NAZAR ILKIV <NIlkiv@luxoft.com>
Javascript developer
April 12, 2017
Hello Vue.js!
Framework Overview




JS frameworks popularity trends
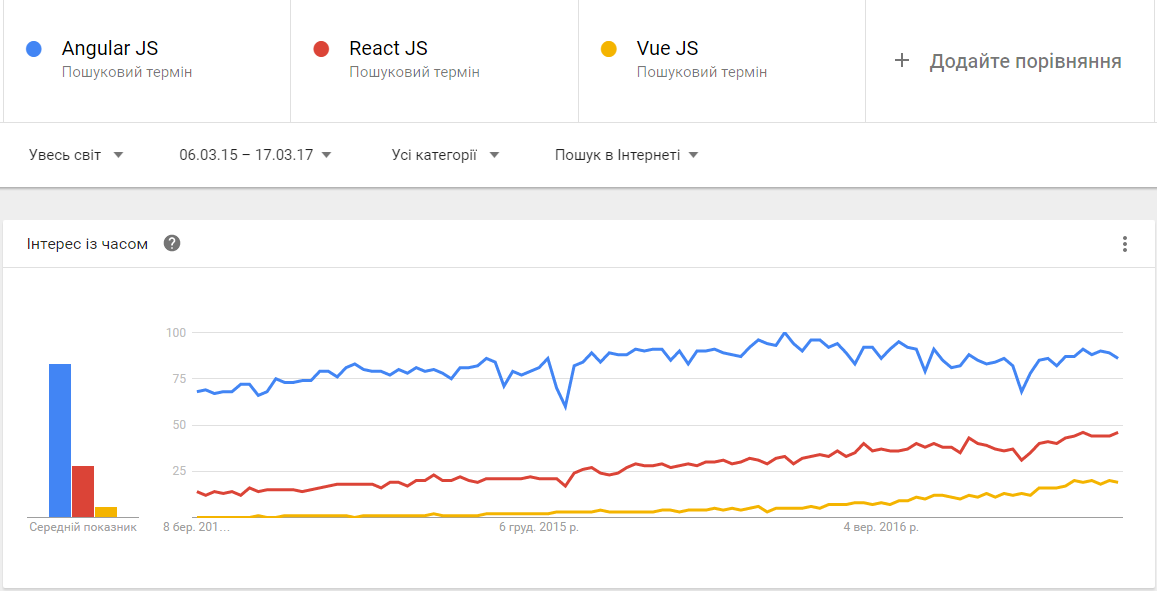
Vue.js is MVVM framework that is very easy to start and also a powerful tool for building UI

