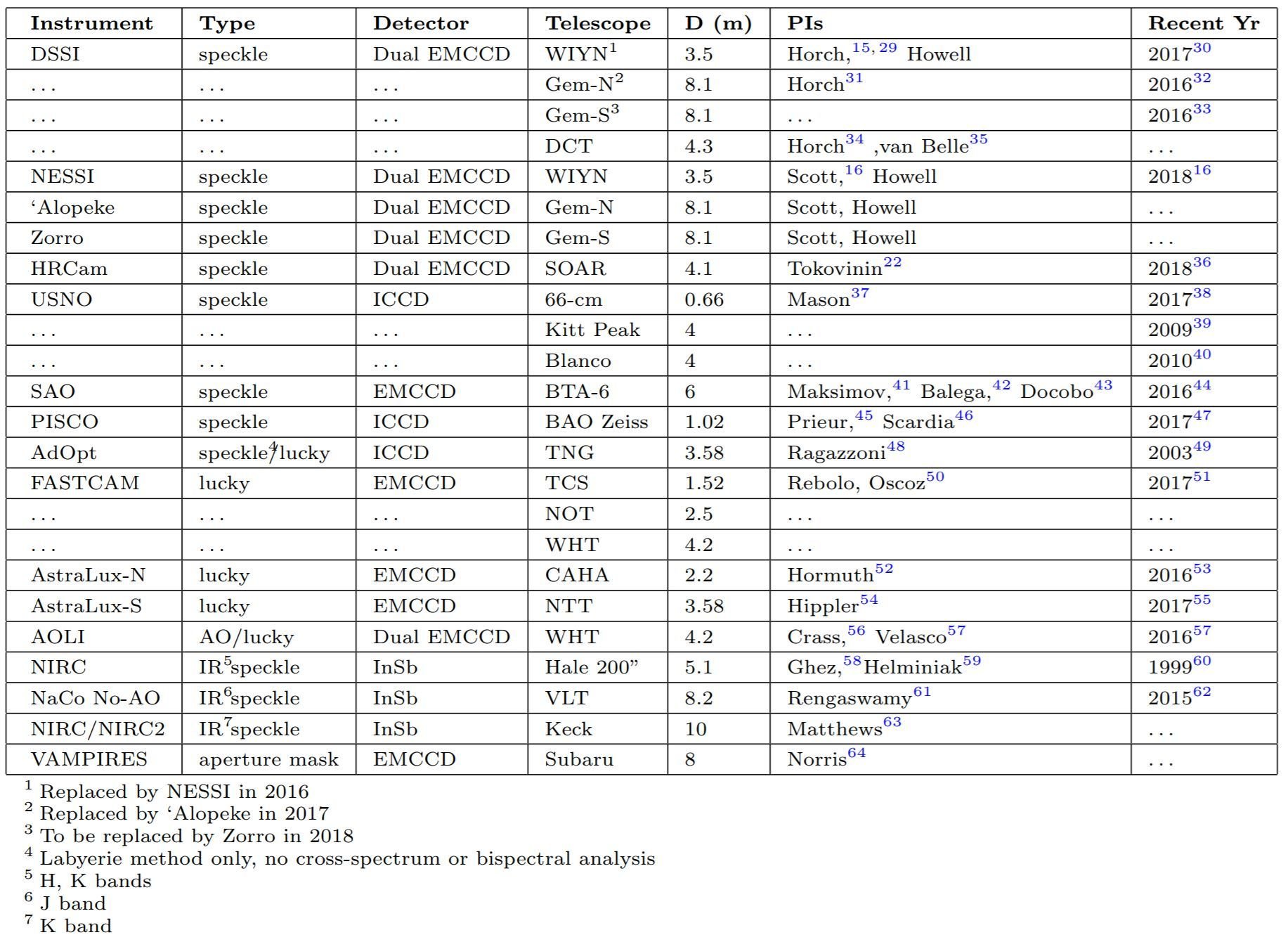
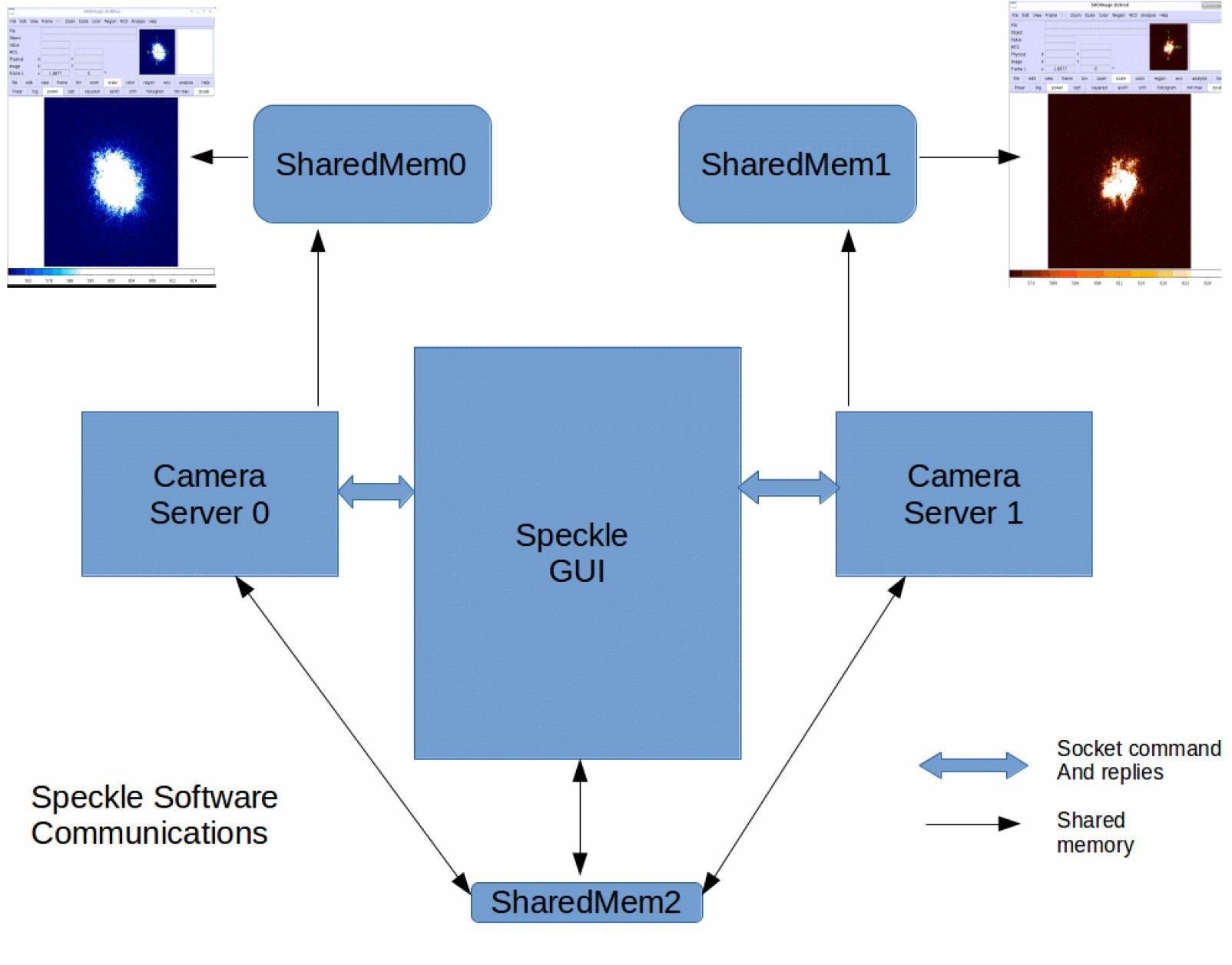
