Beam incident in TT40 transfer line at SPS
GROUP 9
Andrea Apollonio
Timmy Lensch
Taiee Liang
Andrea Santamaria
James Steimel
Newport Beach 2014

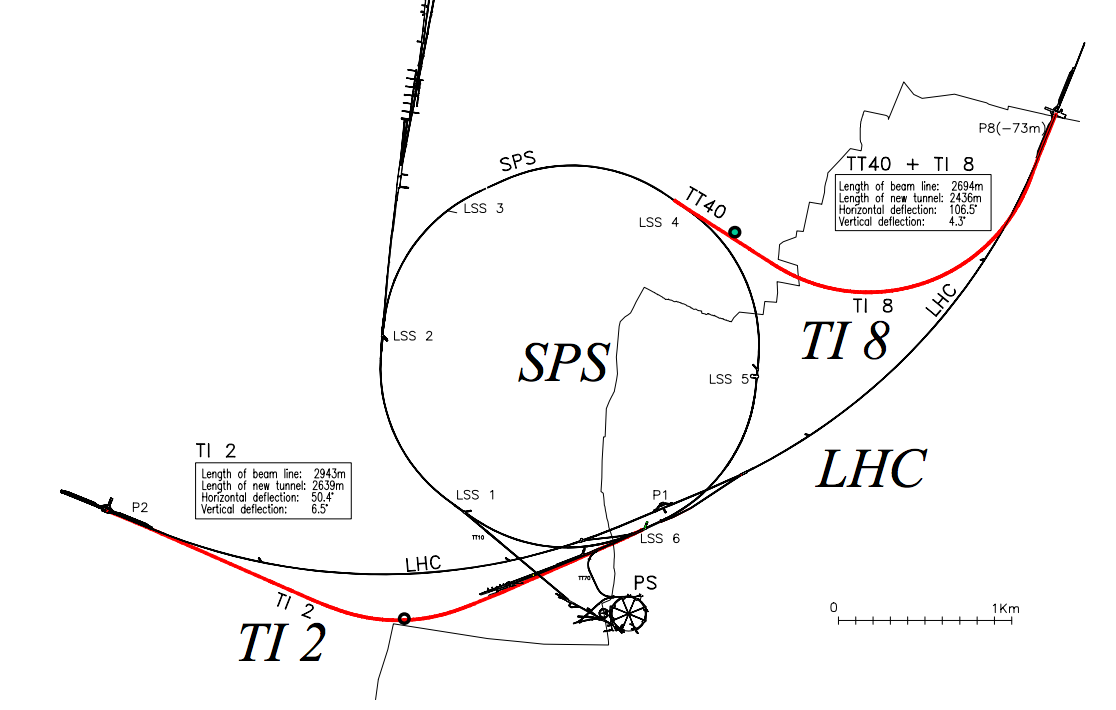
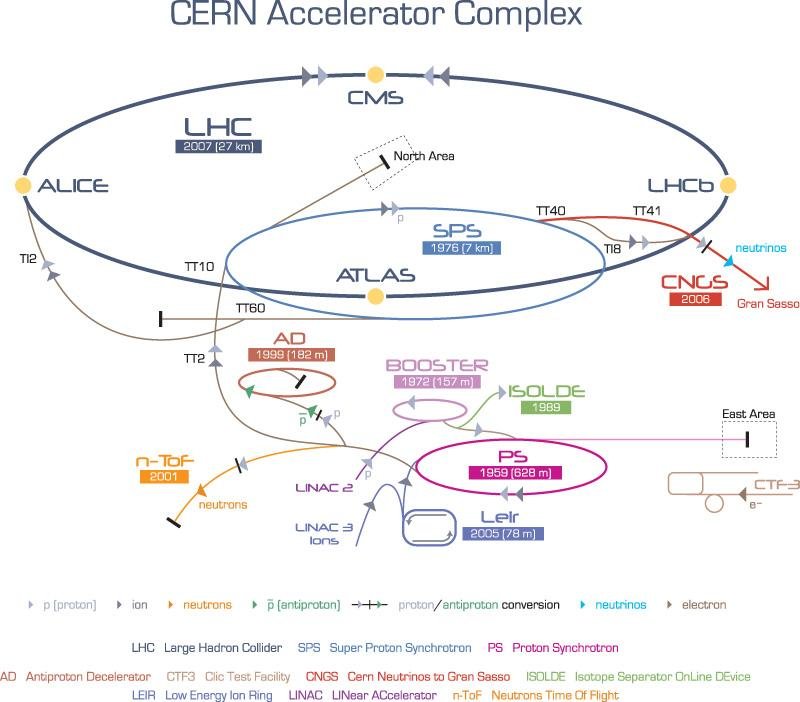
Brings 450 GeV proton beams and heavy ions from the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) to the Large Hadron Collider (LHC).
