ASCII and Unicode
H446 Computer Science
Objectives
- Use names, symbols and corresponding powers of 2 for binary prefixes, e.g., Ki, Mi
- Differentiate between the character code of a decimal digit and its pure binary representation
- Describe how character sets (ASCII and Unicode) are used to represent text
Large Values

- Computers process and store large amounts of bytes, often in the order of millions or billions
- When dealing with large quantities it is more convenient to summarise this using number prefixes
- A common example of this is the kilogram, which is the equivalent of 1000g.
Prefixes for Bytes
- The same number prefixes for decimal values can be used to summarise large quantities of bytes
- This includes:
| Prefix | Symbol applied | Multiple |
|---|---|---|
| kilo | kB | 10^3 = 1,000 |
| mega | MB | 10^6 = 1,000,000 |
| giga | GB | 10^9 = 1,000,000,000 |
| tera | TB | 10^12 = 1,000,000,000,000 |
| peta | PB | 10^15 = 1,000,000,000,000,000 |
| exa | EB | 10^18 = 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
| zetta | ZB | 10^21 = 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 |
Incorrect Prefixes

New Prefixes for CS
- To eliminate the confusion, in 1998 the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) established different prefixes to represent multiples of base 2:
| Prefix | Symbol applied | Multiple |
|---|---|---|
| kibi | kB | 10^3 = 1,024 |
| mebi | MB | 10^6 = 1,048,576 |
| gibi | GB | 10^9 = 1,073,741,824 |
| tebi | TB | 10^12 = 1,099,511,627,776 |
| pebi | PB | 10^15 = 1,125,899,906,842,624 |
| exbi | EB | 10^18 = 1,52,921,504,606,846,976 |
| zebi | ZB | 10^21 = 1,180,591,620,717,411,303,424 |
Representing Text Characters
If a computer only understands 1s and 0s, what happens when the 'M' key is pressed on the keyboard?

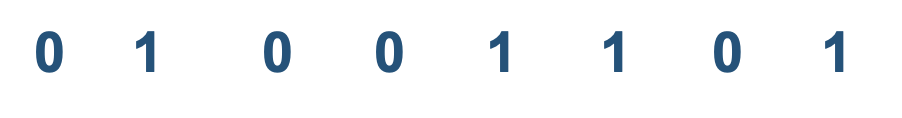
ASCII Code
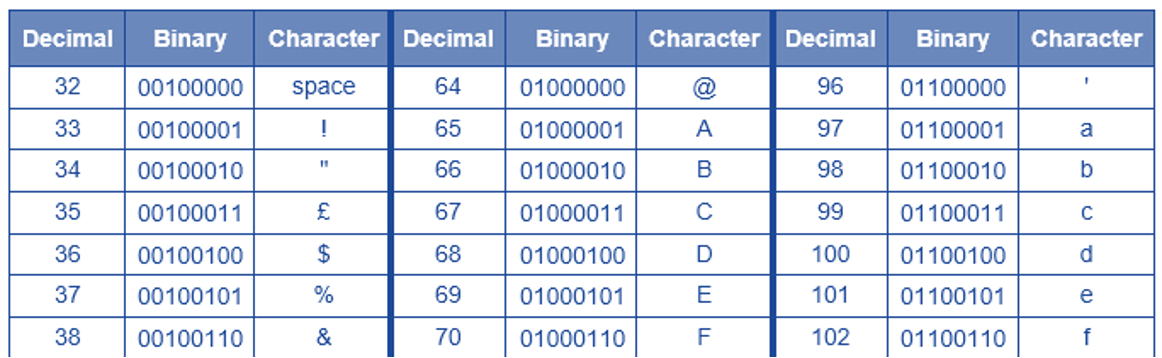
In 1963, the American Standard Code for Information Interchange, (ASCII), was established to encode symbols found in the English alphabet.
It was composed of a 7-bit character set, giving just 128 possible binary codes.
What are the limitations of having only a 7-bit character set?
Representing Characters
- Every character on the keyboard is represented by a binary value
- Uppercase letters (capitals) have different values from lowercase characters
- Punctuation symbols have their own characters
- How many characters are there on a standard keyboard?
- How many bits would be required to represent this many combinations?
- What character is represented by 0100000 (32)?

Characters form of decimal digits
- Numeric characters are also encoded
- The code 0111001 represents the character '9' in ASCII
- The binary byte representing '9' would be 000010012
- What are the implications of this difference?
- What will the following code output?

Hint: ord() will return the unicode representation of a character
Unicode
- Unicode was then introduced to standardise the encoding of characters from every language
- Unicode can apply a variable length of encoding at either 16 bits or 32 bits long
- In order to improve the implementation of this the first 128 Unicode characters were set to be the same as the 128 in ASCII
- What could be a disadvantage of using 4 bytes per character?

Advantage of Unicode
- In Unicode, every character in every language in the world, every mathematical and scientific symbol, etc. can be represented:
Español
한국어
Македонски
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ
ελληνικά

Have a go at the ASCII/Unicode worksheet on Moodle
Extension: Complete the ASCII Exam Questions on Moodle
Student version
By CJackson
Student version
- 103



