COMP2511
Week 2
TUESDAY 1PM - 4PM (T13B)
Today
- Some VSCode, GitLab, Git tips
- Classes
- Commenting & Documentation
- Basic Inheritance
- Access Modifiers
VSCode Config Tips
Ensure that you open the correct folder
example: cs2511-project
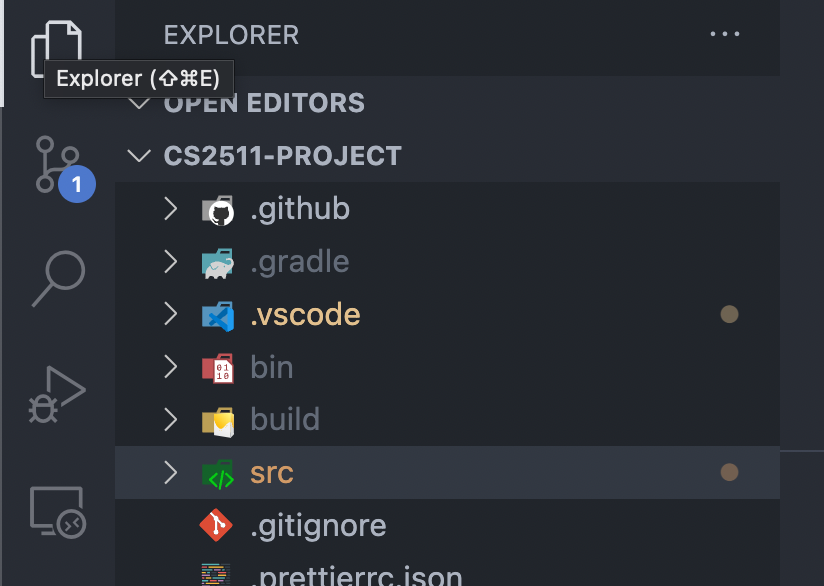
Good
Bad
Name of folder open
The folder I want to actually open
VSCode Config Tips
Ensure you have the correct Java extension installed
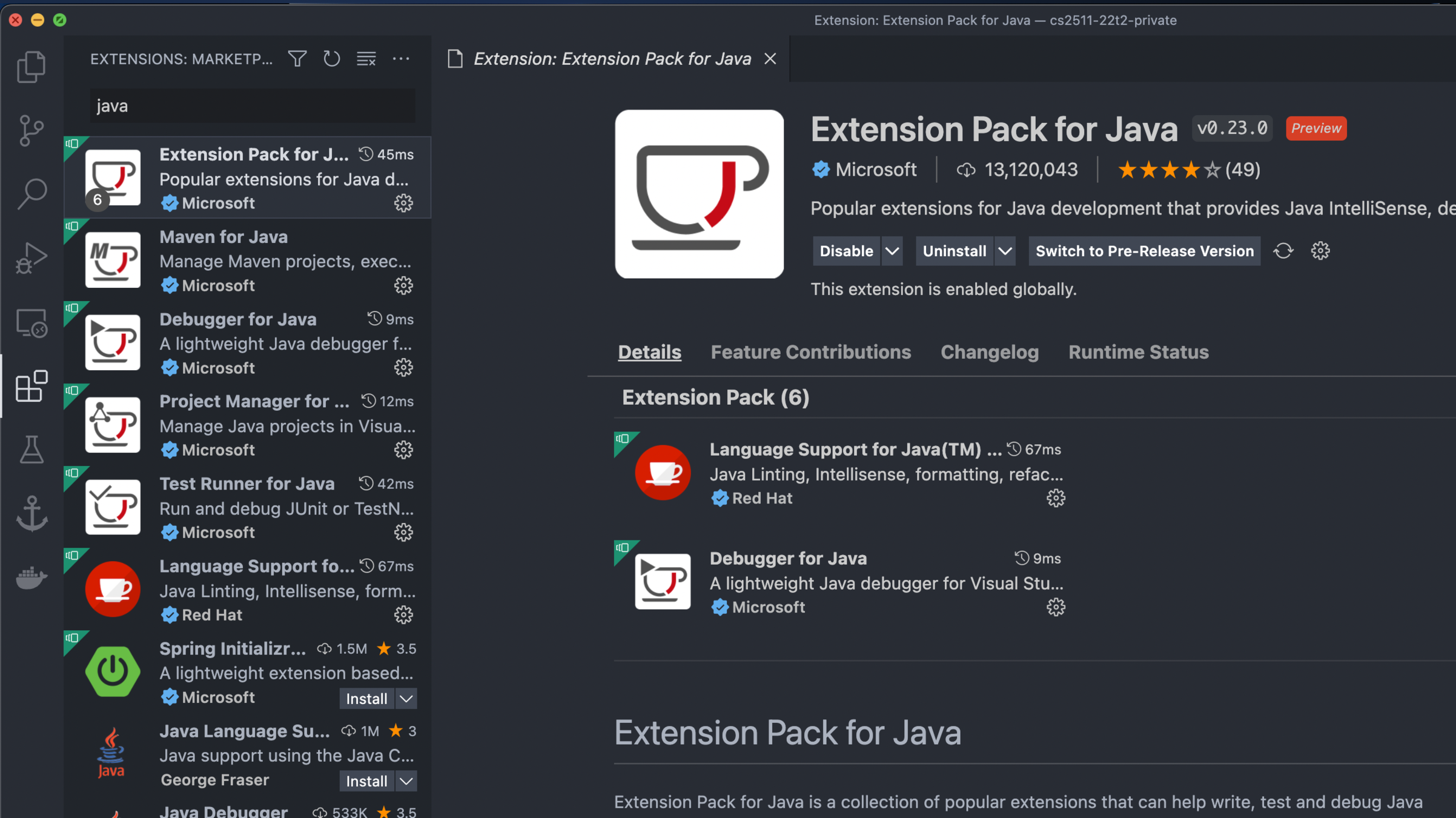
VSCode Config Tips
Ensure you have the correct Java extension installed

