SENG2021
1.3 - Teamwork 🏈
Project Management
In this lecture
- Principles of project management
- Issues in software project management
- Agile software development principles
- Software project management with scrum
- Constraints Analysis
- Teamwork
What is a project?
- A large-scale task to complete
- Definite time of delivery (start and finish date)
- Capitalised set budget
- An end product (Solution presentation)
- Benefit realisation (Value Creation)
- Most projects fail
Factors in Project Management
time + quality + resources = scope
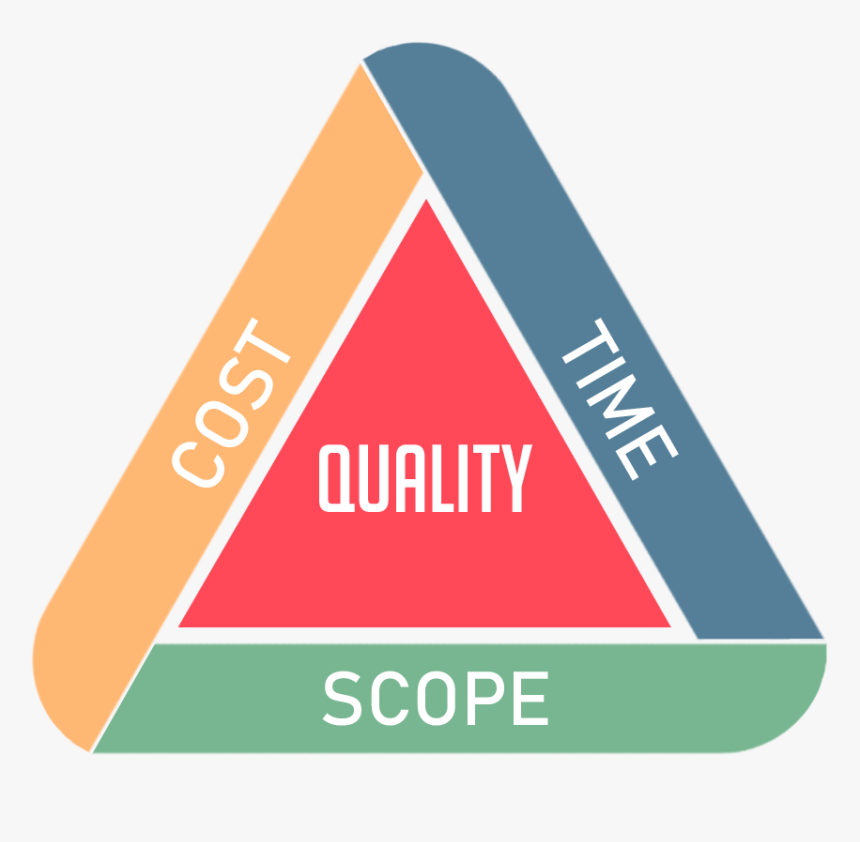
- What happens if we...
- Decrease/increase time?
- Decrease/increase resources?
- Decrease/increase quality?
