incoming requests to handlers and a list of pre- and post-processors (handler interceptors) based on some criteria the details of which vary by HandlerMapping implementation. The most popular implementation supports annotated controllers but other implementations exists as well. |
| HandlerAdapter | Helps the DispatcherServlet to invoke a handler mapped to a request regardless of the handler is actually invoked. For example, invoking an annotated controller requires resolving various annotations. Thus the main purpose of a HandlerAdapter is to shield the DispatcherServlet from such details. |
| HandlerExceptionResolver | Maps exceptions to views also allowing for more complex exception handling code. |
Special Bean Types
| ViewResolver | Resolves logical String-based view names to actual View types. |
| LocaleResolver & LocaleContextResolver | Resolves the locale a client is using and possibly their time zone, in order to be able to offer internationalized views |
| ThemeResolver | Resolves themes your web application can use, for example, to offer personalized layouts |
| MultipartResolver | Parses multi-part requests for example to support processing file uploads from HTML forms. |
| FlashMapManager | Stores and retrieves the "input" and the "output" FlashMap that can be used to pass attributes from one request to another, usually across a redirect. |
Controllers
- provide access to the application behavior that you typically define through a service interface
- interpret user input and transform it into a model that is represented to the user by the view
- uses annotations such as @RequestMapping, @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute, ...
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping("/helloWorld")
public String helloWorld(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello World!");
return "helloWorld";
}
}@RequestMapping
- URI Template Patterns - access to selected parts of a URL
- When a @PathVariable annotation is used on a Map<String, String> argument, the map is populated with all URI template variables.
- Regulal expressions support
- Ant-style path patterns (for example, /myPath/*.do)
@RequestMapping(path="/owners/{ownerId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String findOwner(@PathVariable String ownerId, Model model) {
Owner owner = ownerService.findOwner(ownerId);
model.addAttribute("owner", owner);
return "displayOwner";
}
@RequestMapping("/spring-web/{symbolicName:[a-z-]+}-{version:\\d\\.\\d\\.\\d}{extension:\\.[a-z]+}")
public void handle(@PathVariable String version, @PathVariable String extension) {
// ...
}
}| ServletRequest or HttpServletRequest | Request or response objects (Servlet API). |
| java.util.Locale | current request locale |
| java.io.InputStream / java.io.Reader | access to the request’s content. |
| ava.io.OutputStream / java.io.Writer | aw OutputStream/Writer as exposed by the Servlet API. |
| java.security.Principal | containing the currently authenticated user. |
| @PathVariable | annotated parameters for access to URI template variables. |
| @RequestParam | specific Servlet request parameters |
| @RequestHeader | specific Servlet request HTTP headers |
| @RequestBody | HTTP request body |
| java.util.Map / org.springframework.ui.Model / org.springframework.ui.ModelMap | model that is exposed to the web view |
| org.springframework.validation.Errors / org.springframework.validation.BindingResult | validation results for a preceding command or form object |
| java.security.Principal | containing the currently authenticated user. |
| ... | ... |
| ModelAndView | object, with the model implicitly enriched with command objects and the results of @ModelAttribute annotated reference data accessor methods. |
| Model | object, with the view name implicitly determined through a RequestToViewNameTranslator and the model implicitly enriched with command objects and the results of @ModelAttribute annotated reference data accessor methods. |
| Map | object for exposing a model, with the view name implicitly determined through a RequestToViewNameTranslator and the model implicitly enriched with command objects and the results of @ModelAttribute annotated reference data accessor methods. |
| View | object, with the model implicitly determined through command objects and @ModelAttribute annotated reference data accessor methods. The handler method may also programmatically enrich the model by declaring a Model argument (see above). |
| String | value that is interpreted as the logical view name, with the model implicitly determined through command objects and @ModelAttribute annotated reference data accessor methods. The handler method may also programmatically enrich the model by declaring a Model argument (see above). |
| ... | ... |
@RequestParam
- bind request parameters to a method parameter in your controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/pets")
@SessionAttributes("pet")
public class EditPetForm {
// ...
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String setupForm(@RequestParam("petId") int petId, ModelMap model) {
Pet pet = this.clinic.loadPet(petId);
model.addAttribute("pet", pet);
return "petForm";
}
// ...
