CSS Properties & Flexbox
Joel Ross
Autumn 2024
View of the Day
-
Q & A
-
CSS Class Semantics (lecture)
-
CSS Properties (demos)
-
Fonts
-
Box Model
-
Flexbox
-
This Week in Git Etiquette News


Updating Lecture Code
# switch to starter branch to get new starter code
git checkout starter
# download new starter code
git pull
# switch back to main branch for coding
git checkout main
# merge in new starter code (use default msg)
git merge starter --no-edit
# code and enjoy!Get the starter code from the starter branch, but do all of your work on main.
Q&A
CSS Class Names
There are only two hard problems in computer science: cache invalidation and naming things - Phil Karlton
CSS Class Names
Goals when naming classes (or anything):
-
Understandability: explain what kind of styling is being applied
-
Modifiability: make it easier to change styling later
Semantic Class Names
Name CSS classes based on the semantic meaning (purpose) of the element they are styling.
<div class="forum-post">...</div>
<nav class="side-nav">...</div>
<img class="avatar-icon">...</div>
<article class="breaking-news">...</article>/* can use descendant selectors for more detail */
.forum-post img { ... }
.side-nav ul a { ... }Modular Class Names
Name CSS classes based on the (single) styling they apply. Combine multiple classes to style elements.
<div class="font-large text-red bg-secondary">...</div>
<img class="small rounded shadow">...</div>.font-large {
font-size: 2em;
line-height: 1.4em;
}
.bg-secondary { background: #bbb; }
img.small { width: 140px; }
.rounded { border-radius: 50%; }
A Naming Schema: BEM
<div class="block__element--modifier"><form class="form form--theme-xmas form--simple">
<input class="form__input" type="text">
<input
class="form__submit form__submit--disabled"
type="submit" />
</form>The "part" of the page
navbar
An element in that block
tab
Flags or types; differentiators
selected
<div class="navbar">
<div class="navbar__tab">A tab</div>
<div class="navbar__tab--selected">Selected Tab</div>
</div>Fonts
Fonts are installed "per computer", so not every computer has the same fonts (which is why you set a default with font-family).
Fonts are installed "per computer", so not every computer has the same fonts (which is why you set a default with font-family).
p {
font-family: 'Helvetica', 'Arial', sans-serif;
}Use this font
If first isn't available,
use this
If nothing else,
use this style of font-face
Generic Fonts
All fonts are categories in 1 of 5 different "categories", each of which has a generic style.
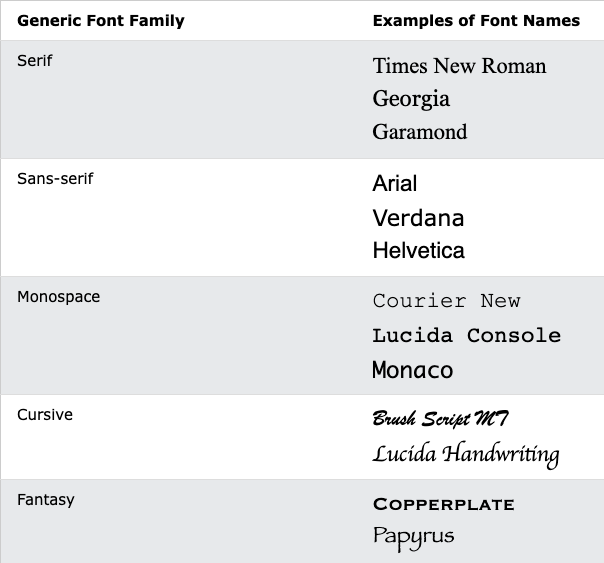
Serif vs. Sans-Serif

Research (roughly) suggests that sans-serif fonts are easier to read on screens, as well as more accessible for users with e.g., dyslexia.
Font Units
All browsers have a "default" font size--generally 16px. We use relative font sizing in case of variations.
