Ember.JS
Oct 7th, 2014

AGENDA
- Who uses it?
- Naming Conventions
- Template
- Routing
- Objects
- Models
- Controllers
- Views
- Workflow
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Prerequisites
- HTML
-
Javascript
- Handlebars Template
-
MVC knowledge
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Who Uses it?
______________________________________________
Ember.js




Naming Conventions
- If you want a page that will be acessed via /avenuecode, you will need:
- a template named avenuecode
- a route named AvenuecodeRoute
- a controller named AvenuecodeController
- and a View named AvenuecodeView
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Template
- Er... I mean, Handlebars!
- Default template engine for Ember.js
- Active community
- Helpers: #link-to, #each, #if, ...
-
Context usage example
<script type="text/x-handlebars-template" data-template-name="index">
<p>Guess who talks today? {{your-variable-name}}</p>
</script>
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Handlebars
Ways of organizing your code:


- Type the template snippet directly into your index.html file, and deal with the enormous amount of scripts in one file as your project grows, or
- Use .hbs files for each template: Template precompiling
______________________________________________
Ember.js


Outlet
- Reserved expression
- Place a template there
<script type="text/x-handlebars-template" data-template-name='application'>
<p>Static content shown in all pages</p>
<p>{{#link-to 'about'}}Link for About{{/link-to}}</p>
{{outlet}}
</script>
<script type="text/x-handlebars-template" data-template-name='about'>
<h1>I will be rendered when the route /about is reached!</h1>
</script>
______________________________________________
Ember.js


RoutING
- Router encapsulate the routes and resources
- Resources group routes together
- Routes tell templates which model to display
- Translate URL into nested templates
- Other cool features including:
- Path alias
- Dynamic Segments
- Objects generated when not found
- Convention over configuration
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Router - Example
App.Router.map(function(){
this.route("about");
this.resource("posts", function(){
this.route("new");
});
this.resource("post", { path: "/post/:post_id" });
});
App.PostRoute = Ember.Route.extend({
model: function(params){
return this.store.find('post', params.post_id);
// return [ { id: 1, title: "Bla", author: "Dude" } ];
}
setupController: function(controller, model) {
this.controllerFor('topPost').set('model', model);
}
});
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Objects
- Classes will extend Ember objects
App.Person = Ember.Object.extend({
helloWorld: function(){ alert("Hi, my name is " + this.get('name')); }
});
var leo = App.Person.create({ name: 'Leonardo Vasconcelos' });
leo.helloWorld();- Ember also has a bunch of helpers
App.User = Ember.Object.extend({
validUsername: Ember.computed.match('username', /^[a-z0-9]+$/),
adult: Ember.computed.gte('age', 18),
canadian: Ember.computed.equal('country', 'CA'),
canVote: Ember.computed.and('adult', 'canadian')
});
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Computed Properties
- Watch changes on object fields
- Update resulting property dynamically
- Chain watches and updates
App.Person = Ember.Object.extend({
fullname: function(){
return this.get('firstName') + ' ' + this.get('lastName');
}.property('firstName', 'lastName')
});
App.Person = Ember.Object.extend({
fullname: Ember.computed('firstName', 'lastname', function(){
return this.get('firstName') + ' ' + this.get('lastName');
})
});
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Observers
- Default synchronous watchers
- Fire whenever a change happens
myObserver: function(){
alert('Wow! What a view!');
}.observes('bird', 'cloud')
myObserver: Ember.observer('bird', 'cloud', function(){
alert('Wow! What a view!');
})
- Outside class definitions
person.addObserver('bird', function(){});
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Bindings
- Link between two properties
- One updates, so does the other (on sync)
- Bindings can happen with any pair of objects
wife = Ember.Object.create({
householdIncome: 80000
});
husband = Ember.Object.create({
wife: wife,
householdIncome: Ember.computed.alias('wife.householdIncome')
});
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Summing Up
- Use computed properties to build a new property by synthesizing other properties. It should not contain application behavior. Multiple calls should always return the same value.
- Observers should contain behavior that reacts to changes in another property.
- Bindings are most often used to ensure objects in two different layers are always in sync.
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Models
- Class that defines properties and behavior of data
- Deals with data that might appear in all sessions
- Can describe relationships with other objects
App.Book = DS.Model.extend({
title: DS.attr(),
launchedAt: DS.attr('date'),
rating: DS.attr('number'),
genre: DS.belongsTo('genre')
});
App.Genre = DS.Model.extend({
name: DS.attr(),
books: DS.hasMany('book', {async: true})
});
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Data Inside Models
- There are a bunch of ways to access:
- Hardcoded data inside route objects
- Local Storage
- FIXTURES - Ember Data
- RESTful JSON API
______________________________________________
Ember.js

