F1 - Legal and Ethical Issues
Data social media companies might collect
Personal information: Name, date of birth
Content: Images, status updates, emojis created
User behaviour: What pages you visited, groups you are a member of, what you have 'liked'
Data you have on others: Names of your friends and their numbers
How do you think social media companies make money if they are free to use?
What do they do with your data?
Data Protection Act 2018
All organisations and people using and storing personal data must abide by the following principles.
Data must be:

Data Protection Act 2018
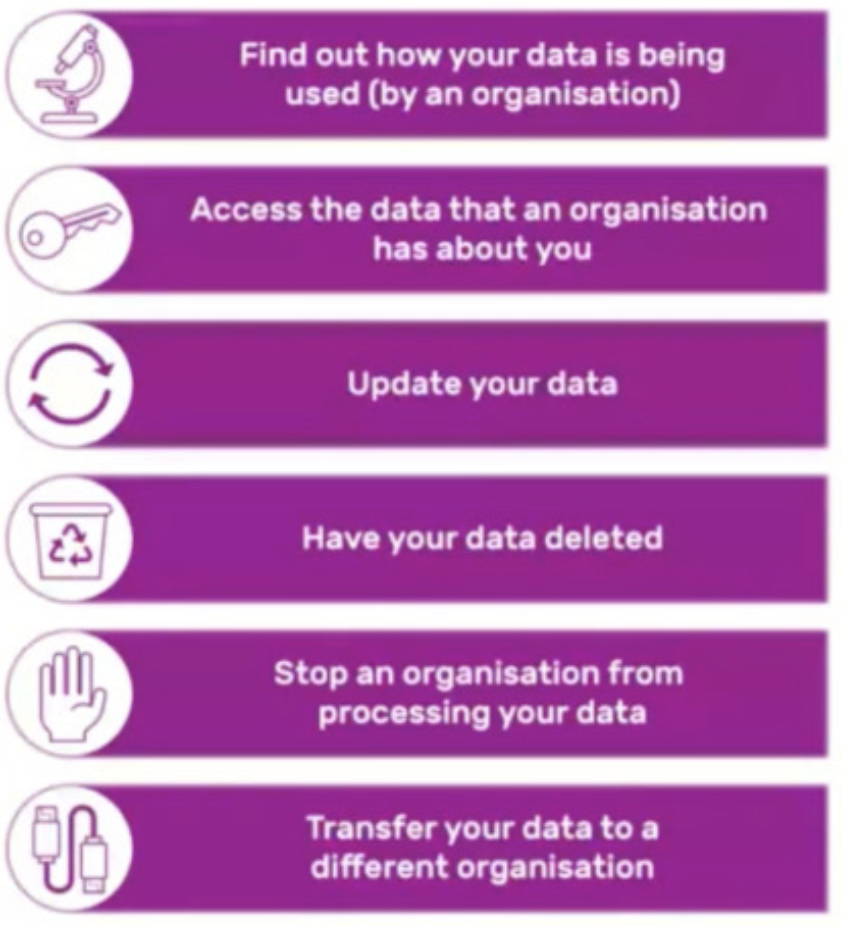
As a data subject, you have the right to find out what information the government and other organisations store about you.
You have the right to:
Instagram Privacy Policy
Look at the privacy policy for Instagram (link provided below) and state one piece of information that is collected about you:
You can write it down in your notebooks.
Data Protection Act 2018
Identity theft
One way hackers profit from stolen data is selling it in masses to other criminals on the dark web. These collections can include millions of records of stolen data. The buyers can then use this data for their own criminal purposes.

Data Protection Act 2018
Account takeover
Many online services require users to fill in personal details such as full name, home address and credit card number. Criminals steal this data from online accounts to commit identity theft, such as using the victim’s credit card or taking loans in their name.

Activity
Fill in the blanks in your OneNote
You have 3 minutes!