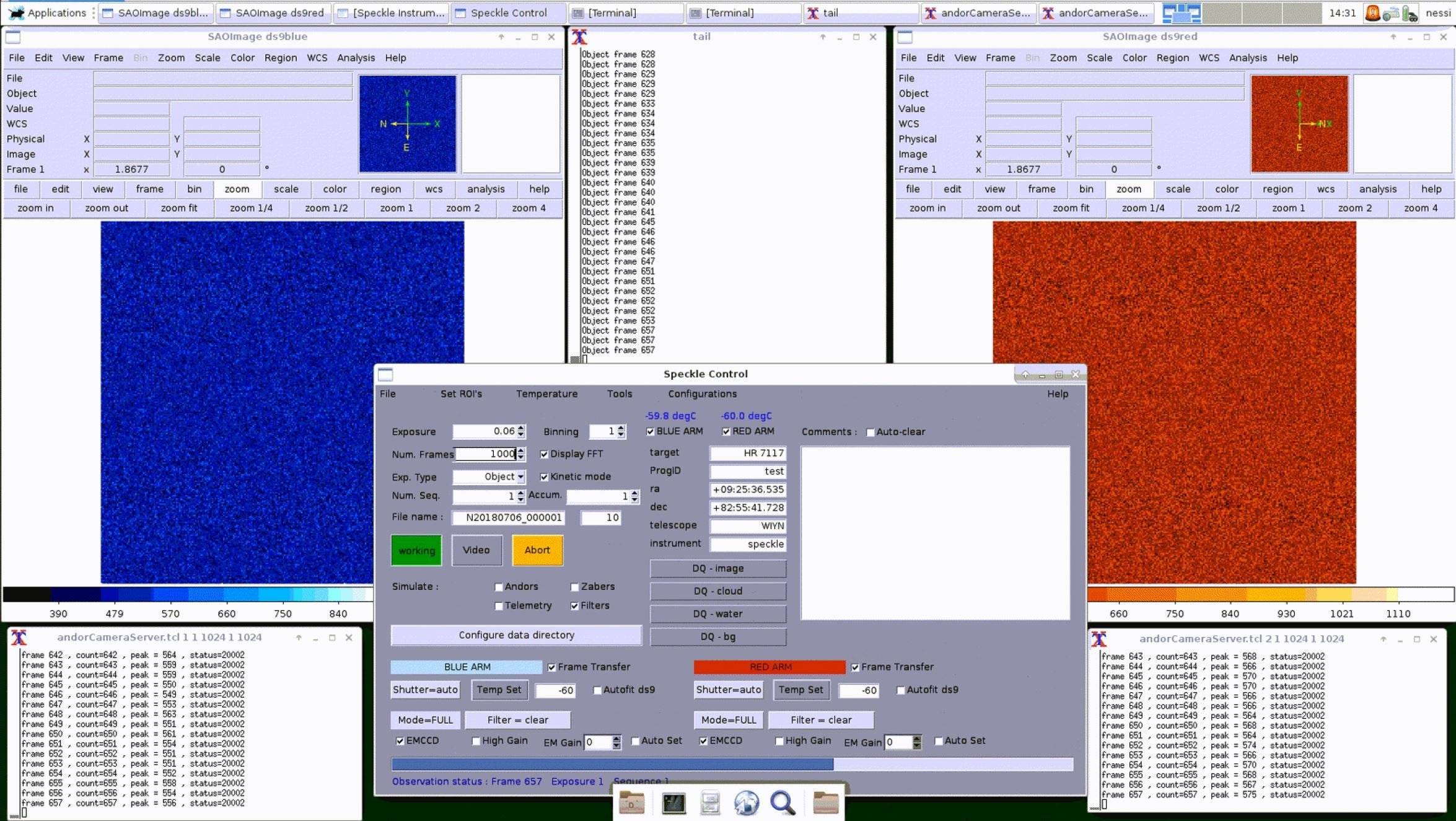
NESSI, 'Alopeke, and Zorro
Nic Scott
NASA ARC