TT40 transfer line layout
TT40 transfer line setup
Septum
Kicker
Beam momentum (GeV/c)
Gap height (mm)
Max. current (kA)
Deflection (mrad)
450
20
24
2.25
450
32 to 35
2.56
0.48
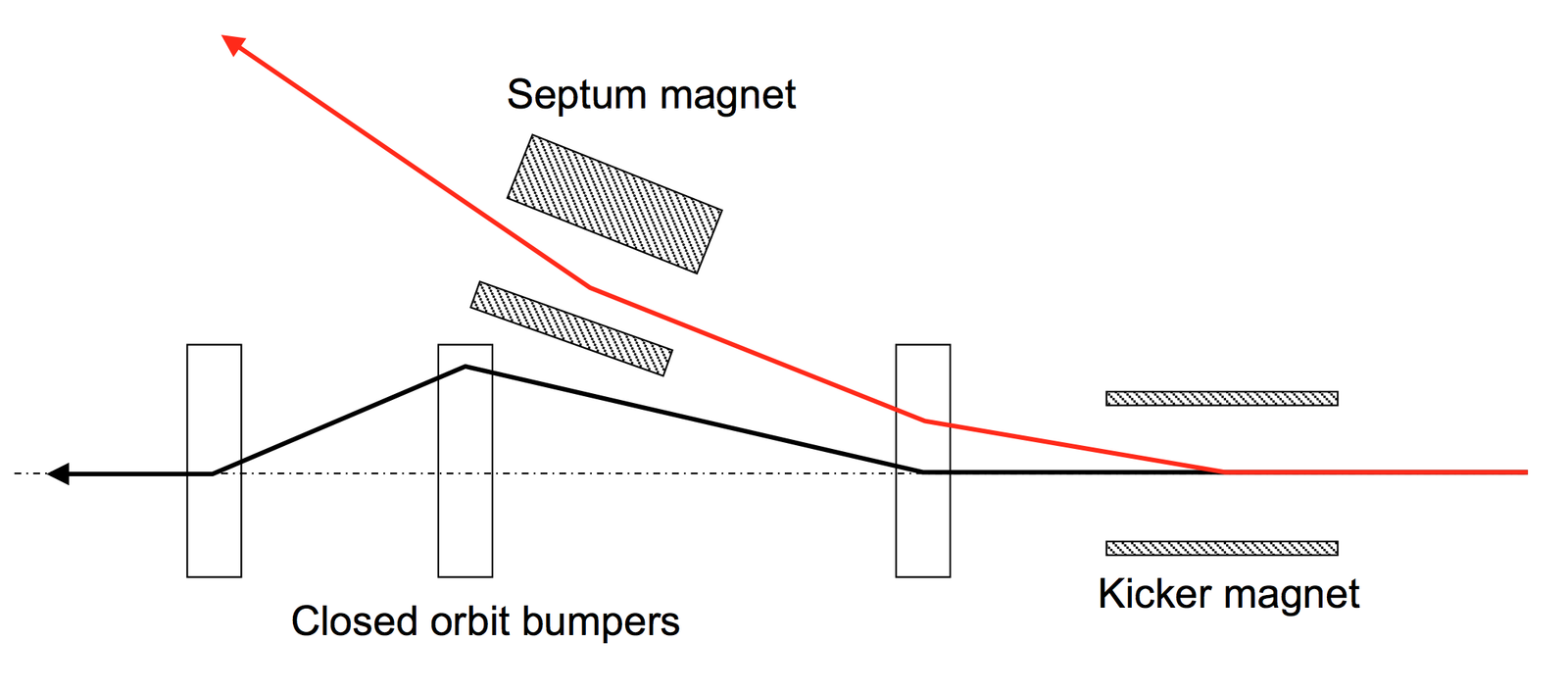

The incident
A beam was deflected into the aperture
Number of protons
Beam energy
Damage
