
syntax vs. semantics
syntax
- Spelling
- Punctuation
- Characters
semantics
- Grammar
- Meaning
- Intent
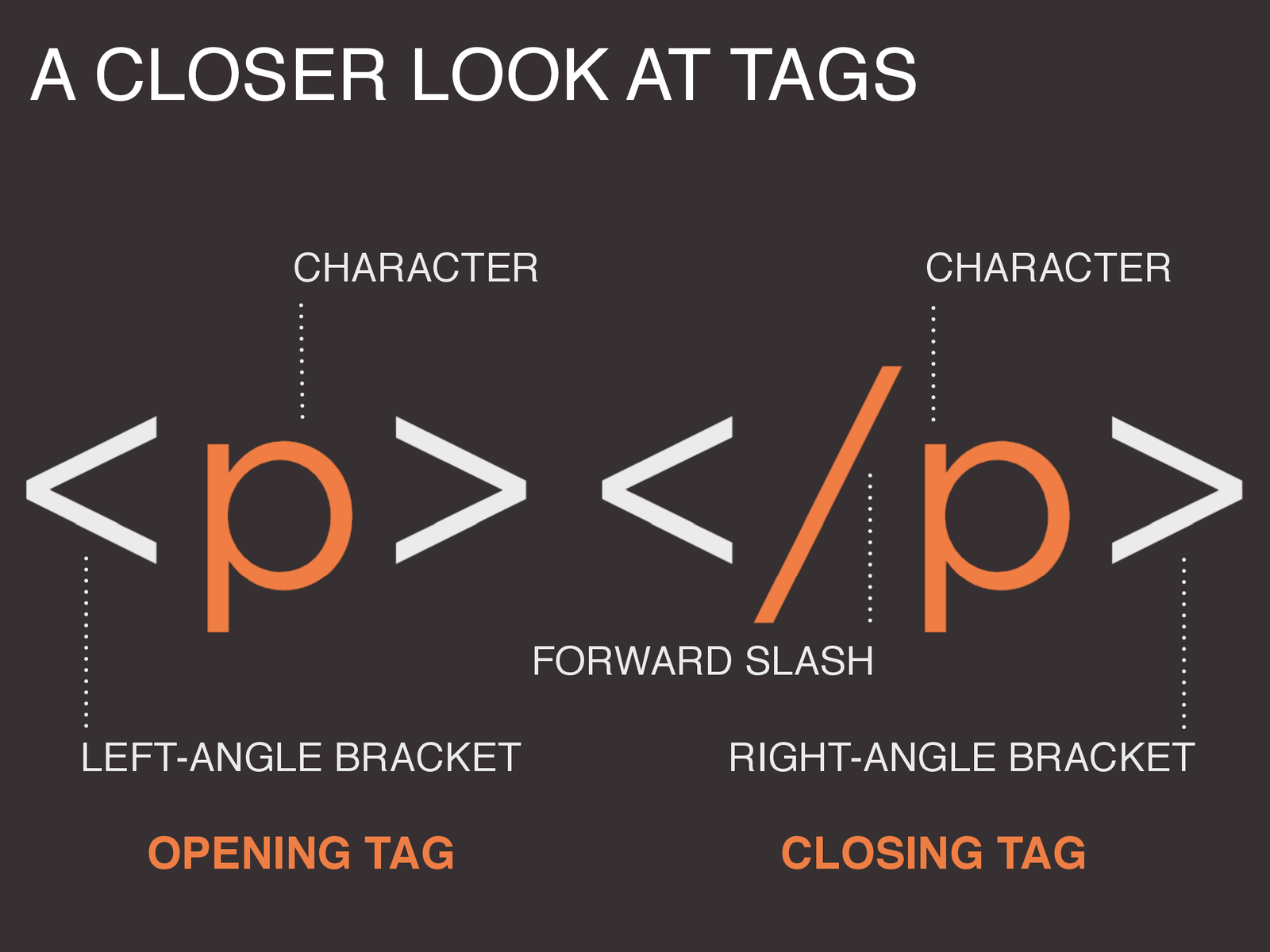
<!-- The characters -->
< >
< / >
-
=
" "
' '
!<!-- This is the Primary heading -->
<h1>Primary Heading</h1>
<!-- This is my selfie -->
<img src="selfie.jpg" />
<!-- This is footer -->
<footer></footer><--
Syntax Error
Typed the wrong characters
-->
<html> <//html>
<!-- Semantic Error
It works, but meaning is wrong.