BAEM 2018
3 new speckle imagers






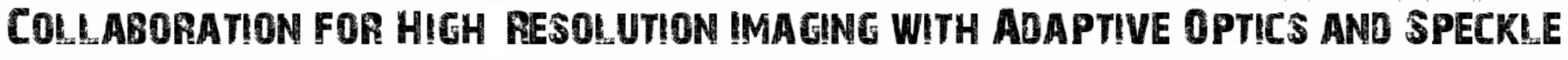
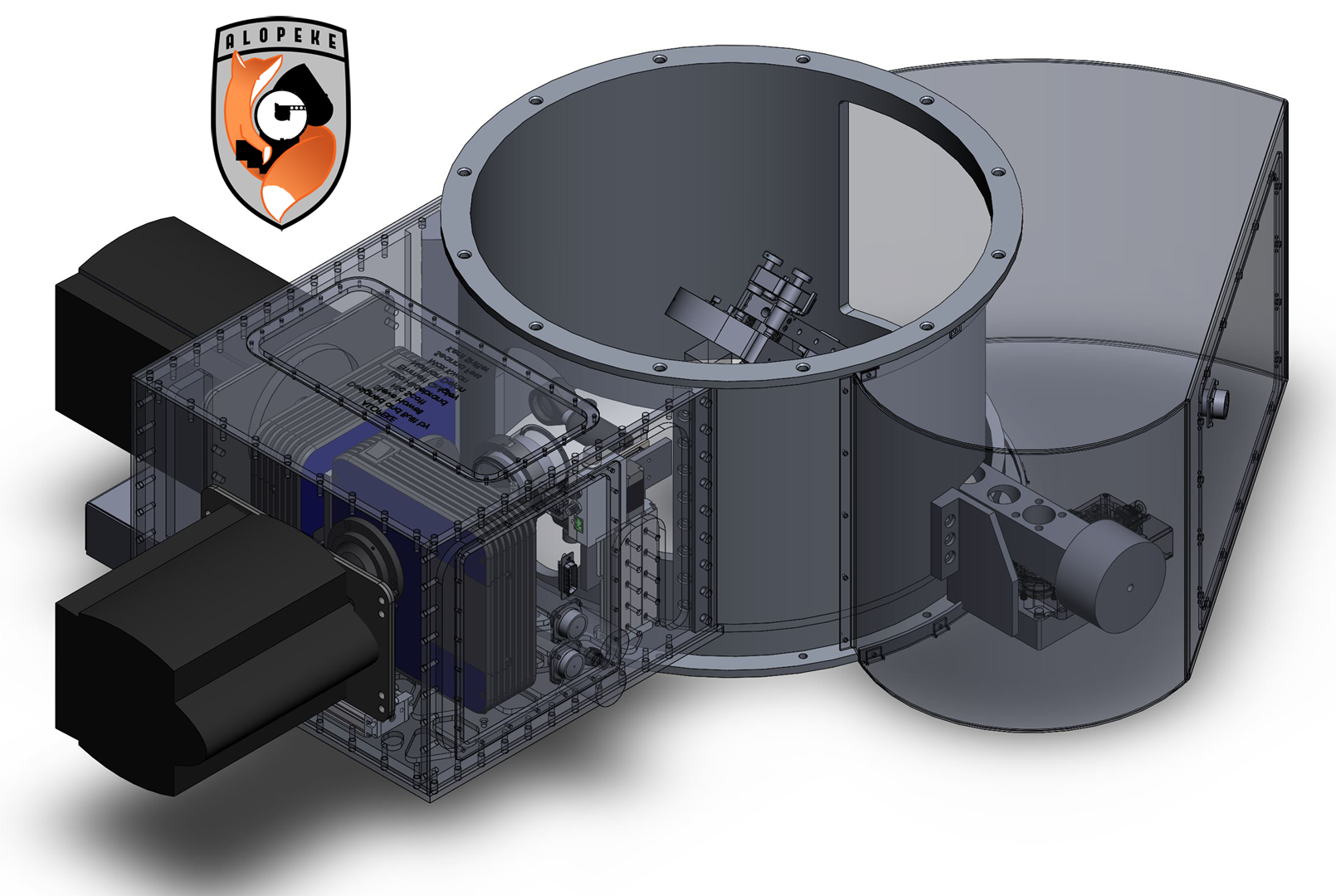
DSSI/NESSI/`Alopeke/Zorro






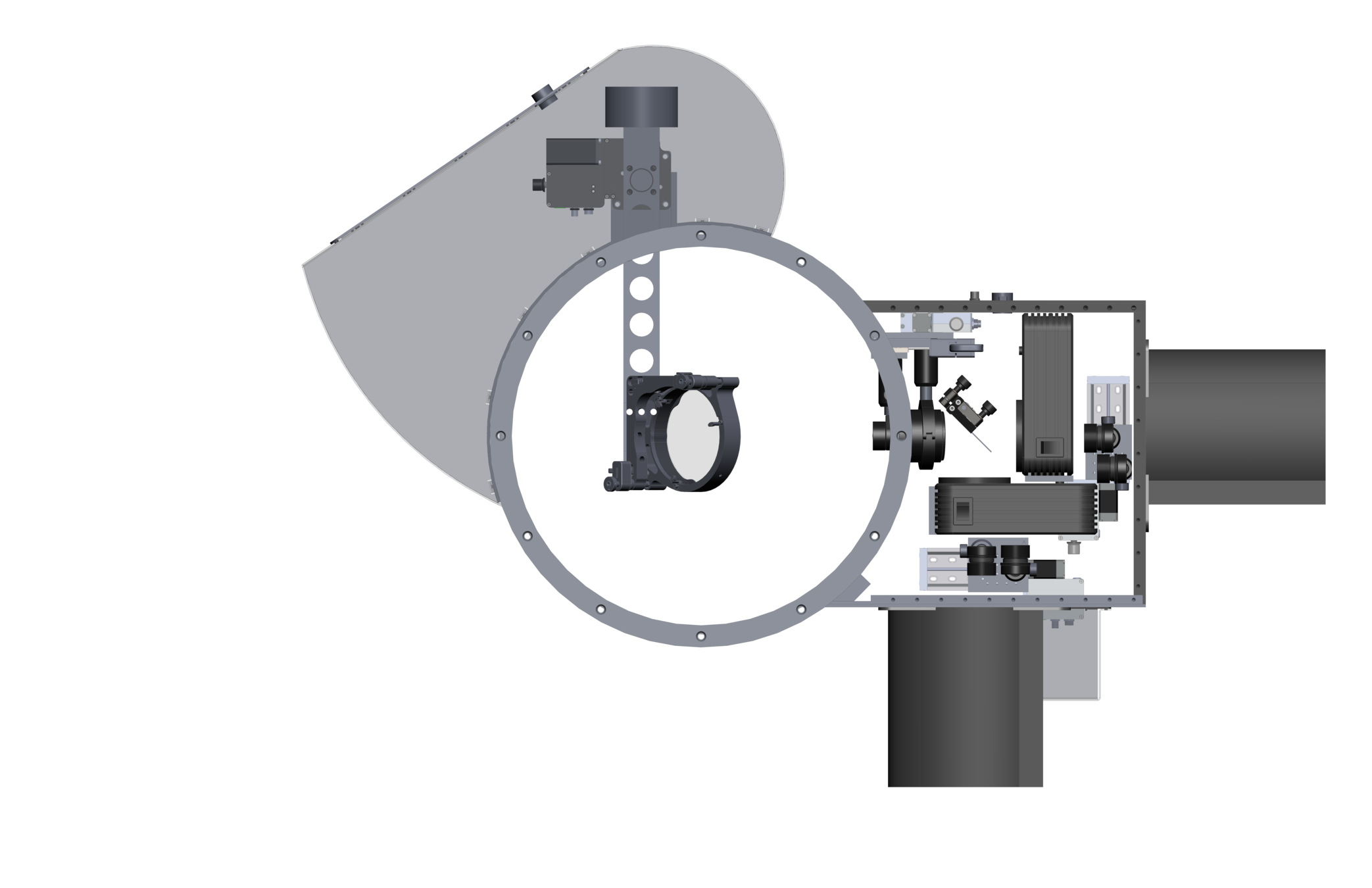


Speckle
- 10mas/pxl
- mag limit ~17
- contrast limit ~8
Wide Field
- 73mas/pxl
Speckle
- 18mas/pxl
- mag limit ~14
- contrast limit ~6
Wide Field
- 81mas/pxl


0.011'' @u
0.026'' @832nm
0.025'' @u
0.060'' @832nm
6.7''
60''
19''
56''