Note that units are "measurement units" (think: inches)
| em | relative to the parent font size | By default 2em = 32px But if the parent's font-size was 20px, then 2em = 40px |
| rem | relative to the root (body's) font size of 16px | 2rem = 32px usually |
| % | relative to parent font size or dimension, can use for width or height | if parent width is 300px, then 50% = 150px |
| px | absolute measurement (do not use for fonts) | 16px = 16px |
It is also possible to specify an online font that the browser will download and display.
Fonts
Fonts are installed "per computer", so not every computer has the same fonts (which is why you set a default with font-family).
Fonts are installed "per computer", so not every computer has the same fonts (which is why you set a default with font-family).
p {
font-family: 'Helvetica', 'Arial', sans-serif;
}Use this font
If first isn't available,
use this
If nothing else,
use this style of font-face
Box Model
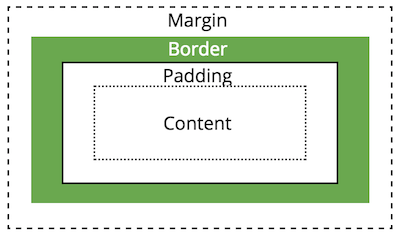
All HTML elements take up space on a page based on their "box size". You can manipulate the box model to change the size and appearance of the element
Display Property
You can customize whether an element is displayed as a block or inline element using the display property.
Choose elements based on their semantics, not their appearance!
