COMP2511
25T1 Week 4
Thursday 9am-12pm (H09B)
Start 9:05am
By: Sam Zheng (z5418112)
Original Slides by: Alvin Cherk
Today
- Assignment Tips
- Refactoring
-
Design Principles
- Law of Demeter
- Liskov Substitution Principle
- Design by Contract
- Streams & Lambdas
slido.com 7530 335
Assignment Tips
Use .equal() for String (or any Class) comparison instead of ==
public class EqualsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Hello"; // string literal
String s2 = new String("Hello"); // string class
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false, as its comparing the addresses of s1 and s2
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true, compares the values at the addresses
// ^ do this
}
}Correctness + style issue
slido.com 7530 335
Assignment Tips
Avoid the use of magic numbers, assign them to final variables (readability - style issue)
public class MagicNumbers {
List<String> files = new ArrayList<>();
public void doSomething() {
if (files.size() == 5) { // 5 here is a magic number
// What does it mean?
}
}
}
public class MagicNumbers {
List<String> files = new ArrayList<>();
private final static int MAX_FILES = 5;
// declare constant with good name ^
public void doSomething() {
if (files.size() == MagicNumbers.MAX_FILES) {};
double angle = 750; // ^ use constant here
angle = angle % 360; // This is more OK, since theres context
}
}
slido.com 7530 335
Assignment Tips
Don't use super.x to set attributes in the super class in the subclass's constructor. Pass variable into super constructor as argument (single responsibility - design issue)
// Example: What not to do
public class Shape {
private String name;
private double length;
public Shape(String name) {
this.name = name;
// length is currently unset
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public Rectangle(String name, double length) {
super(name);
this.length(length); // bad
this.length = length; // also bad if not private
}
}slido.com 7530 335
Assignment Tips
Don't use super.x to set attributes in the super class in the subclass's constructor. Pass variable into super constructor as argument (single responsibility - design issue)
// Example: What to do
public class Shape {
private String name;
private double length;
public Shape(String name, double length) {
this.name = name;
this.length = length;
this.setLength(length); // this is ok as well
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
private String somethingElse;
public Rectangle(String name, double length, String somethingElse) {
super(name, length);
this.somethingElse = somethingElse;
}
}slido.com 7530 335
Assignment Tips
Use instanceof for type comparison (open/close - design issue)
public abstract class Shape {
public abstract String getType();
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public void doSomething(List<Shape> shapes) {
for (Shape s : shapes) {
// v1: kinda ok but overly verbose, does not include subclass
if (s.getClass().equals(Rectangle.class)) {
// do something only on exactly the Rectangle class
}
// v2: very bad, relies on string which can be incorrectly handled
if (s.getType().equals("Rectangle")) {
// do something on all rectangles
}
// v3: good, supports polymorphism + subclasses
if (s instanceof Rectangle) {
// do something on all rectangles
}
}
}
}
public class Square extends Rectangle {}slido.com 7530 335
Assignment Tips
Polymorphism is preferred over typechecking to perform a specific action (open/closed - design issue explored next week)
// Example: What not to do
public abstract class Shape {
public abstract String getType();
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {}
public class Square extends Rectangle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Shape> shapes = new ArrayList<>();
shapes.add(new Rectangle());
shapes.add(new Square());
for (Shape s : shapes) {
if (s.getType().equals("Rectangle")) {
// calculate the area this way
} else if (s.getType().equals("Square")) {
// calculate the area a different way
}
}
}
}slido.com 7530 335
Assignment Tips
Polymorphism is preferred over typechecking to perform a specific action (open closed - design issue explored next week)
// Example: What to do
public abstract class Shape {
public abstract String getType();
public abstract double area();
// ^ declare method in superclass
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public double area() {
// calculate the area this way
}
}
public class Square extends Rectangle {
public double area() {
// calculate the area a different way
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Shape> shapes = new ArrayList<>();
shapes.add(new Rectangle());
shapes.add(new Square());
for (Shape s : shapes) {
s.area(); // no more type checking
}
}
}slido.com 7530 335
Law of Demeter
"Principle of least knowledge"
slido.com 7530 335
Law of Demeter
What is it?