3-4x improvement over native seeing


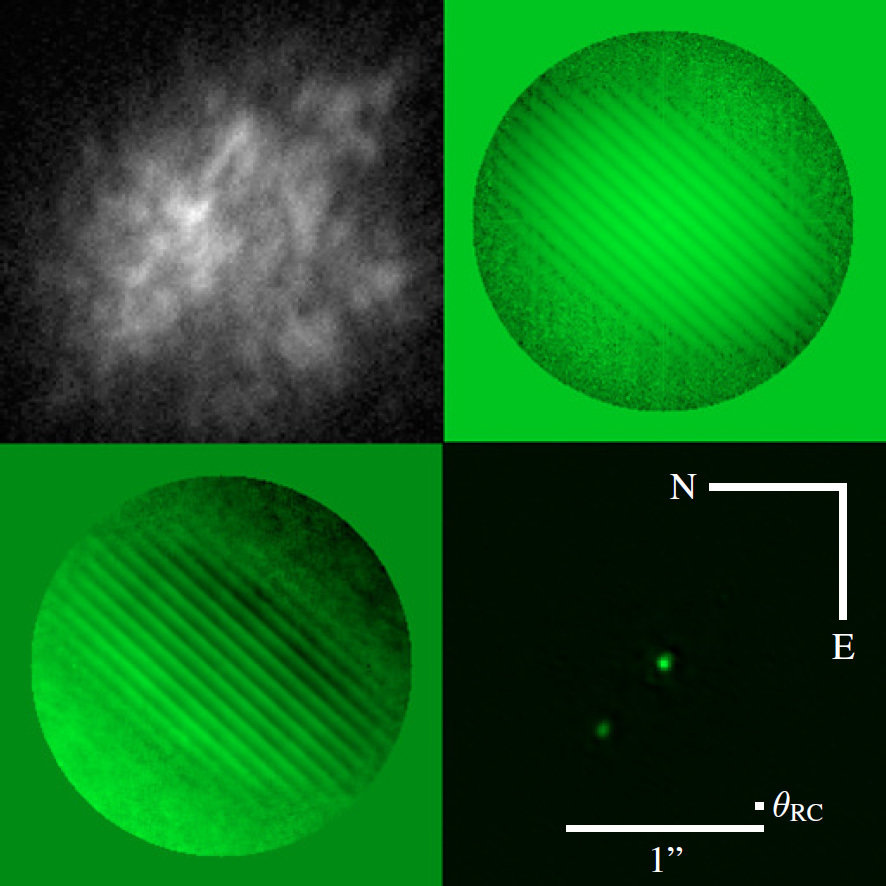

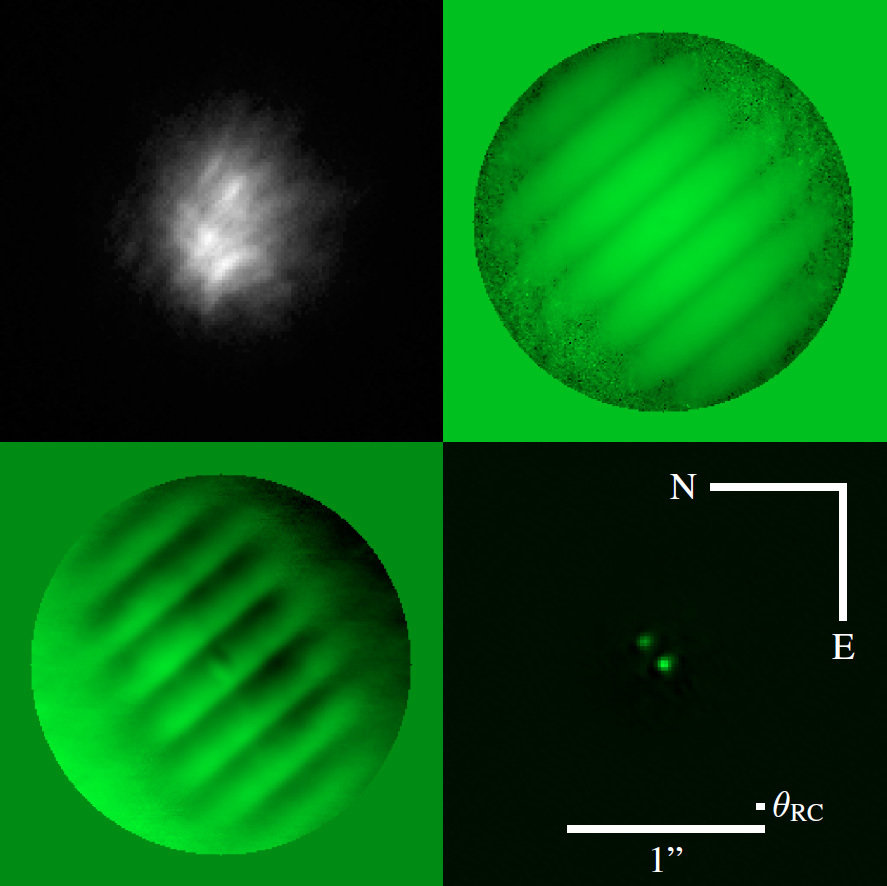


1s
40s
20min
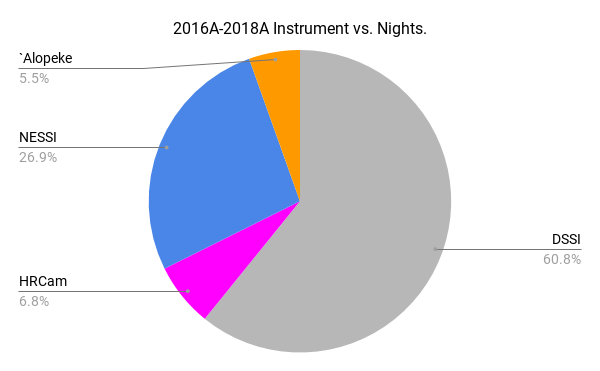
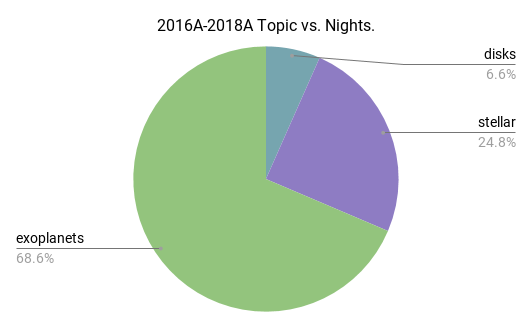
Science Programs
40 total proposals
110.04 total nights
(NOAO 2016A to 2018B)
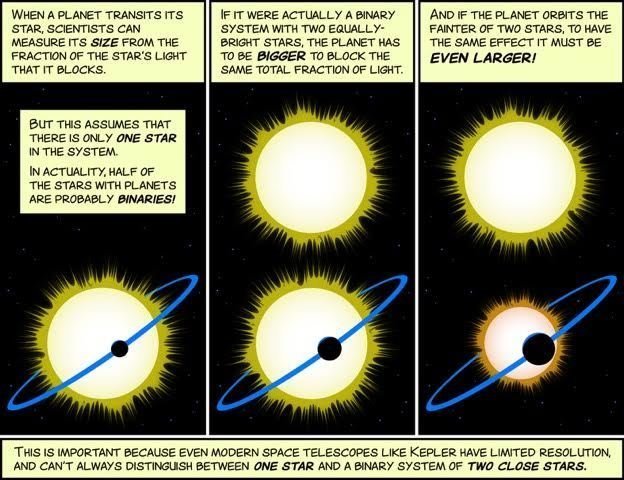
- Constrain NEA diameters. Image SS objects
- Determine multiplicity of nearby K and M-dwarfs, does it vary across spectral type?
- Imaging of brown dwarfs and distant large planets, particularly around M dwarfs
- Investigate differences in planetary system architectures between multiple vs not (known) multiple host stars
- Examine long-term RV trends/determine binarity of RV planet hosts.
- K2, TESS follow-up
- Provide an unbiased sample for TESS, so statistical determinations of planet occurrence rates can be made
- Occultations, transit photometry, pulsar time scales, observe pulsating WDs at high cadence