Speed vs Quality
- A foundational problem in software engineering
- We care more about quality than quantity in this course
The Waterfall Approach
- Sequential approach to developing software
- Ensure the current step is perfect before moving onto the next one
- Projects take months - years to complete
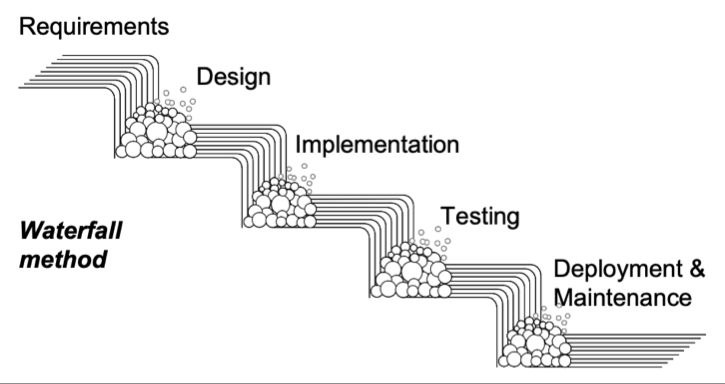
Problems with Waterfall
- The game changes
- Changing market
- Changing client expectations
- Changing technical world
- The Evolution of Requirements
- We can't predict everything up-front
- Known unknowns
- Unknown unknowns
"Agile"
- There is no golden solution to project management
- Agile philosophies and methodologies are an improvement, but still have flaws
- Different companies, systems and projects have different requirements - and hence ways of management
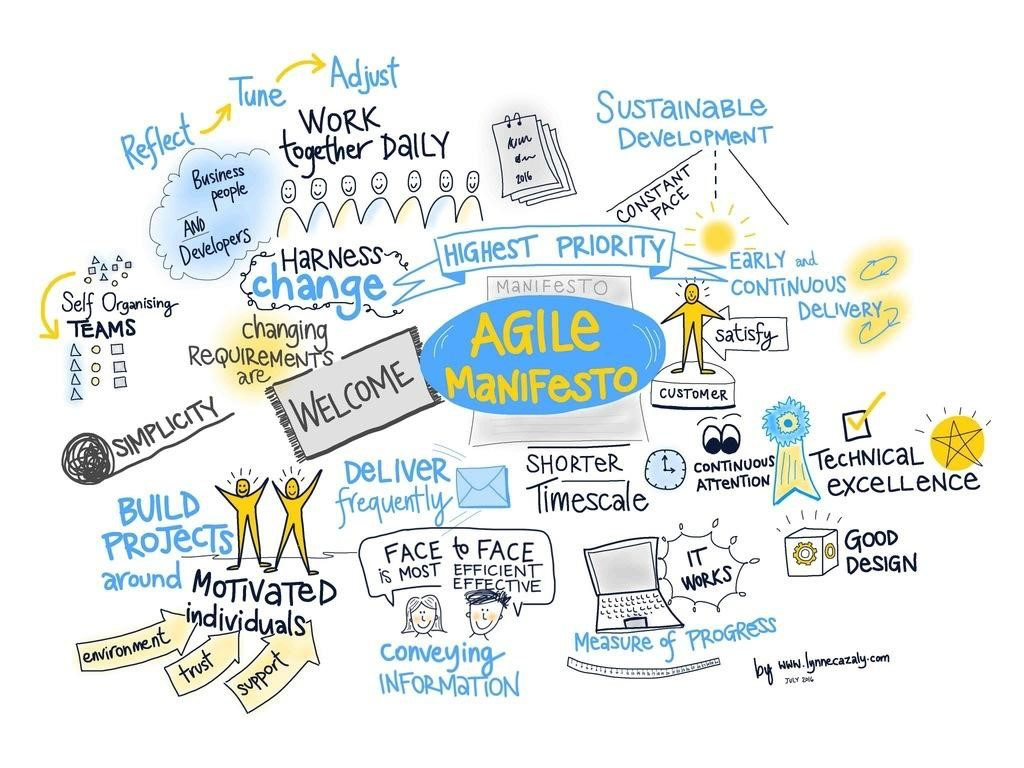
Agile Philosophy
-
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Projects are all about people - put people at the centre of how they are planned
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
-
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Making the customer part of the team
- Keeping the customer in the loop and engaged
-
Responding to change over following a plan
- Being prepared for changes and unknowns
Agile Characteristics
- Short release cycles
- Iteration and incremental improvement
- Frequent communication
- Making the team part of the decision-making - a democratic approach to leadership
Agile Variations
- Scrum
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Kanban
- Crystal
- Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
- Agile Unified Process
- Feature-Driven Development
- Adaptive Software Development
Scrum
Team Lead / Scrum Master
- Responsible for enacting Scrum Values & Practices
- Ensures that the team is fully functional and productive
- Removes impediments / blockers
- Ensure close co-operation across the team
-
ManagerLeader of People - In software
- Usually the most (or one of) technically capable member in the team
- Responsible for engineering decisions ("How")
- Oversees planning, implementation, incident response
Product Owner
- An expert on the domain
- Visionary - CEO as Product Owner (Steve Jobs)
- Link between the team and broader community
- Market
- External stakeholders (can be one of them!)
