SOLID
SOLID Design Principles
These are class level design principles. They allow you to minimize coupling and dependencies. The result is code that is easy to read and refactor.
-
Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
-
Open/Closed Principle (OCP)
-
Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP)
-
Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
-
Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
public Map<String, AppFeature> getAllFeature(DomainProfile domainInfo) {
Map<String, AppFeature> appFeatureMap = new Hashtable<String, AppFeature>();
if (domainInfo.getSystemOfRecord().equalsIgnoreCase(FeatureToggleConstants.DB_SYSTEM_STORAGE)) {
try {
readItFromDB(domainInfo, upfAppFeatureMap);
}
catch (RuntimeException dbError) {
logger.error("Error reading from Database, the provided details were: App Name: " + domainInfo.getAppName()
+ " Domain Name:" + domainInfo.getDomainIndentifier()
+ ". Will try reading it from backup source (file system)", dbError);
readItFromFileSystem(domainInfo, upfAppFeatureMap);
}
}
else if (domainInfo.getSystemOfRecord().equalsIgnoreCase(FeatureToggleConstants.FILE_SYSTEM_STORAGE)) {
readItFromFileSystem(domainInfo, upfAppFeatureMap);
}
else {
logger.error("ERROR fetching features from system of record, no matching system of record found: ",
domainInfo.getSystemOfRecord());
return null;
}
return appFeatureMap;
}private void readItFromDB(DomainProfile domainInfo, Map<String, AppFeature> appFeatureMap) {
logger.debug("Fetching features data from DB system, the system of record value is: "
+ domainInfo.getSystemOfRecord() + "App Name: " + domainInfo.getAppName() + " Domain Name:"
+ domainInfo.getDomainIndentifier());
Map<String, Feature> featureFromDB;
if (isMongoDBImpl()) {
featureFromDB = mongoDBFeatureStore.readAll(domainInfo.getAppName(), domainInfo.getDomainIndentifier());
}
else {
featureFromDB = jdbcFeatureStore.readAll(domainInfo.getAppName(), domainInfo.getDomainIndentifier());
}
loadUPFFeaturesMap(featureFromDB, appFeatureMap);
// write it to the file system for backup activities:
try {
writeFeaturesOnFilesystemForBackup(featureFromDB);
}
catch (Exception excpetion) {
logger.error("Could not write to file system path: " + domainInfo.getFeaturesFilePath(), excpetion);
}
}public void toggleFeature(DomainProfile domainProfile, String regionIdentifier, String toggle, String featureName, String featureGroup) {
if (domainProfile.getSystemOfRecord().equalsIgnoreCase(FeatureToggleConstants.DB_SOR)) {
if (toggle.equalsIgnoreCase("enable")) {
if (isMongoDBImpl()) {
mongoDBFeatureStore.enable(featureName, featureGroup, regionIdentifier);
}
else {
jdbcFeatureStore.enable(featureName, featureGroup, regionIdentifier);
}
}
else if (toggle.equalsIgnoreCase("disable")) {
if (isMongoDBImpl()) {
mongoDBFeatureStore.disable(featureName, featureGroup, regionIdentifier);
}
else {
jdbcFeatureStore.disable(featureName, featureGroup, regionIdentifier);
}
}
else {
Message error = new Message(appConfiguration.getString(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_ERROR_CODE));
error.setInputParams(appConfiguration.getString(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_MESSAGE));
throw new RuntimeException(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_MESSAGE);
}
}
else if (domainProfile.getSystemOfRecord().equalsIgnoreCase(FeatureToggleConstants.FS_SOR)) {
if (toggle.equalsIgnoreCase("enable")) {
fileSystemStore.enable(featureName);
}
else if (toggle.equalsIgnoreCase("disable")) {
fileSystemStore.disable(featureName);
}
else {
Message error = new Message(appConfiguration.getString(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_ERROR_CODE));
error.setInputParams(appConfiguration.getString(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_MESSAGE));
throw new RuntimeException(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_FLIPPING_OPTION_MESSAGE);
}
}
else {
throw new EPFSystemException(FeatureToggleConstants.INVALID_SYSTEM_OF_RECORD_OPT);
}
}SOLID (SRP)
A class should have only one reason to change and when making that change it should only effect the class.
