Intro to React
Joel Ross
Getting Started with React
Joel Ross
-
Dynamically generate and interact with the DOM
-
Organize the DOM into User Interface "Components" for easy page design
-
Efficiently make changes to the rendered DOM

Ethical Consumption of Libraries?



Transpiling with Vite
React uses a language (JSX) that is not actually valid JavaScript. So we will need to "translate" it into real JavaScript, called transpiling.
There are a number of tools that can do this work; we'll be using a build tool called Vite.js

Vite Dev Server
Vite provides a development server which will:
- Automatically transpile React code into pure JavaScript
- Manage module dependencies, including external libraries
- Show build and syntax errors in the console
- Automatically reload the page (replaces live-server)!
# Make sure you are in the project directory
cd path/to/project
# Install dependencies for existing project (installs vite)
npm install
# Run the development server script
npm run dev -- --hostsome Windows machines
JSX
Joel Ross
Creating DOM Elements
//DOM - element to show
const msgElem = document.createElement('h1');
msgElem.id = 'hello';
msgElem.classList.add('myClass');
msgElem.textContent = 'Hello World!';
//show the content in the web page
//(inside #root)
document.getElementById('root').appendChild(msgElem);

Hello React
//React - element to show
const msgElem = React.createElement(
//html tag
'h1',
//object of attributes
{ id: 'hello', className: 'myClass' },
//content
'Hello World!'
);
//Create a "React root" out of the `#root` elemment
//then render the React element at that root
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(msgElem)can't use "class" since a keyword
React can be used to create and render DOM elements.
React v18 (March 2022)
JSX
An XML syntax extension for the JavaScript language. You define React elements in a way that looks like HTML!
//JSX - element to show
const msgElem = <h1 id="hello" className="myclass">Hello World</h1>;
//Create a "React root" out of the `#root` elemment
//then render the React element at that root
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(msgElem)shortcut syntax for React.createElement()