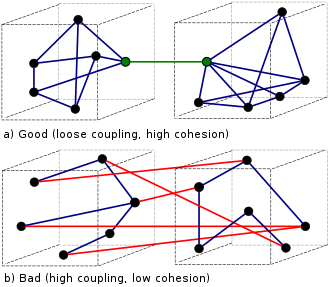
Law of Demeter (aka principle of least knowledge) is a design guideline that says that an object should assume as little as possible knowledge about the structures or properties of other objects.
It aims to achieve loose coupling in code.
slido.com 7530 335
Law of Demeter
Cohesion: how closely related individual functions and responsibilities of a class/module are
Coupling: how much a class is reliant on other classes
We want to aim for high cohesion & low coupling
Law of Demeter
What does it actually mean?
A method in an object should only invoke methods of:
- The object itself
- The object passed in as a parameter to the method
- Objects instantiated within the method
- And not those of objects returned by a method
E.g., don't do this
o.get(name).get(thing).remove(node)*Caveat is that sometimes this is unavoidable
slido.com 7530 335
Code Review
Law of Demeter
slido.com 7530 335
Code Review
In the unsw.training package there is some skeleton code for a training system.
- Every employee must attend a whole day training seminar run by a qualified trainer
- Each trainer is running multiple seminars with no more than 10 attendees per seminar
In the TrainingSystem class there is a method to book a seminar for an employee given the dates on which they are available. This method violates the principle of least knowledge (Law of Demeter).
Code Review
In the unsw.training package there is some skeleton code for a training system.
- Every employee must attend a whole day training seminar run by a qualified trainer
- Each trainer is running multiple seminars with no more than 10 attendees per seminar
In the TrainingSystem class there is a method to book a seminar for an employee given the dates on which they are available. This method violates the principle of least knowledge (Law of Demeter).
slido.com 7530 335
/**
* An online seminar is a video that can be viewed at any time by employees. A
* record is kept of which employees have watched the seminar.
*/
public class OnlineSeminar extends Seminar {
private String videoURL;
private List<String> watched;
}
/**
* An in person all day seminar with a maximum of 10 attendees.
*/
public class Seminar {
private LocalDate start;
private List<String> attendees;
public LocalDate getStart() {
return start;
}
public List<String> getAttendees() {
return attendees;
}
}
public class TrainingSystem {
private List<Trainer> trainers;
public LocalDate bookTraining(String employee, List<LocalDate> availability) {
for (Trainer trainer : trainers) {
for (Seminar seminar : trainer.getSeminars()) {
for (LocalDate available : availability) {
if (seminar.getStart().equals(available) &&
seminar.getAttendees().size() < 10) {
seminar.getAttendees().add(employee);
return available;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* A trainer that runs in person seminars.
*/
public class Trainer {
private String name;
private String room;
private List<Seminar> seminars;
public List<Seminar> getSeminars() {
return seminars;
}
}
How and why does it violate this principle?
What other properties of this design are not desirable?
slido.com 7530 335
/**
* An online seminar is a video that can be viewed at any time by employees. A
* record is kept of which employees have watched the seminar.
*/
public class OnlineSeminar extends Seminar {
private String videoURL;
private List<String> watched;
}
/**
* An in person all day seminar with a maximum of 10 attendees.
*/
public class Seminar {
private LocalDate start;
private List<String> attendees;
public LocalDate getStart() {
return start;
}
/**
* Try to book this seminar if it occurs on one of the available days and
* isn't already full
* @param employee
* @param availability
* @return The date of the seminar if booking was successful, null otherwise
*/
public LocalDate book(String employee, List<LocalDate> availability) {
for (LocalDate available : availability) {
if (start.equals(available) &&
attendees.size() < 10) {
attendees.add(employee);
return available;
}
}
return null;
}
}
public class TrainingSystem {
public List<Trainer> trainers;
/**
* Try to booking training for an employee, given their availability.