Different Scams to be aware of
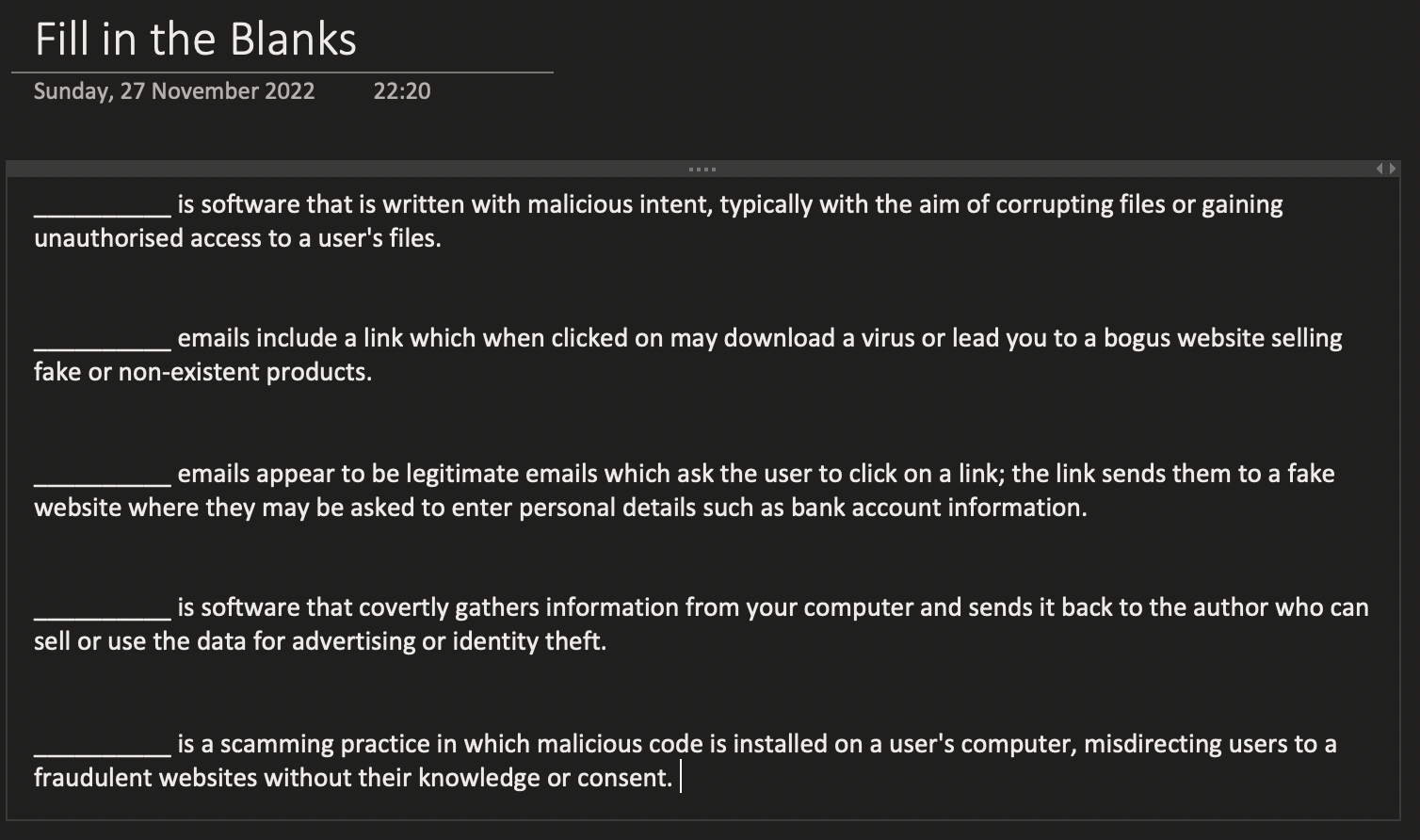
Worms
It is a standalone program that does need to attach itself to an existing program in order to spread
Viruses
A computer virus is one type of malware (malicious software) which is installed without your knowledge, with the purpose of doing harm
Shoulder surfing
Shouldering involves direct observation of a user entering their security details.
Phishing
A phishing email is one that tricks you into handing over sensitive or personal information (login details, bank details, etc.)


Lesson Objectives
- Understand the purpose and use of codes of conduct
- Understand the legislation in place to:
- Facilitate Safe Access
- Prevent misuse
What we will cover
- Codes of practice
- What are they?
- Why are they used?
- Legislation
- Enabling access/Health and Safety
- Preventing Misuse
Accessibility
- Accessibility isn't about promoting access or giving advantage; it ensures equal access to all, regardless of any impairment or condition.