Some proposals so far:
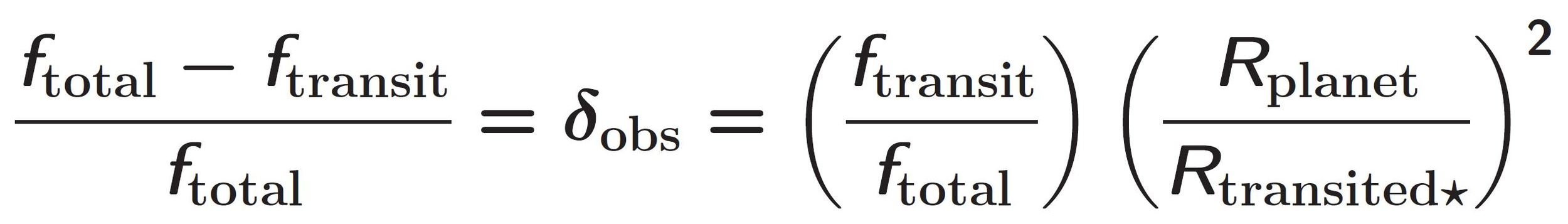


- optical, NIR imaging of host stars of KOIs
- ~ 90% of the confirmed and candidate exoplanet hosts
-
separations, PA, and dm for all detected, bound and
LoS companion stars. - 2297 companions around 1903 primary stars ~ 10% of the observed stars 1+ companions detected w/
i 1” - correction factors for exoplanet radii caused by the dilution of the transit depth
decreases the number of KOI planets with radii smaller than 2 Earth radii by 2% - 23%

Furlan's previous results applied to planets w/ known masses & radii, analyze the effects of a close stellar companion on planetary density.
- 50 planets orbiting 26 stars in the Kepler field
- a transit dilution requires the planet radii to be revised upward, decreasing the density of the planet
- if
planet orbits a faint companion star,density may decrease by ~ 3x
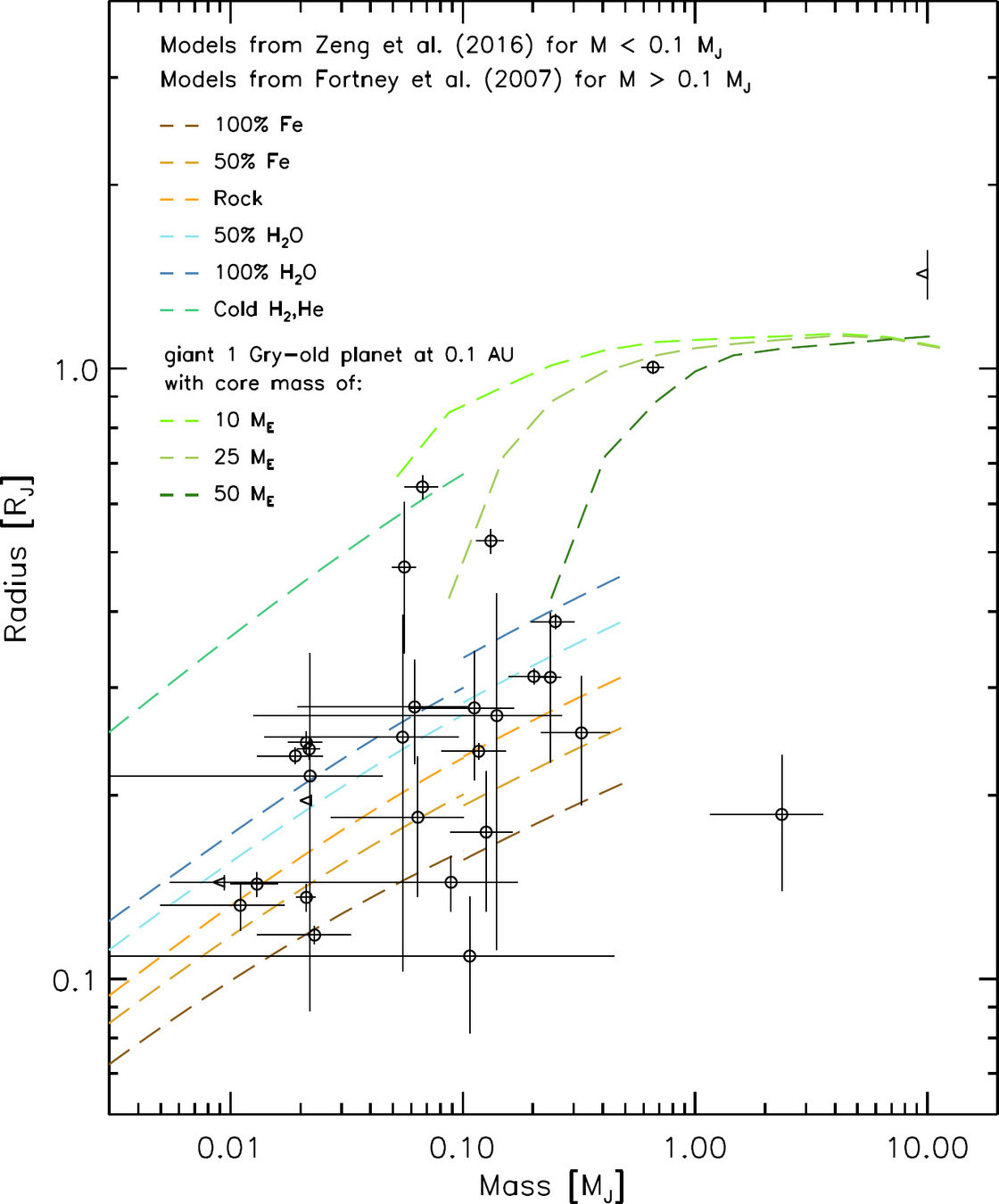



