COMP2511
🎨 9.2 - Introduction to Microservices (Bonus)
In this lecture
- Service-Oriented Architecture
- Monolith vs Microservices
- Microservice Ecosystem and technologies
- Trade-offs of a Microservice Approach
Service-Oriented Computing
- The era of cloud computing - a move from software as products to software as services
- Infrastructure as a Service - physical / virtual machines to run code on is provided as a service
- Platform as a Service - hardware and operating system are provided and accessed remotely by developers
- Software as a Service - hardware, operating system and software are outsourced and accessed remotely and used by users
- Platform layers and platformisation in PaaS
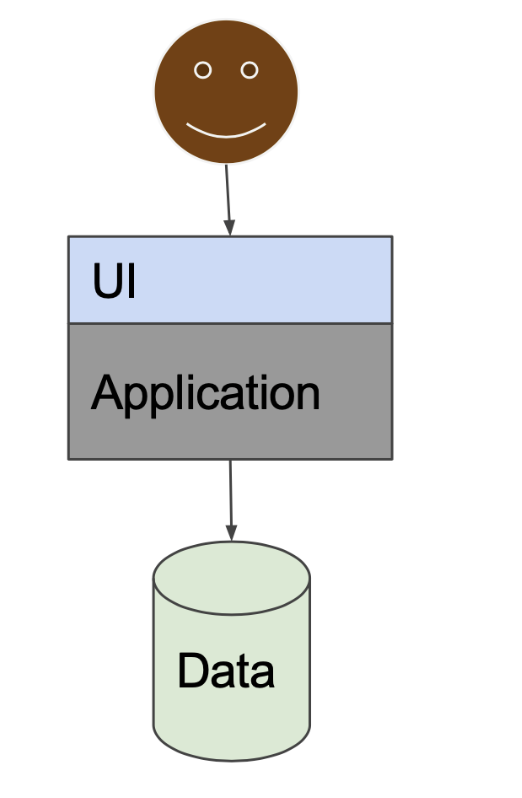
Monolith vs Microservices
-
Monolith: a single large application that contains the entire software solution
- One service to rule them all
-
Microservices: A series of small-scale services that communicate with one another
- Each service does one task well
- Where have we seen this before?
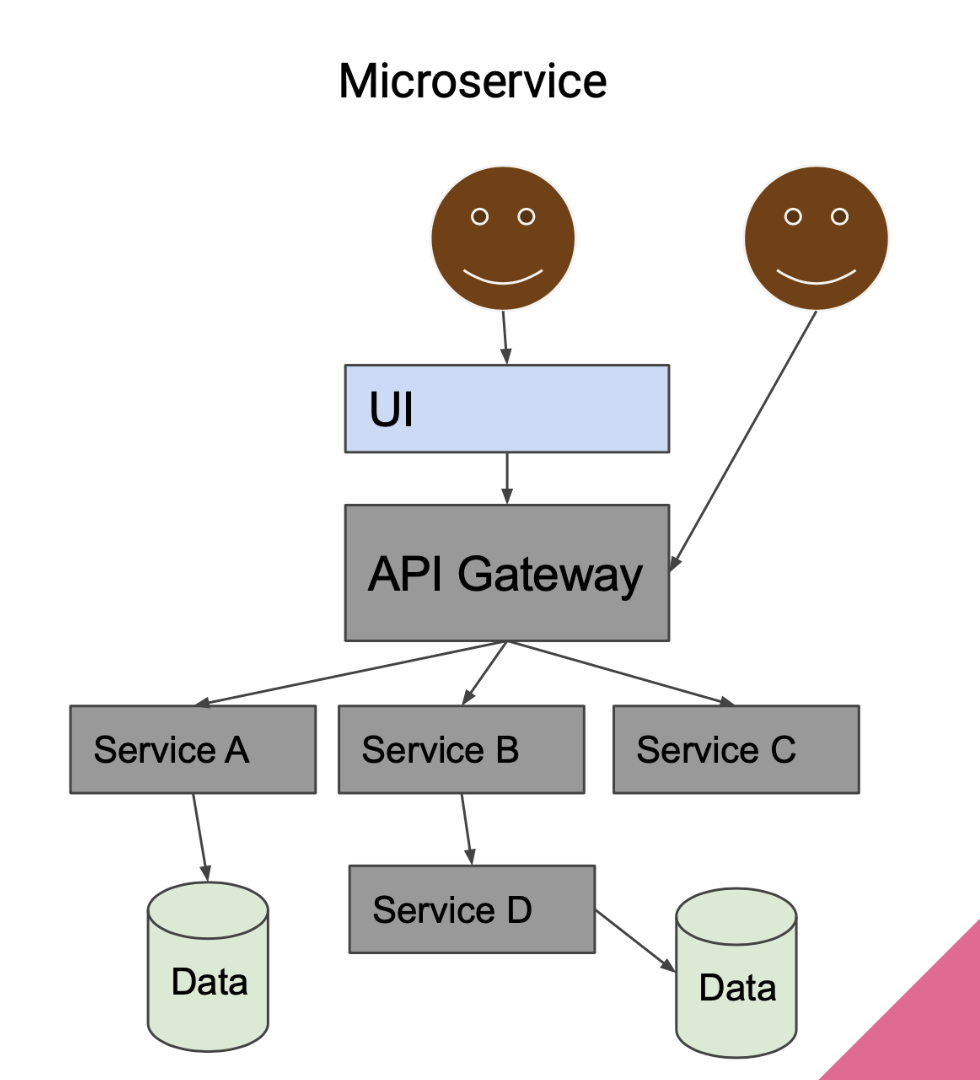

Microservices Example
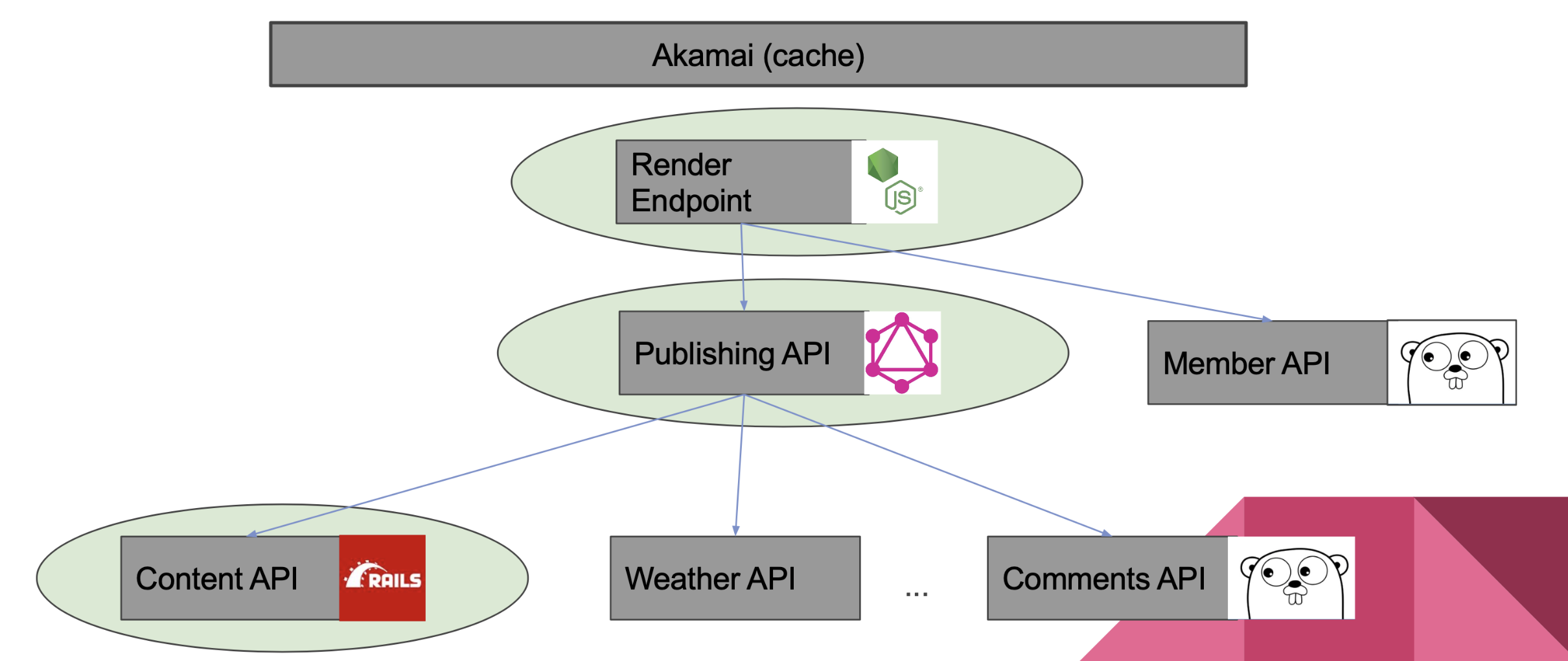
Microservice Ecosystem: Data Interchange
- Services need to be able to communicate to one another over a common interface
- Synchronous interchange technologies
- REST
- gRPC - uses Protobuf, good for Service to Service communication
- GraphQL - a query languages allowing for dynamic querying of data - good for public-facing APIs
- Asynchronous interchange technologies
- Apache Kafka
- Amazon SQS / SNS
- Eventual consistency - propagation of state so that Services have same logical state model
