Programming in the Large
+ The Project
COMP2511
In this lecture
Why?
- Understand the broader context of the project and software design & development
- Compare sequential and iterative development
- Introduce the project
- Discuss project management relevant to Milestones 1, 2, 3
The Software Development Lifecycle
- Bullet One
- Bullet Two
- Bullet Three

Requirements to Design: An Abstraction
- What problem are we trying to solve?
- What does a good outcome look like - start with the end
- Then come up with a solution
Requirements to Design:
A Series of Abstractions
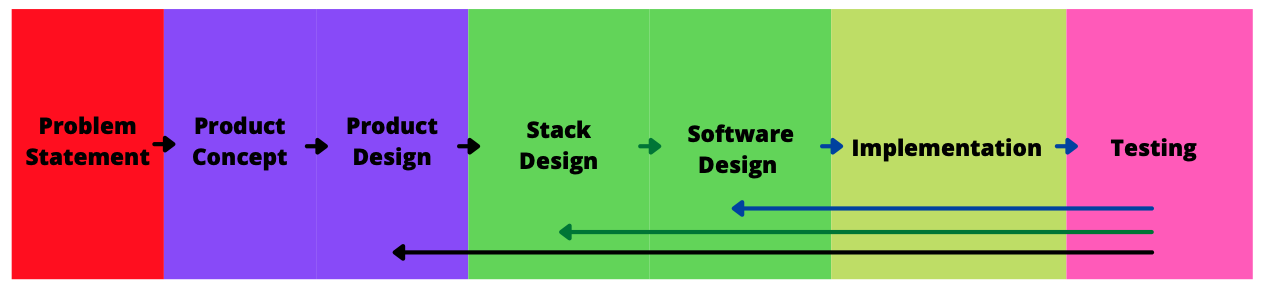
- Product concept: How can we solve the problem with software?
- Product design: Epics, user stories, acceptance criteria, UI design
- Stack design: frontend, backend, data layer, integrations
- Software design (OO): Entities, objects, relationships (UML diagram)
Project Intro
The Big Design Up-Front vs Incremental Design
"Traditional Engineering"
- One step at a time
- Ensure the current step is perfect before moving onto the next one
- A big design up front
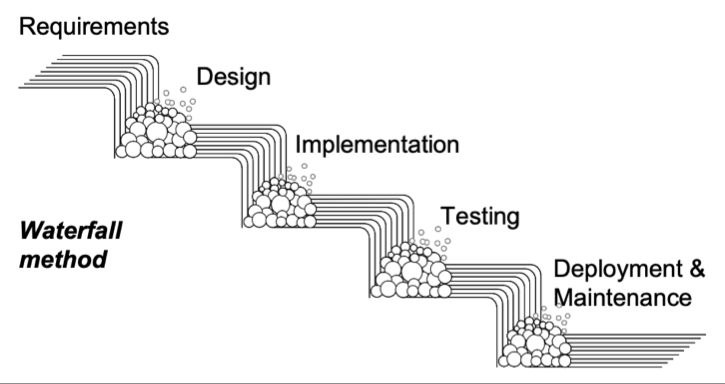
Problems with Designing Up-Front
- Too many unknown unknowns
- What if the requirements change?
Iterative Design
- Work in sprints, iterations, milestones
- 'Agile' software development
- Many variants - eXtreme programming, Rapid Application Development, Kanban, Scrum
- Design incrementally
- Adapt to changes in requirements
- Discover and deal with problems in design as they arise
Problems with Incremental Design
- No clear sense of direction/trajectory
- In poorly designed systems, adaptations to new requirements become smaller-scale 'workarounds' - limit functionality/decrease maintainability
- Tendency to 'make it up as we go along'
A solution?
- Design a broad overview up-front
- A framework to begin development
- Adapt and change the design during development as needed
- Set the trajectory and boundaries of work at the start
- Design up-front a solution that is open for extension, reusable, etc.
- Milestone 1
Project Management
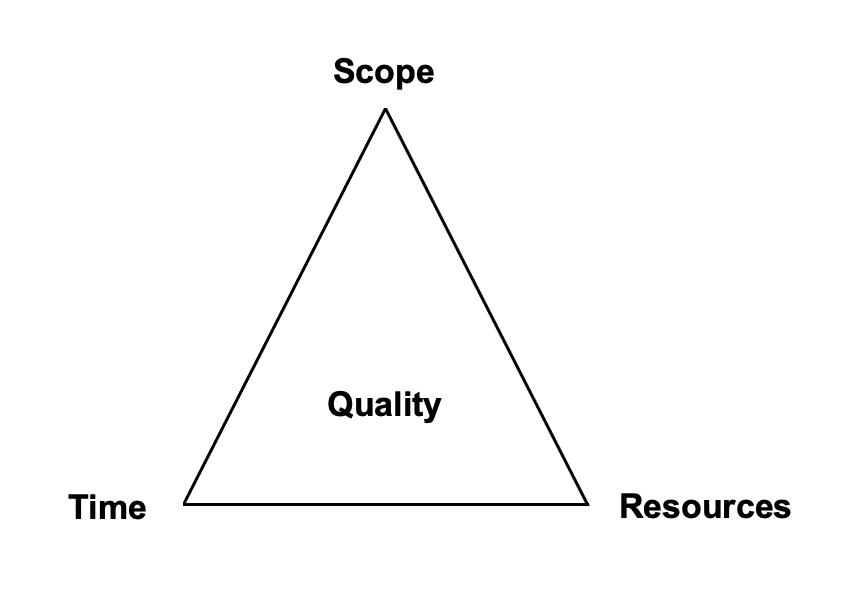
- Scope - requirements to implement
- Time
- Resources
- Outcome - quality
- We care more about quality than quantity in this project
What even is Software Quality?