- Vacuum chamber ripped open
- Damage in quadrupole coil
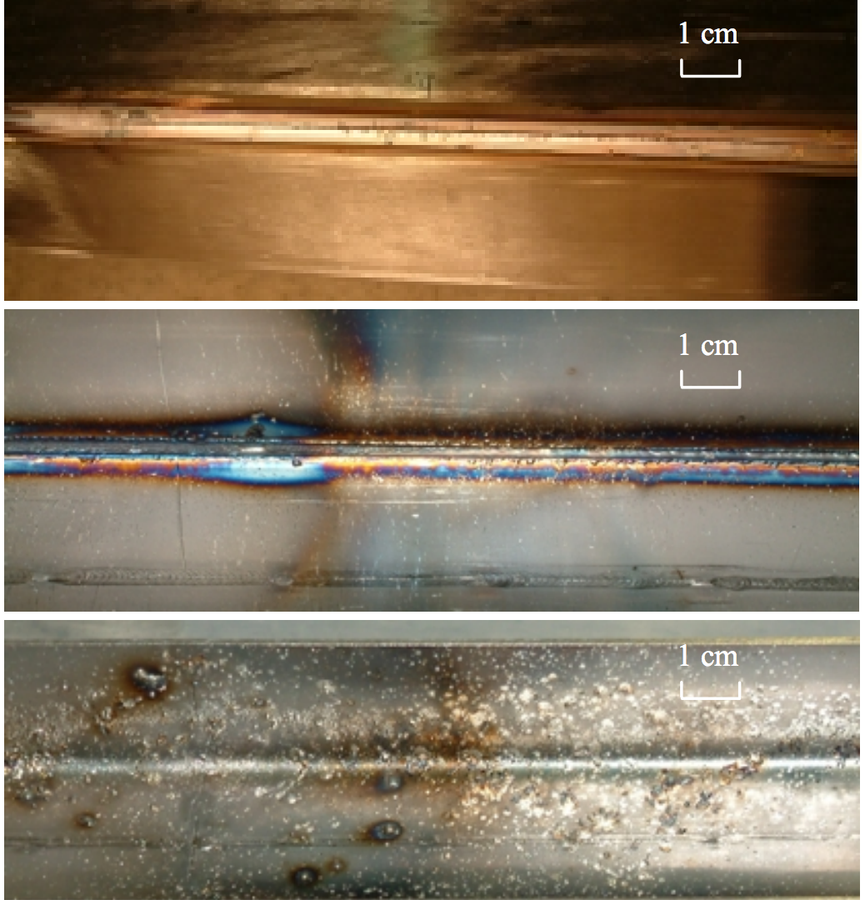
TRANSFER LINE DAMAGE DURING HIGH INTENSITY PROTON BEAM
EXTRACTION FROM THE SPS IN 2004 - B.Goddard (HB2006, Tsukuba, Japan)
The septum (MSE) tripped just before the extraction, and this was not seen by the interlock system in time.