FIXTURES
- Mock the data, no back-end
-
Requires id property
App.ApplicationAdapter = DS.FixtureAdapter.extend();
App.Todo = DS.Model.extend({
title: DS.attr('string'),
isCompleted: DS.attr('boolean')
});
App.Todo.FIXTURES = [
{ id: 1, title: 'Learn Ember.js', isCompleted: false },
{ id: 2, title: 'Work for Avenue Code', isCompleted: true },
{ id: 3, title: 'Learn Javascript', isCompleted: true }
];
______________________________________________
Ember.js

REST API
- Determine the URL based on model names
App.ApplicationAdapter = DS.RESTAdapter.extend({
namespace: 'api/1',
host: 'http://api.example.com'
});
store.find('user', 1).then(function(user){});
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Controllers
- Handle non-persisted logic
- Wrap the model
- Hold functions, properties and observers
- 3 types:
- ObjectController: single model
- ArrayController: array of models
- Controller: no model
App.BooksController = Ember.ArrayController.extend({
sortProperties: ['title'],
sortAscending: false
});
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Actions
- All action handlers wrapped in one object
- Ember convention to keep code organized
App.ReviewsNewController = Ember.Controller.extend({
actions: {
createReview: function(){
var controller = this;
this.get('model').save().then(function(){
controller.transitionToRoute('index');
});
}
}
});
<script type="text/x-handlebars" data-template-name="reviews/new">
<button type="submit" {{action 'createReview'}}>Save Review</button>
</script>
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Views
- Created only when dealing with:
-
Event handling
-
Components
- Often not needed: Handlebars
- Lots of hooks
var view = Ember.View.create({
templateName: 'say-hello',
name: "Bob"
});
<script type="text/x-handlebars" data-template-name="say-hello">
Hello, <b>{{view.name}}</b>
</script>
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Event Handling
- A view can call an action from the controller
- If there is none, it will bubble up to the route
App.ClickableView = Ember.View.extend({
click: function(event) {
this.get('controller').send('turnItUp', 11);
}
});
App.PlaybackController = Ember.ObjectController.extend({
actions: {
turnItUp: function(level){ /*Do your thing*/ }
}
});
{{#view "clickable"}}
This is a clickable area!
{{/view}}
______________________________________________
Ember.js

COMPONENTS
-
Don't Repeat Yourself!
- Clean up multiple code with same behavior
- Create reusable script modules
<script type="text/x-handlebars-template" data-template-name='book'>
{{book-details book=this tag='div' class='row'}}
</script>
<script type="text/x-handlebars-template" data-template-name='components/book-details'>
<img {{bind-attr src='book.image'}} />
</script>
______________________________________________
Ember.js


Workflow
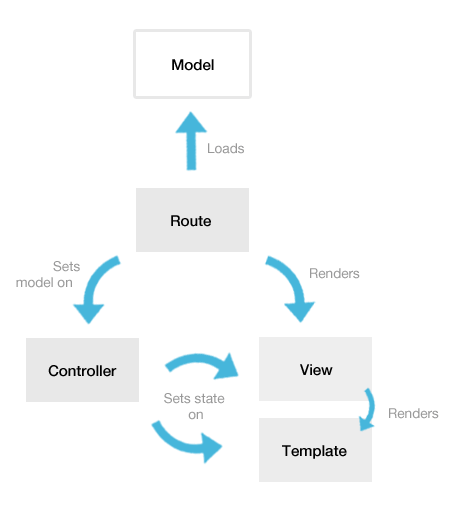
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Conclusion
- Ember is indicated to a quick-start
- No boilerplates needed
- Organized code with naming conventions
- Relies a lot on Handlebars
- Easy persistence handling
- Helpful Object APIs
______________________________________________
Ember.js

References
-
Ember JS Guides
-
An In-Depth Introduction to Ember JS
- Vic Ramon's Ember Tutorial
-
Code School - Warming Up With Ember.js
______________________________________________
Ember.js

LEARN MORE
-
Blog - Ember Zone
-
Code School Screencast about Firebase
-
Talk - Awesome Ember Tricks - Robin Ward
- EmberWatch
- AC Talk about Handlebars
- Pre-compiling separate files of Handlebars
- Yehuda Katz talk on EmberJS concepts
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Challenge
- Build a TODO app using Ember.js
- Use different types of data storage (at least Fixtures and Local Storage)
- Improve your layout with Handlebars helpers
- Use this tutorial as a starting point
- Send me your solution using a GitHub repository
______________________________________________
Ember.js

Rate My Talk
Got nothing!
Average!
Good job!
Ember.js
By Leonardo Dias de Vasconcelos
Ember.js
A brief introduction of Ember.js and some features that makes it a good pick to develop your application. By Leonardo Vasconcelos
- 1,020






