COMP2511 Week 2
Agenda
- Admin Stuff
- Code Review
- Documentation
- Basic Inheritance & Polymorphism (Code Demo)
- Access Modifiers & Packages
Admin Stuff
-
Assignment 1 has been released
- Due Week 5 Friday, 5pm (17th March)
- 20% of the Course mark
- Help sessions exist!
- Solutions for tute1
Code Review
package shapes;
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color);
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String name, int width, int height) {
this(name);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}- What is the difference between super and this?
Shape.java
Rectangle.java
Code Review
package shapes;
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color);
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String color, int width, int height) {
this(color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}-
What is the difference between super and this?
- super refers to the superclass whereas this refers to the current class
Shape.java
Rectangle.java
Code Review
package shapes;
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color);
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String color, int width, int height) {
this(color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}-
What is the difference between super and this?
- super refers to the superclass whereas this refers to the current class
- What about super(...) and this(...)?
Shape.java
Rectangle.java
Code Review
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color);
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String color, int width, int height) {
this(color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}-
What is the difference between super and this?
- super refers to the superclass whereas this refers to the current class
-
What about super(...) and this(...)?
- super() calls the parent class constructor
- this() calls the current class constructor
Shape.java
Rectangle.java
Code Review
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color);
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String color, int width, int height) {
this(color);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}-
What is the difference between super and this?
- super refers to the superclass whereas this refers to the current class
-
What about super(...) and this(...)?
- super() calls the parent class constructor
- this() calls the current class constructor
Shape.java
Rectangle.java
Code Review
public class Circle {
private static final double pi = 3.14159;
private int x, y;
private int r;
// Only 1 variable for all Circle objects
public static int numberOfCircles = 0;
public Circle() {
numberOfCircles++;
}
public double circumference() {
return 2 * pi * r;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 0
Circle c1 = new Circle();
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 1
Circle c2 = new Circle();
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 2
}
}- What are static fields and methods?
Code Review
public class Circle {
private static final double pi = 3.14159;
private int x, y;
private int r;
// Only 1 variable for all Circle objects
public static int numberOfCircles = 0;
public Circle() {
numberOfCircles++;
}
public double circumference() {
return 2 * pi * r;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 0
Circle c1 = new Circle();
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 1
Circle c2 = new Circle();
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 2
}
}-
What are static fields and methods?
- Static fields are variables that are common and available to all instances of a Class. They belong to the Class, rather than an instance.
Code Review
public class Circle {
private static final double pi = 3.14159;
private int x, y;
private int r;
// Only 1 variable for all Circle objects
public static int numberOfCircles = 0;
public Circle() {
numberOfCircles++;
}
public double circumference() {
return 2 * pi * r;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 0
Circle c1 = new Circle();
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 1
Circle c2 = new Circle();
System.out.println("Number of circles: " + Circle.numberOfCircles); // 2
}
}-
What are static fields and methods?
- Static fields are variables that are common and available to all instances of a Class. They belong to the Class, rather than an instance.
- Methods are a block of code that performs a task. You can think of them as functions of a class.
Code Review
Documentation
Documentation
- What is meant by self-documenting code?
Documentation
- What is meant by self-documenting code?
- It is inherently easy to read through the use of meaningful variables, function names, clear logic.
Documentation
- What is meant by self-documenting code?
- It is readable inherently, through things like meaningful variables and function names.
- When can comments be bad (code smell)?
Documentation
- What is meant by self-documenting code?
- It is readable inherently, through the use of meaningful variables and function names.
- When can comments be bad (code smell)?
- Comments go stale/outdated comments
- Comments are literally reiterating your code.
Documentation
- JavaDoc is one way of documenting in Java.
- JavaDoc is a way of writing your comments
- It mainly targets class definitions and method/function definitions.
- in COMP2511, you will not have to use JavaDoc documentation unless asked.
/**
* File class that stores content under a file name
*/
public class File {
/**
* Constructor used to create a file
* @param fileName the name of the file
* @param content contents of the file
*/
public File(String fileName, String content) {}
/**
* Constructor used to make a partial file when receiving a new file
* I.e., content.length() != fileSize with no compression
* @param fileName
* @param fileSize
*/
protected File(String fileName, int fileSize) {}
/**
* Checks if transfer has been completed
* @return true if it has been completed
*/
public boolean hasTransferBeenCompleted() {}
}Documentation
VSCode Extensions
- Java Code Generators: generate methods for classes such as getters and setters (recommend)
- Javadoc Tools: generate Javadoc comments for methods within a class


Code Demo
Code Demo
- Create an Employee class with a name and salary
- Create a constructor which sets the name and salary
- Create getters & setters with JavaDoc
- Create a Manager Class that inherits Employee with a hireDate
- Override toString() method for both classes
- Override equals() method for both classes
Access Modifiers
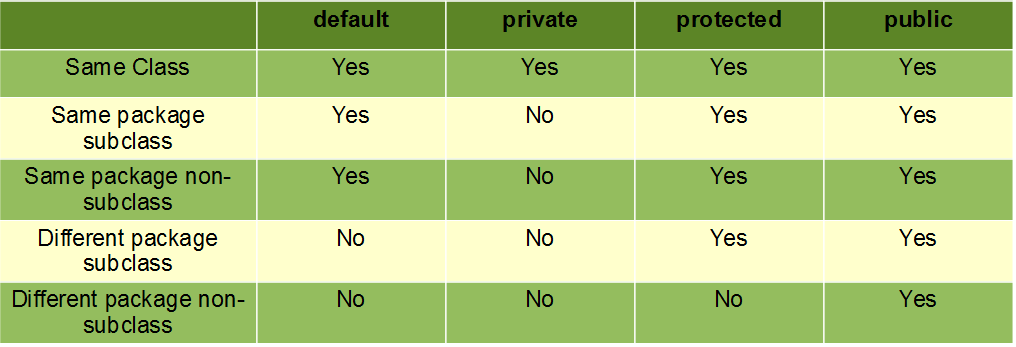
Access Modifiers
public class Circle {
int a; // Default
private int b; // Private
protected int c; // Protected
public int d; // Public
}COMP2511 Tutorial 2
By Matthew Liu
COMP2511 Tutorial 2
- 223