Beam size
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp.sensor
Operators
Switch off PC
Temp. sensor
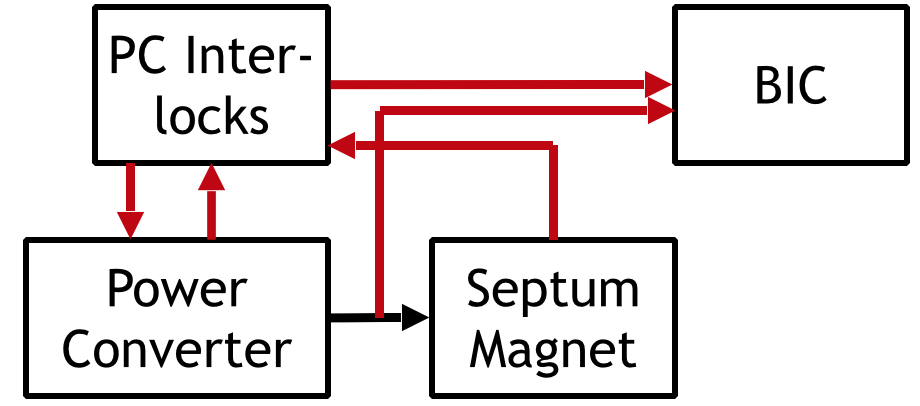
How the system works
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
Water
Interlock configuration
Signal is communicated after taking control actions
(...)
Beam
Switch off PC
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
What happened
EM coupling
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
Beam
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
What happened
EM coupling
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
Beam
Unphysical temperature
CONTROL ROOM
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
What happened
EM coupling
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
Beam
INTERLOCK
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
PC kicker PC septum
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
What happened
Masking of temperature interlock
EM coupling
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
Beam
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
What happened
EM coupling
Water cooling
Switch off PC
EM coupling
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
Beam
Masking of temperature interlock
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
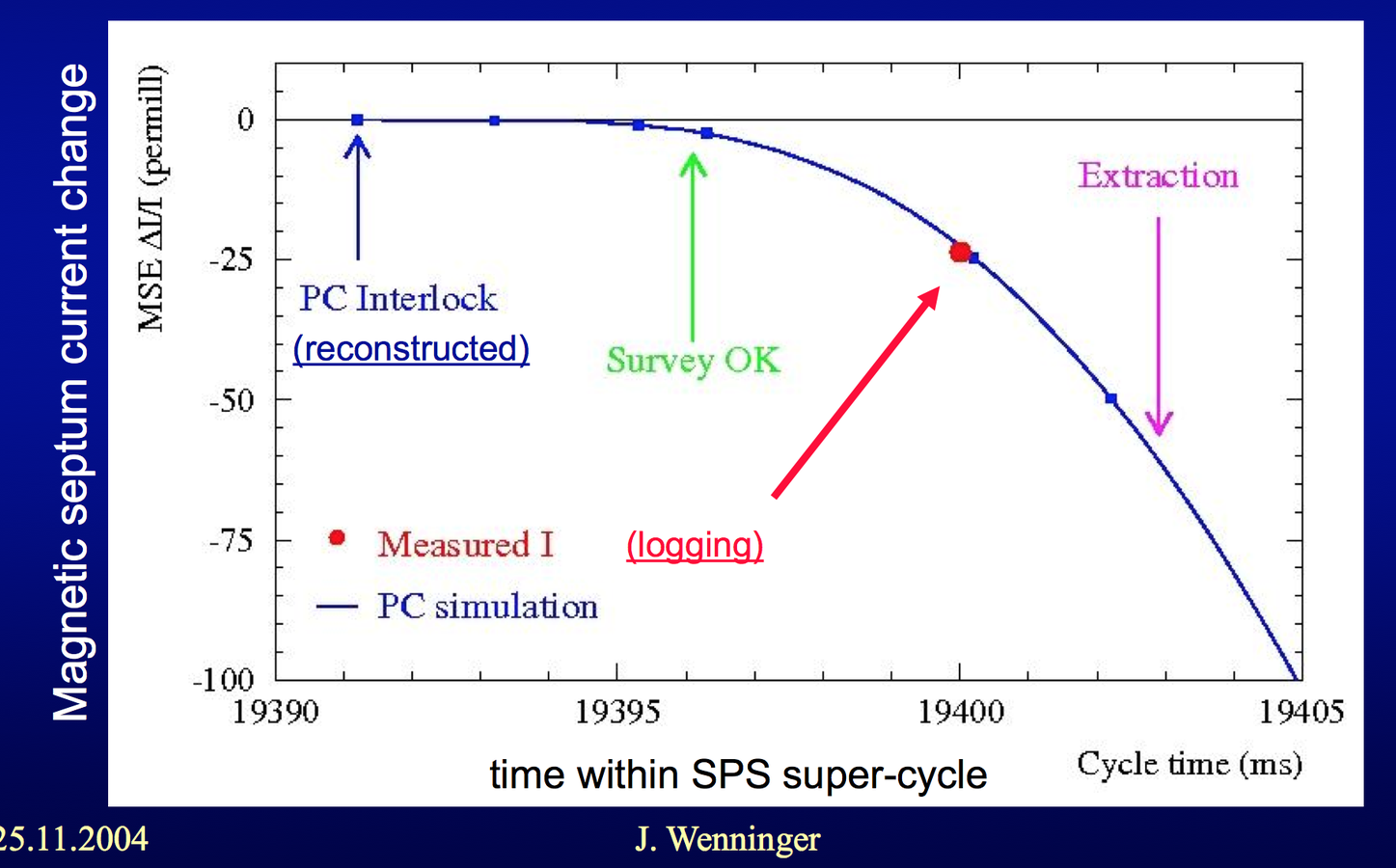
Evolution of the septum current
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
What happened
EM coupling
Water cooling
Switch off PC
Wrong beam deflection
EM coupling
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
Beam
Masking of temperature interlock
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
Beam
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
What happened
EM coupling
Water cooling
Switch off PC
Wrong beam deflection
Switch off PC
Delayed extraction inhibit
EM coupling
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