VSCode Config Tips
Ensure that you are running code using the "Run" button
GitLab Tips
How to view pipeline output
GitLab Tips
How to view pipeline output

GitLab Tips
How to view pipeline output

Test File
How to view pipeline output
#!/bin/bash
function run_junit() {
exercise=$1
rm -rf bin/$exercise
javac -d bin -cp "$JUNIT" $(find src/$exercise -name "*.java")
java -jar "$JUNIT" -cp bin:src/$exercise --scan-class-path --disable-ansi-colors --disable-banner 2>&1
}
cd src
# Average
javac average/Average.java || exit 1
diff <(java average/Average) <(echo "The average is 3.5") || exit 1
# Splitter
javac splitter/Splitter.java || exit 1
diff <(java splitter/Splitter <<< "Welcome to my humble abode") <(printf "Enter a message: \nWelcome\nto\nmy\nhumble\nabode\n") || exit 1
# Satellite
javac satellite/Satellite.java || exit 1
diff <(java satellite/Satellite) <(printf "I am Satellite A at position 122.0 degrees, 10000 km above the centre of the earth and moving at a velocity of 55.0 metres per second\n2.129301687433082\n0.04303052592865024\n4380.0\n") || exit 1
cd ..
JUNIT="lib/junit-platform-console-standalone-1.7.0-M1.jar"- Compares the difference between your output and what is expected
- Runs test in order. Average -> splitter -> satellite
- No output == good
Test File