The effect of close ~ 0.5” companions of Kepler and K2 planet candidate hosts had on the inferred exoplanet radius distribution.
- Fulton gap is robust regarding undetected stellar companions
- gap became broader & shallower when accounting for possible undetected stellar companions
- core composition of super-Earth and sub-Neptune exoplanets may not have so strong a divide as is suggested initially
- w/o high-resolution imaging of Kepler and TESS host stars, the exoplanet radius distribution will be incorrectly inferred.
(2018, in press)

Fulton
mini-neptunes
super-Earths
- Large radius errors originally hid distribution features
- Fulton gap revealed after CKS (10% stellar radius errors)
- Accounting for binarity shifts gap in the distribution

brightest companion 1''
brightest companion 2''
Shift from 1.8 to 2.2
- increased water/ice vs pure Si rock

- 170 KOI companions < 2” using AO, speckle, lucky, or the HST
- constrained their stellar properties and assessed the probability that the companions are physically bound
- 60 - 80% of companions < 1” & > 90% of companions < 0.5” were found to be bound
- assuming the planet is equally likely to be orbiting the primary or
secondary, unless they are vetted, nearly half of all Kepler planets may have radii underestimated by an average of 65%.


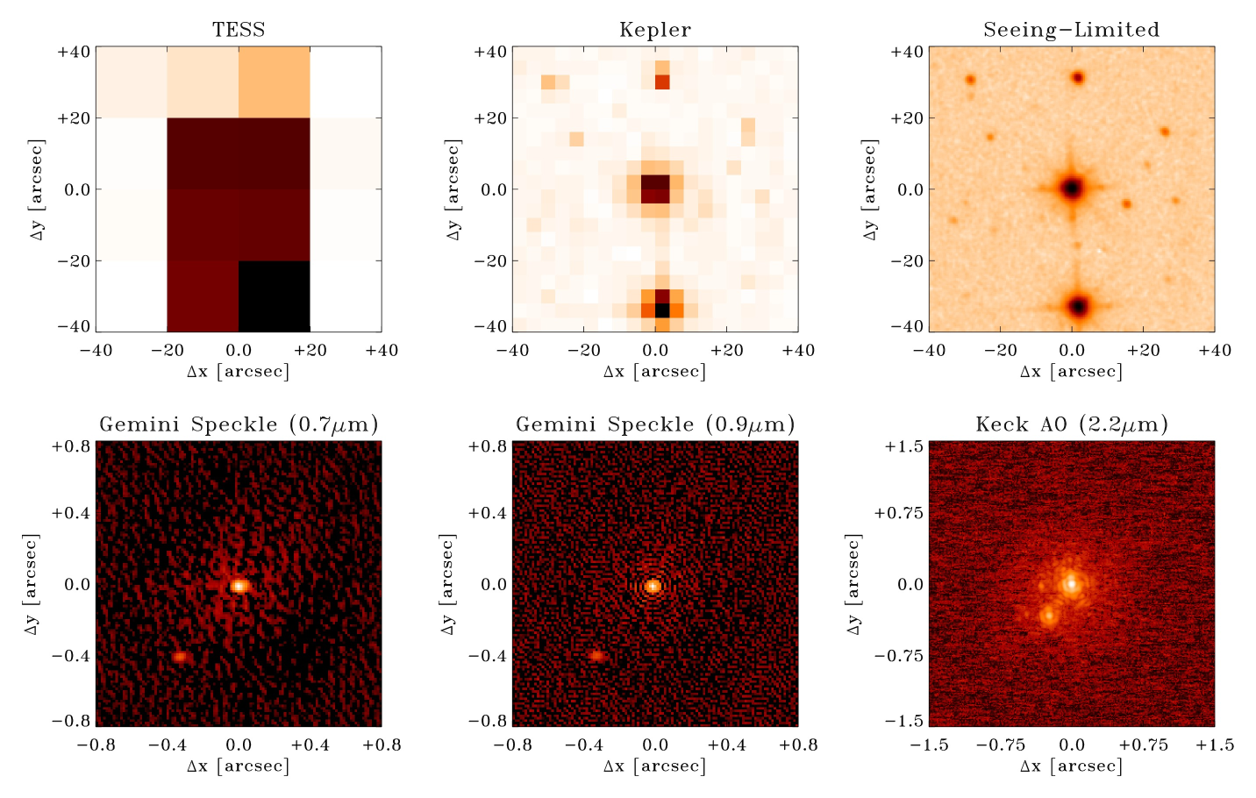
- DSSI @ G-S
- highest-resolution images to date
- 27 mas
- imaging from 0.32 to 14.5
au - excludes all possible stellar and brown dwarf companions