- Take strategic / revenue responsibility
- Requirements Engineering
- Usability and customer acceptance
- Does not need to be technically proficient - but this helps significantly
- Good with people, requirements, HCI, UX
Delivery Manager
- AKA Iteration Manager
- Arrange and organise work to make engineers' jobs as simple as possible
- Keep engineers productive:
- Removing blockers
- Facilitating communication between teams
- Organising / administrating backlog
- Co-ordinating meetings / standups
- End goal is delivery - throughput
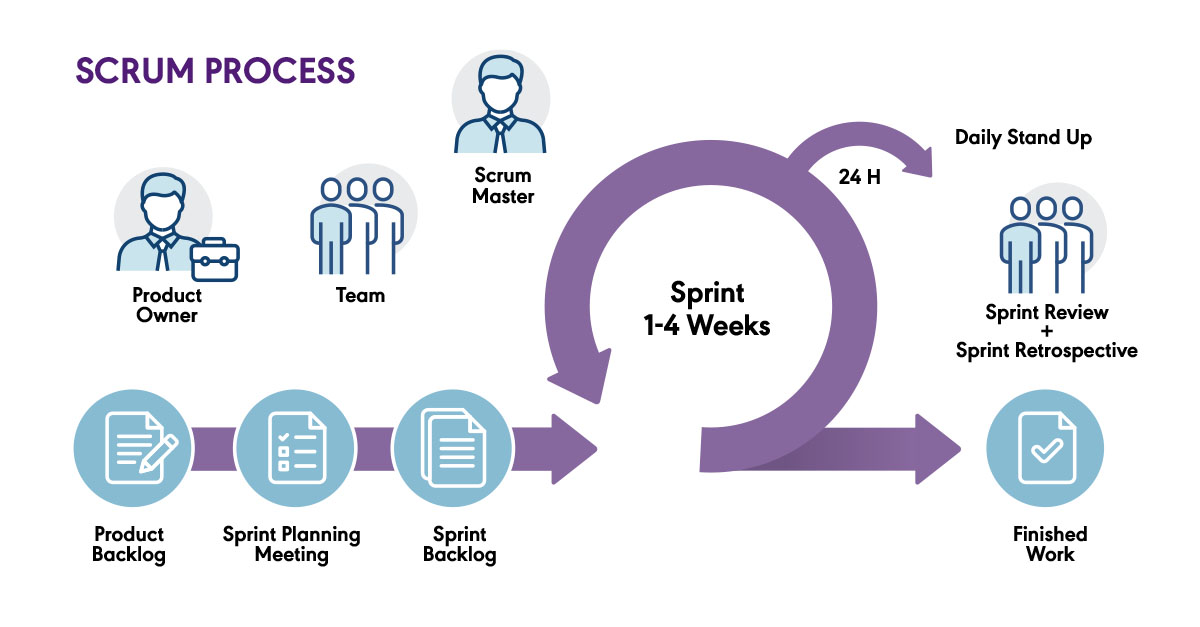
Product Backlog
- A list of all work that needs to be done at some point in future
- Ordered by priority
- Maintained by Product Owner
- Regularly updated
- Can contain
- User Stories / General Requirements
- Technical Stories
- Spikes
- Research stories
Sprint Planning Meeting
- Team selects items from the backlog they can commit to completing
- Sprint backlog created
- Tasks are identified and estimated (Story Points)
- A collaborative process
- Often occurs at the beginning of a sprint
- Preparation for sprint planning:
- Ticket Grooming
- Ticket Prioritising
- Set sprint goal
Sprints
- 1 - 4 weeks
- Small chunks of work are completed and checked-in
- Have something to show by the end of the sprint
- Demo or die
- Iterative development - each ticket is its own SDLC
- Economies of scale

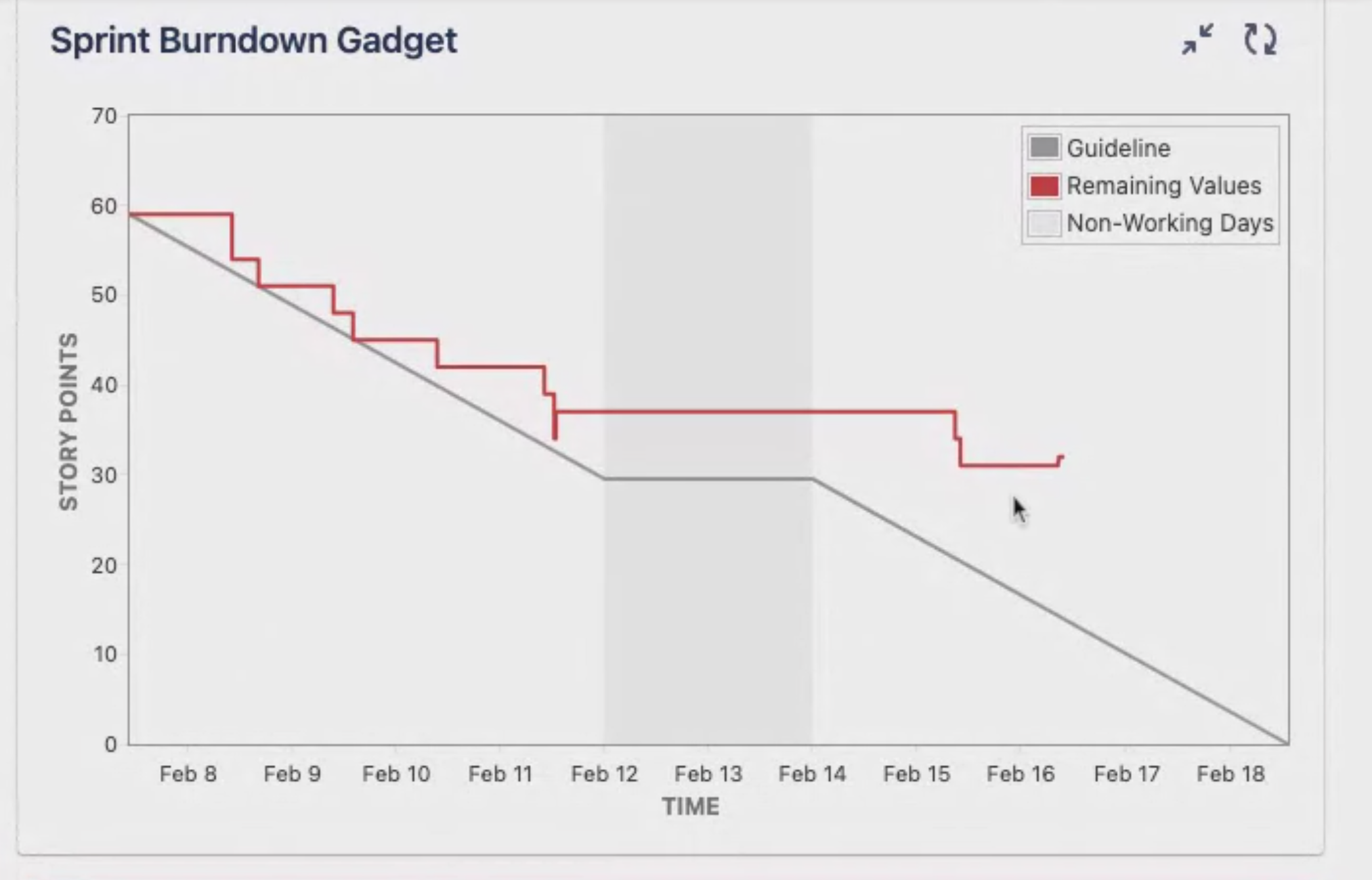
Measuring Progress
- Measurements are a core part of management
- Many measurements in management don't mean anything
- Burndown: a measure of throughput in a sprint
- Y-Axis - Work to complete (Story Points)
- X-Axis - Time of the Sprint
Standups
- "Communication saturation" - frequency
- Communication is central to teamwork
- Daily at work
- 3 times a week for the project
- Each member says
- What they have completed
- Any blockers / issues they encountered
- What they are going to do next
- Short & sharp
- Synchronous or asynchronous
Sprint Review & Retrospective
-
Review
- Team demos & presents what it accomplished
- No slides
- Whole team participates
- Invite everyone
-
Retrospective
- Whole team participates
- What went well? What can we do better?