Beam
Masking of temperature interlock
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
Beam
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
Beam
EM coupling
Water cooling
Switch off PC
Beam
Wrong beam deflection
Switch off PC
Delayed extraction inhibit
Systemic view of the accident
No component failures: everything behaved as designed, but ...
Masking of temperature interlock
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
EM coupling
Systemic view of the accident
... unforseen interactions
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
Beam
EM coupling
Water cooling
Switch off PC
Beam
Wrong beam deflection
Switch off PC
Delayed extraction inhibit
Masking of temperature interlock
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
EM coupling
Systemic view of the accident
... lack of information
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
Beam
EM coupling
Water cooling
Switch off PC
Beam
Wrong beam deflection
Switch off PC
Delayed extraction inhibit
Masking of temperature interlock
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
EM coupling
Systemic view of the accident
... wrong control logic
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
Beam
EM coupling
Water cooling
Switch off PC
Beam
Wrong beam deflection
Switch off PC
Delayed extraction inhibit
Masking of temperature interlock
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
EM coupling
Systemic view of the accident
... 'unlucky' extraction timing
CONTROL ROOM
INTERLOCK
PC kicker PC septum
EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Kicker Septum Water cooling Temp. sensor
Operators
Temp. sensor
Beam
EM coupling
Water cooling
Switch off PC
Beam
Wrong beam deflection
Switch off PC
Delayed extraction inhibit
Masking of temperature interlock
Unphysical temperature
Spurious signal
CONTROL
ACTIONS
FEEDBACK
EM coupling
Not only component failures lead to accidents...!