Quickstart
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Quickstart with Vue.js</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Hello World!'
}
});
</script>
<body>
</html>Template Syntax
- Text interpolation
- Attribute binging
- Built-in directives
<div>Message: {{ message }}</div><div v-html="message"></div><a v-bind:href="linkHref">Dynamic link</a><button v-bind:disabled="someDynamicCondition">Button</button><div v-if="isShown">This content is shown</div><ul>
<li v-for="fruit of fruits" :key="item.id">{{ fruit }}</li>
<ul><!-- shorthand -->
<a :href="url">Some link</a>Class and Style Bindings
<div v-bind:class="{ active: isActive }"></div><!-- Vue accepts array, object, expression and even function -->
<div id="app">
<div v-bind:class="classObject"></div>
</div>const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isActive: true,
error: null
},
computed: {
classObject: function () {
return {
active: this.isActive && !this.error,
'text-danger': this.error && this.error.type === 'fatal'
}
}
}
});<!-- Inline style bindings -->
<div v-bind:style="styleObject"></div>data: {
styleObject: {
color: 'red',
fontSize: '13px'
}
}Event handling
<div id="example">
<button v-on:click="say('hi')">Say hi</button>
<button v-on:click="say('what')">Say what</button>
</div>const app = new Vue({
el: '#example',
methods: {
say: function (message) {
alert(message)
}
}
});// or pass original DOM event
const app = new Vue({
el: '#example',
methods: {
say: function (message, event) {
event.preventDefault();
alert(message);
}
}
});Event modifiers
<!-- the click event's propagation will be stopped -->
<a v-on:click.stop="doThis"></a>
<!-- the submit event will no longer reload the page -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent="onSubmit"></form>
<!-- modifiers can be chained -->
<a v-on:click.stop.prevent="doThat"></a>
<!-- just the modifier -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent></form>
<!-- use capture mode when adding the event listener -->
<!-- i.e. an event targeting an inner element -->
<!-- is handled here before being handled by that element -->
<div v-on:click.capture="doThis">...</div>
<!-- only trigger handler if event.target is the element itself -->
<!-- i.e. not from a child element -->
<div v-on:click.self="doThat">...</div>
<!-- the click event will be triggered at most once -->
<a v-on:click.once="doThis"></a>Key modifiers
<!-- submit() method when hit Enter key -->
<input v-on:keyup.enter="submit"><!-- or use keycode -->
<input v-on:keyup.13="submit"><!-- even mouse button modifiers -->
<div v-on:click.right="customTaskMenu"></div>Form Input Bindings
<!-- Text -->
<input v-model="message" placeholder="edit me">
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p><!-- Multiple checkboxes, bound to the same Array -->
<input type="checkbox" id="jack" value="Jack" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="jack">Jack</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="john" value="John" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="john">John</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="mike" value="Mike" v-model="checkedNames">
<label for="mike">Mike</label>
<br>
<span>Checked names: {{ checkedNames }}</span>
new Vue({
el: '...',
data: {
checkedNames: []
}
})Components
// register globally
Vue.component('my-component', {
template: '<div>A custom component!</div>'
})
// create a root instance
new Vue({
el: '#example'
})<div id="example">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>// register locally
new Vue({
el: '#example',
components: {
// <my-component> will only be available in parent's template
'my-component': {
template: '<div>A custom component!</div>'
}
}
})<div id="example">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<div id="example2">
<!-- not available here -->
<my-component></my-component>
</div>Component props
Vue.component('someComp', {
props: ['text'],
template: '<span>{{ message }}</span>'
})<some-comp message="hello!"></some-comp>
<!-- will render -->
<span>hello!</span>Every component instance has its own isolated scope.
Data can be passed down to child components using props.
Only one way data flow. Never mutate prop inside child component
Vue.component('example', {
props: {
// basic type check (`null` means accept any type)
propA: Number,
// multiple possible types
propB: [String, Number],
// a required string
propC: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// a number with default value
propD: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// object/array defaults should be returned from a
// factory function
propE: {
type: Object,
default: function () {
return { message: 'hello' }
}
},
// custom validator function
propF: {
validator: function (value) {
return value > 10
}
}
}
})Prop validation
<div id="counter-event-example">
<p>{{ total }}</p>
<button-counter v-on:increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>
<button-counter v-on:increment="incrementTotal"></button-counter>
</div>Component communication
Vue.component('button-counter', {
template: '<button v-on:click="increment">{{ counter }}</button>',
data: function () {
return {
counter: 0
}
},
methods: {
increment: function () {
this.counter += 1
this.$emit('increment')
}
},
})
new Vue({
el: '#counter-event-example',
data: {
total: 0
},
methods: {
incrementTotal: function () {
this.total += 1
}
}
})Directives
Built-in
- v-for
- v-model
- v-show
- etc.
Custom
// Register a global custom directive
Vue.directive('focus', {
// When the bound element
// is inserted into the DOM...
inserted: function (el) {
// Focus the element
el.focus()
}
})// Register a local custom directive
const app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
someData: 'hello'
},
directives: {
focus: {
// directive definition
}
}
});Directive hook functions
- bind: called only once, when the directive is first bound to the element. This is where you can do one-time setup work.
- inserted: called when the bound element has been inserted into its parent node (this only guarantees parent node presence, not necessarily in-document).
- update: called after the containing component has updated, but possibly before its children have updated.
- componentUpdated: called after the containing component and its children have updated.
- unbind: called only once, when the directive is unbound from the element.
Computed Properties
<div id="example">
<p>Original message: "{{ message }}"</p>
<p>Computed reversed message: "{{ reversedMessage }}"</p>
</div>const app = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
message: 'Hello'
},
computed: {
// a computed getter
reversedMessage: function () {
// `this` points to the vm instance
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
});Watchers
<div id="watch-example">
<p>
Ask some question:
<input v-model="question">
</p>
<p>{{ answer }}</p>
</div>const app = new Vue({
el: '#watch-example',
data: {
question: '',
answer: ''
},
watch: {
// whenever question changes, this function will run
question: function (newQuestion) {
this.answer = `Answer to question: ${this.question}`
}
}
});Vue instance lifecycle
- beforeCreate
- created
- beforeMount
- mounted
- beforeUpdate
- updated
- beforeDestroy
- destroyed
How to put things together

Single File Component
<template>
<p>{{ greeting }} World!</p>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: function() {
return {greeting: 'Hello'}
}
}
</script>
<style>
p { font-size: 2em; }
</style>Hello.vue file
What about scaling?
- Vue-router: https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router
- Vuex: https://github.com/vuejs/vuex
- Redux: https://github.com/revue/revue
Tools for building SPAs:
Additional tools:
- JSX support: https://github.com/vuejs/babel-plugin-transform-vue-jsx
- TypeScript support: https://github.com/vuejs/vue/tree/dev/types
LINKS
https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/
https://github.com/vuejs/vue
Q&A Time
Nazar Ilkiv <NIlkiv@luxoft.com>
Javascript developer
April 12, 2017
Hello Vue.js!
Framework overview
Hello Vue.js
By Nazar Ilkiv
Hello Vue.js
- 991