}- indicates that a method parameter should be bound to the value of the HTTP request body
@RequestMapping(path = "/something", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public void handle(@RequestBody String body, Writer writer) throws IOException {
writer.write(body);
}- indicates that the return type should be written straight to the HTTP response body
@RequestMapping(path = "/something", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String helloWorld() {
return "Hello World";
}- very common use case to have Controllers implement a REST API, thus serving only JSON, XML or custom MediaType content
- combines @ResponseBody and @Controller
- result of data binding there may be errors such as missing required fields or type conversion errors
- to check for such errors add a BindingResult argument immediately following the @ModelAttribute argument
Data binding
@RequestMapping(path = "/owners/{ownerId}/pets/{petId}/edit", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String processSubmit(@ModelAttribute("pet") Pet pet, BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "petForm";
}
// ...
}Data binding
@RequestMapping(path = "/owners/{ownerId}/pets/{petId}/edit", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String processSubmit(@Valid @ModelAttribute("pet") Pet pet, BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "petForm";
}
// ...
}- validation invoked automatically by adding the JSR-303 @Valid annotation
- allows you to configure web data binding directly within your controller class
- initialize the WebDataBinder that will be used to populate command and form object arguments of annotated handler methods
- support all arguments that @RequestMapping supports, except for command/form objects and corresponding validation result objects
@Controller
public class MyFormController {
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder) {
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
dateFormat.setLenient(false);
binder.registerCustomEditor(Date.class, new CustomDateEditor(dateFormat, false));
}
// ...
}- filter contextually the object that will be serialized to the HTTP response body
- @JsonView - specifying the view class or interface to be used
@RestController
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/user", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@JsonView(User.WithoutPasswordView.class)
public User getUser() {
return new User("eric", "7!jd#h23");
}
}
public class User {
public interface WithoutPasswordView {};
public interface WithPasswordView extends WithoutPasswordView {};
private String username;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
@JsonView(WithoutPasswordView.class)
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
@JsonView(WithPasswordView.class)
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
}- Servlet 3 based asynchronous request processing
- instead of returning a value method can now return a java.util.concurrent.Callable
- Spring MVC invokes the Callable in a separate thread with the help of a TaskExecutor and when the Callable returns, the request is dispatched back to the Servlet container to resume processing using the value returned by the Callable.
@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.POST)
public Callable<String> processUpload(final MultipartFile file) {
return new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
// ...
return "someView";
}
};
}- ResponseBodyEmitter return value type which can be used to send multiple Objects
@RequestMapping("/events")
public ResponseBodyEmitter handle() {
ResponseBodyEmitter emitter = new ResponseBodyEmitter();
// Save the emitter somewhere..
return emitter;
}
// In some other thread
emitter.send("Hello once");
// and again later on
emitter.send("Hello again");
// and done at some point
emitter.complete();- write result directly to the response OutputStream
- by StreamingResponseBody return value type
@RequestMapping("/download")
public StreamingResponseBody handle() {
return new StreamingResponseBody() {
@Override
public void writeTo(OutputStream outputStream) throws IOException {
// write...
}
};
}- enable with MultipartResolver
<bean id="multipartResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!-- one of the properties available; the maximum file size in bytes -->
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="100000"/>
</bean>@Controller
public class FileUploadController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/form", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String handleFormUpload(@RequestParam("name") String name,
@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
if (!file.isEmpty()) {
byte[] bytes = file.getBytes();
// store the bytes somewhere
return "redirect:uploadSuccess";
}
return "redirect:uploadFailure";
}
}- HandlerExceptionResolver implementations deal with unexpected exceptions that occur during controller execution.
- @ExceptionHandler method for array of Exception types
- @ControllerAdvice - global configuration of excetption handlers
@Controller
public class SimpleController {
// @RequestMapping methods omitted ...
@ExceptionHandler(IOException.class)
public ResponseEntity<String> handleIOException(IOException ex) {
// prepare responseEntity
return responseEntity;
}
}Spring MVC testing
Q&A
ITA-04-JavaEE, Workshop 7
By IT-absolvent
ITA-04-JavaEE, Workshop 7
Workshop #7
- 478