Energy deposition of mis-steered SPS proton beam
- Number of protons
- Proton energy
- Energy of proton beam
- Proton beam size:
- Impact angle (Kain 2005):
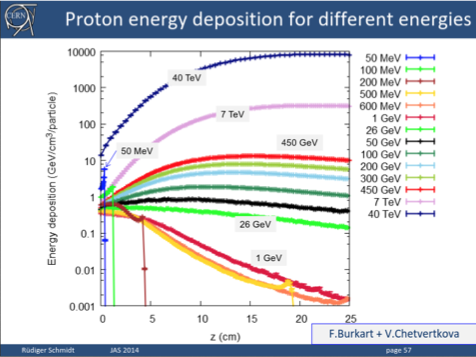
Proton beam source term
3.2 x
450 GeV
2.31 MJ
0.7 x 0.7
0.6
2.31 MJ
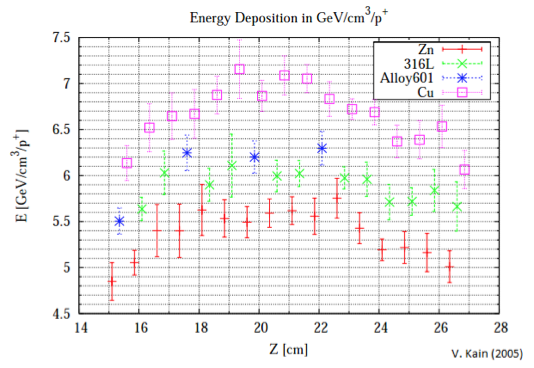
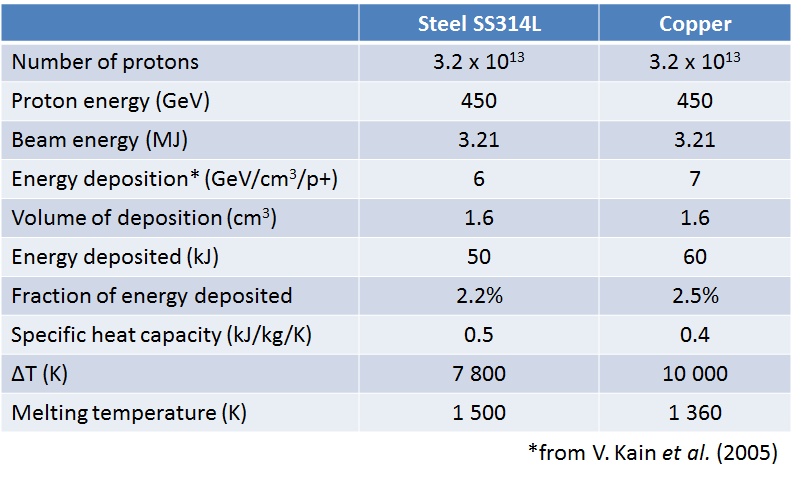
Energy Deposition in Steel and Copper
Energy deposition and eventual ΔT highly dependent on number of incident protons
Objectives
- Damage potential of proton beam
-
Maximum allowable intensity without damage
- Start at low intensity and increase incrementally
- Change beamsize
- Monitor hydrodynamic tunneling
Sensors for experiment
- Diamond detectors for monitoring beam loss
- Acoustic sensors
- Visual inspection of damage to material
- Imaging to observe absorber penetration
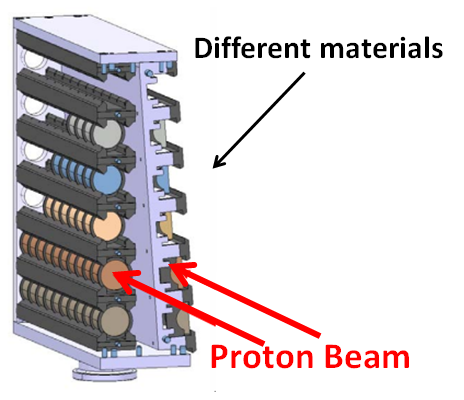
Material Qualification Test (1)
Materials of interest
- Carbon/graphite (absorbers)
- Steel (beam pipe)
- Copper (coils)
Material Qualification Test (2)
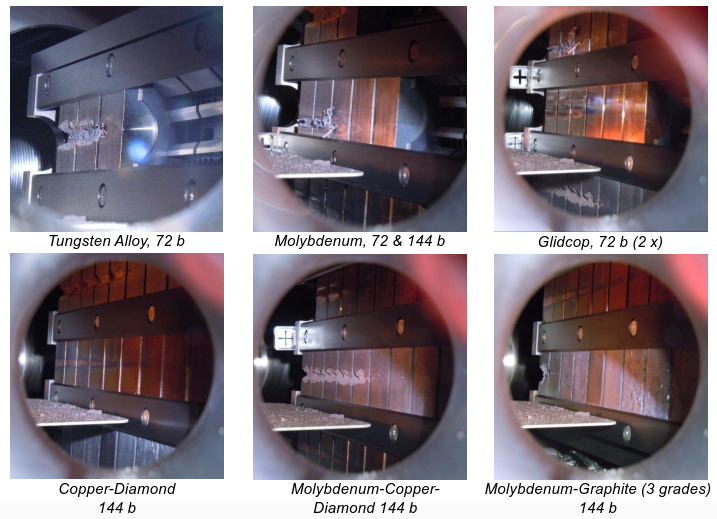
Text
Maximum allowed intensity at 450 GeV
New protection measures