- The '-' (minus) line is your output
- The '+' (plus) line is expected
Git Config
When you commit something, you are effectively saving the staged files as a new snapshot and signing it with your name and email.
You have to configure your git identity if you haven't done it before
git config --global user.name "Your Name Here"
git config --global user.email "z555555@unsw.edu.au"You then can add whatever email you have set in user.email on GitLab, so that it recognises all the commits that have been pushed to GitLab.
Please do this, its important Git etiquette
Code Review
Code Review
package shapes;
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color);
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String name, int width, int height) {
this(name);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}- What is the difference between
superandthis?-
superrefers to the immediate parent class whereasthisrefers to the current class
-
- What about
super(...)andthis(...)?-
super()acts as a parent class constructor and should be the first line in a child class constructor -
this()acts as a current class constructor (can be used for method overloading)
-
Code Review
package shapes;
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color); // => Calling constructor of parent `Shape(String color)`
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String name, int width, int height) {
this(name); // => Calling constructor `Rectangle(String color)`
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Rectangle(3 arguments) => Rectangle(1 argument) => Shape(1 argument)
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}- What is the difference between
superandthis?-
superrefers to the immediate parent class whereasthisrefers to the current class
-
- What about
super(...)andthis(...)?-
super()acts as a parent class constructor and should be the first line in a child class constructor -
this()acts as a current class constructor (can be used for method overloading)
-
Code Review
package circle;
public class Circle extends Object {
// Every class extends Object, it is not needed though
private static final double pi = 3.14159;
private int x, y;
private int r;
// Only 1 variable for all Circle objects
static int no_circles = 0;
public Circle() {
super(); // not needed
no_circles++;
}
public double circumference() {
return 2 * pi * r;
}
}What are static fields and methods?
Static fields are variables that are common and available to all instances of a Class. They belong to the Class, rather than an instance.
Methods are a block of code that perform a task. You can think of them as functions of a class.
Code Review
package circle;
public class Circle extends Object {
// Every class extends Object, it is not needed though
private static final double pi = 3.14159;
private int x, y;
private int r;
// Only 1 variable for all Circle objects
static int no_circles = 0;
public Circle() {
super(); // not needed
no_circles++;
}
public double circumference() {
return 2 * pi * r;
}
}What are static fields and methods?
Static fields are variables that are common and available to all instances of a Class
Methods are a block of code that perform a task. You can think of them as functions of a class.
What are static fields and methods?
Static fields are variables that are common and available to all instances of a Class.
Documentation
JavaDoc
Documentation
- Why is documentation important? When should you use it
- What does the term "self-documenting" code mean?
- Code that documents itself. It is readable inherently. Usually accomplished through variable name and function names
- When can comments be bad (code smell)?
- Comments become stale & does not get updated with new changes