-->
<p>Your Name</p>
<p>Your Student ID</p><!--
Syntax Error
Typed the wrong characters
-->
<html> </html>
<!-- Semantic Error
It works, but meaning is wrong.
-->
<h1>Your Name</h1>
<data>Your Student ID</data>hypertext markup language
HTML is the content layer
CSS is the presentation layer
JS the behavioral layer
Plain text
- Plain text, interpreted as HTML (CSS or JS)
- It's just plain text, until it's not e.g. rich text
- LOTS of apps make HTML
- Even MS Word can make websites
- Pros/Cons
- Even MS Word can make websites
Like PDF from exported from InDesign, websites are the product/result HTML (CSS and JS)
language
- Has structure and rules
- Has old, new, and made up words
- Has many dictionaries
- Is flexible and forgiving
- Accessible to everyone
Best way to learn any language is immersion.
English changes and evolves. Words are added, removed, made up, changed, etc.
NEW Words
- LOL
- Selfie
- Bling
- Emoji
- Cryptocurrency
- Influencer
- Onboarding
- Deepfake
- etc.....
OLD Words
- Crapulous
- Fudgel
- Hornswoggle
- Twattle
- Tittynope
OLD HTML words
<blink>
<marquee>
<center>
<font>
<big>
NEW HTML words
"Words" are analogous to HTML elements.
HTML DICTIONARIES
aka Dictionaries
- "Dictionary" is a loose analogy.
- Technically a specification or standard
- Official specification and standard
- In depth, not practical for everyday use
- Intended for Browser makers e.g. Apple, Microsoft, Google, etc.
Too many to list here. Find your trusted source.
References
HTML "dictionaries" for Web Design 1
- HTMLReference.io
- Mozilla Developer Network or MDN
- Other sources as needed
FYI. ANY "W3C Schools" website will be ignored. There are better resources.
STructure
elemEnts
- HTML elements are the "words in the dictionary"
- Elements (NOT tags) are what CSS and JS reference
- Past and current HTML elements
Elements are the "words in the HTML Dictionary"
Structure element
- Tags
- Attributes
- Values
An element is composed of tags, attributes, and values.

< /a>
GET Used to looking at code.
HTML Comments
- Notes within code
- For documentation, help, logging, communication, etc.
- Shoud not show after build of Web: site, app, product, service, etc.
<!-- Start of Comment
Comment(s)
end of Comment --> <!-- TAGS
* Tag Pairs
* Self Closing
-->
<!--
Tag Pairs Examples
-->
<h1>
Heading Content
</h1>
<p>
Paragraph Content
</p>
<!--
Self Closing
-->
<img />
<br />
<!-- ATTRIBUTES and VALUES
* Left of equal sign
* Elements can have any number attributes
* Can be true/false
-->
<!--
Element: Image
Self Closing or Tag Pair: self closing
Attribute(s): src
Value(s): selfie.jpg
-->
<img src="selfie.jpg" />
<!--
Element: Image
Self Closing or Tag Pair: self closing
Attribute(s): src, alt
Value(s): selfie.jpg, My Selfie
-->
<img src="selfie.jpg" alt="My Selfie" />
<!-- ATTRIBUTES and VALUES Continued -->
<!--
Element: anchor
Self Closing or Tag Pair: tag pair
Attribute(s): href, target
Value(s): ewu.edu, _self
-->
<a href="ewu.edu" target="_self"> EWU Website </a>
<!--
Element: video
Self Closing or Tag Pair: tag pair
Attribute(s): src, autoplay
Value(s): ewu.mp4
-->
<video src="ewu.mp4" autoplay /></video>Tag(s)
ATtribute(s)
Value(s)
HTML : First Principles
By Manikoth
HTML : First Principles
HTML First Principles
- 695