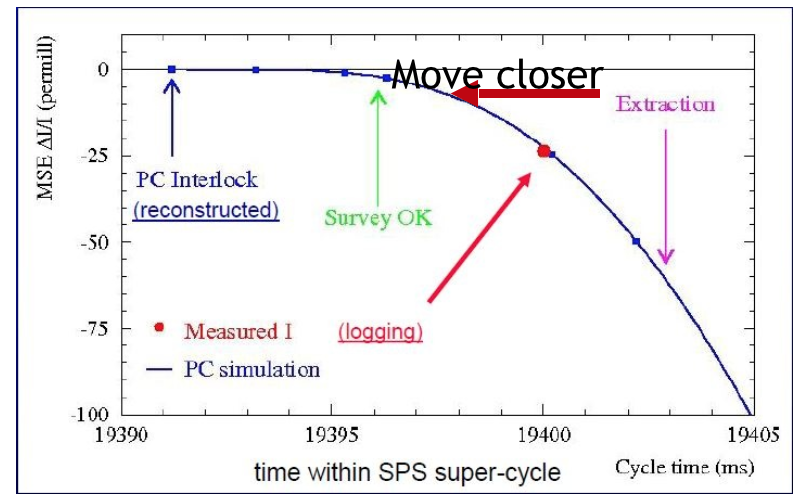
- Improve time delay of Beam Interlock Controller (BIC) monitor by replacing CPU with FPGA and move “Survey” time closer to extraction
- Measure both I and dI/dt (FMCM) from output of Power Converter (PC)
- Shield interlock cables close to beam signals (twisted pair wiring)
- Critical PC faults will trip BIC directly
- Feed LHC status into SPS extraction interlock
- Foresee passive protection in case of wrong extraction
- Assign a MPS (commissioning) coordinator and require that no interlocks are bypassed without coordinator approval.
- Diagnostics: latch all tripping interlocks and provide an intuitive method for diagnosing trip (i.e. an alarm tree, post-mortem analysis).
- Document standard procedures and approvals for bypassing interlocks.
Management suggestions
Beam off
- Measure delay between survey trigger and extraction trigger.
- Verify interlock trigger at design current level.
- Verify PC interlock inhibits extraction before turning off power supply of septum.
Beam on
- Reproduce operating conditions: continue with standard LHC injection process (probe bunch, maximum allowed intensity without damage).