- IT and computing offer a great deal by way of assistive technology.
- As more of the services that people depend on move online, it is essential that everyone has equal ease of access.
Codes of Practice
What?
- They are guidelines provided by independent organisations
- They recommend "Best Practice" in a field
- They accompany laws to provide safe rules for IT in organisations
Why?
- To protect users & customers
- To provide assurance regarding data protection
- To provide clear guidance around laws
Codes of Practice
Examples:
- Information Commissioner's Office
- Institute of Library & Information Professionals
- Care Quality Commission
Codes of Practice
Complete the worksheet in your notebooks on the impacts and benefits of having codes of practice.
You have 8 minutes!
Codes of Practice
Impact:
An independent body monitors any breaches in the DPA 2018 and CMA 1990.
Organisations can be certified for complaints
Benefits:
Provides common ground rules
Can help standardisation across organisations
Reassures customers
Legislation - Accessibility
Equality Act 2010
Replaces the Disability Discrimination Acts 1995 & 2005
https://equalityhumanrights.com/
Health and Safety (Display Screen Equipment) Regulations 1992
Part of a broader suite of Health & Safety regulations to ensure a safe working environment
Legislation - Accessibility
What are the nine pieces of legislations under the Equality Act 2010?
Answer in your notebooks
The nine main pieces of legislation that have merged are:
- Equal Pay Act 1970
- Sex Discrimination Act 1975
- Race Relations Act 1976
- Disability Discriminations Act 1995
- Employment Equality (Religion or Belief) Regulations 2003
- Employment Equality (Sexual Orientation) Regulations 2003
- Employment Equality (Age) Regulations 2006
- Equality Act 2006, Part 2
- Equality Act (Sexual Orientation) Regulations 2007
Equality Act 2010
Businesses cannot discriminate against:
- Employees or applicants for employment
- Customers wanting to access their products/services
Based on the protected characteristics:
- Age,
- Disability
- Gender reassignment
- Marriage and civil partnership
- Pregnancy and maternity
- Race
- Religion or belief
- Sex
- Sexual orientation.
Health & Safety
Health and Safety (Display Screen Equipment) Regulations 1992
- Applies to workers who spend at least 1 hour a day working with display screens
- Applies whether they are working in an office, at home or on site