- Software that works
- Software that is well tested
- Provides assurance that the software does actually work
- Software that is well designed
- What happens when the requirements evolve?
- Milestone 3
Building an MVP
- Focus of Milestone 2
- Get something basic working that is well tested and well designed
- Break the requirements up into small features
- Prioritise the most important features and complete first
- Approach:
- Make a new branch for a single feature e.g. nick/battle
- Design and stub out classes / functions
- Write failing unit tests
- Implement so the tests pass
- Merge branch into master
Project Management
- Test-Driven Development
- Git practices
- One feature, one branch, one merge request into master
- Approve merge requests & code reviews
- Code on master should always be stable
- Meeting minutes
- Use of GitLab Taskboard or Jira Taskboard
- Timeline (next slide)
Timeline
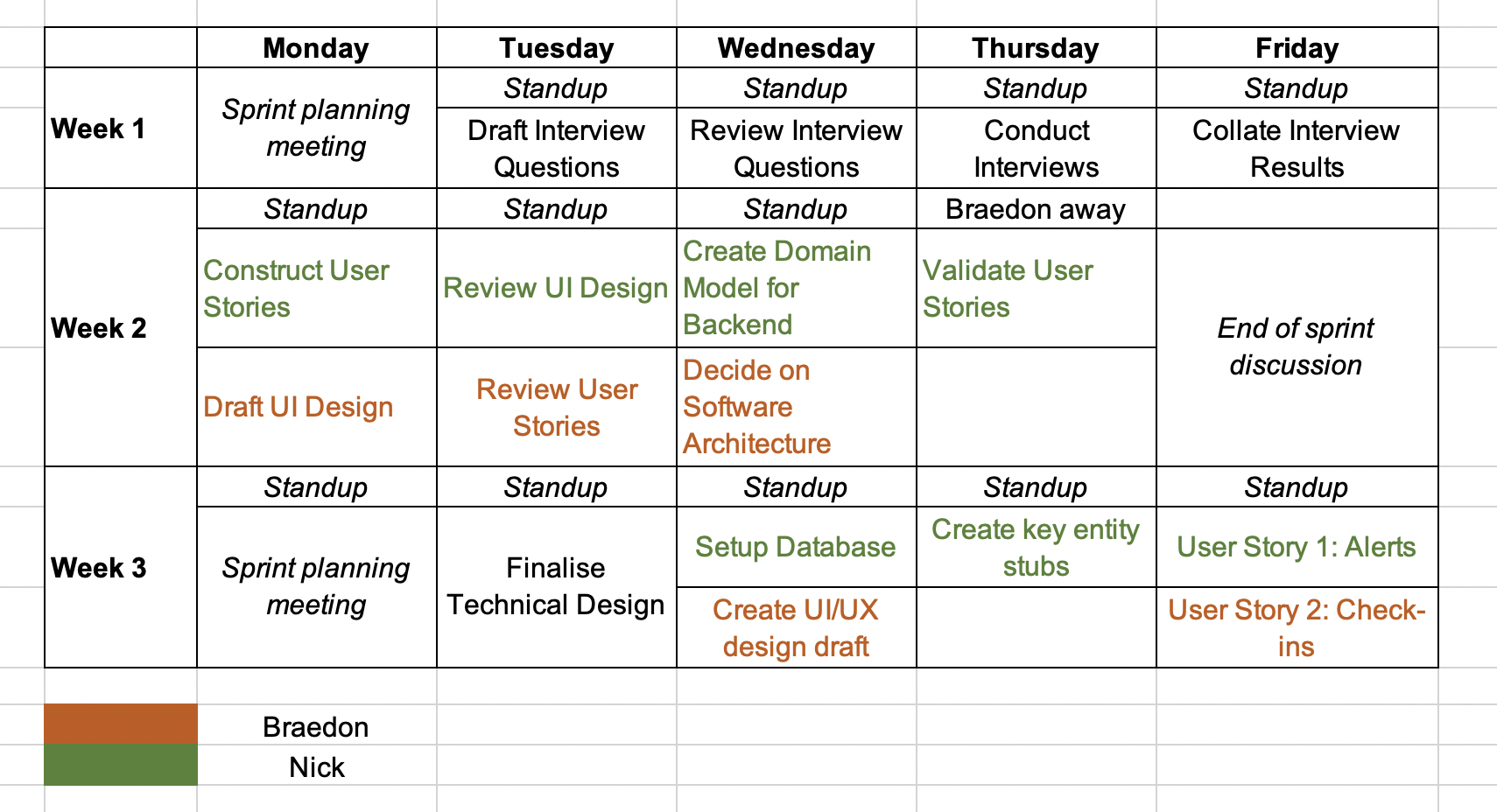
- Delegate requirements to each person
- Considerations
- Sequencing of Tasks - which tasks are most important? Which need completing first for others? (prerequisites)
- Allocation of Tasks - allocate equally and based on availability
- Timespan of Tasks - how long will each task take?
Teamwork
- Designing as a team - everyone needs to be on the same page
- Everyone needs to write code and contribute to documentation (PM, UML, etc.)
- Tutor & project check-ins - mentoring & guidance
- Dealing with teamwork problems:
- Make an active effort to resolve internally
- Speak to your tutor
- Email cs2511@cse.unsw.edu.au
COMP2511: Programming in the Large
By npatrikeos
COMP2511: Programming in the Large
- 1,426