/* <li> elements will be inline (an inline list!) */
li {
display: inline;
}display: inline-block
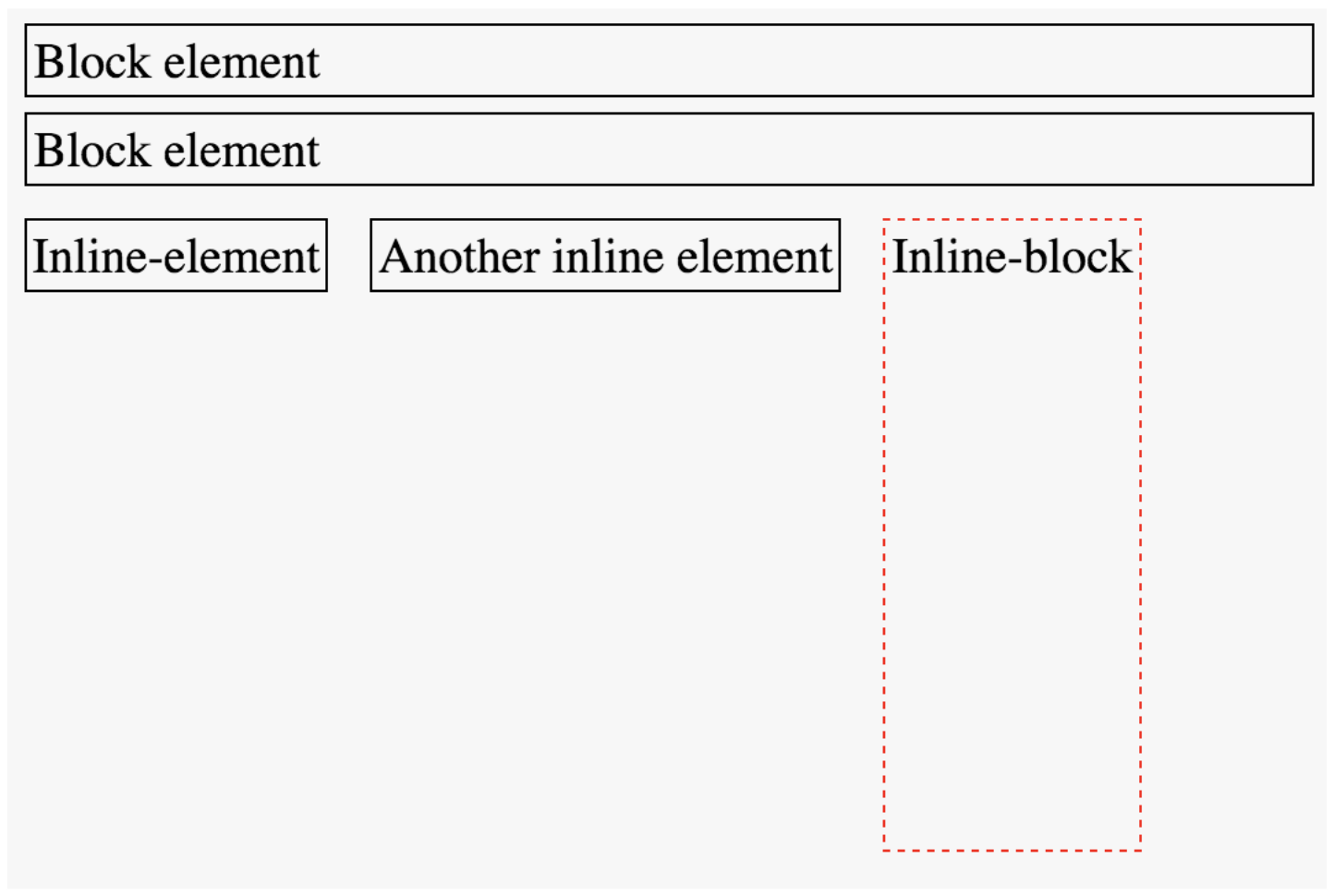
You cannot set the width or height of an inline element, but you can adjust the size of an inline-block element.
Position
You can use the position property to adjust where an element appears on the page from its normal layout. You will also need to set position adjustment values top, left, bottom, and/or right
/* position element 20px up and to the right
* of where it "normally" would be */
img.badge {
position: relative;
top: 20px;
right: 20px;
}LIMIT USE OF THE
position AND float
PROPERTIES!
Flexbox
A flexbox is an element that allows you to flexibly customize the layout of its children.
An element is made into a flexbox by giving it the display: flex CSS property.
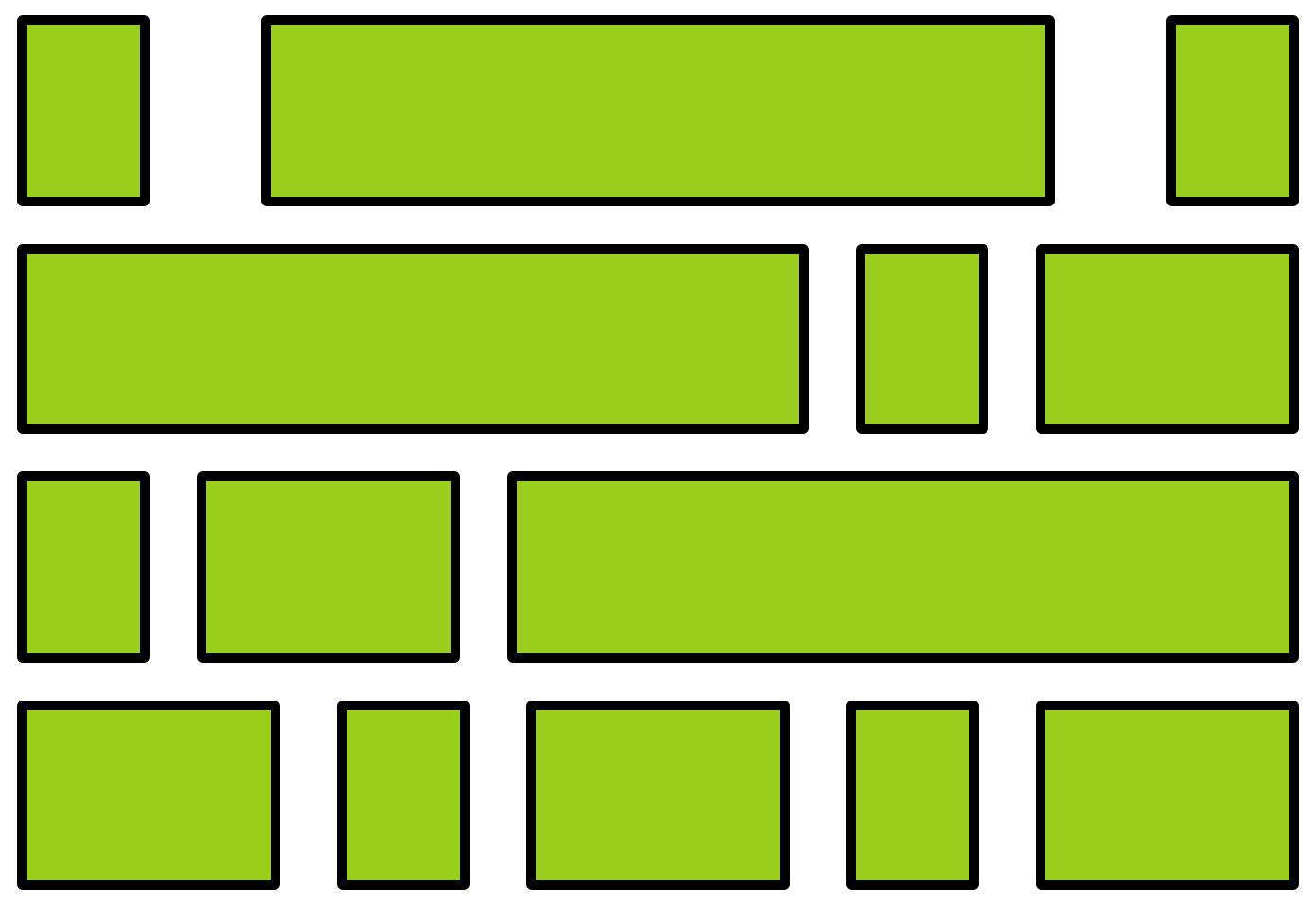
flexbox
child elements
Flexbox Properties
Customize the layout of the flexbox's children by given the flexbox additional CSS properties. For example:


flex-wrap
justify-content
Child Properties
You can also customize the children of the flexbox (the elements that are inside the box) by giving them additional CSS properties. For example:
flex-grow

Flexbox vs. Children