*
* @param employee
* @param availability
* @return The date of their seminar if booking was successful, null there
* are no empty slots in seminars on the day they are available.
*/
public LocalDate bookTraining(String employee, List<LocalDate> availability) {
for (Trainer trainer : trainers) {
LocalDate booked = trainer.book(employee, availability);
if (booked != null)
return booked;
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* A trainer that runs in person seminars.
*/
public class Trainer {
private String name;
private String room;
private List<Seminar> seminars;
public List<Seminar> getSeminars() {
return seminars;
}
/**
* Try to book one of this trainer's seminars.
* @param employee
* @param availability
* @return The date of the seminar if booking was successful, null if the
* trainer has no free slots in seminars on the available days.
*/
public LocalDate book(String employee, List<LocalDate> availability) {
for (Seminar seminar : seminars) {
LocalDate booked = seminar.book(employee, availability);
if (booked != null)
return booked;
}
return null;
}
}TrainingSystemno longer has knowledge ofSeminar- Each class has their own responsibility (good cohesion)
slido.com 7530 335
Liskov Substitution Principle
Liskov Substitution Principle
What is it?
Liskov Substitution Principle (LSP) states that objects of a superclass should be replaceable with objects of its subclasses without breaking the application.
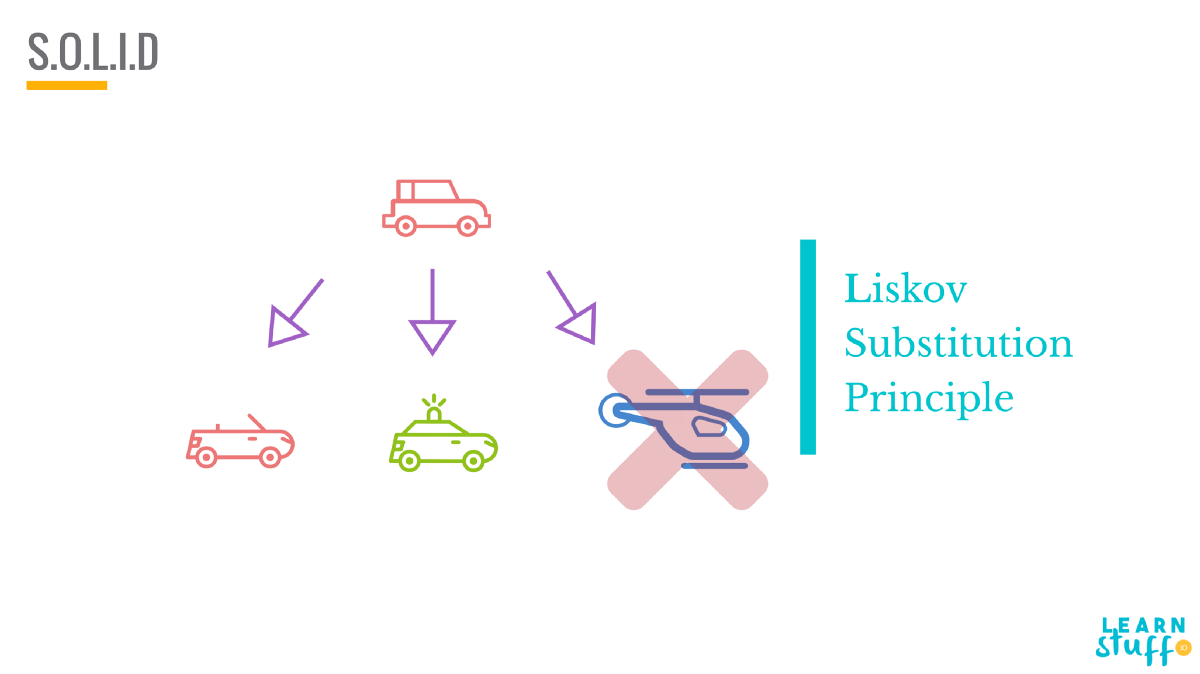
*inheritance arrows are the other way around
slido.com 7530 335
Liskov Substitution Principle
Solve the problem without inheritance
- Delegation - delegate the functionality to another class
-
Composition - reuse behaviour using one or more classes with composition
Design principle: Favour composition over inheritance
If you favour composition over inheritance, your software will be more flexible, easier to maintain, extend.
slido.com 7530 335
That being said, inheritance can have its place!