- Possibly hinting that your design/code is too complex
Documentation
Single Line
// Single line commentMulti-line comment
/**
* This is multi-line
* documentation
*/JavaDoc
- JavaDoc is one way of documenting in Java.
- JavaDoc is a way of writing your comments
- It mainly targets class definitions and method/function definitions.
- in COMP2511, you will not have to use JavaDoc documentation unless asked.
JavaDoc
/**
* File class that stores content under a file name
*/
public class File {
/**
* Constructor used to create a file
* @param fileName the name of the file
* @param content contents of the file
*/
public File(String fileName, String content) {}
/**
* Constructor used to make a partial file when receiving a new file
* I.e., content.length() != fileSize with no compression
* @param fileName
* @param fileSize
*/
protected File(String fileName, int fileSize) {}
/**
* Checks if transfer has been completed
* @return true if it has been completed
*/
public boolean hasTransferBeenCompleted() {}
}Inheritance
Inheritance
What is it?
In Java, a class can inherit attributes and methods from another class. The class that inherits the properties is known as the sub-class or the child class. The class from which the properties are inherited is known as the superclass or the parent class.
Known as a "is-a" relationship
Code Demo
Employee.java & Manager.java
Code Demo
- Create a Employee class with a name and salary
- Create setters & getters with JavaDoc
- Create a Manager class that inherits Employee with a hireDate
- Override toString() method
Code Demo
The java extension packs come with some features you can use to generate boilerplate code
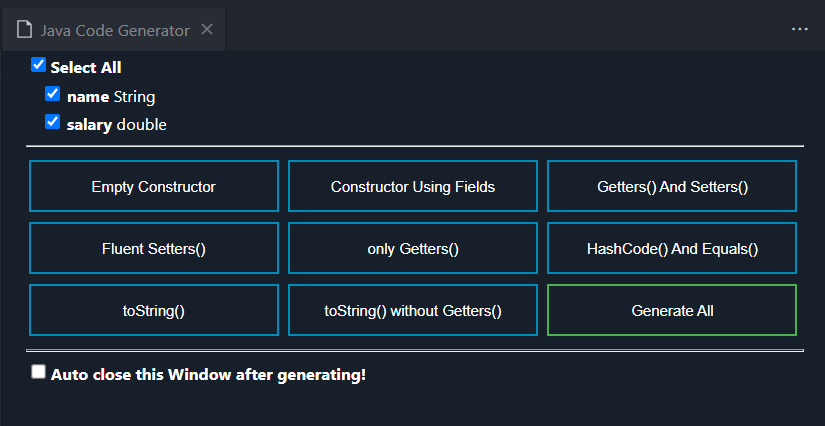
Code Demo
How many constructors does a class need?
Technically none. If a class is defined without a constructor, Java adds a default constructor
However, if a class needs attributes to be assigned (e.g., has a salary), then a constructor must be assigned
package employee;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class Employee {
private String name;
private double salary;
/**
* Creates an Employee with the given name and salary
* @param name The full name of the employee
* @param salary The employee's yearly salary
*/
public Employee(String name, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
/**
* Gets the name of the Employee
* @return full name of employee
*/
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
/**
* Sets the name of the Employee
* @param name new full name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return this.salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
}
package employee;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class Manager extends Employee {
private LocalDate hireDate;
/**
* Creates a manager with a given name, salary and hiring date
* @param name
* @param salary
* @param hireDate
*/
public Manager(String name, double salary, LocalDate hireDate) {
super(name, salary);
this.hireDate = hireDate;
}
public LocalDate getHireDate() {
return this.hireDate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + "[hireDate=" + hireDate + "]";
}
}
Access Modifiers
Access Modifiers
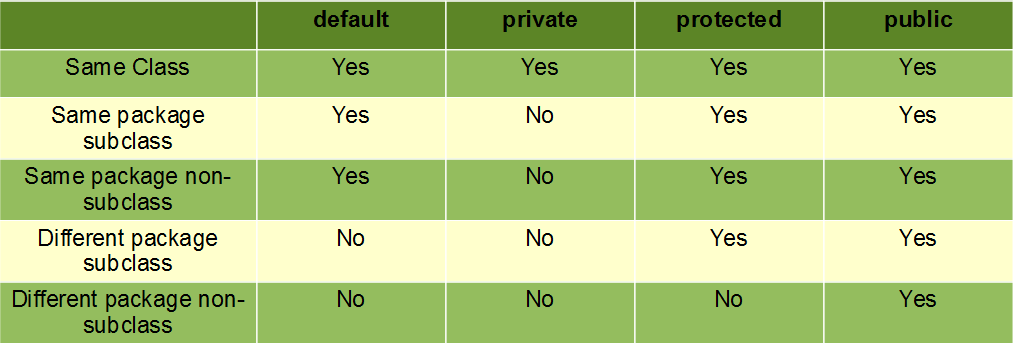
Private

It is accessible only to the same class (not including main). The most restrictive modifier.
Public

It is accessible to everything. The least restrictive modifier.
Protected

Can be accessed in the same package and in inheritance.
Default

The default access modifier is also called package-private, which means that all members are visible within the same package but aren't accessible from other packages
Attendance
Feedback

COMP2511 Week 2 22T3
By kuroson
COMP2511 Week 2 22T3
- 135