-
Every class should only have a single responsibility.
-
The single responsibility should be entirely encapsulated by its class.
A single responsibility
a single reason for change
class Book {
function getTitle() {
return "A Great Book";
}
function getAuthor() {
return "John Doe";
}
function turnPage() {
// pointer to next page
}
function printCurrentPage() {
echo "current page content";
}
}The function printCurrentPage changes depending on how you want to output the page's content.
Console, File, or DataBase. All require altering the Book class.
A single responsibility
a single reason for change
class Book {
function getTitle() {
return "A Great Book";
}
function getAuthor() {
return "John Doe";
}
function turnPage() {
// pointer to next page
}
function getCurrentPage() {
return "current page content";
}
function getLocation() {
// returns the position in the library
// ie. shelf number & room number
}
}Location is only meaningful in the context of a library, so the library should handle the location.
Location is only meaningful in the context of a library, so the library should handle the location.
class Book {
function getTitle() {
return "A Great Book";
}
function getAuthor() {
return "John Doe";
}
function turnPage() {
// pointer to next page
}
function printCurrentPage() {
echo "current page content";
}
function save() {
$filename = '/documents/'. $this->getTitle(). ' - ' . $this->getAuthor();
file_put_contents($filename, serialize($this));
}
function printCurrentPage() {
echo "current page content";
}
}Lets break it into multiple classes each with a single responsibility.
public class AreaCalculator {
public double pi = Math.PI;
public double calculateArea(Shape[] shapes) {
double area = 0;
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
if (shape instanceof Rectangle) {
Rectangle rectangle = (Rectangle) shape;
area += rectangle.getWidth() * rectangle.getHeight();
} else {
if (shape instanceof Circle) {
Circle circle = (Circle) shape;
area += circle.getRadius() * circle.getRadius() * pi;
}
}
}
return area;
}
}SOLID (Open/Closed)
Software entities should be open for extension,
but closed for modification.
You should be able to add new features to and existing system without modifying preexisting code.
The concepts for "extension" are language specific, for example subclasses, extension methods, or categories.
This seems obvious but why is it important?
@implementation C1NetworkOperation
- (NSString *)endpoint
{
NSString *base = @"http:someurl/api";
if (self.command != None)
base = [base stringByAppendingFormat:@"/%@", [self commandEnumToString]];
return base;
}
- (NSDictionary *)parameters
{
return @{
@"amount" : self.amount
};
}
- (C1CSSerializerType)responseSerializerType
{
return C1CSSerializerTypeJSON;
}
@endSOLID (Open/Closed)
public class Blah {
private HashMap<String, String> map;
public ArrayList<String> getUniqueValues(TreeMap<Integer, String> map) {
. . .
}
}
public class Square extends Rectangle {
public void setHeight(int height) { . . . }
public void setWidth(int width) { . . . }
}SOLID (Liskov Substitution Principle)
Functions that use pointers or references to base
classes must be able to use objects of derived
classes without knowing it.
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle();
rect.SetHeight(10); rect.SetWidth(2);
assert(rect.CalculateArea() == 20);
Rectangle rect1 = new Square();
rect1.SetHeight(10); rect1.SetWidth(2);
assert(rect1.CalculateArea() == 20);
public class Rectangle
{
private int height, width;
public void SetHeight(int height) { this.height = height; }
public void SetWidth(int width) { this.width = width; }
public int CalculateArea()
{
return this.Height * this.Width;
}
}
public class Square : Rectangle
{
public override void SetHeight(int height) {
base.height = height;
base.width = height;
}
public override void SetWidth(int width) {
base.height = width;
base.width = width;
}
}IList<Card> cards = new ArrayList<Card>();
void setUp() {
cards.add(new DebitCard());
}
void testProcessTransaction() {
for (Card card : cards) {
Card.setAvailableFunds(300);
assert(Card.canDebit(320) == false);
}
}public class Card {
protected int availableFunds;
public void setAvailableFunds(int funds) {
availableFunds = funds;
}
public virtual bool canDebit(int amount) {
return (availableFunds > amount);
}
}public class DebitCard : Card {
private int overdraftProtection;
public DebitCard(int odProtection) {
overdraftProtection = odProtection;
}
public override bool canDebit(int amount) {
return (super.availableFunds + overdraftProtection > amount);
}
}public interface Bank {
public void addAccount(Account account);
public Account getAccount(String accountNumber);
public void deposit(String accountNumber, double amount);
public void withdraw(String accountNumber, double amount);
public void applyInterest(String accountNumber);
public void applyFee(String accountNumber, double fee);
}
SOLID (Interface Segregation Principle)
The interface-segregation principle (ISP) states that no consumer should be forced to depend on methods it does not use.