Liskov Substitution Principle
/**
* An online seminar is a video that can be viewed at any time by employees. A
* record is kept of which employees have watched the seminar.
*/
public class OnlineSeminar extends Seminar {
private String videoURL;
private List<String> watched;
}
/**
* An in person all day seminar with a maximum of 10 attendees.
*/
public class Seminar {
private LocalDate start;
private List<String> attendees;
public LocalDate getStart() {
return start;
}
public List<String> getAttendees() {
return attendees;
}
}
Where does OnlineSeminar violate LSP?
OnlineSeminar doesn't require a list of attendees
slido.com 7530 335
Streams
slido.com 7530 335
Streams
Streams abstract away the details of data structures and allows you to access all the values in the data structure through a common interface
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] {"1", "2", "3", "4", "5"}));
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string);
}
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] {"1", "2", "3", "4", "5"}));
strings.stream().forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("One", 1);
map.put("Two", 2);
map.put("Three", 3);
map.entrySet().stream().forEach(x -> System.out.printf("%s, %s\n", x.getKey(), x.getValue()));slido.com 7530 335
Streams
Common uses of streams are:
- forEach
- filter
- map
- reduce
Sort of similar to the Array prototypes/methods in JavaScript
slido.com 7530 335
Code Demo
Streams
slido.com 7530 335
Code Demo
Convert the following to use streams
package stream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5" }));
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string);
}
List<String> strings2 = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5" }));
List<Integer> ints = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (String string : strings2) {
ints.add(Integer.parseInt(string));
}
System.out.println(ints);
}
}slido.com 7530 335
package stream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> strings = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5" }));
// Same thing
strings.stream().forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
// Use if there is more than one line of code needed in lambda
strings.stream().forEach(x -> {
System.out.println(x);
});
List<String> strings2 = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5" }));
List<Integer> parsedStrings = strings2.stream().map(x -> Integer.parseInt(x)).collect(Collectors.toList());
strings2.stream().map(x -> Integer.parseInt(x)).forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
}
}slido.com 7530 335
Design By Contract
slido.com 7530 335
Design By Contract
At the design time, responsibilities are clearly assigned to different software elements, clearly documented and enforced during the development and using unit testing and/or language support.
- Clear demarcation of responsibilities helps prevent redundant checks, resulting in simpler code and easier maintenance
- Crashes if the required conditions are not satisfied. May not be suitable for highly availability applications
slido.com 7530 335
Design By Contract
Every software element should define a specification (or a contract) that govern its transaction with the rest of the software components.
A contract should address the following 3 conditions:
- Pre-condition - what does the contract expect?
- Post-condition - what does that contract guarantee?
- Invariant - What does the contract maintain?
slido.com 7530 335
Design By Contract
slido.com 7530 335
public class Bird {
private int height;
public void fly(int height) {
if (height <= 5) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Height must be greater than 5 meters to fly.");
}
this.height = height;
}
}
public class Penguin extends Bird {
@Override
public void fly(int height) {
if (height != 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Penguins cannot fly! Height must be 0 meters.");
}
// does nothing
}
}- Pre-condition has strengthened - inputs for birds don't apply for penguins
- Post-condition has weakened - additional states/outputs expected
Precondition Weaking
- An implementation or redefinition (method overriding) of an inherited method must comply with the inherited contract for the method
- Preconditions may be weakened (relaxed) in a subclass, but it must comply with the inherited contract
- An implementation or redefinition may lesson the obligation of the client, but not increase it
from 0 <= theta <= 90 to 0 <= theta <= 180 is weakening
[0, 90] => [0, 180]
Why?
LSP. I should be able to use the subclass's implementation in place of my super class.
slido.com 7530 335
COMP2511 Week 4 24T1
By Sam Zheng
COMP2511 Week 4 24T1
- 123