Open to the community
- NOAO proposal process
- NESSI - WIYN@KPNO
- `Alopeke - Gemini-N
- DSSI -> Zorro - Gemini-S
- Transitioning from visitor to ''Resident'' instrument
backup slides
Science Programs
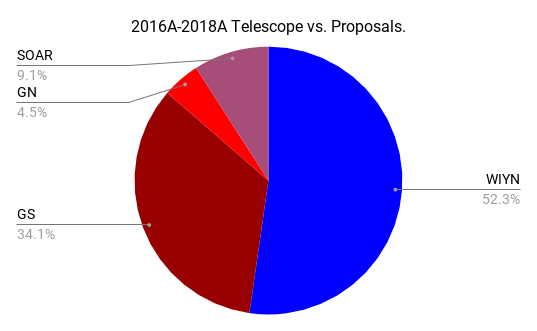
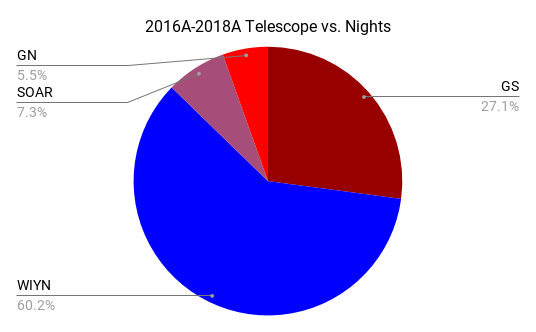
40 total proposals
110.04 total nights
(NOAO 2016A to 2018B)
Title Text
Text
Publications
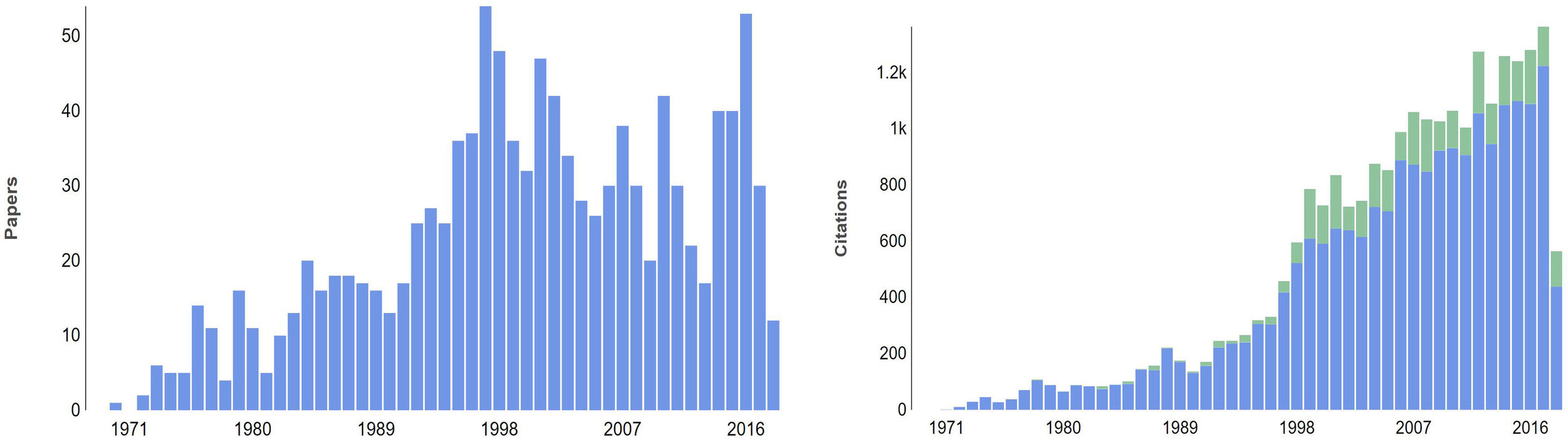
Text
blue bars are refereed citations to refereed papers
green bars are non-refereed citations to refereed papers
SAO/NASA ADS “Bumblebee” search: ‘‘speckle’’ - ‘‘speckle noise’’
- limited to astronomy and refereed
- removed AO speckle noise references
- excluded AO and spectroscopic techniques
- constrained to 1970+ sorted by citation count
This search returned 1,139 papers with 24,181 total citations
rise of EMCCDs & start of large speckle survey programs (& Kepler)?

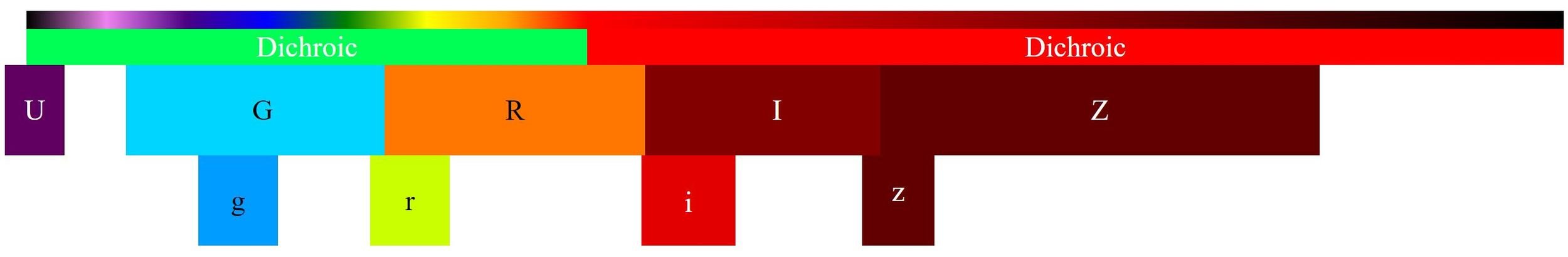
672.9
11
15
17
22
26
mas
Seeing-limited
Reconstructed

42''
Two-color wide-field speckle reconstruction
from NESSI
- 0.25'' resolution from 500 frames (20s)
- compromise b/t angres and contrast
- Seeing ~ 0.85''
Urban telescope WF speckle
Wide-field speckle techniques for small, urban telescopes, Nicole M. Granucci, Elliott P. Horch, Southern Connecticut State Univ. (USA) talk Tues (coming up next actually)[10701-20]
Pluto opposition
SOFIA occultation target duplicity


WF and speckle optics
Conv and EMCCD imaging
466/832 and g/i filters
New Horizons (not us.....yet)
TNO Varda ⌀~700km, d~50au
multiplicity is the single largest source of error to occultation path prediction

NEAs
- sizes
- radar typically quotes 40% uncertainties
- albedo/radar size mismatch
- shapes
- adapt stellar surface modeling tools
- light curve inversion/illumination model

a~2.8AU
d~270km x 80km
(neck~50-65km)

model: Franck Marchis


Phaethon
Dec 2017 ~ 0.07AU
d~6km


Point source PS
Phaethon power spectrum (resolved)