Don't get the flexbox (sometimes called the flex container) mixed up with the child elements (sometimes called the flex items) that are inside of it!
- The flexbox specifies how its children are positioned.
- The child elements specify how much space they should take up.
Nesting Flexboxes
A flexbox can contain other flexboxes inside of it!
That is: a child of a flexbox can itself be a flexbox (specifying how its children are positioned).
But a flexbox only influences its children, not its grandchildren! A flexbox lays out its child boxes; what happens inside those boxes is their own business.
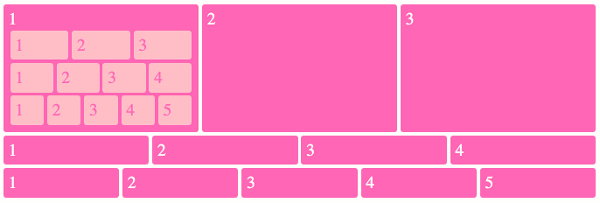
Using Flexboxes
Flexboxes are great solutions for:
- Centering block elements (use justify-content)
- Creating "columns" for a page"
- Making an element fill a space larger than its content (use flex-grow)
- ... and more!
Flexboxes are not great solutions for:
- Having block elements stack on top of each other (just use normal elements!)
- Adding specific spacing between elements (use margin/padding)
- ... doing anything else that the browser does by default!
Action Items!
Complete task list for Week 3 (all items!)
Read: Chapter 8 AND 9 for next week
Problem Set 03 due Friday
Project Proposal due Friday
Next: Responsive Design; Media Queries; Bootstrap
info340au24-css-flexbox
By Joel Ross
info340au24-css-flexbox
- 841