Transpiling

JSX
JS
JSX
JSX
JS
JS
CSS
JPG
CSS
JS
CSS
JPG
JPG
combined
minimized
compressed
etc.
JSX
Elements defined using JSX can include children.
const headerElem = (
<header>
<h1>Hello world!</h1>
<p>This is a fine demo</p>
</header>
);
//values need to have a "single" parent
const invalidCode = (
<p>First sentence</p>
<p>Second sentence</p>
)
const validCode = (
<> {/* a fragment: a parent that won't be rendered */}
<p>First sentence</p>
<p>Second sentence</p>
</>
);use parentheses for JSX on multiple lines
a comment in JSX!
Inline Expressions
Use {} to include JavaScript expressions in the JSX. These expressions will be evaluated and inserted into the element's "HTML".
//Can include JavaScript expressions in React elements
const message = "Hello world!";
const element = <h1>{message}</h1>;
//Can include arbitrary expressions
const element = (
<p>
A leap year has {(365 + 1) * 24 * 60} minutes!
</p>
);
//Can use inline expressions in attributes
const imgUrl = 'path/to/my_picture.png';
const pic = <img src={imgUrl} alt="A picture" />;replace with expression (value)
React elements
must be closed
React: Components
Joel Ross
Components
React lets us describe the page in terms of UI components, instead of HTML elements.
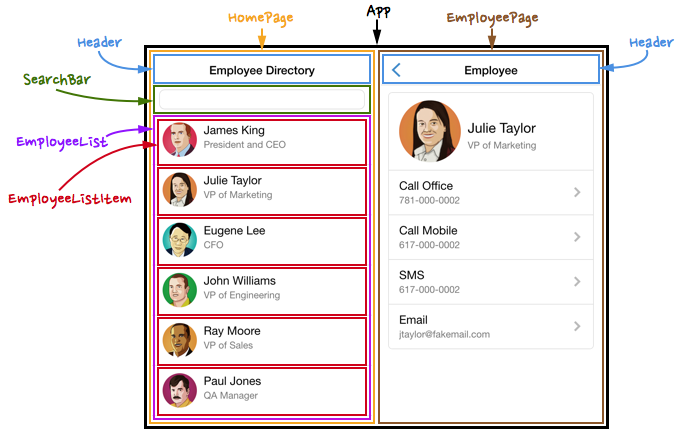
React lets us describe the page in terms of UI components, instead of HTML elements.
In effect, we will create our own XML Elements!
<App>
<HomePage>
<Header />
<SearchBar />
<EmployeeList>
<EmployeeListItem person="James King" />
<EmployeeListItem person="Julie Taylor" />
<EmployeeListItem person="Eugene Lee" />
</EmployList>
</HomePage>
<EmployeePage>
<Header />
...
</EmployeePage>
</App>
Components
React Components
We define components as functions that return the DOM elements to be rendered
//declare a function to define a component -- this is like a class
function HelloMessage(props) {
//this function returns the elements (JSX)
//that make up the component
return (
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
);
}
//"call" function to create a new element value!
const msgElem = <HelloMessage />;
//show the content in the web page (inside #root)
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(msgElem)what is rendered when
component is shown
our own HTML tags!
Capitalize!
NEVER CALL A COMPONENT FUNCTION WITH ()
ALWAYS RENDER AS A COMPONENT WITH <>
Composing Components
function HelloMessage(props) {
return <p>Hello World!</p>;
}
function GoodbyeMessage(props) {
return <p>See ya later!</p>;
}
function MessageList(props) {
return (
<div>
<HelloMessage /> {/* A HelloMessage component */}
<GoodbyeMessage /> {/* A GoodbyeMessage component */}
</div>
);
}
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(msgElem)Components can render other components ("call" functions to create new elements), and mix those with regular DOM elements
comments in JSX
Component Modules
Components are usually defined in separate modules (files), and then imported by modules that need to use them.
/*** in App.js ***/
//import from other components; HelloMessage.js, Messages.js, etc
import { HelloMessage } from './Messages.js'
//declare a function component
export default function App(props) {
return (
<HelloMessage /> {/* render imported Component */}
)
}/*** in index.js ***/
import App from './App.js' //default import
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<App />)React: Props
Joel Ross
Properties (props)
//Passing a prop called `message` with value "Hello property"
const messageA = <MessageItem message="Hello property!" />;
//A component can accept multiple props
//This component takes in a `name` prop as well as
//a `descriptor` prop
const userInfo = <UserInfo name="Ethel" descriptor="Aardvark" />;
//Passing a value as a prop using an inline expression
const secret = "Shave and a haircut";
const messageB = <MessageItem message={secret} />;We specify attributes for a component (called "props") when we instantiate a component by specifying the XML attributes (key-value).
Props are the "input parameters" into a component!
Properties (props)
function MessageItem(props) {
const message = props.message; //access the prop
//can use prop for logic or processing
const messageUpper = message.toUpperCase();
return <li>{messageUpper}</li>; //render based on prop
}
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'))
.render(<MessageItem message="Be quiet" />)Inside the Component function definition, all the passed in props are collected in as a single argument object (conventionally called props). This object is the collection of all of the attributes/arguments.
ALL props stored in this object
Properties (props)
//Pass an array as a prop!
const array = [1,2,3,4,5];
const suitcaseElem = <Suitcase luggageCombo={array} />;
//Pass a function as a prop (like a callback)!
function sayHello() {
console.log('Hello world!');
}
const greetingElem = <Greeting callback={sayHello} />;Importantly, props can be any kind of variable! This includes arrays, objects and functions
Props and Composition
function MessageList(props) {
//msgComponents will be an array of components!
const msgComponents = props.messages.map((msgStr) => {
const elem = <MessageItem message={msgStr} key={msgStr} />; //pass prop down!
return elem
}
return (
<ul>
{/* An array of components renders as siblings */}
{msgComponents}
</ul>
);
}
const messagesArray = ["Hello world", "No borders", "Go huskies!"];
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'))
.render(<MessageList messages={messagesArray} />)Props will often need to be "passed down" to child components. A common pattern is to map an array of prop values to an array of children components to render!
unique "id" for the element
info340-react-intro
By Joel Ross
info340-react-intro
- 676