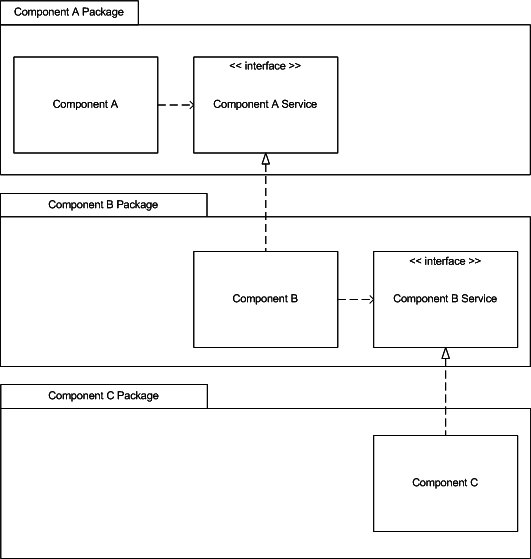
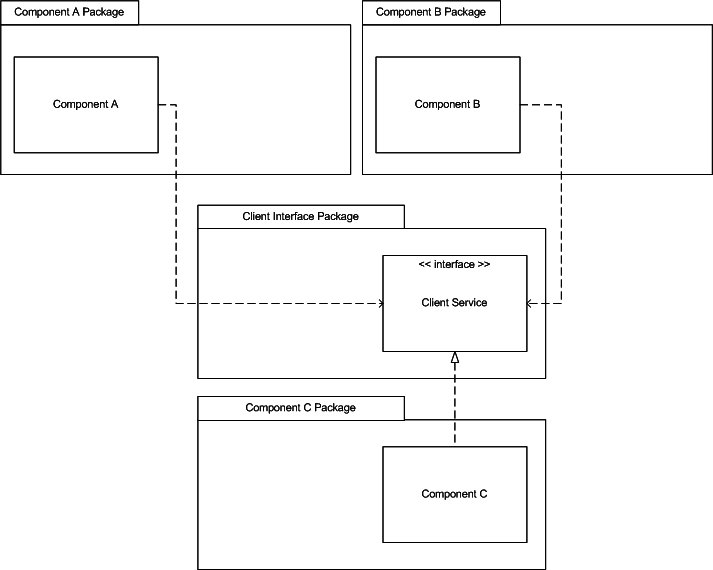
SOLID (Dependency Inversion Principle)
A. High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions.
B. Abstractions should not depend upon details. Details should depend upon abstractions.
class GameBoard {
private List<MonopolyPlayer> players;
private Dice dice;
}
class MonopolyPlayer implements Player {
void playTurn() {
Dice di = GameBoard.getdice(); // or GameBoard.DICE [Test dependency!]
int numMoves = di.roll();
. . .
}
}
interface Dice {
public int roll();
}
class Player {
void playTurn(Dice di) {
int numMoves = di.roll(); // or 'inject' numMoves if 'di' (analogy) is not needed further
. . .
}
}@Repository
public class UserDao extends JdbcDaoSupport {
@InjectLogger
private Logger logger;
@Inject
public UserDao(final DataSource dataSource) {
setDataSource(dataSource);
}
}
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydb");
dataSource.setUsername("username");
dataSource.setPassword("password");
return dataSource;
}
}SOLID
By Reid Harrison
SOLID
- 949