Labeyrie

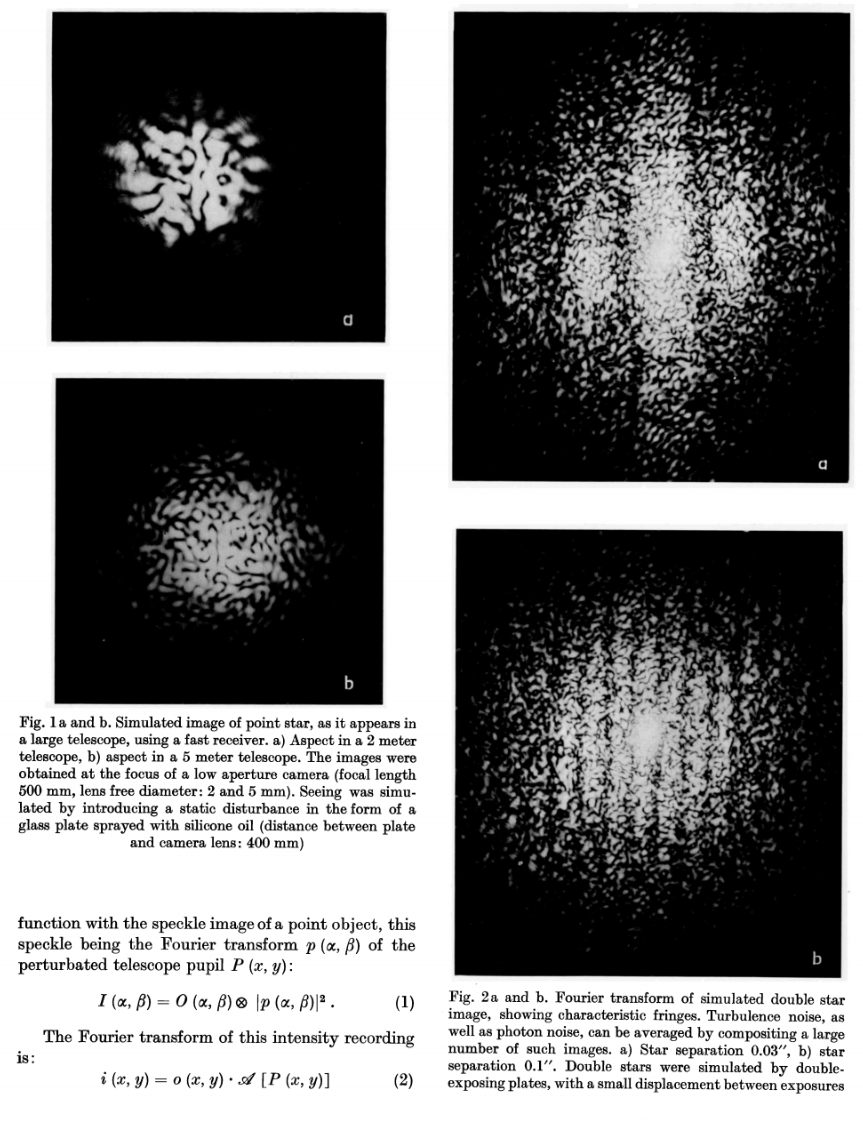
1970
Text
long exposure
speckles blur
produce Airy pattern
true images are impossible, only centrosymmetric objects can be reconstructed
speckle pattern is the Fourier transform of telescope pupil
Fourier autocorrelation of speckles
modulus
(time-averaged intensity)
Knox & Thompson
cross-spectrum, a 2nd order correlation
1974
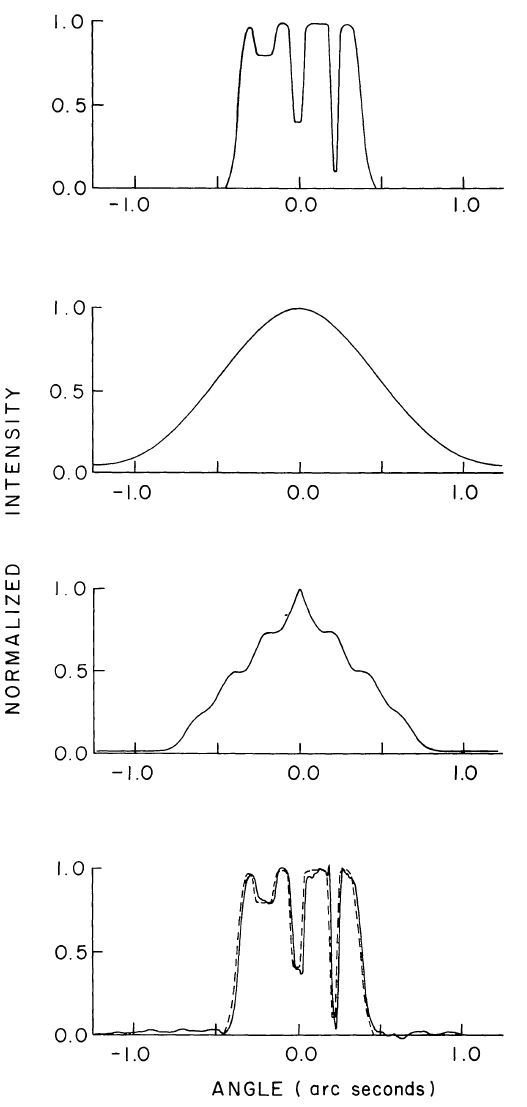
non-symmetric input
long exposure avg
Labeyrie technique
Knox & Thompson method
mean square of the image transform
modulus of the object transform
autocorrelation of the image transform
phase of the object transform
diffraction-limited image of the object
+
Weigelt & Lohmann
1977-1983
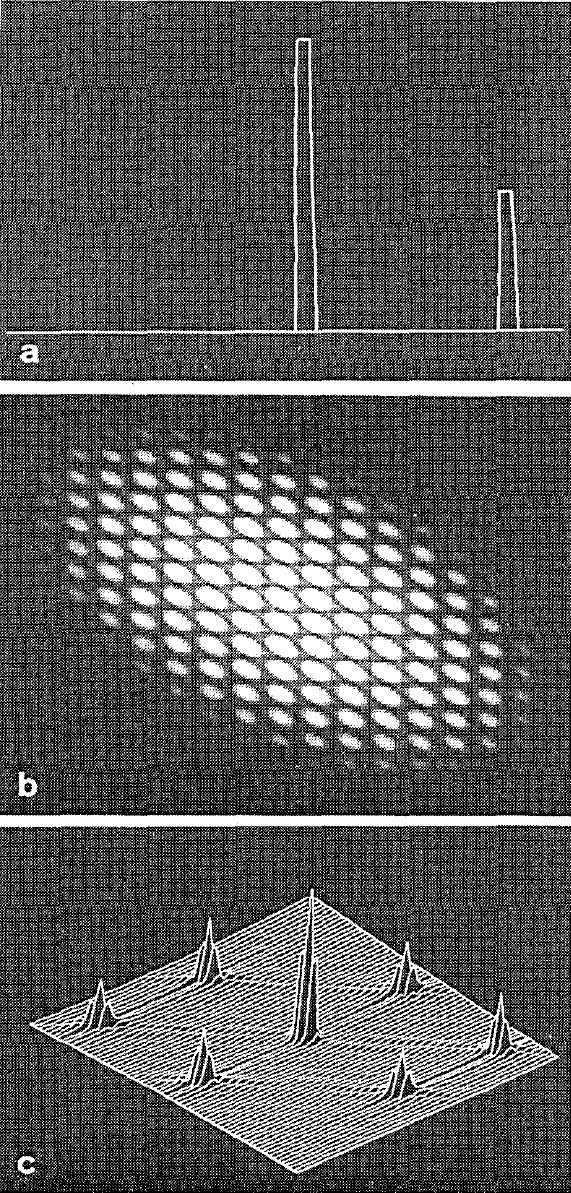
double star simulation
bispectrum modulus
triple correlation
record PSF of object
produce synthetic reference star by shifting the speckle pattern
phase is preserved
Speckle masking/triple correlation theory/bispectral analysis, a 3rd order correlation
deconvolve
true images
An aside on Lucky Imaging
- reaches higher resolution than typical seeing
- does not utilize Fourier analysis
- not capable of reaching the diffraction limit
- requires a very large number of images

http://inspirehep.net/record/823349/plots
Fried
1978
record a large series of images
discard instances of poor resolution
combine the remainder through shift-and-add techniques
Can reach

NESSI, Alopeke, and Zorro: 3 new speckle imagers
By Nic Scott
NESSI, Alopeke, and Zorro: 3 new speckle imagers
- 1,145