Commissioning plan
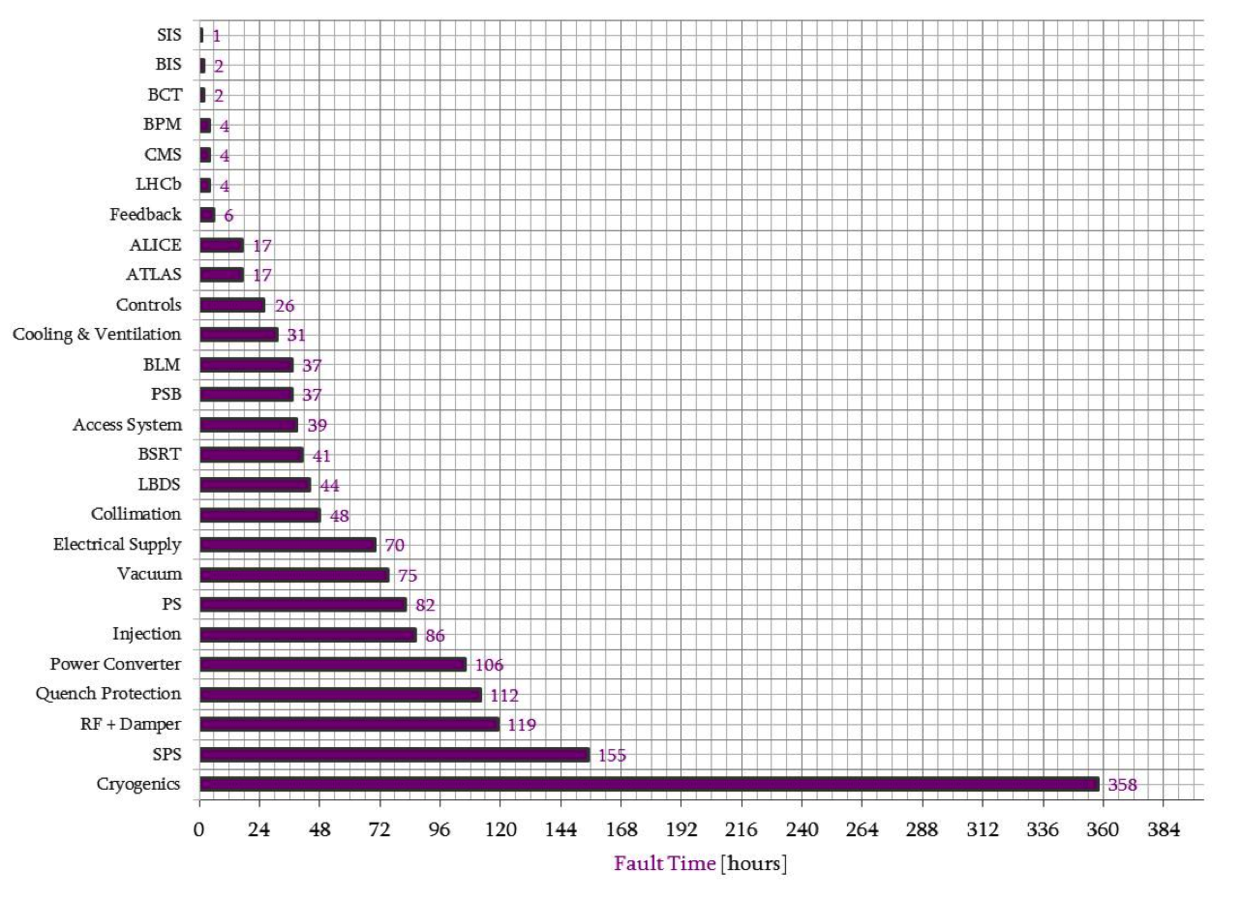
SPS is one of the main contributors to LHC unavailability
B. Todd
Impact on availability
Impact on availability
Downtime caused by the accident:
(magnet replacement, vacuum pumping...)
HL-LHC aims at
per day
2 days
16% of the luminosity production in 2012
in 160 days of operation
For two days we get
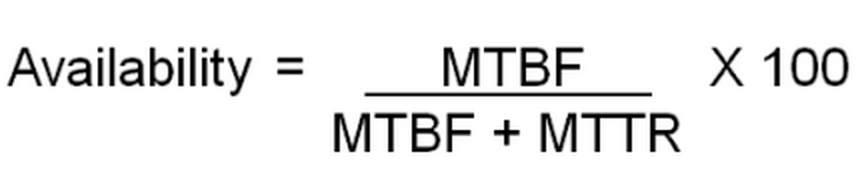
99.8%
Expert estimation of MTBF:
3 years
Summary
- Uncontrolled release of SPS beam can lead to significant damage and downtime of the accelerator complex.
- The accident was analyzed and understood: a systemic interpretation is proposed (STPA).
- No proper component failures occurred.
- An estimate of the damage potential of the SPS beam was calculated.
- Experiments and related diagnostics to quantify the damage potential were proposed.
- A different MPS strategy, management recommendations and commissioning procedures were illustrated.
- The impact on availability was quantified.

Thank you!
Copy of SPS
By Lauri Hellstén
Copy of SPS
- 509