Employers must:
- Do a workstation assessment
- Reduce risks, including making sure workers take breaks from display screen work or do something different
- Provide an eye test if a worker asks for one
- Provide training and information for workers
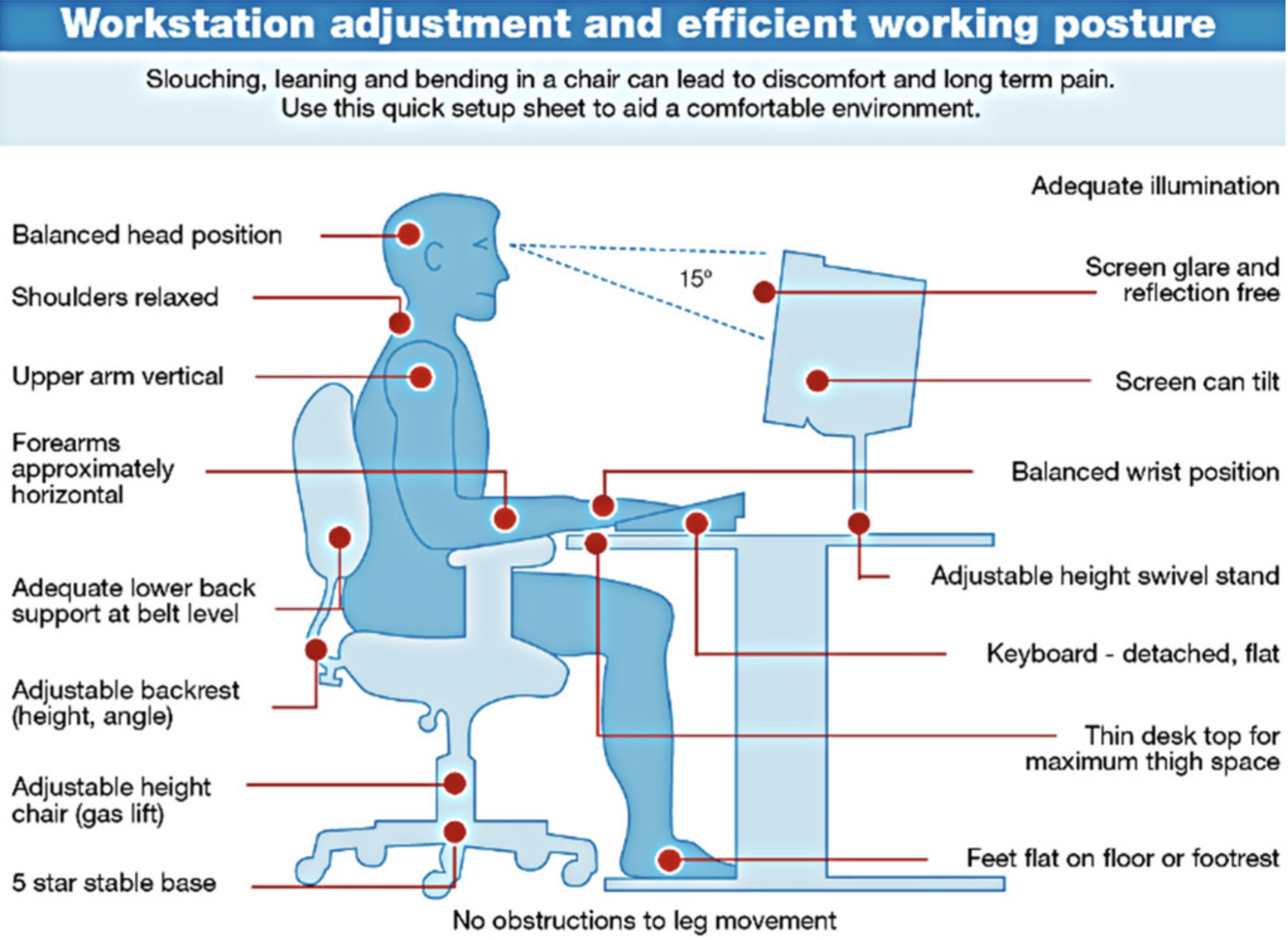
Activity
Label the diagram in your notebooks
You have 10 minutes!
Accessibility Guidelines
Guidelines
NOT legislation (Law)
Not Codes of Conduct
Accessibility Guidelines
- Open Accessibility Framework (OAF)
- The European Research Project sets out a process for ensuring IT systems are accessible
- Provides outline steps that must be in place in order for any computing platform to be considered accessible
"Create" Steps
- Define "Accessible"
- Provide User Interface Elements
- Provide Authoring Tools
"Use" Steps
- Provide Platform Supports
- Provide Accessible Software
- Provide Assistive Technologies
Accessibility Guidelines
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
- Developed by Worldwide Web Consortium (W3C)
- Guidance for creating non-discriminatory content
- This covers:
- Visual design & user interface
- Writing and presenting content
- Mark-up and coding

Accessibility Guidelines
- British Standards Institution (BSI) Codes of Practice
- Produce Codes of Practice and Standards for many areas of workplace safety and accessibility
- In concert with the Equality Act, in 2010 published: BS8878 - Web Accessibility Code of Practice
Intended to be a detailed guide for businesses and organisations to make web products more accessible to disabled and older users.
Accessibility Features
Apple Mac
- Zoom
- VoiceOver
- Sticky Keys/Slow Keys
- Mouse Keys
- Inverted Display Colours
Microsoft Windows:
- Narrator & Braille
- Magnifier
- Text Size
- On-Screen Keyboard
- Speech Recognition
- High Screen Contrast
- Accessible Input Devices (e.g. eye-tracking)
Explore Accessibility Options
- Try out the accessibility options on your computer
- Can you find:
- Narrator
- Magnifier
- On-Screen Keyboard
- Speech Recognition
- High Screen Contrast
- Be a good citizen - put things back to normal afterwards!
Summary - Accessibility
- What are Codes of Conduct?
- Who creates them?
- What is their purpose/ impact?
- How is technology made accessible to all?
- Legislation
- Development Guidelines
Answer the following in your notebooks:
F1 - Legal and Ethical Issues
By CJackson
F1 - Legal and Ethical Issues
- 112