Microservice Ecosystem: Deployment
- Amazon & AWS - IaaS
- Applications - Elastic Beanstalk
- Compute - EC2
- Compute - Lambdas - Serverless Deployment
- Storage - S3
- Database - DynamoDB / RDS
- Containerisation - Docker images
- Observability - tools to help you understand what's happening inside a deployed application
- Feature Flags - switchboards to toggle and incrementally release new parts of code
- ... and much, much more
Trade-offs: Microservice Benefits
- Freedom for service-specific programming languages / technology stacks
- Less responsibility, less coupling
- Easier to test
- Faster build and release cycles
- Lower risk per-microservice
- Not a single point of failure
- Easier to scale individual services
Trade-offs: Microservice Costs
- Either everything breaks, or the glue breaks - how much time and money is actually saved?
- Dealing with distributed systems
- Reliance on network connections
- Communication latency
- Consistency between services running in parallel
- Overhead, complexity and risk in orchestrating services in an end-to-end use case
- More complex deployment
- Security - now need to authenticate for every service, not just one
- Debugging is more difficult as control flows over different services (distributed tracing)
Summary
- All Software Architecture is making trade-offs
- Monoliths grow too large, complex and risky and too difficult to scale
- Microservices present an alternative, which have their own challenges
COMP2511 23T2 - Introduction to Microservices (Bonus)
By npatrikeos
COMP2511 23T2 - Introduction to Microservices (Bonus)
- 903