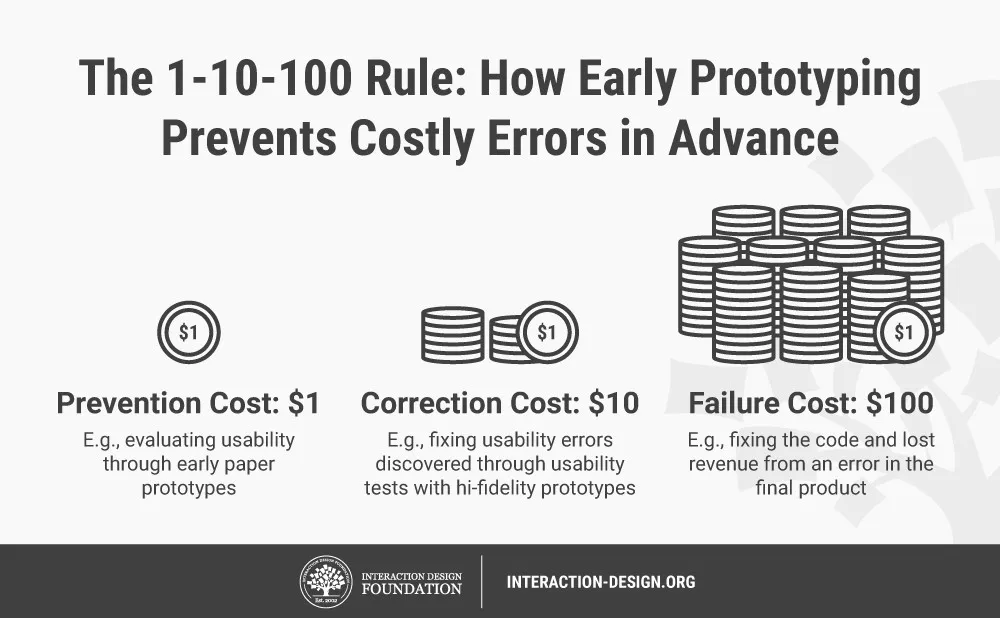
Prototyping
- An Agile approach involving building a Proof of Concept
- Illustrates the proposed product to stakeholders
- "Minimum Viable Product"
Further Viewing
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1ZXe9iczGok
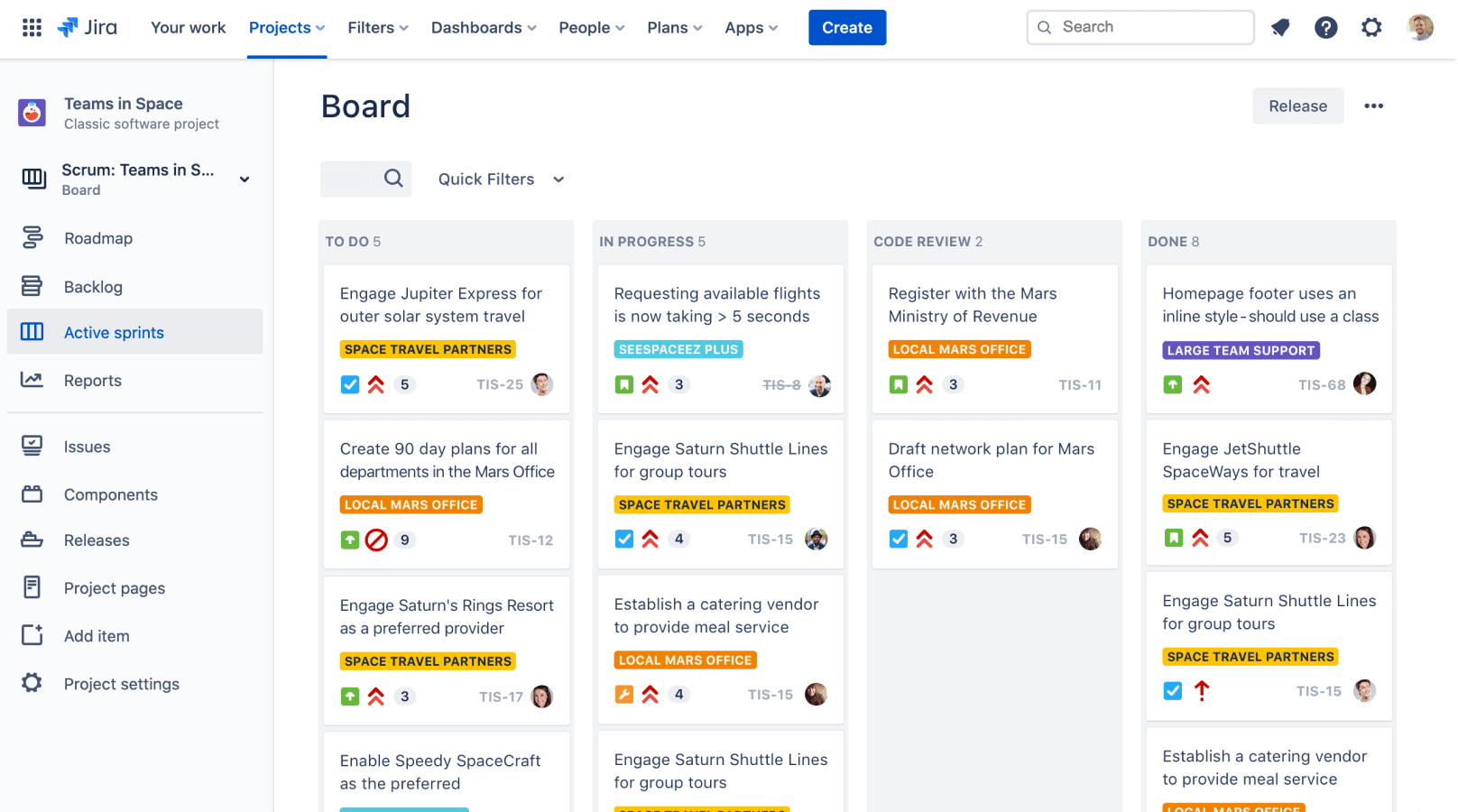
Task Tracking & Management
- Kanban
- Columns
- Backlog
- In Progress
- Review
- On Dev / Test / Prod
- Done
- Blocked
What's in a ticket
- Description - needs detail / link to documentation
- Assignee
- Reporter / Reviewer
- Story Points
- Fibonacci sequence (1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, ...)
- Priority
- Definition of done
Constraints
- What are the potential limitations / factors that prevent us from achieving the goal?
- What are things that will slow throughput?
- In real life?
- Time, budget, resources, expert knowledge...
- In this course?
- Time, knowledge, communication overhead
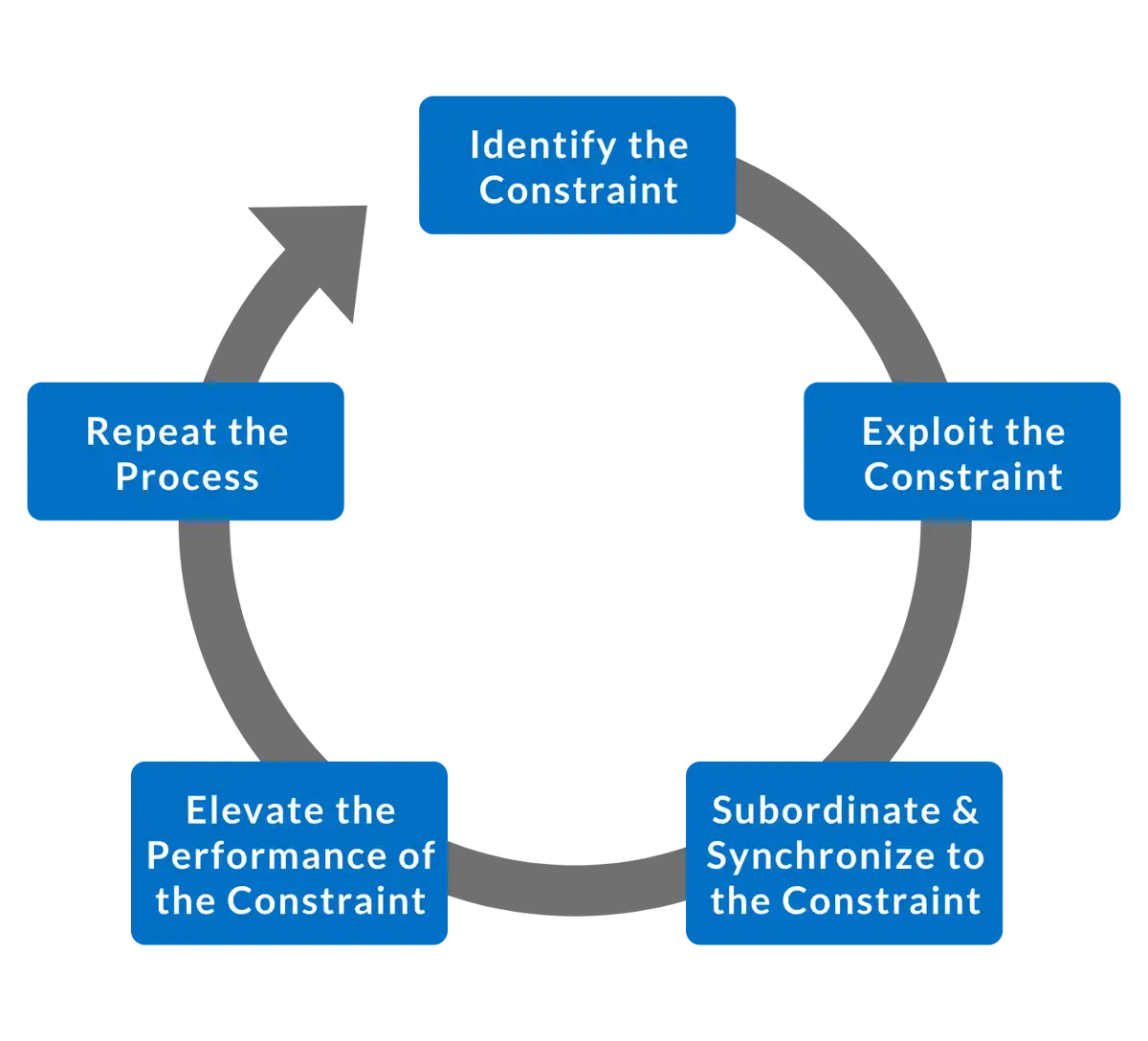
Theory of Constraints
- Every process has a constraint, and the process can only be improved when the constraint is improved
- "As fast as the slowest person"
- https://www.leanproduction.com/theory-of-constraints/
- The Goal
Theory of Constraints
- Identify - what is the constraint?
- Exploit - make quick improvements through existing resources
- Subordinate - ensure all other links in the chain support the constraint
- Elevate - further actions
Teamwork
- Teamwork is hard
- Professional maturity
- Raising concerns
- Making an active effort to resolve issues
- Email se2021@cse.unsw.edu.au to escalate concerns
- Reflect in your blog posts / resumes

SENG2021 1.3 - Teamwork - Project Management
By npatrikeos
SENG2021 1.3 - Teamwork - Project Management
- 2,320



